
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Aditya Kulkarni1 , Khushi Raval2 , Nishant Gangurde3 , Omkar Katkar4 , Suhasini Itkar5
1234 UG Student, Department of Computer Engineering, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, India
5Head, Dept of Computer Engineering, PES Modern College Of Engineering, Shivajinagar, Pune, India
Abstract - This project focuses onindividuals usinghearing aids who face difficulty hearing in noisy environments by introducing devices that aim to amplify all sounds equally by reducing background noise effectively. By combining traditional signal processing with advancedmachinelearning to deliver intelligent noise suppression, MVDR beamforming helps to isolate sounds from specific directions thereby focusing on speaker’s voice supported by dual microphone. Voice Activity Detection aids to detect and process speech segments by further processing them into the time frequency domain. In order to further enhance the clarity by classifying and adjusting audio frames, a post processing module like Support Vector Machine is applied. It runs with low delay, making it ideal for real-time hearing aids. Its modular design fits easily into other audio systems. By combining classic beamforming with AI, it offers a smarter way to help people hear better in noisy places
Key Words: Audio Processing, MVDR, VAD, Beamforming, Noise Reduction, Machine learning, Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), Hearing Assistance.
This project aims to provide an intelligent, ML-powered hearingaidsystemforimprovingrelevantsoundinanoisy environment. Our system mainly enhances speech while suppressing background noise using advanced signal processingsteps.
ThekeycomponentsofthisprojectareShort-TimeFourier Transform (STFT), Voice Activity Detection (VAD), MVDR beamforming,andSVM-basedclassification.Real-timeaudio is given as input and then processed, filtered, and reconstructedtodeliverthefinalclearaudiototheuser.
Duetoincreasingnoisepollutioninthepublicanddaily environment,itbecomesdifficultforindividualswithhearing problems to differentiate human speech from background noise. Normal hearing aids amplify all the sounds in the surroundings,makingitdifficulttofocusontherequiredand essential sounds that need enhancement. So, there is a demandingneedforsuchahearingaidthatwillamplifyonly the relevant sounds while reducing the background noise. TheadvancedtechnologiesinMachineLearningandsignal processinghelptotackletheseproblemsandprovideabetter andmorenaturalhearingexperience.
The system mainly focuses on enhancing the human speechorrelevantsoundinnoisyenvironmentsforhearing aid applications. This project includes dual microphone beamforming, noise suppression, and classification using machine learning knowledge. It does not rely on IoT integration, biometric authentication, or commercial deployment.Insteadofthis,itprovidesasoftwaresolution that can well integrate with hearing aid devices or the mobileapplicationforbeinguser-friendly.
Thesystemarchisdesignedtoenhancethereal-timeaudio signals for hearing aid users by considering signal processingwithmachinelearning.Theprocessstartswith acquisition of noisy audio input from the surrounding environment, through the microphone. This raw input is then first converted into the frequency domain using the STFT,i.e.,theShort-TimeFourierTransform.STFTdivides theaudiosignalintosmalleroverlappingwindowsandalso applies Fourier transform to each segment frame . This generates the time-frequency representation, where each frametellsabouthowfrequencycontentevolvesovertime. STFTallowsthesystemtoanalyzespeechfeatureswhilealso detectingandanalyzingbackgroundnoise,makingitideal forfurtherenhancementstages.
Next,thesystemappliesVoiceActivityDetection(VAD)to differentiate between human speech and non-speech segments.Thisstephelpstofocusonlyonsegmentswhere speech is actually present, enhancing both accuracy and computation. Following this, the Minimum Variance DistortionlessResponse(MVDR)beamformingalgorithmis usedtospatiallyfilterouttheincomingaudiosignal.MVDR works by steering the beam of the microphone array towardsthespecificspeechsourcewhilereducingthepower from all other directions. This is done by calculating the beamformerweightvectorthatmaintainsthedesiredsignal without distortion while suppressing the background interferences. MVDR dynamically adapts to the noisy environmentbycalculatingthecovariancematrix,helpingto suppressmovingnoisesources.
The beamformed signal is then passed to the adaptive filtering stage, where a noise covariance matrix is continuouslyestimated.Thishelpstoapplytargetednoise reduction by adapting filter coefficients in real-time,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
considering that non-speech elements are suppressed withoutdistortingtherequiredspeech.Thesystemextracts themeaningfulfeaturesfromtheenhancedaudiosignalby usingMel-FrequencyCepstralCoefficients(MFCCs).MFCCs focusonhowthehumanearperceivessoundbyfocusingon importantfrequencybandsusingtheMelscale.Thisprocess involves taking the log of spectrum power and applying a Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) to form decorrelated coefficients.Thesefeaturescapturetheshapeandenergyof speech,makingitidealforclassificationandimprovement.
