
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sevanthi S1, L. Govindaraju2 ,
1Post Graduate Student Department of Civil Engineering, UVCE College (University), Banalore 2Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, UVCE College (University), Karnataka, India 560056
Abstract - This study presents a performance based analysisofa40-storeyhigh-risebuildingwithandwithout outrigger systems, focusing on its seismic performance in ZonesIVandVasperIS1893(Part1):2016.Theobjectiveis toevaluatetheeffectivenessofoutriggersinreducinglateral displacement and inter-storey drift under seismic loading conditions. The building is modeled and analyzed using ETABSandSAP2000software,considering irregularplan configurations.Keyparameterssuchasstoreydisplacement and drift are compared for models with and without outriggersusingtheEquivalentStaticMethodandResponse Spectrum Method. Further, advanced seismic analysis techniques such as Pushover Analysis and Time History Analysis are performed to understand the building's nonlinear behavior and dynamic response to actual earthquake records. The influence of Soil-Structure Interaction(SSI)isalsoincorporatedtoassesshowdifferent soil conditions affect structural performance. The results indicate a significant reduction in both displacement and drift when outriggers are used, especially in Zone V. The additionofoutriggersgreatlyenhancesthelateralstiffness and stability of the structure. The study concludes that outriggers are a highly effective structural solution for improvingtheseismicperformanceoftallbuildingsinhighriskseismiczones.
Key Words: Outrigger System, High-Rise Building, Seismic Analysis, Story Drift, ETABS, SAP2000, SoilStructure Interaction, Performance-Based Design.
Tallbuildingsareincreasinglycommoninurbanareasdue to the growing demand for vertical expansion in densely populatedregions.Thesestructuresfacesubstantiallateral forcesgeneratedbywindandseismicactivity,necessitating advancedstructuralsystemstoensuresafetyandstability. Theoutriggerstructuralsystemhasemergedasaprominent solution, effectively linking a building's central core to its perimeter columns to distribute lateral loads more efficiently. This configuration significantly improves the building'slateral stiffnessandminimizessway,enhancing occupantcomfortandstructuralintegrity.
In high seismic zones, where the risk of ground motion is considerable, such reinforcement becomes even more critical.Theintegrationofoutriggersystemshelpscontrol
inter-storeydriftandreducestheoveralldeformationofthe structure during seismic events. This paper explores the performance of various outrigger configurations and evaluatestheireffectivenessusingcomputationalmodeling andrealseismicdata.Additionally,thestudyincorporates theimpactofSoil-StructureInteraction(SSI),acknowledging thatfoundationflexibilitycanalterthedynamicresponseof tallbuildings.Byaddressingthesefactors,theresearchaims toprovidevaluableinsightsintooptimizingstructuraldesign for earthquake resilience, ultimately contributing to the development of safer and more sustainable urban infrastructure.
Numerous studies have underscored the benefits of outriggersystemsintallstructures.Fawzia&Fatima(2010) demonstrated substantial reductions in lateral deflection withmulti-leveloutriggers.Changetal.(2013)introduced semi-activedampedoutriggersusingMRdampers,showing enhanced seismic control. Chopra (2017) emphasized the roleofpushoveranalysisincapturingnon-linearbehavior. Otherresearchers,suchasKogilgeri&Shanthapriya(2015), examined the effect of varying outrigger depths and concluded that full-height outriggers provide optimal performance.Despitethesefindings,researchgapsremainin understandingvirtualoutriggers,soil-structureinteraction, and the response of irregular building geometries under actualseismicconditions.
2.1
Theprimaryobjectiveofthisstudyistoevaluatetheseismic performanceoftallbuildingwithandwithoutoutrigger
1. To compare the lateral displacements (story displacement) and story drifts of a building structurewithandwithoutanoutriggersystem.
2. To analyze the behavior and performance of the structure when subjected to seismic forces, particularlyinhighseismiczones
3. To evaluate the overall performance of the structure, focusing on how the outrigger system enhances the building’s ability to resist lateral forces.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4. Toassessthestructure’sperformanceundermore realistic conditions, such as actual earthquake records,ratherthansimplifiedloadmodels.
