
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Prof. S.A. Dabhade*1 , Aditya Wable*2 , Dev Chavan*3, Aishwarya Shinde*4, Atole Akansha*5
1* Professor, Dept Of Computer Engineering, SVPM COE, Malegaon Bk (Pune), India. 2,3,4,5*Student, Dept Of Computer Engineering, SVPM COE, Malegaon Bk (Pune), India.
Abstract :- This study describes a blockchain-based strategy to improving traceability in the pharmaceutical supply chain, with the goal of combating counterfeit pharmaceuticals and increasing product legitimacy. The suggested approach removes middlemen, guarantees data provenance, and gives users a safe, unchangeable transaction history by utilizing smart contracts and decentralized storage. Centralized control, a lack of information, and complicated stakeholder behavior make it difficult to track products effectively in a healthcare supply chain that includes raw material suppliers, manufacturers, distributors,pharmacies,hospitals,andpatients.
Thisintricacymakesiteasierforcounterfeitmedicationsto infiltrate,whichtheWorldHealthOrganizationreportsarea majorcauseofdeath,especiallyforchildren,andmakeupas much as 30% of medications sold in developing nations. Additionally, counterfeit medications cause the pharmaceutical industry to suffer significant financial losses.Theproposedmethodoffersadistributedandeasily accessible way to keep an eye on every phase of the medication supply chain by introducing a smart contract architecture that verifies data provenance, traceability, and immutability.
We describe the entity-relation diagram, operational algorithms,andarchitectureofthesmartcontractsystemin detailandverifythatitiseffectiveinenhancingsupplychain transparency. As evidencedby our findings, this blockchain frameworkprovidesageneral,scalableapproachforsecure traceability that can be applied to a variety of pharmaceuticals supply chains, helping to create a reliable, impenetrabledrugtrackingandverificationsystem.
KEYWORDS: Blockchain,PharmaSupplyChain,Counterfeit, Medicines,Drugs
In order to ensure product authenticity, reduce the risk of counterfeit medications, and eliminate reliance on central authorities or intermediaries, this project proposes a blockchain-based framework that uses smart contracts and decentralized storage to improve traceability and data provenance within the pharmaceutical supply chain. A key
component of the project is the smart contract system architecture, which provides an immutable transaction history accessible to all supply chain stakeholders, including raw material suppliers, manufacturers, distributors,pharmacies,hospitals,andpatients.
This transparency across each stage of drug distribution improves efficiency and accountability, addressing the essential requirement for traceable information within a complex network of multiple stakeholders. The pharmaceutical supply chain faces significant challenges related to transparency and control, which are exacerbated by its multi-tiered structure and a lack of information-sharing among participants. Issues such as centralized control, fragmented information flow, and stakeholder competition lead to inefficiencies and enable counterfeitpharmaceuticalstoenterthemarket.
Counterfeit drugs pose severe risks to public health, particularly in underdeveloped nations where up to 30% of drugs may be counterfeit. This blockchain- based solution tackles these issues by introducing smart contracts that facilitate reliable traceability and validation processes, making it more difficult for counterfeit drugs tobypasscheckpointsundetected.
The project describes the smart contract code and algorithms controlling pharmaceutical product traceabilityandverification inordertoverifytheefficacy ofthesystem.Thesealgorithmsareintendedtotrackand record every transaction in the supply chain, providinga continuous and unalterable record of the drug's journey from manufacturer to end user. In order to evaluate the system's performance, we also offer a variety of implementation techniques and testing scenarios. Accordingtoourresearch,thesuggestedapproachgreatly improves traceability, lowers inefficiencies, and offers a general framework that can be used to other pharmaceutical goods. The system's decentralized and transparent architecture fosters stakeholder confidence while also setting a new standard for combating counterfeitsintheglobalpharmaceuticalsupplychain.
This blockchain-based system for pharmaceutical supply chain traceability aims to improve transparency, security,

Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
and operational efficiency within the complex network of the healthcare supply chain. In order to guarantee the integrity and provenance of data for all supply chain participants including raw material suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, hospitals, and patients the system first seeks to create an unchangeable, decentralized storage framework. By leveragingsmartcontracts,
The proposed solution seeks to remove intermediaries, streamlining data transactions and providing a secure, automated mechanism to verify each stage in the drug supply journey. Additionally, this solution targets a significant reduction in counterfeit pharmaceuticals by enabling constant, real-time tracking of drug movement across the supply chain. This will help reduce risks associated with fake medications reaching the end-user market, a problem that has led to severe health consequences, especially in underdeveloped countries. Anotherobjectiveistoenhancetraceabilityinresponseto supply chain inefficiencies that became evident during crisesliketheCOVID-19pandemic.Byimprovingvisibility, thesystemenablesrapidresponsetopotentialdisruptions, protectingthesupplyofauthenticmedications.
