
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 09 | Sep 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 09 | Sep 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
P Sanyasi Naidu1 , Beena Renuka2
1Professor, Department of Computer Science and System Engineering, Andhra University College of Engineering, Andhra Pradesh, India.
2Student, Department of Computer Science and System Engineering, Andhra University College of Engineering, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Abstract – This study presents a hybrid forecasting framework that integrates Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models to improve stock price prediction. ARIMA is effectivein identifying short-term trends and linear components in time series data, while LSTM excels in capturing nonlinear dependencies and long-range patterns. By combining these two approaches, theproposedmodelleveragesthestrengthsof both statistical and deep learning methods. In the two-stage design, ARIMA first models the linear structure of the stock data, and the residual errors are subsequently processed by the LSTM to account for nonlinear fluctuations.MeanSquared Error (MSE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and the coefficient of determination (R2) are among the error metrics used to validate the efficacy of the hybrid model. Experimental results show that the ARIMA–LSTM model consistently outperforms standaloneARIMAandLSTM, achieving lower error values and a high R² score of 0.9546. These findings indicate that the hybrid approach provides more accurate forecastsanddemonstratesstrongpotentialfor practical applications in financial forecasting and decision support.
Key Words: ARIMA, Deep Learning, Financial Forecasting, Hybrid Model, LSTM, Stock Price Prediction
Forecasting stock market prices remains a complex challengeduetothehighlyvolatile,nonlinear,anddynamic nature of financial data. Traditional econometric models such as the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)havebeenwidelyappliedbecauseoftheirabilityto captureautocorrelationandlineardependencies.However, these models are limited in representing nonlinear behaviours that are common in real-world financial time series. On the other hand, deep learning techniques, particularly Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, haveshownconsiderablesuccessinmodelingsequentialand nonlinear patterns. LSTM, a variant of recurrent neural networks(RNNs),incorporatesmemorycellsthatenablethe networktoretaininformationoverlongsequences,making itsuitableforlearninglong-termdependencies.Despiteits
advantages, LSTM models are prone to overfitting when trained on limited datasets and require significant computationalresources.
ToovercomethelimitationsofusingARIMAorLSTMalone, researchershaveproposedhybridforecastingframeworks thatcombinestatisticalandmachinelearningapproaches. Previous studies, such as ARIMA–ANN and ARIMA–neural networkmodels,havedemonstratedthatintegratinglinear and nonlinear modelling techniques can lead to improved accuracy.Morerecently,theARIMA–LSTMhybridapproach hasgainedattentionforitsabilitytocapturebothshort-term linearstructuresandlong-termnonlineardependenciesin financialdata.
Motivated by these insights, this study develops and evaluates a hybrid ARIMA–LSTM model for stock price prediction. Thisworkmakesthreecontributions:
•Creatingatwo-stagehybridmodelinwhichLSTMmodels nonlinearresidualsandARIMAcaptureslinearcomponents.
UsingerrormetricslikeMSE,RMSE,MAE,MAPE,andR2to assessthemodel.
•Demonstratingthatthehybridapproachachievessuperior accuracy,explainingover95%ofthevarianceinstockprice movements.
This paper’s research approach blends the statistical soundnessoftheAutoregressiveIntegratedMovingAverage (ARIMA)modelandthenon-linearlearningLongShort-Term Memory(LSTM)networks.Itsworkflowincludessixstages: datacollectionandpreprocessing,ARIMAmodeling,residual extraction, LSTM modeling, hybrid integration, and performanceevaluation.Figure1displaystheoverallsystem framework.
Stockmarketdatacoveringmultipleyearswascollectedfrom publiclyavailablefinancialdatabases.Thedatasetcontained daily values such as open, high, low, close, and trading volume, ensuring representation of diverse market

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 09 | Sep 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
conditions. To improve predictive capability, additional technicalindicatorsweregenerated,including:
Simple Moving Average (SMA): Toobservebothshortandlong-termmarketmovements.
ExponentialMovingAverage(EMA):Emphasizing recentpricechangesbyassigninghigherweights.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Identifying overboughtandoversoldstates.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Identifiesperceivedmomentumandtrend reversals.
Skipping of data or inaccuracy while performing dateconversionalsoleadstotheremovaloftrends tocauseanimpairment.