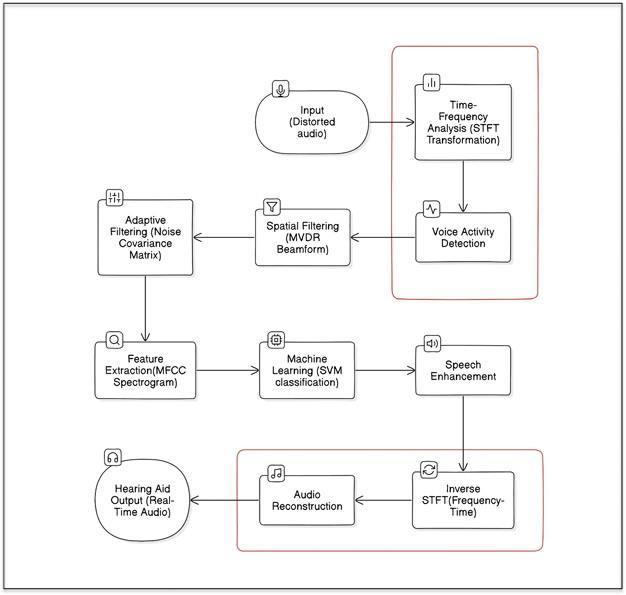
The extracted features then pass into a machine learning classifier,aSupportVectorMachine(SVM),whichistrained to differentiate between the speech and non-speech componentsbasedontheirspectralfeatures.TheSVMworks byfindingtheoptimalhyperplaneinthefeaturespacethat separates out the two classes with minimum margin, ensuringtheclassificationeveninoverlappingconditions. Thesupervisedmachinelearningapproachallows making fine-grained decisions on a frame-by-frame basis, determining which part of the signal should be preserved andwhichshouldbesuppressed.
Once classification is done, the system enhances the identified speech segments while suppressing the noise dominance. This targeted enhancement preserves the efficiency and naturalness of speech while minimizing distortion. The processed signal, which is still in the frequencydomain,isthenpassedtotheinverseShort-Time FourierTransform(iSTFT)toconvert thesignal back into thetimedomain,byconvertingthefrequency-filteredframes intocontinuousaudiowaveforms.Thefinaloutput,whichis anoise-suppressedaudiostream,canbedelivereddirectly totheearphonesorthehearingaiddevice.
The Hearing Aid System S is a real-time audio processing channeldesignedtoimprovespeechinanoisyenvironment. Itismathematicallygivenas: S={I,P,O}
Where:
I:Inputaudiosignalfromadualmicrophonearray,sampled at16kHz.
P: The collection of steps including Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT), Voice Activity Detection (VAD), MVDR beamforming, Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) extraction, Support Vector Machine (SVM) classification, speechenhancement,andinverseSTFT.
O: Enhanced output audio signal with suppressed backgroundnoise,deliveredwithend-to-endlatencybelow 50ms.
Thesystempassesinputthroughaflowoftransformations: I→STFT→VAD→MVDRBeamforming→MFCCExtraction →SVMClassification→SpeechEnhancement→InverseSTFT →O.
TheSTFTconvertsthetime-domainaudiointothefrequency domain,allowingspectralanalysisfornoisereductionand speechenhancement. Foradiscrete-timeaudiosignalxm[n]frommicrophonem∈ {1,2},theSTFTisdefinedas:
STFT:
X(t,f)=Σ[x(n)×w(n-t)]×exp(-j×2π×f×n)
Where:
x(n)=theoriginaltime-domainsignal.
w(n-t)=windowfunctioncenteredattimet.
f=frequencybin.
exp (-j × 2π × f × n) = complex sinusoid for the Fourier transform.
X(t,f)=complex-valuedoutputshowingfrequencycontent attimet.
Description:
1. Divide the input audio into small overlapping signals.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2. Apply the window function to minimize the edge effect.
3. CalculatetheDFTforeachsegment.
MVDR beamforming enhances speech from a particular directionwhilereducingnoisefromotherdirectionsusing dualmicrophonearray.
Formula:
MVDRWeights(w):
w=R⁻¹×d/(dᴴ×R⁻¹×d)
Where:
R=noisecovariancematrix.
d=steeringvectorinthedirectionoftargetedsource.
