
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
A. Athulya
Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering National Institute of Technology, Srinagar ***
Abstract - Corrosion is a major industrial issue causing severe material degradation and economic losses. Surface coatings serve as an efficient and economical approach to mitigate corrosion by providing a barrier between the metal surface and its environment. This paper reviews recent advancements in coating technologies such as nanocomposite coatings, sol–gel coatings, plasma-assisted processes, and environmentally friendly alterna- tives to traditional chromium-based systems. It also highlights emerging smart and self-healing coatings and the integration of AI-assisted monitoring for sustainable corrosion control.
Key Words: Corrosion,SurfaceCoating,Nanocomposite,Sol–gel,Self-healing,Eco-friendlycoatings,AImonitoring
INTRODUCTION:
Corrosion is an electrochemical process leading to the degradation of metals in the presence of moisture, oxygen, or aggressive environments. Globally, corrosion results in massive economic losses and safety risks in industries such as automotive,aerospace,marine,andconstruction.Surfacecoatingsareoneofthemosteffectiveandeconomicalmeansof corrosion protection due to their versatility and adaptabil- ity. Traditional coatings like zinc, nickel, and chromium are effectivebutfacechallengesinenvironmentalcomplianceandlong-termperformance.Recentdevelopmentshavefocused onnanocomposite,sol–gel,plasma,andsmartcoatingsthatenhancecorrosionresistanceandsustainability
A. Electrochemical and Electroplating Coatings
Electroplatingisoneoftheoldestandmostreliablecoat-ingtechniques,usedfordepositingmetalcoatingssuchaszinc, nickel, and chromium. Recent innovations like pulse electrodepositionandalloy coatings (e.g.,Zn–Ni,Ni–W) have shown improved corrosion resistance and hardness. Nanoparti- cle incorporation (SiO2, Al2O3, TiO2) leads to nanocomposite coatingswithsuperiorwearandcorrosionresistance[1].
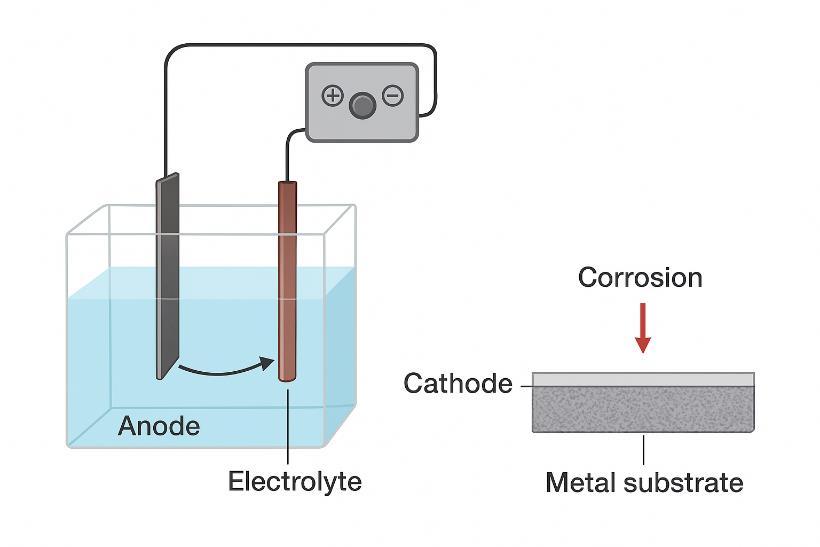
Fig.1:Electroplating processsetup.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
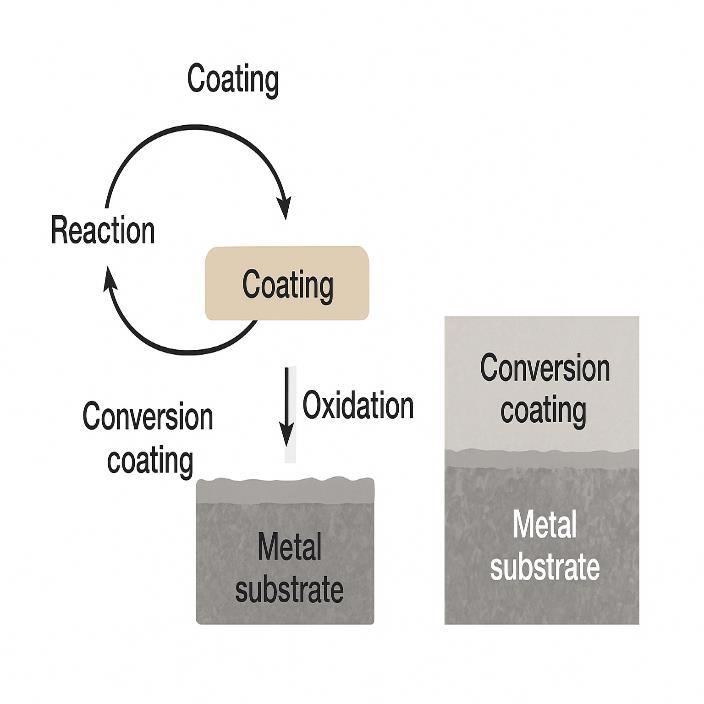
B. Conversion Coatings
Conversion coatings react chemically with the metal sub- strate to form a protective film. Chromium-free conversion coatingsbasedonzirconium,titanium,orrareearthelementshaveemergedasenvironmentallyfriendlyalternatives[2].
