
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Avadh Nagaralawala
Controls Engineer, Tucson, Arizona 85653. Email: Avadh4may@gmail.com ***
TheintegrationofProgrammableLogicControllers(PLCs)andSupervisoryControlandDataAcquisition(SCADA)systems has emerged as a transformative approach to enhancing automation, safety, and operational efficiency in the mining industry. As mining operations become more complex and geographically dispersed, the need for reliable, real-time control and monitoring systems becomes increasingly critical. PLCs provide robust, real-time control of machinery and processes, while SCADA systems offer centralized supervision, data collection, and analysis capabilities. Together, these technologies enable mining companies to optimize production, reduce downtime, and respond promptly to hazardous conditions.
This paper investigates the role of integrating PLC and SCADA systems in mining, with a focus on how these systems contribute to safer and more efficient operations. It delves into architectural design, communication standards, and the technical interdependencebetweenthesesystems. Theresearch alsoexamines theeconomicandenvironmental benefits of implementing integrated control systems, including improved maintenance planning, energy efficiency, and more effectiveresourceoptimization.
The discussion is supported by case studies demonstrating successful applications of PLC and SCADA integration across diverse mining functions, including mineral processing, coal operations, underground ventilation control, and haulage system automation. While the benefits are substantial, the paper also acknowledges key obstacles such as high capital costs,cybersecurityvulnerabilities,andtheongoingneedforskilledLabor.
By providing a comprehensive analysis of current technologies, implementation challenges, and future trends, this researchunderscoresthecriticalimportanceofPLCandSCADAsystemsindrivingthedigitaltransformationofthemining industry.Thepaperconcludeswithrecommendationsforbestpracticesandstrategicconsiderationsforminingoperators aimingtoadoptorupgradeautomationinfrastructure.
Keywords: Mining Automation, SCADA System, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), Industrial Internet of things (IIOT),SmartMiningTechnologies,SustainableMiningTechnology.
The mining sector ranks among the most resource-intensive and high-risk industries worldwide, frequently operating in harshenvironmentalsettingswhilegrapplingwithsignificantlogisticalandsafetyconcerns (Rawashdeh,Campbell,&Titi, 2016) Traditional mining operations have been labour-intensive and prone to inefficiencies, human error, occupational hazard and unsafe practices. In recent years, however, the emergence of automation and advanced control systems has revolutionizedhowminingprocessesaremanaged (Aly,2024).Amongthemostsignificantadvancementsinthisdomain are the integration of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems,whichtogetherprovideapowerfulplatformforenhancingprocessefficiency,ensurebettersafetyoutcomes,and operationalvisibility(Shahzad,Bouri,Mokni,&Ajmi,2021)
PLCsarerugged,industrial-gradedigitalcomputersdesignedtoperformdiscreteorcontinuouscontroltasksinrealtime, often used to automate equipment such as conveyor belts, pumps, ventilation fans, and crushers (PLC Controllers in MiningOperations:DiggingDeeperwithControl,2023).SCADAsystems,ontheotherhand,serveassupervisoryplatforms that gather data from sensors and field devices via PLCs and present them to operators in real time through humanmachine interfaces (HMIs). This supervisory layer allows for the monitoring, control, and analysis of critical mining operationsacrossgeographicallydispersedsites (LyudmilaSamorodova,2016)
TheconvergenceofPLCandSCADAtechnologiesisnotjustatechnicalintegrationbutastrategicone drivenbytheneed toimprovedecision-making,reducedowntime,andincreaseminesiteefficiency.Furthermore,withrisingglobalemphasis on sustainable and safe mining, automation through PLC and SCADA has become indispensable for mining companies striving to meet environmental, social, and governance (ESG) objectives (Aly, 2024). However, while the benefits of

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
integration are substantial, there are also notable challenges, including high initial investment costs, cybersecurity concerns,andtheneedforskilledtechnicalpersonnel (Yarakaraju,2024)
The adoption of automation systems in the mining sector is rooted with a foundational understanding of the two core components: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems. While both technologies, although distinct in function, they work collaboratively to establish a robust and integrated controlframeworkwithinindustrialcontrolsystemoperations.
