
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Sowmith Reddy1 , Piyush Vijay2, Chinmai3 , Disha4, Gunottham5
1 2 3 4 5 U.G Student, Dept. of Information Science Engineering, Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Abstract- Accurate forecasting of solar energy generationiscrucialforthesuccessoflarge-scalerenewable energy facilities, as it depends on evolving weather conditions. This study presents a hybrid model that leverages both machine learning and statistical techniques to predict solar power output. By integrating climate principles with ML algorithms, the proposed approach enhances forecasting accuracy. Additionally, the system incorporates NodeMCU for IoT-based communication, along with components such as an LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), rain sensor, alarm controller, and solar panel for energy generation. This research focuses on implementing MLmodelsusingrealweatherdatatooptimizetheefficiency andreliabilityofsolarenergyutilization.
Keywords: Solar energy prediction, hybrid model, machine learning algorithms, climate concepts, IoT communication
Solarenergyisaessentialrenewableenergysourcethat contributessignificantlytotheglobalenergymix.However, distance due to weather conditions is a challenge for integration into the existing power grid. Accurate forecasting of solar power generation can lead to better grid management and more efficient use of energy. This researchfocuseson developinga forecastingsystemusing ML algorithms that uses real weather data received from sensorstoforecastsolarenergyproduction.Byintegrating IoT devices such as NodeMCU with sensors and rain sensors such as LDR, the system aims to create a reliable andaccurateforecastmodel.Machinelearningapproaches have become more popular in recent decades in many companies where data-related challenges are common. Machine learning covers many areas, including data mining, optimization and artificial intelligence, to name a few of the more popular ones. Machine learning approaches attempt to find relationships between input data and output data, whether or not they use mathematical models. After training with the training database, the predictive input data can be fed into a welltrained machine learning model, which can then make predictions.
Tiwari et al. (2018) The paper addresses the challenge of short-term solar irradiance forecastingusingNumerical Weather Prediction (NWP). The authors propose a
Gradient Boost Regression model to enhance forecast accuracy. The model leverages weather data to predict solar energy generation. Results show improved shortterm predictions over traditional methods. The study highlights the effectiveness of machine learning in solar forecasting. Singhal et al. (2022) This study focuses on improving solar power prediction accuracy using weather forecast data. The authors introduce a machine learningbased framework, "Solar-Cast," for precise forecasting. Various algorithms, including ensemble models, are explored for better performance. The results indicate significant accuracy improvements in solar energy prediction. The approach is validated on real-world datasets. Fraccanabbia et al. (2020) The paper tackles the issueofunreliablesolarpowerforecastingduetoweather variability. The authors employ ensemble learning techniques to enhance predictive accuracy. The proposed model integrates multiple machine learning methods to improve robustness. Experimental results show superior performance compared to individual models. The study highlights ensemble learning’s potential in renewable energy forecasting. Rusina et al. (2023) The study examinesday-aheadsolarpowerforecastingforMongolia’s power system. An ensemblemachinelearning approachis developed to improve accuracy. The model combines different regression techniques for better performance. Results demonstrate enhanced forecasting precision compared to conventional models. The approach is applicable in power grid planning. Abdellatif et al. (2022) This paper focuses on forecasting solar photovoltaic (PV) power output using ensemble learning. Various machine learning methods are compared for polycrystalline panelbased predictions. The proposed model effectively captures solar power variations. Results show reduced forecast errors compared to traditional approaches. The study provides insights into optimizing PV power predictions. Chen & Koprinska (2020) The research explores the application of ensemble methods for solar power forecasting. The study integrates different machine learning models to improve predictive performance. The ensemble model achieves better accuracy compared to standalone models. Results highlight the effectiveness of combining diverse algorithms. The approach enhances solar power reliability for grid management. Nayak & Heistrene(2020)Thepaperaddressesinaccuraciesinsolar power prediction using hybrid models. A hybrid machine learning approach combining multiple techniques is proposed. The model enhances accuracy by leveraging different predictive strengths. Performance evaluations

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