Anygapsinthedataandthedateconversionprocess
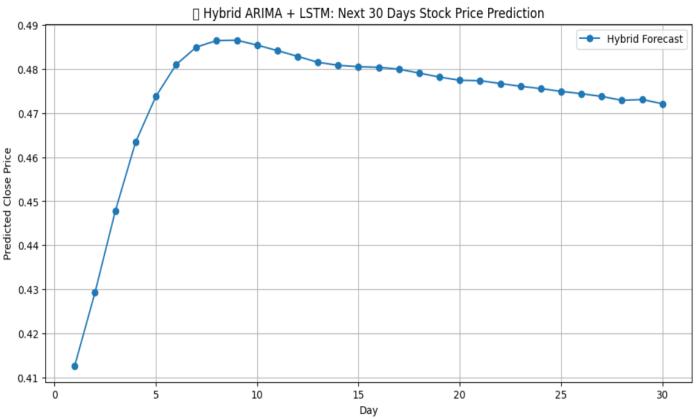
The ARIMA model was applied to capture the linear dependencies present in stock price series. Its structureis determinedbythreeparameters:
• p: Thenumberofautoregressiveterms,
• d: Thelevelofdifferencingneededtomaketheprocess stationary,
• q: Theorderofthemovingaverage.
Toidentifythemostsuitableconfiguration,autocorrelation (ACF)andpartialautocorrelation(PACF)plotswereanalysed alongsideAkaikeInformationCriterion(AIC)values.Based on this evaluation, ARIMA (5,1,0) was selected, providing baselinepredictionsthatrepresentthelineartrendsofstock prices
AlthoughARIMAiseffectiveinmodelinglinearcomponents, itfailstoaccountfornonlinearvariationsinstockdata.To address this limitation, we computed residuals as the difference between observed stock values and ARIMAgenerated forecasts: Residual(t) = Actual(t)–ARIMA Prediction(t).Theseresidualswerethenusedasinputtothe LSTMmodel.
TheresidualsobtainedfromARIMAforecastsweremodeled usinganLSTMnetworktocapturenonlineardependencies. The residual series was reformatted into a supervised learningdatasetthroughaslidingwindowof60-timesteps, wherethefirst59observationsservedasinputfeaturesand the60thvalueasthepredictiontarget
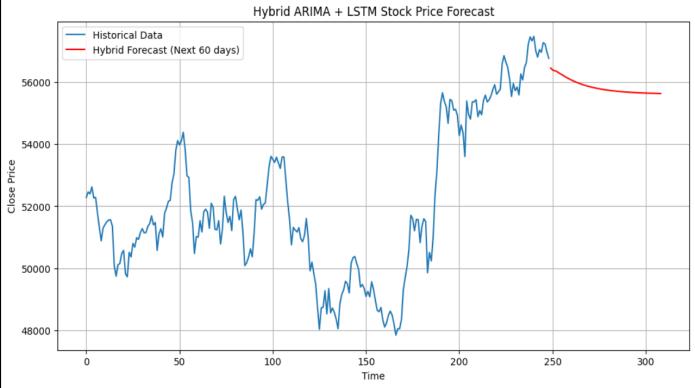
Fig:260dayspredictionusingHybridARIMA+LSTM
Two 50-unit stacked LSTM layers made up the network design,whichwasfollowedbyafullyconnectedoutputlayer. Dropout regularization was applied to reduce overfitting, whiletheAdamoptimizerwasemployedforefficientlearning rate adaptation. The loss metric of choice was the Mean SquaredError(MSE)function.Thisconfigurationenabledthe LSTM to capture complex sequential relationships in the residualdata
The final forecast was generated by integrating the baseline ARIMA predictions with the residual estimates producedbytheLSTMnetwork:
Hybrid Prediction(t) = ARIMA Prediction(t) + LSTM Residual(t).
Thistwo-stageintegrationcombinesARIMA’scapability tocapturelinearstructureswithLSTM’sstrengthinmodeling nonlinearsequences, thereby enhancing overall predictive accuracy and robustness in highly volatile financial environments.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 09 | Sep 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Toassessmodelperformance,severalevaluationmetrics wereemployed:
MeanSquaredError(MSE): calculatestheaverage squared deviation between predicted and actual values.
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): expresses prediction errors in the same unit as stock prices, makinginterpretationeasier.
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): represents the averageabsolutedifferencebetweenpredictedand observedvalues.
Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): now enables comparison as it presents the error magnitudeinactualpercentage
Coefficient of Determination (R²): measures the proportion of variance in actual stock values explained by the model; values closer to 1 imply strongerpredictivecapability.