5. Toinvestigatetheeffectofsoil-structureinteraction (SSI) on the performance of the building with an outriggersystem.
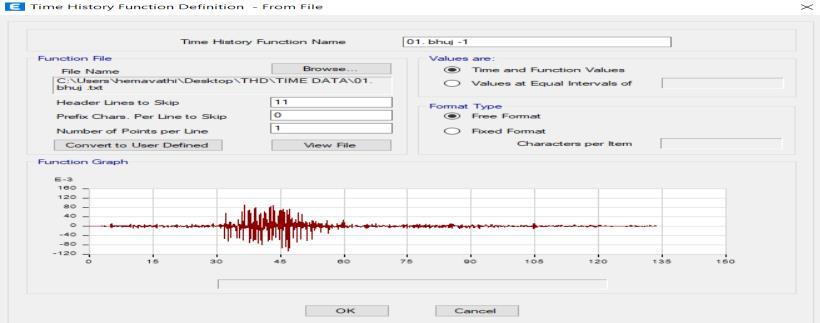
Seismic analysis included Equivalent Static Method, ResponseSpectrumAnalysis,PushoverAnalysisandTime HistoryAnalysisusingrealearthquakedata(Bhuj2010).For SSI analysis, modeled using springs with defined stiffness values were evaluated to determine their impact on structuralperformance.
ANALYSIS METHODS:
1. Equivalentstaticanalysis(ESA)
2. Responsespectrumanalysis(RSA)
3. Lineardynamicmodalanalysis
4. Nonlineardynamictimehistory
5. NonlinearStaticPushoverAnalysis(NSPA)
6. Soil-StructureInteraction(SSI)
3. MODELS CONSIDERED FOR ANALYSIS
A 40-storey, 30x30m reinforced concrete building was modelled using ETABS and SAP2000. The analysis considered two main configurations: with and without outriggersystems.Thebuildingwassubjectedtogravityand seismicloadsaccordingtoIS1893(Part1):2016andIS875 (Part3).
InPresentstudy,fourmodelsareconsideredforanalysisas follows:
MODEL1- In model 1 40-story without outriggers is consideredandanalyzedforsoftsoilinzoneIV&zoneV.
MODEL 2-Inmodel140-storywithoutriggersisconsidered andanalyzedforsoftsoilinzoneIV&zoneV
3.1 Geometry of the Model Considered
Table -1: Geometryofthemodelconsidered
No. of storey’ s G+39
No. of bays in X-direction 5
No. of bays in Y- direction 5 X-direction bay width 6m Y-direction bay width 6m
Height of bottom storey 3.2m
Height of storey 3.2m
3.2 Section Properties
Table -2: SectionProperties
PARAMETERS BUILDING CONFIGURATION
LengthinX-direction 30m
LengthinY-direction 30m
No.ofstoreys G+39
Beam
B=400X700mm,M40grade concrete
Column C=800X1200mm,M40grade concrete
Slab 150mmM25gradeconcrete
Bracing 600X600X30Steelhollowsection
3.3 Loads considered
Table -3: Loadsconsidered Load Type

Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net
3.4 Seismic Parameters
Table -4: seismicparameters
Structure type RC building with special moment resisting frame (SMRF)
Typeofsoil SOFT,TYPEIII
Zone IV&V
Damping
Importance
4.1 RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS
4.1.1 STOREY DISPLACEMENT
Themaximumstoreydisplacementofthestructureisin Y-direction. Hence the results are taken in Y-direction for zoneIV&zoneVwithsoftsoilcondition.Storeydisplacement variations are shown in chart below. The inclusion of fullheightoutriggersresultedinan80%reductionintop-story displacement. Structures without outriggers exhibited excessivelateralmovement,makingthemvulnerableduring earthquakes.