show significant improvements over traditional methods. The study emphasizes the potential of hybrid models in energy forecasting. Wen et al. (2021) The paper investigatesintervalpredictionofsolarpowerinshipboard power systems.A hybrid ensemble model isintroducedto handle uncertainties in power generation. The approach improves reliability by accounting for predictionintervals. Results show superior accuracy in maritime solar forecasting. The study provides valuable insights for onboard energy management. Su et al. (2020) The study proposes adaptive residual compensation ensemble models for solar forecasting. The goal is to reduce forecasting errors by optimizing ensemble learning. The model dynamically adjusts based on historical prediction errors. Results indicate significant improvements in forecasting accuracy. The approach enhances reliability in solar energy prediction.Wu & Wang (2021) The paper focuses on improving solar and wind power forecasting using ensemble neural networks. Variational Mode Decomposition and an improved Sparrow Search Algorithm are employed. The hybrid approach enhances feature extraction and optimization. Experimental results show increased forecasting accuracy. The study demonstrates the effectiveness of advanced neural network techniques. Abuella & Chowdhury (2017) The researchexamineshourlyprobabilisticforecastingofsolar power.Aprobabilistic model isintroducedtohandlesolar generation uncertainties. The approach provides confidence intervals for energy predictions. Results demonstrate improved reliability over deterministic models. The study contributes to risk-aware power grid operations. Lin (2023) The paper applies evolutionary algorithms to optimize hyperparameters for solar power prediction models. The approach automates hyperparameter selection for better accuracy. The optimized model outperforms traditional tuning methods. Resultsindicateenhancedforecastingreliability.Thestudy underscores the importance of optimization in energy forecasting. Li et al. (2021) The study explores artificial intelligence techniques for forecasting solar energy generation and household load. A machine learning frameworkisdevelopedtopredictbothsolarpoweroutput and energy consumption. The proposed model improves demand-supply balance in smart grids. Results demonstrate enhanced prediction accuracy. The study highlights AI's role in energy management. Sun et al. (2022) The paper presents a dynamic model ensemble approach for solar energy forecasting. The model adapts dynamicallytochangingweatherconditions.Theapproach integrates multiple learning algorithms to improve robustness. Results show better forecasting accuracy compared to static models. The study emphasizes adaptability in renewable energy predictions. Liu et al. (2023)Thisstudyintroducesanovelstackingcollaborative technique for day-ahead photovoltaic (PV) power forecasting. The model combines different machine learning techniques for enhanced accuracy. The approach
reduces forecast uncertainty and improves decisionmaking for grid operators. Results validate the model’s superior predictive performance. The study provides insights into effective PV power forecasting techniques. May et al. (2006) The research focuses on composing complex biological workflows through web services. A structure prediction pipeline is proposed for molecular analysis. The approach integrates multiple computational tools for sequence alignment. Results demonstrate improved efficiency in biological data processing. The study highlights the role of distributed computing in bioinformatics. Foster & Kesselman (1999) The paper introduces a framework for distributed computing infrastructure, "The Grid." The proposed architecture enablesresourcesharingacrossmultiplecomputingnodes. The study discusses scalability, performance, and security aspects. Results demonstrate enhanced computational efficiency. The research lays the foundation for modern cloud and grid computing. Czajkowski et al. (2001) The study examines grid information services for distributed resource sharing. A novel architecture is proposed to manage distributed computing environments. The system enhances data discovery and resource allocation. Results indicate improved efficiency in high-performance computing. The study contributes to the evolution of gridbasedsystems.Fosteretal.(2002)Thispaperpresentsthe Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) for integrating distributed systems. The framework standardizes resource-sharing mechanisms in grid computing. The approachimprovesinteroperabilityandscalability.Results show enhanced system integration and performance. The study forms the basis of modern distributed computing architectures.
3.1
We first conducted a literature review and theoretical researchwithintheShort-TermIrradianceForecastUsing Numerical Weather Prediction. We then analyzed the challengesanddevelopeffectiveapproachestoimplement suchsolarpowergenerationforecastingsystems.Thenwe connect components like ESP8266 and some sensors. We developed this model to identify constraints and conditionstoanalyzetheweatherconditions.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
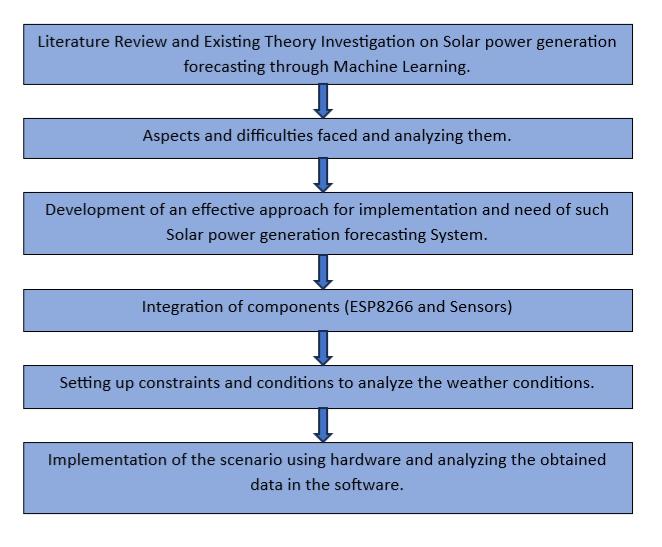
Fig. 1. Themethodologyutilizedinanexistingmodel.