The smart contract architecture aims to provide a robust framework that enforces secure, transparent,and tamperresistant transactions, enabling seamless tracking and accountability from the source to the end consumer. To support system scalability and flexibility, the design is made adaptable, ensuring that it can accommodate the tracing and verification needs of any pharmaceutical product, regardless of its specifics. This adaptability will allow healthcare organizations to incorporate the system broadly and manage complex, cross-border drug supply chainseffectively.
Furthermore, the solution seeks to optimize data accessibility across stakeholders while safeguarding privacythrough distributed ledgertechnology, offering all participants a trusted and transparent view of the drug's journeywithoutcompromisingconfidentiality.Byfocusing on secure, real-time data sharing, this blockchain framework intends to foster collaboration among various stakeholders, promoting unified efforts to safeguard patients and uphold regulatory compliance across jurisdictions. Lastly, the validation and testing of the proposed solution aim to confirm its operational efficiency, resilience, and overall effectiveness in improving traceability and reducing counterfeit risks withinpharmaceuticalsupplychains
This project's scope includes developing and deploying a blockchain-based solution to improve pharmaceutical supply chain traceability, with an emphasis on getting rid of fake medications and guaranteeing
product authenticity. By utilizing blockchain technology, thesystemenablesdecentralized data storage and employs smart contracts to establish an immutable and secure transaction history. This approach removes the need for intermediaries, allowing all stakeholders, including raw material suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, hospitals, and patients, to access a transparent and verified chain of custody for eachproduct.
The smart contract system architecture and algorithms provide a secure foundation for data provenance, establishing a trustworthy network that is crucial in tracking the movement of pharmaceuticals from production to end-users. Moreover, this solution addresses specific challenges in the pharmaceutical supply chain, such as the complexity of distribution, lack of transparency, and limited control over data accuracy, which often contribute to the infiltration of counterfeit drugs. By continuously monitoring each transaction within the blockchain framework, the project aims to improve overall supply chain efficiency, prevent counterfeit drugs from entering the market, and significantlyreducetheriskstopublichealth.Thegeneric framework provided by this project can be adapted to various drug types within the pharmaceutical supply chain, thus establishing a universal standard for secure anddistributedtraceability.
Sr.no Title Author Description
1 Smart Contract ForPharma SupplyChain Rahul RKonapure, Shankar DNawale
2 BlockchainBased Systemsin Transportati on
3 Drugledger -APractical Blockchain System
AstaritaV, Giofre VP
Thispaperpresentsa blockchain-basedsolution fordecentralizedstorage
Thispaperpresentsa literaturereviewabout theapplicationof Blockchainbasedsystems intransportation
YanHuang, JingWu
Inthispaper,we proposeascenarioorientedblockchain systemfordrug traceabilityand regulationcalled Drugledger
The pharmaceutical supply chain is a complex, multilayered network involving numerous stakeholders, including raw material suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, hospitals, and patients. This intricate network faces significant challenges in ensuring

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
efficient tracking and tracing of products,exacerbatedby centralized control, lack of transparent data sharing, andcompeting stakeholder interests. Theseissues haveled toserious inefficiencies, as seenduring the COVID-19pandemic, and have facilitated the infiltration of counterfeit drugs into the market, especially in developing countries. Counterfeit pharmaceuticals not onlythreaten public health and safety but also result in substantial financial losses for the pharmaceutical industry.