PLCs are specialized industrial computers used for automation of electromechanical processes. In mining, these include machinery such as conveyors, crushers, fans, pumps, and hoisting systems. PLCs are favoured for their robustness, reliability, and ability to operate under extreme environmental conditions, which are common in mining environments. Designedforreal-timecontrol,PLCscontinuouslyscaninputsignalsfromfielddevices,processthemthroughuser-defined logic,andsendoutputcommandstoactuatorsandcontrolelements(Mello,2024)
One of the main defining features of PLCs is their modular architecture, which enables for flexible customization and scalability depending on the size and complexity of the mining operation. For example, a surface mining operation may deployafewdozenPLCstocontrolandmonitortheminingprocesses,Onthecontraryanundergroundminingplantand facility may require hundreds of PLCs connected via industrial communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, or Ethernet/IP.
SCADA systems serve a complementary role to PLCs by enabling operators to visualize, monitor, and control the entire miningprocessfromcentralizedlocations.ThroughHuman-MachineInterfaces(HMIs),SCADAsystemscollectdata from PLCsandsensorsandpresentitinaneasilydigestibleformat.Thisallowsoperatorstomakeinformeddecisions,identify bottlenecks,trackperformancemetrics,andrespondtofaultsinrealtime(Cubizolles,2025)
Beyond Real time visualization, SCADA systems also offer cumulative and historical data logging, alarming, trends and reporting functionalities. These features play a very critical role in meeting safety and environmental compliance requirements. Forinstance,SCADAsystemscanissuealarmandwarningmessageswhengaslevelsinundergroundmines exceedsafelimitsorwhenmachineryoperatesfromitsnormaloperatingrange.
While PLCs handle localized machine-level automation, SCADA systems oversee plant-wide or mine-wide operations. When integrated, these systems offer synergistic benefits: PLCs ensure deterministic control, and SCADA ensures datadrivendecision-making.Theinteractionbetweenthetwoistypicallyfacilitatedthroughindustrialnetworks,withSCADA pollingdatafromPLCsatregularintervals.(Shewale,Patil,Borkhade,&Shinde,2020)
This layered architecture provides both granularity and comprehensiveness. For example, if a PLC detects a fault in a ventilationfan,theSCADAsystemcaninstantlylogthefault,alerttheoperator,andtriggerapre-definedsafetyprotocol, suchassystemshutdownorreroutingairflow.
Inthehigh-stakesenvironmentofmining,rapiddecision-makingandreliabledataarecritical.TheintegrationofPLCand SCADA control system plays a vital role in minimizing human error, lower maintenance expenses, and improve overall equipmenteffectiveness(OEE).Theseautomationtechnologiesnotonlyimproveproductivitybutalsoeffectivelyenhance workplace safety a crucial factor in mines with hazardous conditions, including the presence of toxic gases, high temperatures,andconfinedspaces.