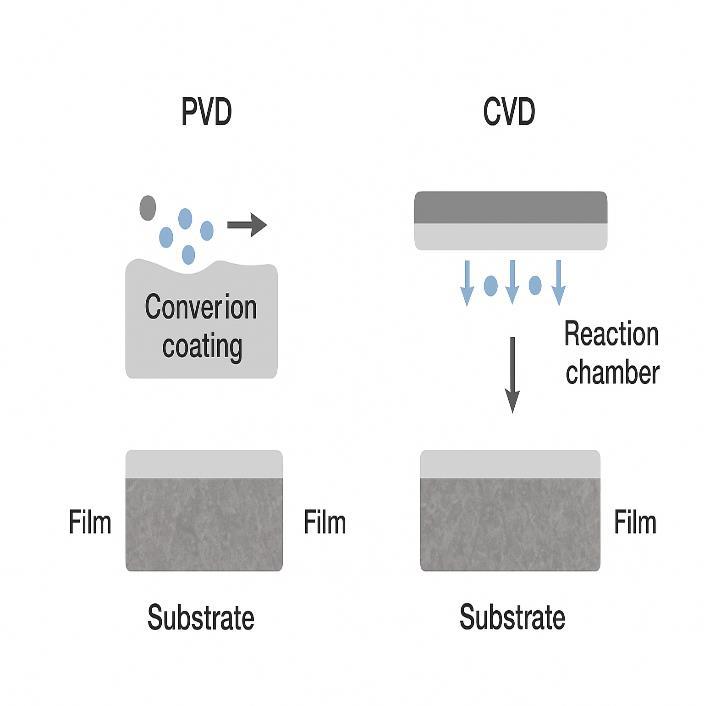
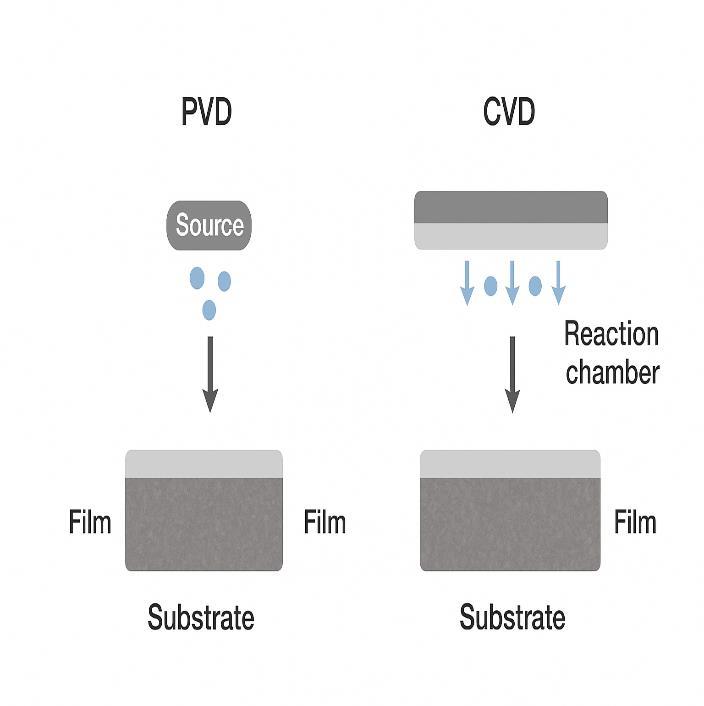
C. Physical and Chemical Vapor Deposition (PVD/CVD)
PVD and CVD techniques produce hard, dense coatings such as TiN, CrN, and AlTiN. Plasma-assisted versions en- hance coatinguniformityandadhesion.Thesearewidely usedinaerospaceandtoolingapplicationsduetotheirhighdurability [3].
D. Sol–Gel and Nanocomposite Coatings:
Sol–gel coatings are eco-friendly and allow incorporation of nanoparticles such asSiO2, TiO2, and graphene oxide. These coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance and are particularly suitable for lightweight alloys like aluminum and magnesium[4]
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page706

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Sol–gel coatingmechanism.
Polymer-based coatings like epoxy, polyurethane, and polyaniline act as effective barriers. Modern research focuses on self-healing coatings containing microcapsules that au- tonomously release inhibitors or monomers to repair damaged regions[5].