Addressing these problems demands a solution that provides continuous monitoring, clear data provenance, and tamper-proof documentation of drug movements acrosstheentiresupplychain.Thisprojectismotivatedby the need to establish a secure, reliable, and decentralized system for tracking pharmaceutical products, thereby enhancing traceability and ensuring authenticity. By leveragingblockchaintechnologyandsmartcontracts,this proposed solution aims to provide an immutable, transparent transaction history that is accessible to all stakeholders, eliminating interme- diaries and reducing vulnerabilities to counterfeit drugs. Such a system would allow stakeholders to trace a drug’s journey from productiontotheenduser,ensuringachainofcustodythat is both verifiable and accessible. This not only fosters accountabilitywithinthesupplychainbutalsostrengthens efforts to protect public health by preventing counterfeit medicationsfromreachingpatients
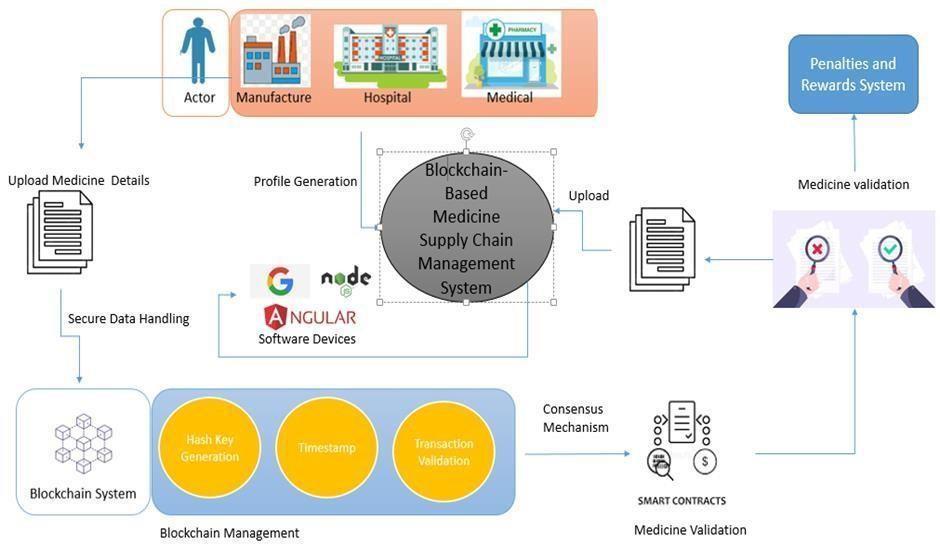
Smart contracts and decentralized storage are used in the paper's blockchain-based pharmaceutical supply chain traceabilitysystemtoguaranteethesafe,transparent,and unchangeable tracking of pharmaceutical products from suppliers of raw materials toendconsumers. Suppliers of raw materials, manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, hospitals,andpatientsareallpartofthe intricatenetwork thatisthesupplychain..Itischallengingtoproperlytrack
itemsbecauseofitscomplexity,centralization,andlackof transparency, which can lead to the supply chain becoming infiltrated by fake drugs. To overcome these issues,theproposedsolutionuse blockchaintoofferdata provenance, eliminating the need for middlemen and allowing secure, traceable transactions among all participants.
Smartcontracts,whichareself-executingagreementswith predetermined rules, uphold the system's operating principles by guaranteeing that transactions are carried out in accordance with established conditions and that everysupplychainstageisaccuratelydocumented.These contracts are immutable, which means that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed, ensuring the highest level ofsecurity and trust among all parties. All players may access the same version of the truth about the product's route through the supply chain since the blockchain is decentralized, meaning that no singleentitycontrolsthedata.
Thesystemworksbyintegratingsmartcontractsintothe variousstagesofthepharmaceuticalsupplychain.Whena pharmaceutical product is produced, its details such as the manufacturer, raw material source, production batch number,andotherrelevantinformation arerecordedon the blockchain. As the product moves through the distribution process, each transfer or transaction is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring that the product’s journey is fully traceable. This allows stakeholders, such as manufacturers, distributors, and pharmacies, to verify the product’s authenticity and ensure it has not been tampered with. Additionally, the system allows real-time monitoring and tracking of pharmaceuticals, preventing counterfeit products from entering the market and improvingoverallsupplychainefficiency.
Smart contracts automatically verify that all required conditions are met before a transaction is approved, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and preventingfraud.Thedecentralizedledgerensuresthatall parties have access to the same information, and any attempts to alter or falsify the data are easily detectable. Thistraceabilityframeworkisnotlimitedtospecificdrugs; it is designed to be adaptable to any pharmaceutical product, ensuring trusted and distributed traceability across the entire pharma supply chain. The system’s designoffersscalability,enablingittobeimplementedfor a wide range of pharmaceutical products while maintaininghighlevelsofsecurityandtransparency.