Ultimately, the synergy between PLC and SCADA systems forms the backbone of advanced Surface and underground mining operations. Their coordination delivers a dual layer of control and oversight, enabling mines to transition from manual,reactiveoperationstoautomated,predictivesystemsthatalignwiththeindustry’sincreasingdemandforsafety, sustainability,andefficiency.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

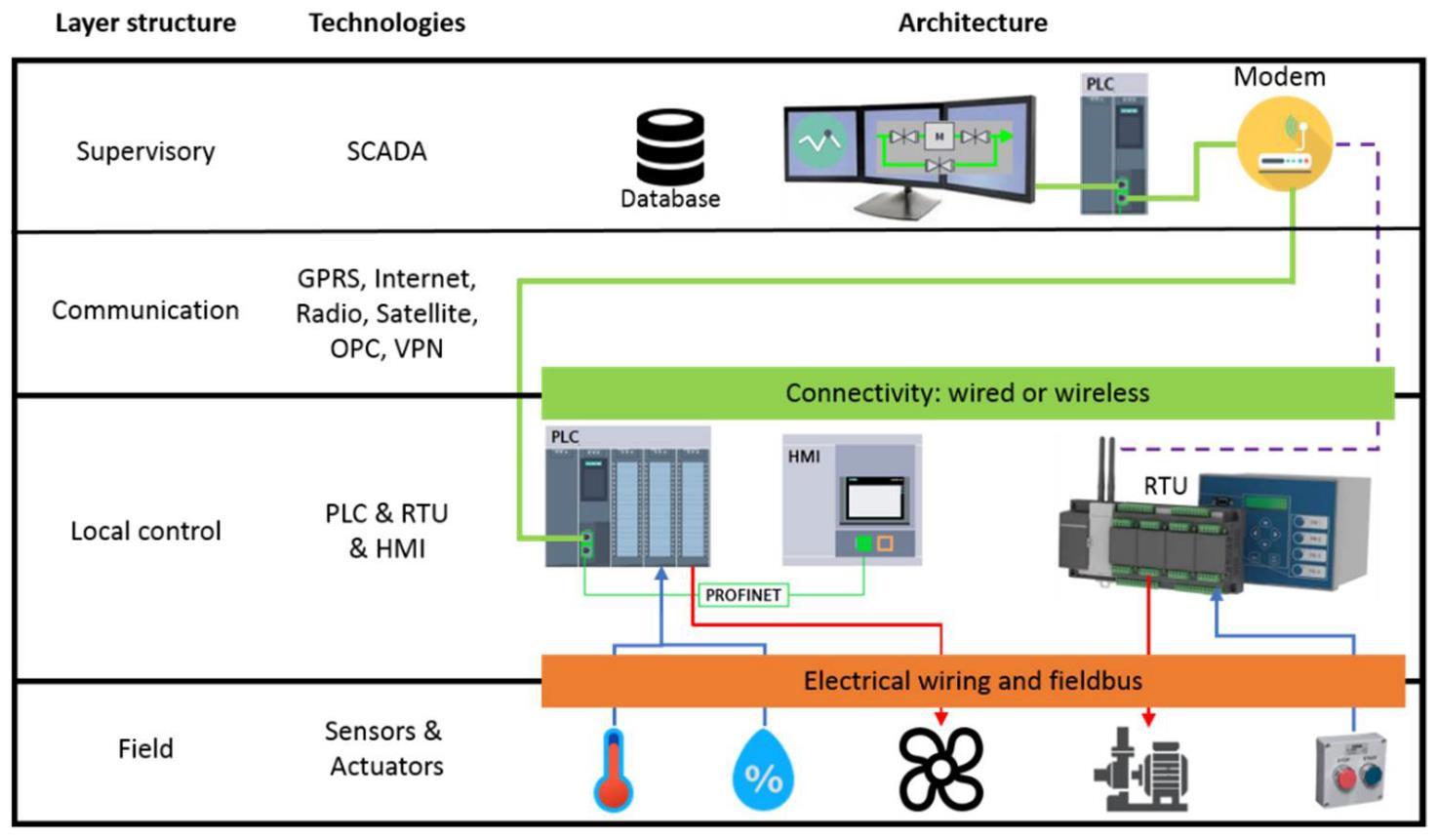
Figure-1TypicalNetworkArchitecturelayoutwiththeintegrationofPLCandSCADASystems
The integration of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) with Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems has brought transformative improvements to mining operations across multiple areas by delivering substantial benefits. From a productivity standpoint, these systems share real-time monitoring of mine data and control of mining equipment and vehicles, leading to optimized processes and lowered downtime. Safety is enhanced through continuous surveillanceofenvironmentalconditionsandautomatedemergencyresponses,mitigatingrisksassociatedwithhazardous miningenvironments.Intermsofcostefficiency,automationreducesmanualLaborrequirements,andenablingpredictive maintenance strategies, which minimizes unexpected equipment failures and associated expenses. Moreover, the environmental sustainability of mining operations is improved through precise control of resource usage and emissions, aligningwithglobaleffortstoreducetheecologicalfootprintofindustrialactivities(Yarakaraju,2024)
The integration of PLC and SCADA technologies greatly enhances efficiency in mining operations by automating both repetitive and complex tasks. PLCs are responsible for real-time control of machinery, ensuring optimal performance of equipment suchashaul trucks,conveyors,andcrushers. Meanwhile,SCADAsystemsprovide centralized monitoringand control capabilities, enabling remote monitoring and control of various processes from control rooms. This setup minimizes the need for manual input, speeds up decision-making, and helps eliminate delays or inefficiencies in the productioncycle.