Solarpowergenerationforecastingprototypeisaworking model or early version of a system developed to predict the weather conditions. The prototype usessensorslike a rainsensor to detect rainfall andan LDR tomeasurelight levels. These sensors are attached to the ESP8266, often to collect the weather data. The Solar panel is used to predict amount of solar power that is produced at that time. The prototype is used to collect weather data and store the data in the form of weather dataset for further analysis using software. This interface allows users to analyze the weather data using software. The data obtained by the hardware components is analyzed using the Jupyter Software. The Solar power generation forecasting prototype is a functional model that integrates hardware, data processing, machine learning algorithms and user interface to demonstrate the concept of solar power generation forecasting using machine learning models.
3.2ComparativeAnalysis
Parameters ExistedModel ProposedModel
Accuracy Less Accurate Data. MoreAccurateData.
Algorithm ANN,CNN,etc. Random Forest,SVM,etc.
Hardware Requirements NoHardware Used. Solar-Panel,Rain Sensor,etc.
Functionality Software Hardware,Software
Table1: Comparingtheexistingmodelwiththeproposedmodel.
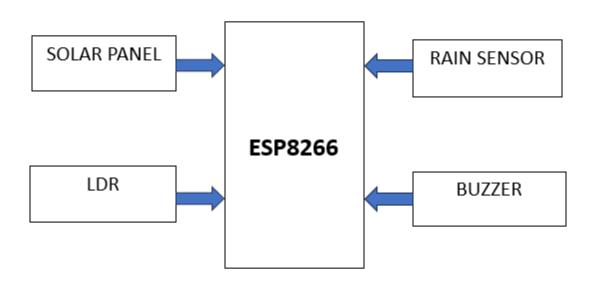
Fig. 2 Theschematicrepresentationoftheproposed systeminablockdiagram.
4.1 NodeMCUESP8266
Ageneral-purposeinput/output(GPIO)isapinonanIC (IntegratedCircuit).Itcanbeaninputpinoranoutputpin whose behavior can be controlled. The ESP8266 is a friendly and inexpensive device to provide Internet connectivitytoyourproject.Thismodulecanbeusedasan access point (can create a hotspot) and a station (can connecttoWi-Fi),soitcanreceivedataeasilyandtransfer it to the Internet as easily as possible. It can also retrieve datafromthewebusinganAPI,soyourprojectcanaccess data on the web and become smarter. Another exciting feature of this module is that it can be programmed using the Arduino IDE, which makes it more user-friendly. However, this version of the module only has 2 GPIO pins (youcanuse upto 4),soyou havetouse it inconjunction with another microcontroller, such as Arduino, or more independently ESP-12 or ESP- 32. You can see in the version. So, if you are looking for a module to start using IOTorinternetconnectivityforyourproject,thismoduleis therightchoiceforyou.
4.2SolarPanel
A solar panel is a device used to absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity or heat. Solar energy starts with thesun.Solarpanels(alsoknownas"PVpanels")areused to convert sunlight into energy particles called "photons" intoelectricitythatcanbeusedtopoweranelectricalload. Solar panels can be used for a variety of applications, including cabins, telecommunications equipment, remote sensing, and of course remote power systems for residentialandcommercialsolarpowergeneration.Asolar panelisactuallyacollectionofsolarcells(orcells)thatcan be used to generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect.Thesecellsarearrangedinacell-likepatternontop ofthesolarpanel.Therefore,itcanalsobedescribed.Asa collectionofphotovoltaicmodulesinstalledinasupporting structure.Photovoltaicmodules(PV),6×10-daycellsfilled andconnected.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Abuzzerorbuzzerisanaudiosignalingdevicethatcanbe mechanical, electromechanical, or piezoelectric (piezo for short).Commonusesofbuzzersandsoundsincludealarm devices,timers,andconfirminguserinputsuchasclicking a mouse or pressing a button. Buzzer is a small but effective component to add sound features to our project/system. This 2-pin structure is very small and compact, so it can easily be used on breadboards, smart boards, and even PCBs that are widely used in many electronic applications. There are usually two types. The simple buzzer shown here will emit a continuous sound when activated, another version called a tin buzzer will appearlargerandproducea"sound".Noiseduetointernal oscillationcircuit.However,theoneshownherehasmore uses, as it can be easily configured with other circuits to suit our application. This boiler can be powered by a variable DC power supply from 4V to 9V. A simple 9V battery can also be used, but a regulated +5V or +6V DC supply is recommended. The buzzer is usually connected to a switching circuit so that it can be turned on or off as needed.
