
Volume:12Issue:08|Aug2025 www.irjet.net
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072



Volume:12Issue:08|Aug2025 www.irjet.net
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072


Dr. R S Prasanna Kumar1 , Chandana T N2 , Deepika J R3 , Deepthi A4 , Harshitha R5
1Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya, 571401, Karnataka,India
1Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya, 571401, Karnataka,India
1Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya, 571401, Karnataka,India
1Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya, 571401, Karnataka,India
1Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya, 571401, Karnataka,India
Abstract Yoga is a centuries-old discipline that enhances both physical and mental well-being. With the increased shift toward self-directed fitness regimes, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, unsupervised at-home yoga practicehasgrownsignificantly. However,engaginginyoga without appropriate instruction may lead to postural misalignments, which can increase the risk of musculoskeletal injuries, as noted in various studies. This study presents a computationally efficient, real-time yoga pose detection system that integrates Google's BlazePose model for pose estimation with the XGBoost algorithm for pose classification. The system was evaluated using a publicly available dataset comprising five distinct yoga poses: Downward Dog, Goddess, Tree, Plank, and Warrior. Three-dimensional pose landmarks (x, y, z coordinates) extracted using the BlazePose model were utilized as input featuresforsixmachinelearning classifiers:RandomForest, Support Vector Machine (SVM), XGBoost, Decision Tree, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and one-dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D CNN). Among these, the XGBoost classifier demonstrated superior performance, achievinganaccuracyof95.14%,precisionof95.36%,recall of 95.02%, and an F1-score of 95.17%, while maintaining a lowinferencelatencyof8millisecondsandacompact model size of 513 KB. " The proposed system is suitable for realtime mobile applications and offers a practical solution for injury-free,self-guidedyogapractice.
Key Words: BlazePose, MediaPipe Framework, XGBoost, OpenCV, Python Programming, Real-time VideoProcessing
Yoga is a centuries-old discipline that promotes holistic health by harmonizing the body, mind, and breath. With the rise of self-guided wellness practices especially duringtheCOVID-19pandemic at-homeyogahasgained significant global traction. While yoga offers numerous

benefits, unsupervised practice increases the risk of incorrectpostureexecution, potentiallyleadingto injuries andreducedeffectiveness.
Traditionally reliant on trained instructors, yoga instruction remains inaccessible to many due to cost, location, and availability. This gap has created a demand foraffordable,intelligentsystemscapableofguiding users inrealtime.Inresponsetotheneedforaccurateandrealtimepostureassessment,thisstudyproposes VirtualYoga Fusion, an AI- and machine learning-powered framework designed for real-time yoga pose detection and feedback. The proposed system leverages Mediapipe’s BlazePose for efficient 3D human pose estimation and integrates it with six machine learning classifiers XGBoost, Random Forest, SVM, Decision Tree, LSTM,and 1DCNN.A publicly available dataset of 1,551 labeled images featuring five yoga poses (Downward Dog, Goddess, Tree, Plank, Warrior)wasusedfortrainingandevaluation.
The system delivers pose predictions, confidence scores, and qualitative feedback with low latency and high accuracy,particularlywithXGBoost.Thisresearch aimsto offer a practical, lightweight, and accessible solution for enhancingsafe,self-directedyogapracticeathome.
Yoga poserecognitionsystemshaveevolvedfrommanual supervision by instructors to computer vision based techniques using 2D keypoint detection (e.g., OpenPose, PoseNet,MediapipePose).
Constraints:
1. 2D Landmark Limitations: Existing models primarily use 2D pose estimation, capturing only x and y coordinates. This approach struggles to interpret depth, leading to inaccuracies, particularlyforcomplex,3Dposes.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:08|Aug2025 www.irjet.net
2. LackofReal-TimeCapability:Systemsrelianton deep neural networks and it lack the real-time feedback. The high computational demands of these systems make them unsuitable for edge devicesorstandardconsumerhardware.
3. Poor Feedback Mechanisms: Many existing systemsofferbinaryfeedback(correct/incorrect), without personalized guidance or grading, hinderinguserprogress.
4. Static Detection: Traditional methods perform fullposedetectiononeachframe,whichincreases computation time and fails to track pose continuityacrossframes.
5. GeneralizationIssues:Manysystemsaretrained onsmall,curateddatasets,limitingtheirabilityto generalize across varied environments, body types,andcameraangles.
To address these issues,the implemented system integrates Mediapipe's BlazePose for 3D pose detection, XGBoost for efficient classification, and OpenCV for realtime video processing. The system provides real-time feedback, dynamicgrading, andisdesignedforscalability, enabling continuous improvements and adaptations for diverseyogaposes.
The"VirtualYogaFusionusingAI-ML"systemintegratesa suiteofsophisticatedmodulestoenablereal-timeposture correction and feedback during yoga practice. These modulesworktogethercohesivelytocreateaninteractive anddynamicuserexperience.Thekeymoduleswithinthe system include the Data Capturing Module, BlazePose
Model,MachineLearningModule(XGBoostClassifier),and the Feedback Module. Each module plays a pivotal role in achieving precise pose detection, classification, and deliveringuser-specificfeedbacktoenhanceperformance. Below, we present a detailed explanation of each module fromaresearchperspective:
3.1.
Objective and Role: This module serves as the foundational entry point for the system by capturingreal-timevideodatathroughawebcam. It ensures high-quality, consistent input for subsequentstagesofposeestimation.
Process: The video stream from the webcam is processed frame-by-frame to extract individual images, are then converted into the appropriate format (RGB) and resized to meet model input requirements.
Significance: The accuracy and quality of the captured video directly influence the subsequent