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that have their terms encoded directly into the code. The smart contract mechanism in this pharmaceutical supply chain systemmakessurethatallproductmovements,transfers, and transactions between various stakeholders

e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
including manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, hospitals, and patients are safely documented on the blockchain.Thealgorithmvalidateseachaction,checksfor required conditions, and ensures immutability of transaction history. It helps to automate processes, eliminate intermediaries, and ensure transparent, trusted execution.
Blockchain systems typically use hashing algorithms to ensure data integrity and immutability. In this solution, a cryptographic hashing algorithm, like SHA-256 (Secure HashAlgorithm),isusedtosecurelyhasheachtransaction, product data, and the entire supply chain history. Once hashed, the data becomes tamper-proof, meaning that if someonetriestoalterthedata,thehash value will change, making it detectable. This ensures that product information, such as the authenticity of drugs and raw materials, is traceable and immutable across all points in thesupplychain.
A consensus algorithm is necessary to guarantee the blockchain's legitimacy and integrity. Since the study proposes a decentralized method, Proof of Stake (PoS) or comparable consensus techniques may be used. In proofof-stake (PoS), miners, also known as validators, are chosen to validate transactions and produce new blocks according to their stake, or the quantity of cryptocurrenciesortokenstheyown.Byavoidingdoubles pending and guaranteeing that data contributed to the blockchain is genuine and validated, the consensus algorithmmakessurethatallnetworkusersconcuronthe blockchain'scurrentstate.
This algorithm helps to model the relationships between various entities in the pharmaceutical supply chain. The Entity-RelationshipDiagram(ERD)isusedtorepresentthe data model, showing how entities such as suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and pharmacies are interconnected. This algorithm helps in organizing and structuring the supply chain data, ensuring that each transaction or record can be traced accurately through its relationshipsacrossthesupplychain.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) algorithms are used to encrypt and secure the communication and transactions within the blockchain system. Each participant (e.g., suppliers, manufacturers, etc.) would be assigned a public and private key pair, enabling secure signing of transactions and authentication. RSA (Rivest-ShamirAdleman) or ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature
Algorithm) are common cryptographic algorithms used for securing transactions, ensuring that each party's identity is verified and their transactions are securely recordedontheblockchain.
To store data off-chain and ensure that the data remains accessible, Interplanetary File System (IPFS) or Storj could be used as the decentralized storage solution. The algorithm ensures that data (such as product details, shipping information, and batch records) is stored in a decentralized, distributed way, allowing participants to retrieve it when needed while maintaining data integrity andsecurity.
This algorithm ensures that all transactions (e.g., product shipments,ownershiptransfers,andproductmovements) across the supply chain are valid and meet predefined conditions before they are recorded on the blockchain. Thevalidationprocessincludescheckingthattheproduct is in the correct state, the correct participants are involved, and that any associated metadata (e.g., batch numbers, expiration dates) is valid. This algorithm helps to prevent fraudulent or invalid transactions from being addedtotheblockchain.
The audit trail algorithm ensures that every action performedonaproduct,fromrawmaterialsourcingtoits final delivery to the patient, is logged and tracked. Each transaction is appended to the blockchain, creating an immutablerecordoftheproduct'sjourney.Thisalgorithm facilitates transparency and accountability, making it possibletotraceaproduct’sentirelifecycleanddetectany discrepanciesorinstancesofcounterfeiting.
These algorithms collectively contribute to enhancing traceability, ensuring data integrity, and supporting the decentralized, transparent, and immutable nature of the blockchain solution for pharmaceutical supply chain management.
The methodology adopted for this project focuses on the development,deployment,andevaluationofablockchainbased framework to enhance the traceability and authenticity of pharmaceutical products. The system is designed around Ethereum smart contracts, IPFS for decentralized data storage, and a role-based model for supply chain participants. This section outlines the major phases of implementation: system design, smart contract development,integration,testing,andevaluation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The architecture consists of the following core components:
Blockchain Network (Ethereum): All transactions related to pharmaceutical products are recorded here. The immutability and transparency of the blockchain ensure securedataprovenance.
SmartContracts:Encapsulatethebusinesslogicforsupply chain operations such as product registration, ownershiptransfer,andverification.