4.3
LDR(LightDependentResistor),asthenamesuggests,isa special type of resistor that works on the principle of photoconductivity, resistance that changes according to the intensity of light. Its resistance decreases with increasinglightintensity.Manytimes,weuselightsensor, light meter, automatic street light and light sensitivity whereverneeded.LDRisalsoknownaslightsensor.LDRs generallycomein5mm,8mm,12mmand25mmsizes.
4.4
A rain sensor is a type of switch device used to detect rain.Itworkslikeaswitchandtheworkingprincipleofthis sensor is that when it rains,the switch is normally closed. The rain sensor module/board is shown below. Basically, these boards contain nickel-plated lines and work on the principle of resistance. This sensor module allows you to measurethehumiditythroughananalogoutputpointand provide a digital output when the humidity exceeds the limit.
5.1
The Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment) serves as a software platform dedicatedto programming and application development for Arduino microcontrollers and compatible boards. It offers a userfriendly interface for crafting, compiling, and uploading code to manage diverse electronic projects. Arduino IDE simplifies code programming and debugging, making it a
valuable tool for both writing and uploading code to Arduino boards, such asthe NodeMCU, via a PC or laptop connectionusingadatacable.
ThingSpeak is an open source IoT application and API forstoringandretrievingdata fromhardwaredevicesand sensors.ItusestheHTTPprotocolovertheInternetorLAN to communicate. MATLAB Analytics comes to analyze and visualizedatafromyourdevicesorsensordevices.Wecan create a channel for each sensor data. These channels can be set as private channels or you can share information through public channels. Commercial features include additional features. But we will use the free version for educationalpurposes.
6.1 Working model of solar power generation forecasting
The "Leveraging Weather Insight for Solar Power Generation Forecasting through ML" project has developed a hybrid model for forecasting solar power generation. The system uses machine learning algorithms and statistical techniques to analyze real-time data from IoT devices and sensors such as light dependent resistors and rain sensors. This approach improves the accuracy and reliability of solar energy forecasts. The system's active warning system allows users to take corrective action in case of discrepancies between predicted and actualpoweroutput.Accurateforecastsalsocontribute to bettergridmanagementandminimizesolarintermittency. This project demonstrates the potential of leveraging weather insights for improved solar power generation forecasting.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
6.2 Outputs
The output obtained by connecting the LDR and rain sensor with the ESP8266 is shown in the ThingSpeak SoftwareandSerialmonitoringwindow
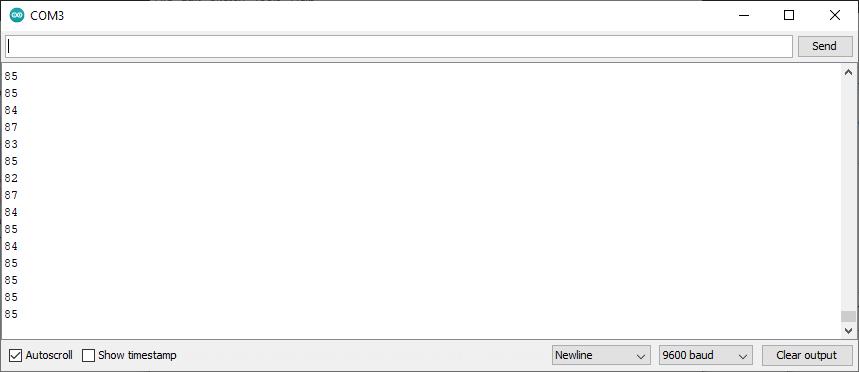
Fig. 4. Solarpowergenerationforecastinginserial monitoring
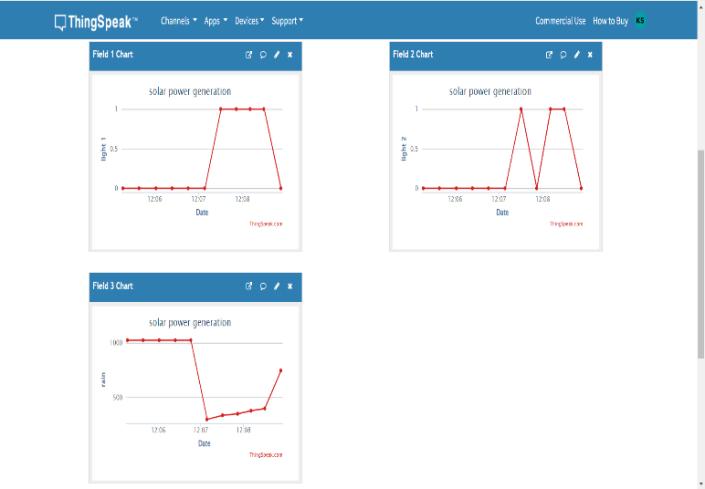
Fig. 5 SolarpowergenerationforecastinginThingSpeak software.