performance of pose estimation. A high-quality videostreamensurestheprecisedetectionofuser body movements, enabling real-time analysis and feedback. Inconsistent or delayed video input wouldimpairthesystem’soverallperformance.
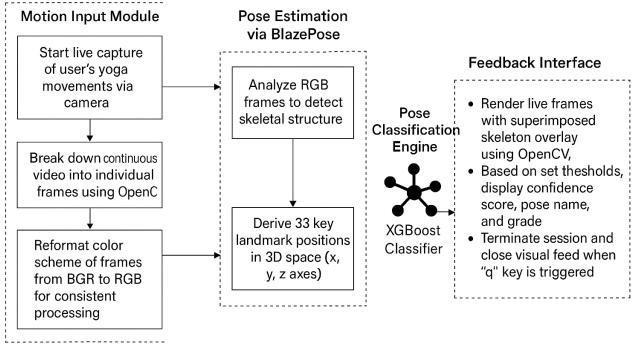
3.2. BlazePose Model :
Objective and Role: BlazePose is a cutting-edge pose estimation model developed by Google, designed to detect and track human body landmarksduringruntimewithhighaccuracy.
Process: This model uses a two-phase pipeline detection and tracking. The detection phase locates the full body in the initial frame and applies a pose detection model. The tracking phase follows the body's movement frame-to-
frame, maintaining real-time analysis without redundantcomputations.
OutputandSignificance: BlazePosegenerates33 key body landmarks, each represented by 3D coordinates (x, y, z), providing a precise mapping of body movements. These landmarks form the basis for pose classification, and the depth information ensures accurate assessment of body alignment,crucialforyogapractice.



Volume:12Issue:08|Aug2025 www.irjet.net

ObjectiveandRole: TheMachineLearningModel classifies the user’s pose based on 3D body landmarks provided by BlazePose. By converting thecoordinates intoa feature vector, thismodule enablesthesystemtoidentifyspecific yoga poses anddeliverrelevantfeedback.
Process: The3Dcoordinatesof33landmarksare flattenedintoavector(99valuesforeachframe). This vector is then input into the XGBoost classifier, a robust gradient boosting algorithm. The model compares the input data to its trained patterns(fromlabeledyoga posedata)toclassify thepose.
OutputandSignificance: Theclassifieroutputsa pose label (e.g., "Warrior Pose") along with a confidence score, indicating the certainty of the prediction. XGBoost is known for its high efficiency and low latency, making it well-suited for real-time applications, especially in resourceconstrained environments. Its ability to handle noise and small variations in input data ensures robust performance in diverse real-world scenarios.
Objective and Role: The Feedback Module provides immediate and intuitive feedback derived from the classification results of the MachineLearningModule, withthe primaryaim of guiding users toward accurate and effective executionofyogaposes..
Process: Once a pose is classified, the module generates visual cues such as confidence scores, performance grading, and color-coded light feedback (green for correct poses and white for incorrect poses). This feedback is presented through a graphical user interface (GUI) that overlays the detected pose on the user’s video feed,helpingthemaligntheirbodyinreal-time.
Significance: The Feedback Module significantly enhances user engagement by offering multiple feedback modalities numerical (confidence score), visual (pose display and grading), and ambient (color-coded lights). This multi-layered approach caters to various learning styles, promoting both instant correction and long-term improvement. The ability to provide immediate, intuitive corrections aids users in refining their alignment and posture during practice, especially for beginners or users unfamiliar with certain poses.