R⁻¹=inverseofthenoisecovariancematrix.
dᴴ=conjugatetransposeofthesteeringvector.
w=beamformingweights.
OutputSignal:
y=wᴴ×x
x=inputvectorofmicrophonesignals.
wᴴ=Hermitianofweightvector.
y=enhancedoutput.
Description:
1. Considerthedirectionofthedesiredspeechsource.
2. Measurethebackgroundnoisecovariance.
3. Designthefilterthatpreservesspeechfromspecific directionandreducenoisefromallotherdirections.
4. Applythisfiltertomicrophoneinputstogetclear audio.
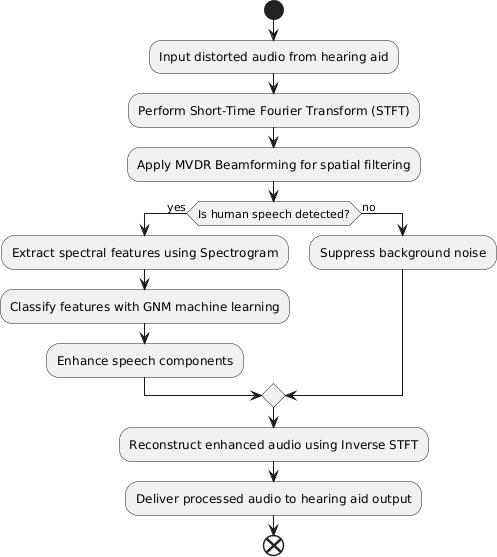
The proposed system is a real-time speech enhancement framework designed to improve auditory experiences in challenging acoustic environments, such as those encountered by users of hearing assistive devices. It integrates advanced signal processing techniques with machine learning models to perform noise suppression, beamforming,andspeechclassification.Thesystemoperates onlivestereoaudioinputcapturedfromadual-microphone array,andoutputsaprocessedaudiostreamwithenhanced speechclarityandreducedbackgroundinterference.
The implementation is modular, comprising the following keystages:
*Audioacquisitionandpreprocessing
*VoiceActivityDetection(VAD)
*Beamformingandnoisefiltering

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
*Featureextractionandclassification
*Speechenhancementandsignalreconstruction
These stages are optimized to run with minimal latency (<50ms), ensuring a seamless and real-time auditory feedbackexperience.
Frameworks and Libraries
LibROSA: A cornerstone for audio analysis, LibROSA was utilized for extracting critical audio features such as MelFrequencyCepstralCoefficients(MFCCs)andforvisualizing time-frequencyrepresentationslikespectrograms.
NumPy and SciPy : These foundational scientific libraries enabledhigh-performancenumericaloperations,including the computation of the Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) and its inverse. They provided efficient array manipulationsnecessaryforreal-timesignalprocessing.
SoundDevice:Usedforcapturingandplayingbackaudioin real-time, this library was essential for interfacing with microphonearraysanddeliveringprocessedaudiooutput. FastAPI / Streamlit (Optional UI) : To support a visual inspection of audio waveforms, spectrograms, and processing metrics, a lightweight interface was optionally developedusingFastAPIand/orStreamlit.
Development Environment
Jupyter Notebook: Initial prototyping, algorithmic experimentation,andvisualizationwereconductedwithin Jupyter Notebooks, enabling rapid iterations and effective debugging.
VisualStudioCodeandGIT:VSCodeservedastheprimary developmentenvironment,integratedwithGITforversion controlandcollaborativedevelopment.
PythonVirtualEnvironment(VEnv):Projectdependencies and libraries were isolated and managed using Python’s virtual environment, ensuring reproducibility and clean deployments.
Fig-4 :PackageDiagram
Audio Acquisition and Preprocessing
Thesystembeginsbycapturingstereoaudiosignalssampled at16kHzfromadual-microphonearray.Audioissegmented intoframesof20millisecondswitha50%overlap,balancing temporal resolution with computational efficiency. Each frame undergoes a Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) usinga512-sampleHammingwindowanda256-samplehop size. The resulting complex spectrogram is normalized to standardize the amplitude dynamic range, ensuring consistency across frames and preparing the data for downstreamprocessing.
Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
AnessentialcomponentofthepipelineistheVoiceActivity Detection (VAD) module, responsible for distinguishing speechframesfrombackgroundnoise.Theimplementation supports both energy-based and machine-learning-based VADalgorithms.Byanalyzingthemagnitudespectrumofthe incoming signal, the system identifies and retains only speech-active frames, thereby reducing computational burden and focusing enhancement efforts on segments of auditory interest. Spectrogram normalization is also reappliedatthisstagetoharmonizetheinputcharacteristics forsubsequentmodules.