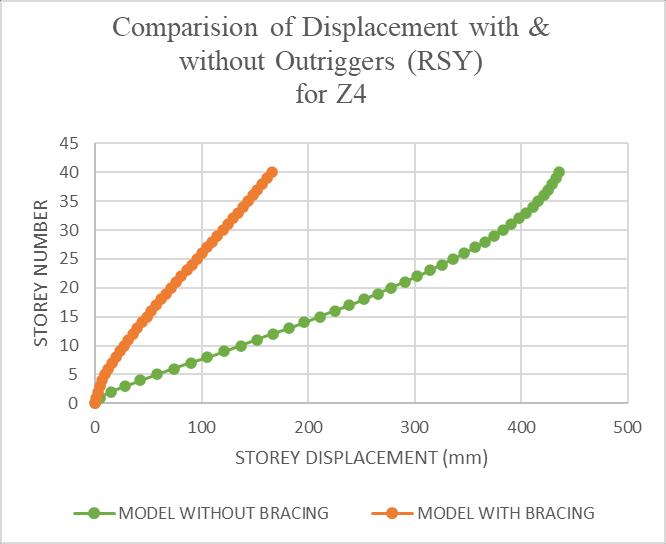
Chart -1:Comparisonofdisplacementwith&without Outriggers(RSY)forZ4
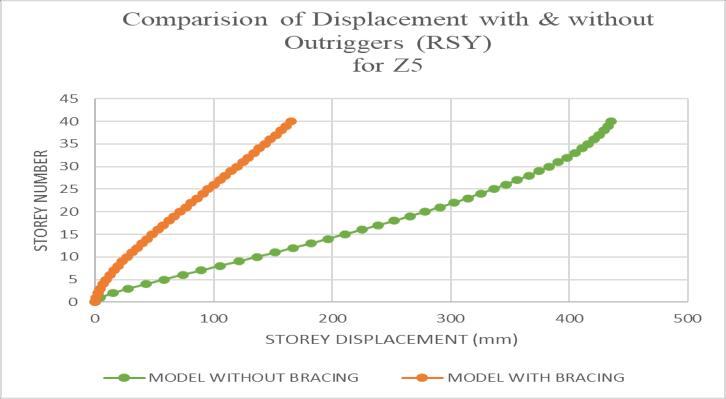
Chart -2:Comparisonofdisplacementwith&without Outriggers(RSY)forZ5
4.1.2 STOREY DRIFT
The maximum drift of the structure is in Y-direction. HencetheresultsaretakeninY-directionforzoneIV&zone Vwithsoftsoilcondition.Storeydriftvariationsareshownin chartbelow.Driftvaluesweresignificantlylowerinmodels withoutriggers.Amaximumreductionofapproximately45% was observed Y directions under seismic loading. This indicatesbettercontroloverrelativefloormovements,which iscrucialforoccupantsafetyandnon-structuralcomponent stability.
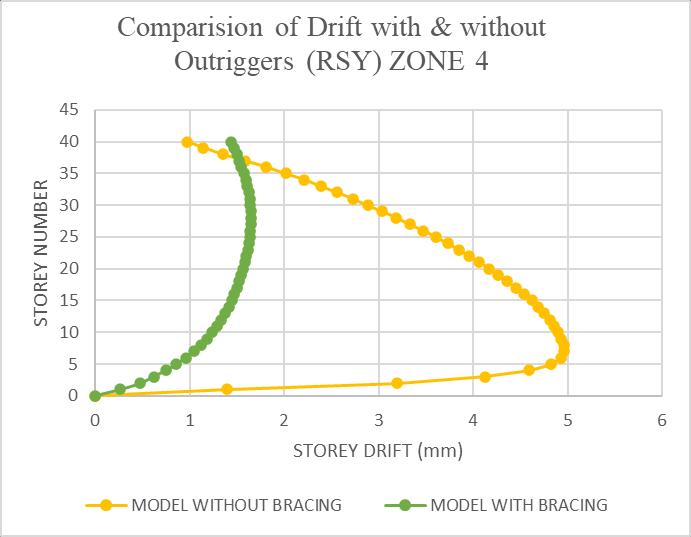
Chart -3:Comparisonofdisplacementwith&without Outriggers(RSY)forZ4
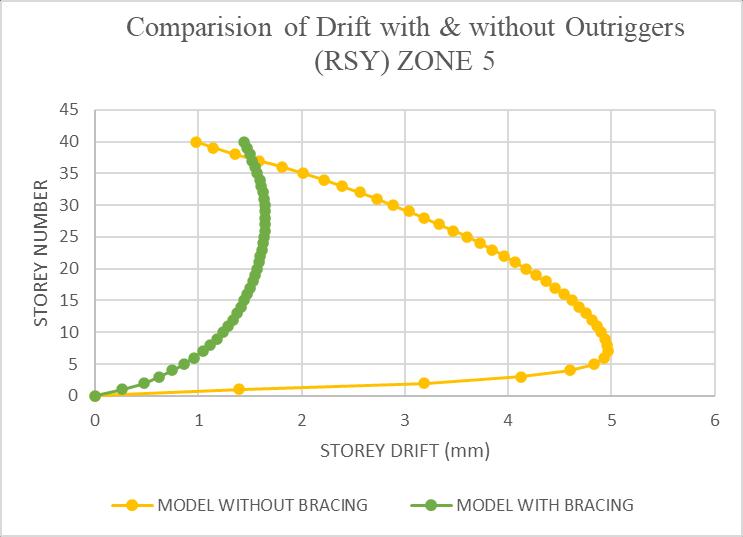
Chart 4:Comparisonofdriftwith&withoutOutriggers (RSY)forZ5

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Non-linear time history analysis is a dynamic analysis method used to evaluate the seismic performance of structures under real earthquake ground motions. Bhuj Groundmotionisconsideredforanalysis.
4.2.1
Themaximumstoreydisplacementoccursattopstoreyof thebuilding.
WhencomparedtoEquivalentstaticandresponsespectrum analysis, in non-linear time history analysis the storey displacementdecreasesandtheresultsobtainedarewithin thelimitsi.e.,H/250aspercoderecommendation.
4.2.2
Theresultsaretakenformodel1andmodel2inzoneIV&V withsoftsoilcondition.
Formodel1zoneIVwithoutbracingsthemaximum storey drift occurs at Storey 7 with a value of 3.318mm.
Formodel1zoneVwithoutbracingsthemaximum storey drift occurs at Storey 7 with a value of 4.963mm.