Using multiple evaluation criteria helps ensure a reliableassessmentofforecastingperformance.
Mean Squared Error (MSE): (1/n)Σ(yₜ−ŷₜ)²
Thisstudyfocusedoncreatingahybridforecastingmethod that combines the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average(ARIMA)andLSTMnetworksforpredictingstock prices.Wecomparedhowthishybridframeworkworkswith traditionalmodelingmethods.Thegoalwastodetermineif the hybrid model could consider both the linear and nonlinearrelationshipsinfinancialtimeseriesdatarelatedto price.
3.1.
We used MSE, RMSE, MAE, MAPE, and R2 as standard metricstoevaluatetheforecastingperformanceofARIMA, LSTM,andHybrid(ARIMA-LSTM)models.
Model performance was evaluated using standard error metricssuchasMSE,RMSE,MAE,MAPE,andR².TheARIMA model successfully captured the linear structure of stock data but exhibited lower accuracy due to its inability to handle nonlinear variations. The LSTM model performed better by learning complex sequential dependencies, achieving reduced error values compared to ARIMA. Nevertheless, the hybrid ARIMA–LSTM framework outperformedbothindividualmodels,recordinganRMSEof 591.21andanR²of0.9546.Thisdemonstratesunequivocally thatcombiningLSTMandARIMAproducespredictionsthat aremoreaccurateanddependable.
Covariance: Shows how two variables move together positivevaluesindicatetheyincreasetogether,andnegative valueswhentheytendtomoveinoppositedirections.
Table:1PerformanceComparisonofARIMA,LSTM,and HybridARIMA–LSTMModels.
Table:2ComparativeAnalysisofR²andCovariancefor LSTMandHybridARIMA–LSTMModels
3.2. Actual vs Predicted Stock Prices
Comparing actual values with predicted outputs revealed that the hybrid ARIMA–LSTM model closely followed real stockmarketmovements.Thisindicatesitseffectivenessin representing both immediate fluctuations and long-term markettrendswithhighfidelity.
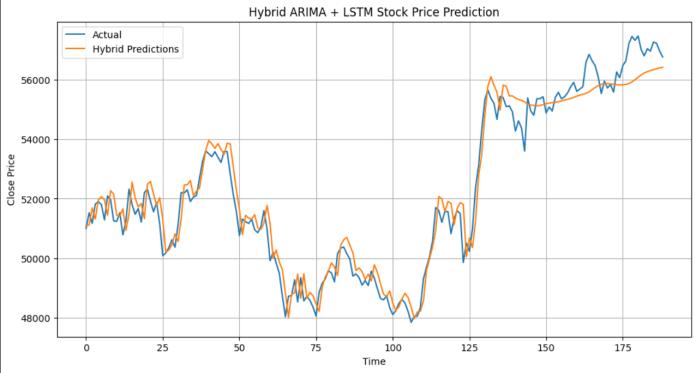
Fig:3ActualvspredictedStockpriceprediction.
3.3. Comparative Analysis with Traditional Models
Whencomparedtootherforecastingmethods,likeARIMA alone or deep learning alone, the Hybrid model produced lower errors and higher accuracy. This implies that by utilizing the advantages of both techniques, combining statisticalmodelsanddeeplearningenhancesperformance.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 09 | Sep 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
An error distribution analysis was conducted to further validate model robustness. The hybrid model’s prediction errorsweretightlycenteredaroundzerointhedensityplot, reflecting strong reliability. Additionally, boxplot results showed that the hybrid framework achieved the lowest median error and exhibited the smallest variability compared with ARIMA and LSTM, reinforcing its superior performance.
3.5.
Theresultshighlightseveralkeyobservations:
Strengths of Hybrid Modeling:IntegratingARIMA andLSTMenableseffectivehandlingofbothlinear andnonlinearcomponents,significantlyimproving accuracy.
Limitations of Standalone Models:ARIMAfailsto capture nonlinear market patterns, while LSTM, though powerful, tends to overfit when data availabilityislimited.
Practical Applications: The hybrid model demonstrates strong potential for real-world applications, including portfolio optimization, algorithmic trading, and risk management in volatilefinancialenvironments.