This section outlines the implementation details of the Virtual Yoga Fusion System, which employs computer vision and machine learning techniques to classify and evaluate yoga poses in real time. The system leverages Mediapipe's BlazePose model for pose estimation and integrates machine learning models for classification and feedbackdelivery.
The system was developed using Python 3.8.8 on Jupyter Notebook and tested on a single CPU machine with 8 GB RAM.Keylibrariesincluded:
Mediapipe forhumanposeestimation,
OpenCV forimageandvideoprocessing,
NumPy and Pandas fordatahandling,
Scikit-learn and XGBoost formachinelearning,
TensorFlow and Keras for deep learning experiments.
The dataset used was a publicly available Yoga Pose Dataset from Kaggle, comprising 1,551 labeled images across five pose classes. BlazePose was employed to extract33three-dimensional(x,y,z)landmarksfromeach image. These landmarks were flattened into 99dimensional vectors and saved in CSV format for model training.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:08|Aug2025 www.irjet.net
4.3 Data Preprocessing
The extracted pose landmark data was normalized to ensurescaleinvariance.Thedatasetwassplitintotraining (70%) and testing (30%) subsets. Categorical pose labels were encoded into numerical values for model compatibility.
4.4 Model Training
Severalclassificationmodelswereevaluated,including:
Machine Learning Models: Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, Decision Tree, and XGBoost.
Deep Learning Models:1DConvolutionalNeural Network(1DCNN)andLongShort-TermMemory (LSTM).
XGBoost was selected for deployment due to its superior performanceintermsofaccuracy,lowinferencetime,and computationalefficiency.
Hyperparameters for all models were tuned using Grid Search combined with 5-Fold Cross-Validation. This helpedoptimizeperformanceandreduceoverfitting.
4.6 Real-Time Pose Detection
The real-time detection framework comprises three key components:
1. Video Capture: Implemented using cv2.VideoCapture()toobtainlivewebcaminput.
2. Pose Estimation: BlazePose detects and tracks bodylandmarksframe-by-frame.
3. PoseClassification:TheXGBoostmodelclassifies theposebasedonextractedlandmarks.
Feedback is generated based on the model's confidence levelanddisplayedtotheuserinrealtime:
Confidence Score


In this research, we developed a "Virtual Yoga Fusion using AI-ML" system aimed at enhancing yoga practice through real-time feedback and pose classification. The system utilizes a combination of computer vision and machinelearning models to detect and assess yoga poses, providing personalized feedback to users. We employed various machine learning algorithms, including LSTMbased deep neural networks, 1D CNNs, and traditional models like XGBoost, to evaluate their effectiveness in pose classification. The XGBoost model outperformed the othermodelsintermsofaccuracy (95.14%)andreal-time efficiency,makingitthebestcandidateforthisapplication.
Our testing framework included unit, integration, and validation testing. Unit testing ensured the correctness of individualcomponents,whileintegrationtestingvalidated the seamless interaction between different system modules. Validation testing confirmed the system’s performance under real-world conditions, ensuring that it could handle varying environmental factors such as lighting and user positioning. The real-time application successfully recognized five key yoga poses, offering feedbackbasedonconfidencethresholds.
The results demonstrate the feasibility of using AI-ML to deliver an interactive and personalized yoga experience. ThisresearchcontributestothegrowingfieldofAI-driven health and wellness applications, offering users a reliable tool to improve their yoga practice with real-time correctionsandguidance.
This study investigates real-time yoga pose detection by leveraging the MediaPipe BlazePose model for pose estimation in conjunction with various machine learning algorithms. Among these, the XGBoost classifier demonstrated the highest performance, achieving an accuracy of 95.14%. The approach efficiently classified poses with minimal latency and was suitable for systems with limited computational resources. While the system supports five poses and single-person detection, it lacks corrective feedback and is limited in scope. Future work will expand the dataset, incorporate angle-based calculations for improved evaluation, enhance feedback mechanisms, and explore multi-person detection. Additionally,developingmobileorwebapplicationscould make this framework more accessible for personal yoga training.
1.Chaudhari, A., Dalvi, O., Ramade, O. and Ambawade, D. (2021a). Yog-guru: Realtime yoga pose correction system using deep learning methods, 2021 International


Volume:12Issue:08|Aug2025 www.irjet.net
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Conference on Communication information and ComputingTechnology(ICCICT),pp.1–6.
2. Garg, S., Saxena, A. and Gupta, R. (2022). Yoga pose classification: a cnn and mediapipe inspired deep learning approach for real-world application, Journal of AmbientIntelligenceandHumanizedComputing pp.1–12.
3. Gupta, A. and Jangid, A. (2021). Yoga pose detection and validation, 2021 International Symposium of Asian Control Association on Intelligent Robotics and Industrial Automation(IRIA),pp.319–324.
4. Huang,X.,Pan,D.,Huang,Y.,Deng,J.,Zhu,P.,Shi,P.,Xu, R., Qi, Z. and He, J. (2021a). Intelligent yoga coaching systembasedonposturerecognition, 2021International Conference on Culture-oriented Science Technology (ICCST),pp.290–293.