For model 2 zone IV with bracings the maximum storey drift occurs at Storey 28 with a value of 1.1mm
For model 2 zone V with bracings the maximum storey drift occurs at Storey 25 with a value of 1.733mm
Pushover analysis is done for G+39 building with and without Outrigger in zone IV and Zone V with soft soil condition.
ResultsaretakenforModel1andModel2 inZone IV&ZoneVwithand withoutoutrigger,eachmodel
exhibits different displacement at performance pointindicatingvaryingstructuralcapacities.
The pushover analysis results provided critical insightsintothenonlinearbehaviorofthestructure under increasing lateral loads. Buildings without outriggersreachedtheiryieldandultimatecapacity much earlier, showing a steep decline in strength post-yield. In contrast, buildings with outrigger systems demonstrated greater displacement tolerance before failure. The pushover curves indicatedenhancedductilityandenergydissipation, reflectingtheimprovedseismicperformancedueto thepresenceofoutriggers.Plastichingeformation wasmoreevenlydistributedinoutrigger-equipped structures, reducing the likelihood of localized failures.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TheanalysiswascarriedoutforaG+39storeybuildingwith andwithoutoutriggers,locatedinSeismicZonesIVandV, knownfortheirhighseismic activity.Thestructureswere supportedonsoftsoilwithabearingcapacityof150kN/m² andadepthof30meters.A5-meter-deepmatfoundation was used to transfer loads from the superstructure to the underlyingsoil.Thebaseofthesoilwasassumedtobefixed, andsurfacespringswereincorporatedatthebaseofthemat foundation to simulate soil-structure interaction. These springs represented the soil's stiffness and damping characteristics,enablinga morepreciseassessmentofthe building'sseismicresponse.