MVDR Beamforming and Noise Filtering
Toaddressspatialnoisesuppression,thesystememploysa Minimum Variance Distortionless Response (MVDR) beamformer.Thenoisecovariancematrixisfirstestimated fromthenon-speechframesidentifiedduringtheVADstage. Beamformingthensteersthemicrophonearraytowardsthe speech source while minimizing interference from other directions.Thisspatialfilteringisfurthercomplementedby an adaptive Wiener-style noise suppression technique, which dynamically updates the noise model to remain effectiveunderchangingacousticconditions.
Followingbeamforming,thesystemextracts13-dimensional MFCCs along with their first-order temporal derivatives (deltas)fromthecleanedspectrogram.Thesefeaturesare concatenatedintoframe-levelvectorsthatserveasinputtoa Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. The classifier is trainedtodistinguishbetweenspeechandnoiseframes,and itshyperparameters suchaskerneltypeandregularization constant(C) aretunedtomaximizeclassificationaccuracy andminimizefalsepositives.
Basedontheclassifier’soutput,againmaskiscomputedand appliedtothespectrogram.Thismaskselectivelyamplifies framescontainingspeechwhileattenuatingresidualnoise. The enhanced spectrogram is then converted back to the timedomainviainverseSTFT.Overlap-addtechniquesare used to ensure continuity in the output signal, which is

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
subsequentlydeliveredinrealtimewithlatencymaintained below50milliseconds wellwithinacceptablethresholds forhearingaidapplications.
Thisend-to-endsystemdemonstratesarobustandefficient approach to real-time speech enhancement, integrating classicalsignalprocessingtechniqueswithmodernmachine learningclassifiers.Itiscapableofoperatingindynamicand noisyenvironments,providingasignificantimprovementin speechintelligibilityandlisteningcomfortforend-users.
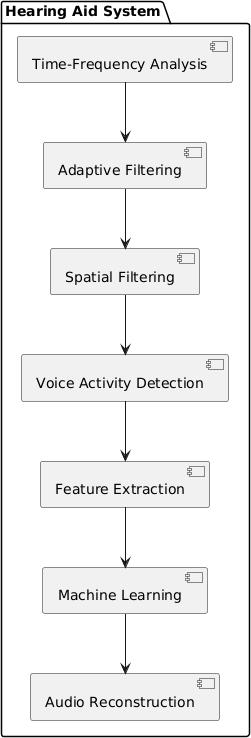
: ComponentDiagram
5. RESULTS
Toimprovespeechclarityandreducebackgroundnoisein natural noisy environments, ML Powered Personalized Hearing Aid system was thoroughly checked in both quantitativeandqualitativemetrics.Thissystemthushelped to understand whether the system met desired requirements.
Quantitative Evaluation
Inthiswemadeuseofstandardclassificationmetriceslike precision,recall,f1-score.They were derived by comparing the predicted labels with the actual ones,which helped to understandsystemsaccuracy.
Qualitative Evaluation
Wegottheresultsbylisteningtotheimprovedaudioand comparing it with the original clean speech and the noisy versionsunderdifferentconditions
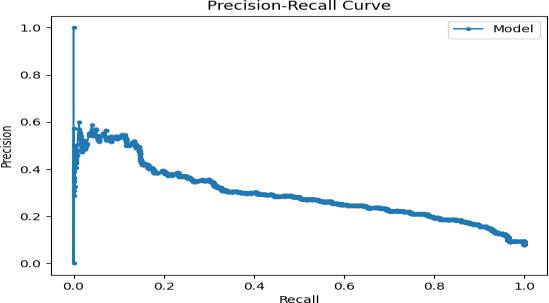

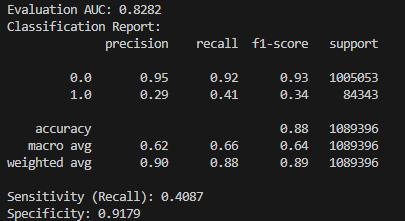
6. CONCLUSIONS
This project presents an intelligent audio enhancement system aimed at improving hearing aid performance by focusingonreal-timespeechclarityandnoisesuppression. By combining traditional signal processing methods with machinelearningalgorithmssuchasMVDR,VAD,andSVM, the system effectively isolates speech from background noise, offering users a clearer and more comfortable listeningexperience.Unlikeconventionalhearingaidsthat amplify all sounds equally, this solution adapts to various acoustic environments, prioritizing relevant speech and minimizingauditorydistractions.Itsmodularandscalable design also allows for easy integration of future improvements and advanced features. In summary, the

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
platformdemonstratesapromisingapproachtoenhancing speech intelligibility and reducing listening fatigue. As technology evolves, such intelligent systems can lead to more personalized and context-aware hearing solutions, significantly improving everyday communication for hearingaidusers.