Miningisinherentlyhazardous,withrisksincludinggasleaks,equipmentfailure,andstructuralcollapses.IntegratedPLC andSCADAsystemsenhancesafetybyenablingautomateddetectionofanomaliesandreal-timeresponsestoemergencies. For instance, if toxic gases are detected in underground tunnels, PLCs can immediately trigger alarms and activate ventilation systems, while SCADA logs the incident and alerts human operators. These systems also help enforce lockout/tagoutproceduresandmachinesafeguarding,reducingtheriskofaccidentsandinjuries(Aly,2024)

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Maintenance is a major cost driver in the mining industry. The integration of PLC and SCADA enables predictive maintenance by monitoring equipment health and performance metrics in real-time. This allows early identification of wear and tear, reducing unplanned downtime and extending machinery life. By collecting and analysing data trends, SCADA systems can schedule maintenance at optimal intervals, avoiding costly breakdowns and increasing overall asset utilization(PLCControllersinMiningOperations:DiggingDeeperwithControl,2023).
OneofthemajoradvantagesofSCADAintegrationistheaccessofreal-timedataandadvancedanalytics.Bycontinuously capturing and storing operational data, SCADA enables mine operators can make evidence-based decisions to optimize throughput, energy efficiency, and resource allocation. Additionally, the system’s ability to generate comprehensive dashboards and reports supports compliance with regulatory standards, facilitates performance evaluations, and drives ongoingimprovementacrossoperationalprocesses.
Modern mining operations are under increasing pressure to reduce their environmental footprint. PLC and SCADA systems can support environmental sustainability by optimizing energy use, minimizing waste, and reducing emissions. Forexample,theycanmonitorfuelconsumption,waterusage,andtailingsdisposalinreal-time,helpingoperatorsidentify inefficienciesandtakecorrectiveactionswiftly.Thisalignswithglobalsustainabilitygoalsandimprovesthesociallicense tooperate.