Coatings protect metal substrates through multiple mecha- nisms including barrier protection, sacrificial protection, passivation,andself-healing.Barriercoatingslimitaccessofcor-rosivespecieslikeoxygenandwater.Sacrificialcoatings(e.g., zinconsteel)corrodepreferentiallytoprotectthebasemetal.Chemicalpassivationlayersformstableoxidesthatprevent furthercorrosion,whileself-healingcoatingsreleaseinhibitors to repair defects.Recent developments include AI-assisted monitoringsystemscapableofdetectingcoatingdegradationinreal-timeusingembeddedsensors[6].
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page707

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
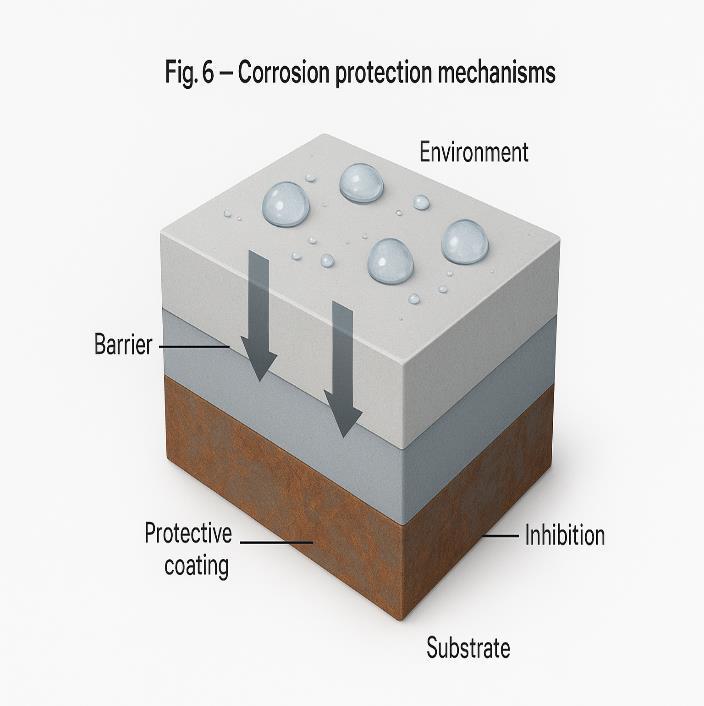
Fig.6:Mechanismsofcorrosionprotection(AI-assistedrendering)
Table -1: Comparison of Major CoatingTechniquess forCorrosionProtection
Technique
Characteristics
Electroplating Economical and adherent, but may involvetoxic chemicals.
ConversionCoating Environmentallysafebutlimitedthickness.
PVD/CVD Hard,densecoatings butexpensive and high-temperatureprocesses.
Sol–Gel Eco-friendlyandadaptable,thoughlesswear-resistant.
Polymer/Hybrid Flexible and self-healing but prone to UVdegradation.
Recent research emphasizes eco-friendly, nanostructured, and smart coatings. Graphene-based barriers, plasma-assisted depositions, and hybrid sol–gel systemsare key trends. Fu- ture directions include bio-based polymer coatings, AI-driven corrosion monitoring,andself-sensingcoatingscapableofadaptiveresponsetoenvironmentalconditions.Theintegration of data-driven predictive models and sustainable materialsis expected to redefine corrosion protection technologies by2030[7].
CONCLUSIONS
Surface coatings continue to play a vital role in corrosion control. Recent progress in nanostructured, hybrid, and selfhealingcoatingshasimprovedbothperformanceandsustain-ability.Futureadvancementswilllikelyfocusonsmart,selfsensing,andenvironmentallysafesystemsintegratedwithAI-baseddiagnosticsforlong-termreliability.
REFERENCES
[1] S. Ramesh et al., “Recent progress in nanocomposite coatings for corrosion protection,” Surface & Coatings Technology,vol.438,2022.
[2] L.Zhangetal.,“Chromium-freeconversioncoatingsforaluminumalloys:Areview,”ProgressinOrganicCoatings, vol.182,2023.
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page708

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page709
[3] N. Gupta and A. Sharma, “Recent developments in graphene-based coatings for corrosion resistance,” Journal of AlloysandCompounds,vol.986,2024.
[4] R. Singh and P. Kumar, “Sol–gel coatings: A sustainable approach for corrosion protection,” Journal of Materials ResearchandTechnology,vol.15,pp.100–115,2021.
[5] Y.Chenetal.,“Self-healingpolymercoatingsforanti-corrosionappli-cations,”CorrosionScience,vol.174,2020.
[6] T.Wangetal.,“AI-drivenmonitoringofcoatingdegradation:Anewparadigmincorrosioncontrol,”Coatings,vol. 15,no.2,2024.
[7] K. Patel and J. Verma, “Smart coatings and predictive corrosion preven- tion,” Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 83,2025.