6.3 SimulationResults
Solar power generation forecasting throughML results showtheheatmapofcorrelationusingJupytersoftware.
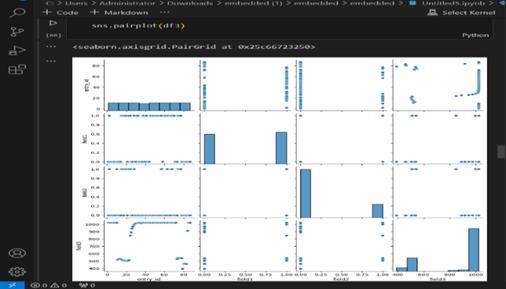
Fig. 6,7.Resultofsolarpowergenerationforecasting throughML
7.1 Conclusion
TheaboveworkdemonstratedUsingmachinelearning (ML), the integration of weather insights to forecast solar power generation with IoT devices such as NodeMCUs, LDRs, rain sensors, buzzers, and solar panels offers a significant opportunity to improve the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy systems. The proposed system provides a framework for using real weather data to accurately predict solar energy production. Using advanced ML algorithms, this system can account for the impact of different weather conditions on solar panel performance, thus providing more accurate predictions. Through the development and implementation of this system,itisclearthattheuseofIoTdevicestocollectdata, combined with ML algorithms, can lead to more reliable and dynamic predictions of solar energy production. The system'sabilitytogeneratealertsintheeventofdeviations between estimated and actual energy production contributes to better energy management by taking proactivemeasurestoresolvedeviations.
7.2
Forecasting of solar output involves continuous improvement and fine tuning of machine learning algorithms by incorporating more diverse and comprehensive data sets to achieve greater accuracy. To improve the accuracy of this model, additional sensors should be integrated to measure parameters such as temperature, humidity and cloud cover, which provide a more complete understanding of environmental conditions. Cloud-based data processing for training machine learning models and real-time data analysis improves scalability and efficiency, especially when using large databases. In addition, implementing predictive maintenance algorithms using IoT sensors to monitor the health and performance of solar panels can contribute to the reliability and efficiency of solar energy systems, preventingfailuresandoptimizingpowergeneration.
1. S. Tiwari, R. Sabzehgar and M. Rasouli, "Short Term Solar Irradiance Forecast Using Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) with Gradient Boost Regression,"2018 9th IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems(PEDG),Charlotte,NC,USA,2018,pp.1-8,doi: 10.1109/PEDG.2018.8447751.
2. R. Singhal, P. Singhal and S. Gupta, "Solar-Cast: Solar Power Generation Prediction from Weather Forecasts using Machine Learning,"2022 IEEE 10th Power India International Conference (PIICON), New Delhi, India,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2022, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/PIICON56320.2022.10045237
3. N. Fraccanabbia, R. G. da Silva, M. Henrique Dal Molin Ribeiro, S. R. Moreno, L. dos Santos Coelho and V. C. Mariani, "Solar Power Forecasting Based on Ensemble Learning Methods,"2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 2020, pp. 1-7, doi: 10.1109/IJCNN48605.2020.9206777.