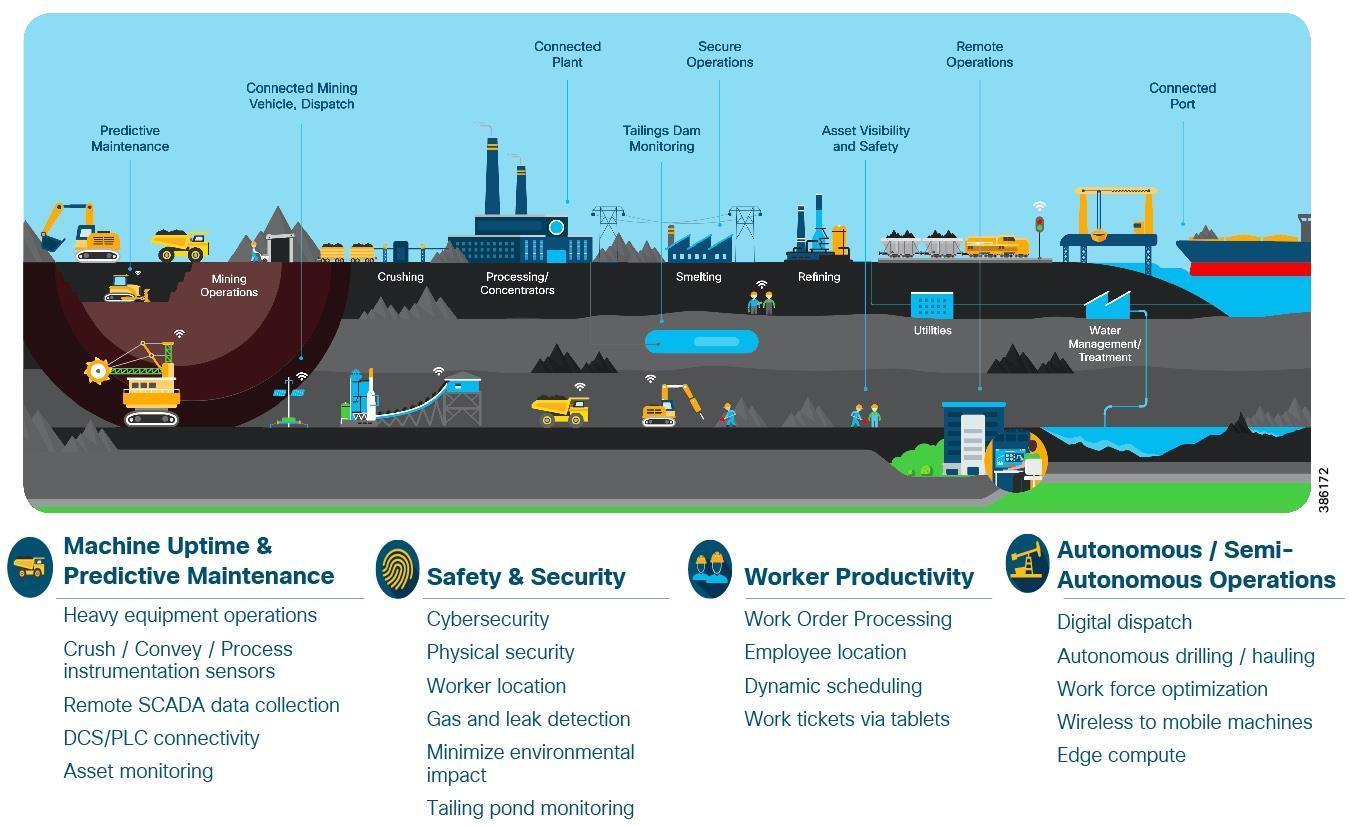
Figure-2BenefitsofPLCandSCADASystemIntegrationchallengesinimplementation
High initial investment
Deploying Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems in mining environments involves significant financial commitment. Expenses extend beyond hardware and software acquisition butalsoinfrastructureupgrades,skilledpersonnel,and implementingcomprehensivetraininginitiatives. For

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
smaller mining entities and companies, these financial expenses can be major challenge. Beyond the initial investment, ongoing costs such as maintenance, system upgrades, and personnel training must also be considered (IndMALL Automation,2024)
Technical Complexity and Integration Issues
Integrating Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems into existing mining operations can present significant technical challenges. Legacy equipment often lacks compatibility with modern control systems, necessitating custom integration solutions or complete equipment replacement. Additionally, configuring these systems to manage complex mining processes requires specialized expertise, as the integration must addresscommunicationprotocols,datasynchronization,andsysteminteroperability.
AsProgrammableLogicControllers(PLCs)andSupervisoryControlandDataAcquisition(SCADA)systemsbecomemore connected to corporate networks and the internet, they face increasing cybersecurity risks. Cyber-attacks targeting industrial control systems can disrupt mining operations, cause equipment damage, and compromise safety. Therefore, implementing strong cybersecurity measures such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems is critical to safeguardingthesevitalsystem (Aly, 2024).