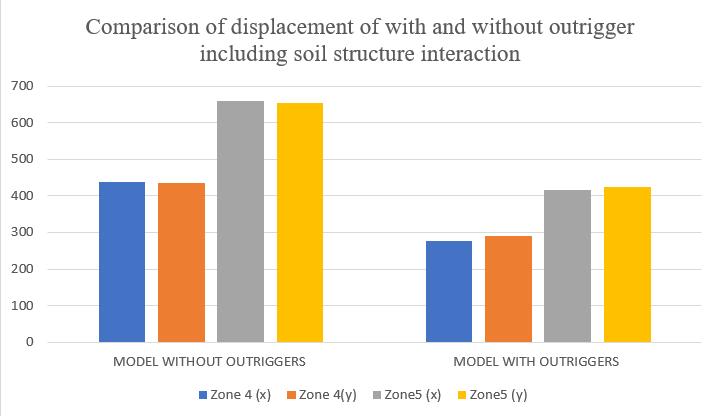
Themaximumstoreydisplacementofthestructureisinboth Xand Y-direction.HencetheresultsaretakeninbothXand Y-direction for zone IV & zone V with soft soil condition. Storey displacement variations are shown in chart below. From chart 6 it can be conclude that the model without outriggers in zone V is showing maximum storey displacementandstructurewithoutriggersshowsminimum displacement.
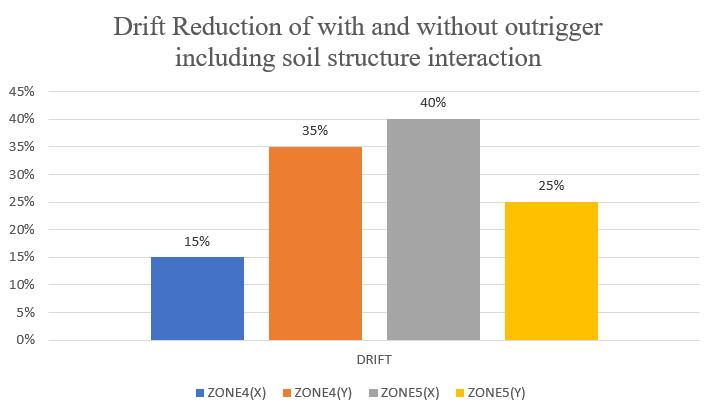
The drift of the structure is taken in both X and Ydirection.HencetheresultsinbothXandY-directionforzone IV&zoneVwithsoftsoilcondition.Storeydrift variations are shown in chart below. From chart 15 & 16 it can be concludethatthemodelwithoutriggersinzoneIVreduces 35%iny-directionandinzoneV40%inx-direction. This improvementminimizestheriskofnon-structuraldamage.
Pushoveranalysisisanonlinearstaticanalysismethodused toevaluatetheseismicperformanceofstructures,including soil-structureinteraction(SSI)effects.Thisanalysisaccounts fornonlinearbehaviourofstructuralelements,foundations, and soil, and applies a lateral load pattern to simulate seismic forces. By considering SSI effects, including soil nonlinearity,foundationflexibility,andstructure-foundation interaction, pushover analysis provides valuable insights intoastructure'sseismicperformance.Theanalysisinvolves creatingadetailedmodelofthestructure,foundation,and soil, applying a lateral load pattern, and performing a nonlinear static analysis to determine the structure's response.Theresultscanbeusedtoevaluatethestructure's performance,includingdeformation,damage,andpotential failuremodes.Pushoveranalysiscanhelpidentifypotential

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
weaknessesinthestructure,foundation,orsoil,andinform retrofitting or design decisions to improve seismic resistance.Theresultscanbeconcludedas;
Models
SpectralDisplacement (mm) x y
Modelwithoutoutriggers(Z4) 200 199
Modelwithoutriggers(Z4) 65 65
Modelwithoutoutriggers(Z5) 250 260
Modelwithoutoutriggers(Z5) 133 144
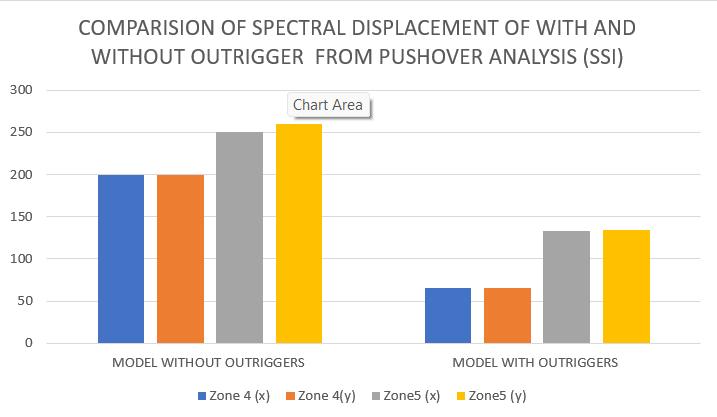
Chart 7:Comparisonofspectraldisplacementofwithand withoutoutriggerfrompushoveranalysis(SSI)
3. CONCLUSIONS
This research aimed to enhance the seismic performanceofa40-storeyhigh-risebuildingthrough theimplementationofoutriggersystems.