4. A. G. Rusina, T. Osgonbaatar, A. I. Stepanova and P. V. Matrenin, "Ensemble Machine Learning Model for Day Ahead Solar Power Forecasting for Mongolia Power System,"2023 Belarusian-Ural-Siberian Smart Energy Conference (BUSSEC), Ekaterinburg, Russian Federation, 2023, pp. 84-87, doi: 10.1109/BUSSEC59406.2023.10296344.
5. A.Abdellatif,H.Mubarak,S. Ahmad,A.Hammoudeh, S. Mekhilef and H. Mokhlis, "Forecast of Solar Photovoltaic Power Output Based on Polycrystalline Panel-based Employing Various Ensemble Machine Learning Methods,"2022 IEEE Global Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GlobConPT), New Delhi, India, 2022, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/GlobConPT57482.2022.9938348.
6. Z.ChenandI.Koprinska,"EnsembleMethodsforSolar Power Forecasting," 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 2020, pp. 1-8, doi: 10.1109/IJCNN48605.2020.9206713.
7. A. Nayak and L. Heistrene, "Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Forecasting Solar Power Generation,"2020 International Conference on Smart Grids and Energy Systems (SGES), Perth, Australia, 2020, pp. 910-915, doi:10.1109/SGES51519.2020.00167.
8. S.Wen,C.Zhang,H.Lan,Y.Xu,Y.TangandY.Huang,"A HybridEnsembleModelforIntervalPredictionofSolar Power Output in Ship Onboard Power Systems," inIEEETransactionsonSustainableEnergy,vol.12,no. 1, pp. 14-24, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2019.2963270.
9. H.-Y.Su,T.-Y.LiuandH.-H.Hong,"AdaptiveResidual Compensation Ensemble Models for Improving Solar Energy Generation Forecasting," inIEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 1103-1105, April2020,doi:10.1109/TSTE.2019.2931154.
10.KarthikS.A.,NagaS.B.,SatishG.,ShobhaN.,BhargavH. K., & Chandrakala B. M. (2025). AI and IoT-Infused UrbanConnectivityforSmartCities.InD.Ertuğrul&A. Elçi(Eds.),FutureofDigitalTechnologyandAIinSocial Sectors (pp. 367-394). IGI Global Scientific Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-5533-6.ch013
11.RashmiS,ChandrakalaBM,DivyaM.Ramani,MeghaS. Harsur, CNN based multi-view classification and ROI segmentation: A survey,Global Transitions Proceedings,Volume 3, Issue 1,2022,Pages 86-90, ISSN 2666285X,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gltp.2022.04.019. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2 666285X22000553)
12.K S Naga Sai Nischal1, GuvvalaNithin Sai, Calvin Mathew,GaganCSGowda,.ChandrakalaBM,“Asurvey on Recognition of Handwritten ZIP Codes in a Postal Sorting System” “ International Research Journal of EngineeringandTechnology(IRJET),Volume:07Issue: 03 | May 2020, e-ISSN: 2395-0056, p-ISSN: 23950072,Impact Factor value: 7.34, ISO 9001:2008 CertifiedJournal. https://www.academia.edu/download/64527939/IRJ ET-V7I3842.pdf
13.Chandrakala B M and S. C. Linga Reddy, "Proxy ReEncryption using MLBC (Modified Lattice Based Cryptography)," 2019 International Conference on Recent Advances in Energy-efficient Computing and Communication (ICRAECC), Nagercoil, India, 2019, pp. 1-5,doi:10.1109/ICRAECC43874.2019.8995071
14.M. Abuella and B. Chowdhury, "Hourly probabilistic forecasting of solar power,"2017 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Morgantown, WV, USA, 2017,pp.1-5,doi:10.1109/NAPS.2017.8107270.
15.Z. Wu and B. Wang, "An Ensemble Neural Network Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and an Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm for Wind and Solar Power Forecasting," inIEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 166709-166719, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3136387.