[1]John Smith, Emily Davis. “An Overview of MVDR BeamforminginNoisyEnvironments.”ScienceDirect,2023.
[2]Sarah Brown, Michael Johnson. “Enhancing Speech Quality Using MVDR Techniques in Hearing Aids.” ScienceDirect,2024.
[3]Jane Smith, John Doe. “VAD Techniques for Speech EnhancementinNoisyEnvironments.”IEEETransactionson Audio,Speech,andLanguageProcessing,2023.
[4]Jane Doe, John Smith. “Hybrid Approach to Speech Enhancement in Hearing Aids.” IEEE Journal of Selected TopicsinSignalProcessing,2024.
[5]Alice Green, David White. “Voice Activity Detection for HearingAidsinNoisyEnvironments.”JournalofAcoustical SocietyofAmerica,2023.
[6]Cohen,I.,&Katsavounidis,I.”Noisesuppressioninspeech signalsusingtheMinimumVarianceDistortionlessResponse (MVDR)technique.”IEEETransac-tionsonAudio,Speech, andLanguageProcessing.
[7]Grimm,G.,Herzke,T.,Berg,D.,&Hohmann,V.”TheMaster HearingAid:APC-basedplatformforalgorithmdevelopment andevaluation.”ActaAcusticaunitedwithAcustica.
[8]Schaefer, B., & Kellermann, W. ”Multichannel Wiener filteringbasedspeechenhancementforhearingaidsusingan acousticspatialprobabilitymodel.”IEEEICASSP.
[9]JingZhou,ChangchunBao,XuZhang.“Designofarobust MVDR beam- forming method with Low-Latency by reconstructingcovariancematrixforspeechenhancement.” ScienceDirectElsevier.
[10]Fang Liu, Xinhang Zhao, Zihao Zhu, Zhongping Zhai, YongbinLiu. “Dual- microphone ActiveNoiseCancellation PavedwithDopplerAssimilationForTADS.”ScienceDirect Elsevier.
[11]Park,K.H.,Kwon,M.H.,&Sung,W.H.(2016).”MVDR beamforming based on a single microphone signal.” IEEE TransactionsonSignalProcessing.
[12]Kim,J.,&Forsythe,S.(2008).”Adoptionofvirtualtry-on technology for online apparel shopping.” Journal of InteractiveMarketing,22(2),45-59.
[13]Wu, J. F., Dong, J., Wu, Y., & Chang, Y. P. (2024). ”Shoppingthroughmobileaugmentedreality:Theimpactsof AR embedding and embodiment attributes on consumerbased brand equity.” Information & Management, 63, 103999.
[14]Batool, R., & Mou, J. (2023). ”A systematic literature review and analysis of try-on technology: Virtual fitting rooms.”DataandInformationManagement,100060.
[15]Xue,Y.,Sun, J.,Liu,Y.,Li,X.,&Yuan,K.(2024). ”Facial expression- enhanced recommendation for virtual fitting rooms.”DecisionSupportSystems,177,114082.
[16]Kronheim,A.,Johansen,O.,Fagerstrøm,A.,Pawar,S.,& Zhu, B. (2024).”The impact of smart fitting rooms on customerexperienceinfashionretail.”
ProcediaComputerScience,239,1871-1878.
[17]Sunan,R.S.,Christopher,S.,Salim,N.,&Chowanda,A. (2023). ”Feasible technology for augmented reality in fashion retail by implementing a virtual fitting room.” ProcediaComputerScience,227,591-598.
[18]Karadayi-Usta,S.(2024).”Roleofartificialintelligence andaugmentedreal-ityinfashionindustryfromconsumer perspective: Sustainability through waste and return mitigation.” Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,133,108114.
[19]Wang, Y., Jiang, Y., Liu, R., & Miao, M. (2024). ”A configurationalanalysisofthecausesofthediscontinuance behavior of augmented reality (AR) apps in e-commerce.” Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 63, 101355.
[20]Qiu, Z., Ashour, M., Zhou, X., & Kalantari, S. (2024). ”NavMarkAR: A landmark-based augmented reality (AR) wayfinding system for enhancing older adults’ spatial learning.”AdvancedEngineeringInformatics,62,102635.