Decentralized Storage (IPFS): Used to store large or sensitivedata (e.g.,certificates,reports),withIPFShashes storedon-chainforintegrityverification.
User Interface (Web3-enabled App): Allows supply chain actors to interact with the system through role- specific dashboards.
Role-Based Access: Defines access permissions for manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, hospitals, and patients.
Smart contracts were written in Solidity and deployed on theEthereumnetwork.Keyfunctionalitiesinclude
Product Registration: Manufacturers can register a new drug batch, including metadata such as name, batch number,manufacturingandexpirydates,and IPFShashofsupportingdocuments.
Ownership Transfer: Each actor in the chain (e.g., manufacturer to distributor) can transfer ownership of a productthroughavalidatedtransaction.
Verification Function: Any stakeholder (e.g., patient or pharmacy) can verify the authenticity of a product by queryingitshistory.
Event Logging: All transactions are recorded as events, allowing users to trace a product’s journey on the blockchain.
Manufacturer registers a product on the blockchain. Transfer of ownership occurs at each stage manufacturer → distributor → pharmacy/hospital → patient.
Eachtransactionislogged,andmetadataisstoredonIPFS.
End users verify authenticity by scanning a QR code or enteringaproductIDintotheinterface.
Implementation Tools and Platforms
Ethereum (Remix IDE / Ganache / Truffle): For developingandtestingsmartcontracts.
Solidity: Programming language used for writingsmart contracts.
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System): For decentralized storage.
Web3.js: For blockchain interaction within the frontend.
Node.js & React.js: For building the web application frontend.
MetaMask: For user authentication and transaction signing.
Testing and Evaluation
Various testing scenarios were conducted to asse ssthesystem'srobustness:
Functional Testing: Ensured that product registration, transfer,andverificationworkedasintended.
SecurityTesting:Verifiedthatonlyauthorizeduserscould performspecificactions.
Traceability Testing: Tracked the complete product historyacrossthesupplychain.
Performance Testing: Measured transaction latencyand systemthroughputundervaryingloads.
In conclusion, this paper presents a blockchain-based solutionthataddressesthecomplexitiesandinefficiencies of the pharmaceutical supply chain, particularly in combating counterfeit drugs. By utilizingsmartcontracts and decentralized storage, the proposed system ensures data provenance, traceability, and immutability without the need for intermediaries, providing a transparent and securetransactionhistoryforallparticipants.
Thesolution'sdesignandalgorithmshavebeenvalidated andtestedtodemonstratetheireffectivenessinimproving traceability,ultimatelyenhancingproductauthenticityand safeguarding public health. This approach offers a scalable and trusted framework that can be applied to ensure the integrity of pharmaceutical supply chains globally

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
[1] T.Guardian.(2017).10%ofDrugsinPoorCountriesAre Fake, Says WHO. Accessed: Jun. 3, 2020. [Online].Available:https://www.theguardian.com/glo baldevelopment/2017/nov/28/10-ofdrugs-in-poorcountries-are-fake-says-who
[2] S. D. Nawale and R. R. Konapure, “Blockchain & IoT based Drugs Traceability for Pharma Industry,”2021 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), 2021, pp.1-4, doi: 10.1109/ICE/ITMC52061.2021.9570251.
[3] A. Marucheck, N. Greis, C. Mena, and L. Cai, “Product safety and security in the global supply chain:Issues, challenges and research opportunities,” J. Oper. Manage., vol.29,nos.7_8,pp.707_720,Nov2011.
[4] Lin, Y.P.; Petway, J.R. Anthony, J.; Mukhtar, H.; Liao, S.W.;Chou,C.F.;Ho,Y.F.Blockchain:Theevolutionarynext stepforICTe-agriculture.Environments2017,4,50.
[5] Rabah, K. Challenges & opportunities for blockchain powered healthcare systems: A review. Mara Res. J.Med. HealthSci.2017,1,45–52.
[6] Amin, A.D. Blockchain technology in banking and finance sector: Its effects and challenges. CARE J.2020,31, 349–358.
[7] Chen, G.; Xu, B.; Lu, M.; Chen, N.S. Exploring blockchain technology and its potential applications for education.SmartLearn.Environ.2018,5,1
[8] Astarita, V.; Giofre, V.P.; Mirabelli, G.; Solina, V. A Review of Blockchain-Based Systems in Transportation. Information2020,11,21
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 |