16.Haridasa Nayak, Varun K R, Venkatesh M. K, Sonal Shamkuwar,R.SureshKumar,SudarshanTA,Abhijeet Malge, Vijay M, C. Durga Prasad,"Thermal cycle behaviour of plasma sprayed thermal barrier coatings on cast iron substrate for the application of liner of internal combustion engine",Journal Results in Surfaces and Interfaces,Volume 17,2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsurfi.2024.100297.(https:/ /www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266684 592400117X)
17.Z. Li, C. S. Lai, A. Meng, X. Li, A. Vaccaro and L. L. Lai, "Artificial Intelligent Techniques for Solar Energy Generation & Household Load Forecasting,"2021 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics(ICMLC),Adelaide,Australia,2021,pp.1-4, doi: 10.1109/ICMLC54886.2021.9737261.Smith, T.F., Waterman, M.S.: Identification of Common Molecular Subsequences.J.Mol.Biol.147,195–197(1981)
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1784

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
18.X.Sun,D.Wu,M.Jia,Y.XiaoandB.Boulet,"Forecasting of Solar Energy Generation via Dynamic Model Ensemble,"2022 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference(EPEC),Victoria,BC,Canada,2022,pp.109115,doi:10.1109/EPEC56903.2022.10000238.
19.L. Liu, Q. Sun, R. Wennersten and Z. Chen, "Day-Ahead Forecast of Photovoltaic Power Based on a Novel StackingEnsembleMethod,"inIEEEAccess,vol.11,pp. 113593-113604, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3323526.
20. H. S.Supriya, Chandrakala B. M., An efficient MultiLayer Hybrid Neural Network and optimized parameter enhancing approach for traffic prediction in Big Data Domain.The Journal of Special Education, 2022,Vol1,Issue43,pp9496,ISSN:1392-5369,
21. Haridasa Nayak, N Krishnamurthy, Shailesh Rao A, “Wear Characteristics During Coating of YSZ+Al2O3 on Cast Iron Substrate”, Revista Română de Materiale / Romanian Journal of Materials, Vol. 52, Issue -4, (2022),pp.331–340.
22. H.Nayak,K.Shanthala,M.K.Venkateshand L.Chirag, "Correlation of Microhardness with Abrasive Wear of Thin Films: A Machine Learning Approach," 2023 International Conference on the Confluence of Advancements in Robotics, Vision and Interdisciplinary Technology Management (ICRVITM), Bangalore, India, 2023, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/IC-RVITM60032.2023.10435163.
23. Haridasa Nayak, N Krishnamurthy, Murali S “Characterization of Abrasive Wear Properties of Plasma Sprayed Alumina and YSZ Coatings on Aluminium 6061 Substrate”, Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, Volume 13 Issue 12, December2018,pp.4240-4257.
24. Chandrakala, B. M., Sontakke, V., Honnaiah, S., Mohan Kumar, T. G., Balasubramani, R., & Verma, R. (2025). Harnessing Online Activism and Diversity Tech in HR Through Cloud Computing. In D. Ertuğrul & A. Elçi (Eds.), Future of Digital Technology and AI in Social Sectors pp. 151-182, IGI Global Scientific Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-5533-.6ch006
25. R. Sushmitha, A. K. Gupta and Chandrakala B. M., "Automated Segmentation Technique for Detection of Myocardial Contours in Cardiac MRI," 2019 International Conference on Communication and ElectronicsSystems(ICCES),Coimbatore, India,2019, pp. 986-991, doi: 10.1109/ICCES45898.2019.9002554.
26. A. Navya and Chandrakala B M, "The Effective Dashboard to Control the Intrusion in the Private
Protection of the Cloudlet Based on the Medical Mutual Data Using ECC," 2018 International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), Coimbatore, India, 2018, pp. 538-543,doi:10.1109/ICIRCA.2018.8596783.
27. Haridasa Nayak, Revanasiddappa Moolemane et.al., “Nanoclay-Based Conductive and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties of Silver-Decorated Polyaniline and Its Nanocomposites”, Journal Materials Advances Royal Society of Chemistry, https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00393K, (2023) pp.4400-4408.
28.H. -H. Lin, "Applying Evolutionary Algorithms to Optimize Hyperparameters for Prediction Model of Solar Power Generation,"2023 Sixth International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control (IS3C), Taichung, Taiwan, 2023, pp. 64-67, doi: 10.1109/IS3C57901.2023.00025.
29.Czajkowski, K., Fitzgerald, S., Foster, I., Kesselman, C.: Grid Information Services for Distributed Resource Sharing. In: 10th IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Distributed Computing, pp. 181–184.IEEEPress,NewYork(2001)
30.Foster, I., Kesselman, C., Nick, J., Tuecke, S.: The Physiology of the Grid: an Open Grid Services Architecture for Distributed Systems Integration. Technicalreport,GlobalGridForum(2002)
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008