The proposed hybrid ARIMA–LSTM model demonstrates strongpredictiveperformance;however,thereareseveral avenues for further development. Future research can exploretheinclusionofadditionalfinancialindicatorssuch as sentiment analysis from news and social media, which may capture market psychology and improve prediction accuracy. Expanding the dataset to cover multiple global stock markets can enhance the model’s generalization ability. Moreover, optimizing the architecture of LSTM layers,integratingattentionmechanisms,orexperimenting with alternative deep learning models like GRU and Transformer networks could provide deeper insights into nonlineardependencies.Finally,deployingthehybridmodel in real-time trading environments would validate its practicalapplicabilityforinvestmentdecision-makingand riskmanagement.
5.Conclusion
ThispaperproposedahybridARIMA–LSTMframeworkfor predicting stock prices by combining the strengths of statisticalanddeeplearningmodels.Theresultsconfirmed thatARIMAeffectivelycapturesthelinearstructureofstock market data, while LSTM successfully models nonlinear fluctuations.Whenintegrated,thehybridmodelsignificantly
reduced forecasting errors and achieved an R² value of 0.9546, outperforming both standalone ARIMA and LSTM models.Theseoutcomeshighlighttheeffectivenessofhybrid approachesinfinancial forecastingand demonstrate their potential for real-world applications such as portfolio optimization,algorithmictrading,andriskmanagement.All thingsconsidered,thestudyemphasizeshowcrucialitisto combine complementary models in order to manage the complexityofstockpricefluctuations.
[1]Bollen,J.A.,Mao,H.,andZeng,X.,"Twittermoodpredicts thestockmarket," Journal of Computational Science,vol.2, no.1,pp.1–8,2011.
[2] Box,G.,Jenkins,G.,andReinsel,G., Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 5th ed., Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley, 2015.
[3] Chen, Z., Chen, Z., and He, Y., "Stock prediction using convolutionalneuralnetworkandlongshort-termmemory," in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Cloud Compute. Big Data Anal., Chengdu,China,Apr.2017,pp.639–643.
[4] Fischer,A.,andKrauss,C.,"Deeplearningwithlongshortterm memory networks for financial market predictions," European Journal of Operational Research,vol.270,no.2,pp. 654–669,Oct.2018.
[5]Guresen,C.,Kayakutlu,G.,andDaim,T.U.,"Usingartificial neural network modelsinstock marketindexprediction," Expert Systems with Applications,vol.38,no.8,pp.10389–10397,Aug.2011.
[6] Hochreiter, H., and Schmidhuber, J., "Long short-term memory," Neural Computation,vol.9,no.8,pp.1735–1780, Nov.1997.
[7] Hyndman, R. J., and Athanasopoulos, G., Forecasting: Principles andPractice,3rded.,Melbourne,Australia:OTexts, 2021.
[8] Kara, F., Boyacioglu, M., and Baykan, D., "Predicting direction of stock price index movement using artificial neuralnetworksandsupportvectormachines:Thesample of the Istanbul Stock Exchange," Expert Systems with Applications,vol.38,no.5,pp.5311–5319,May2011.
[9] Khashei,M.,andBijari,M.,"Anartificialneuralnetwork (p,d,q)modelfortimeseriesforecasting," Expert Systems with Applications,vol.37,no.1,pp.479–489,Jan.2010.
[10]Nelson,R.,Pereira,A.,anddeOliveira,R.,"Stockmarket’s pricemovementpredictionwithLSTMneuralnetworks,"in Proc. IEEE Int. Joint Conf. Neural Netw. (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro,Brazil,Jul.2018,pp.1–8.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 09 | Sep 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[11]Patel,J.,Shah,S.,Thakkar,P.,andKotecha,K.,"Predicting stock and stock price index movement using trend deterministic data preparation and machine learning techniques," Expert Systems with Applications,vol.42,no.1, pp.259–268,Jan.2015.
[12] Siami-Namini, S., Tavakoli, N., and Namin, A. S., "A comparisonofARIMAandLSTMinforecastingtimeseries," in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. Appl. (ICMLA),Orlando, FL,USA,Dec.2018,pp.1394–1401.
[13]Song,H.H.,Park,K.,&Kim,J.,"HybridARIMAandLSTM modelforenergyloadforecasting," Energies,vol.13,no.1,p. 130,Jan.2020.
[14] Wang, J.,Yang,J., andZhang,W.,"Ahybrid forecasting model for stock market prediction based on ARIMA and LSTM,"in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Transp. Syst.,Auckland, NewZealand,Oct.2019,pp.1–6.
[15]Zhang,J.,"TimeseriesforecastingusingahybridARIMA and neural network model," Neurocomputing, vol. 50, pp. 159–175,Jan.2003.