Workforce Adaption
Shifting towards automated systems in the mining industry demands significant cultural and organizational shifts. Workforce resistance is common, often driven by fears of job loss, unfamiliarity with emerging technologies, or doubts aboutadaptingtonewworkflows.Overcomingtheseconcernsrequirescomprehensivetrainingprogramsthatequipstaff with the necessary skills and knowledge to operate new systems confidently. Engaging stakeholders throughout the transition process fosters a sense of ownership and inclusion, mitigating resistance and facilitating smoother implementation. Introducing automation in phases starting with less complex processes and gradually scalingup, allows employees to adapt advancement gradually, reducing uncertainty and promoting acceptance of new technologies. (ManagingEmployeeResistancetoAutomation,n.d.)
Integration with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Theconvergence ofProgrammableLogicControllers(PLCs),SupervisoryControl andData Acquisition(SCADA)systems, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is poised to drive the next wave of innovation in mining operations. By integrating IIoT-enabled sensors and devices, mining companies can collect more granular, real-time data, facilitating smarterandfasterdecision-makingprocesses.Thisenhanceddataacquisitionallowsfordeeperinsightsintooperational performance,enablingpredictivemaintenance,optimizingresourceutilization,andimprovingoverallsafetyandefficiency inminingenvironments(IIoTinMining:TransformingOperationswithSmartTechnology,n.d.)
ThenextgenerationofSCADAsystemsareexpectedto makeagreateruseofedgecomputingtoperformanalyticscloser tothedatasourcewhichminimizeslatencyandlowersthedemandonnetworkbandwidth,enablingfasterresponsetimes and more efficient real-time decision-making. At the same time, cloud computing platforms will be utilized for data storage,backup,andadvancedanalytics, facilitatinggreaterscalabilityandseamlessintegrationwithenterpriseresource planning(ERP)systems(Dsouza&Salcedo,2024).
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and SupervisoryControlandDataAcquisition(SCADA)systemssignificantlyenhancespredictiveanalytics,anomalydetection, andprocessoptimization.Thisintegrationenablesminingoperationstotransitionfromreactivetoproactivemaintenance strategies,therebyimprovingoperationalefficiencyandreducingunplanneddowntime(Garcia,Pena,&Rojas,2025)

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Inthedemandingenvironmentofminingoperations,timelyandinformeddecision-makingisessential.Theintegrationof Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems enhances operational efficiency by minimizing human error, reducing maintenance costs, and improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). These technologies not only boost productivity but also play a critical role in enhancing safety in hazardous mining conditions, such as exposure to toxic gases, extreme temperatures, and confined working spaces (Yarakaraju,2024).

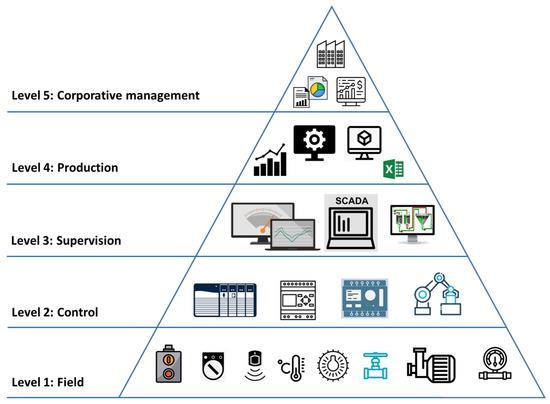
The deployment of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systemshasemergedasatransformativeforceintheminingindustry.Thesetechnologies improveoperationalefficiency, enhance safety, facilitate predictive maintenance, and more sustainable management of natural resources. As mines face mounting pressures to optimize productivity while reducing environmental impact, PLC and SCADA systems offer an indispensableframeworkformodernizationandautomation.