The inclusion of outriggers significantly improved structuralstabilitybylinkingthebuildingcorewith perimetercolumns,therebyallowingthestructureto functionasacohesivelateralload-resistingsystem.
the use of outriggers contributed to substantial displacementreductions,withZoneIVexperiencing anapproximate67%decrease
Decreaseinstorydriftwasobserved,witharounda 35% reduction recorded in Zone IV and approximatelya40%reductioninZoneV
When considering Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI):Displacement reductions remained effective, rangingfrom33–37%inZoneIVand35–37%inZone V,confirmingthefunctionalityofoutriggersonsoft claysoils.
Pushover Analysis showed enhanced post-yield performance;buildingswithoutriggerscouldendure higherloadsanddemonstratedsuperiorductilityand energyabsorption.
Pushover Analysis showed enhanced post-yield performance;buildingswithoutriggerscouldendure higherloadsanddemonstratedsuperiorductilityand energyabsorption.
[1]IS:875(Part1)–1987Codeofpracticefordesignloads (otherthanearthquake)forbuildingsandstructures.
[2]IS:875(Part2)–1987Codeofpracticefordesignloads (otherthanearthquake)forbuildingsandstructures.
[3]IS1893(Part1):2002CriteriaforEarthquakeResistant designofstructures:Generalprovisionsandbuildings.
[4] Deflection control in composite building by using belt trussandoutriggerssystem.S.FawziaandT.Fatima(2010).
[5]Semi-activedampedoutriggersforseismicprotectionof high-rise buildings Chia-Ming Chang, Zhihao Wang. et al.(2013).
[6].Astudyonbehaviourofoutriggersystemonhighrise steel structure by varying outrigger depth. Srinivas Suresh Kogilgeri , Berly Shanthapriya(2015).
[7].Optimizeduseofmulti-outriggerssystemtostiffentall buildings.Z.Bayati,M.Mahdikhani,A.Rahaei(2018).
[8].StabilityEnhancementofOptimumOutriggersandBelt TrussStructuralSystem.ArchitDangi,SagarJamle(2019).
[9].Analysisofhigh-risebuildingwithoutriggerusingnondimensional parameter Varsha Virde, Dr .R. Singh et al.(2020).
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[10].AComprehensiveintroductiontooutriggersandbelttrusssysteminskyscrapers.WaelAlhaddad,YahiaHalabiet al.(2020).
[11].Assessmentofwind-inducedvibrationmitigationina tallbuildingwithdampedoutriggersusingreal-timehybrid simulations. Safwan Al-Subaihawi, Chinmoy Kolay. et al.(2020).
[12]..Seismicperformanceandoptimizationofmultistoryed building by outrigger along belt truss structure Shriya Shetye,S.N.Tande(2021).
[13] .Dynamic analysis of composite structures with outrigger system using response spectrum method. GurkiratSingh,S.K.Singh(2022).
BIOGRAPHIES

SEVANTHIS M.TECH,EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING
UVCE,BANGALORE,KARNATAKA