Despite the numerous advantages, the journey toward full implementation is not without its challenges. High upfront capital costs, integration complexities, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and workforce adaptation barriers can impede adoption, particularly in smaller or remote mining operations. However, as technologies evolve and become more accessible,these barriersarelikelytodiminish.Withtheriseof theIndustrial Internet ofThings(IIoT),edge computing, cloud data integration, artificial intelligence, and sustainability-focused innovations, many of these barriers are expected tofade
To fully realize the benefits of PLC and SCADA systems, mining companies must prioritize strategic adoption, invest in workforce skill development programs, and develop strong cybersecurity infrastructures. The mining sector must also commit to continuous innovation and collaboration with technology providers to ensure systems remain adaptable and resilientinthefaceofdynamicindustrialneeds.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Inconclusion,PLCandSCADAsystemsarenotmerelytoolsbutenablersofasmarter,safer,andmoresustainablemining future.Embracingthesetechnologiesisessentialforminingcompaniesseekingtoremaincompetitiveandresponsiblein anincreasinglydigitalandenvironmentallyconsciousworld.
(2024). Retrieved from IndMALL Automation: https://www.indmall.in/faq/what-are-the-costs-associated-withimplementing-a-scada-system/#google_vignette
Aly, A. (2024, October 28). The future of automation in mining, minerals and metals: Integration, efficiency, and sustainability. Retrieved from Scheider Electric: https://blog.se.com/industry/2024/10/28/the-future-ofautomation-in-mining-minerals-and-metals-integration-efficiency-and-sustainability/
Cubizolles, B. (2025, February 25). HMI / SCADA: Everything You Need to Know. Retrieved from GE VERNOVA: https://www.gevernova.com/software/blog/hmi-scada-everything-you-need-to-know
Dsouza, R., & Salcedo, O. (2024, June 19). Improve your industrial operations with cloud-based SCADA systems. Retrieved from AWS Amazon: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/industries/improve-your-industrial-operations-with-cloudscada/
Garcia, J., Pena, A., & Rojas, L. (2025, March 19). AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance in Mining: A Systematic Literature ReviewonFaultDetection,DigitalTwins,andIntelligentAssetManagement. MDPI.
IIoT in Mining: Transforming Operations with Smart Technology. (n.d.). Retrieved from www.qalhari.com: https://www.qalhari.com/iiot-in-mining-transforming-operations-with-smart-technology/ LyudmilaSamorodova,O.L.(2016).
Managing Employee Resistance to Automation. (n.d.). Retrieved from www.wizata.com: https://www.wizata.com/knowledge-base/managing-employee-resistance-to-automation
Mello, A. (2024, September 2). Forging the Future: The Vital Role of Integrated Process and Power in Mining Operations. Retrieved from Rockwell Automation: https://www.rockwellautomation.com/enin/company/news/blogs/process-power-for-mining.html
PLC Controllers in Mining Operations: Digging Deeper with Control. (2023, October 15). Retrieved from Mochuan Drives: https://www.mochuan-drives.com/a-news-plc-controllers-in-mining-operations-digging-deeper-with-control
Rawashdeh, R., Campbell, G., & Titi, A. (2016). The socio-economic impacts of mining on local communities: The case of Jordan. ScienceDirect
Shahzad, F., Bouri, E., Mokni, K., & Ajmi, A. (2021). Energy, agriculture, and precious metals: Evidence from time-varying Grangercausalrelationshipsforbothreturnandvolatility. ScienceDirect
Shewale, P., Patil, A., Borkhade, H., & Shinde, S. U. (2020). Coal Mine Safety & Monitoring by using PLC & SCADA. InternationalResearchJournalofEngineeringandTechnology(IRJET),1360-1362.
Yarakaraju, R. (2024, February 19). PLCs in Mining Operations: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency. Retrieved from Calterio.com:https://calterio.com/plcs-in-mining-operations-enhancing-safety-and-efficiency/