International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 04 Issue: 07 | July -2017
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
www.irjet.net
A Comparative Analysis of Genetic Algorithm Selection Techniques Nidhi, Research Scholar Department of Computer Science and Applications, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Abstract - The focus of this paper is towards analyzing
the performance of various selection methods in Genetic algorithm. There exist different selection methods that play a significant role in genetic algorithm performance. Some selection methods are taken into consideration. Objective of this paper is to extracting a comparative analysis of the different selection methods. Key Words: Fitness number, Genetic Algorithm, GA operators, Selection Techniques.
1.INTRODUCTION Now a days, Genetic algorithms are broadly used in optimisation problems. With the help of these algorithms a good alternative can be found in such problem areas where the number of constraints is too large for humans to evaluate efficiently. Genetic algorithms (GAs) were invented by John Holland in the 1960s and colleagues at the University of Michigan in the 1960s and the 1970s. His actual aim is to study the phenomenon adapted by the nature for further reproduction system not to design the Genetic algorithms. So that, nature adaption method can be used in computer system to find their offspring. [4]
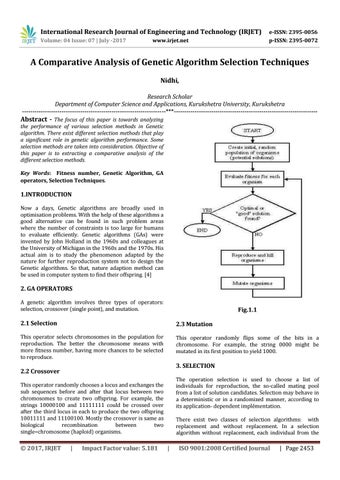
2. GA OPERATORS A genetic algorithm involves three types of operators: selection, crossover (single point), and mutation.
Fig.1.1
2.1 Selection
2.3 Mutation
This operator selects chromosomes in the population for reproduction. The better the chromosome means with more fitness number, having more chances to be selected to reproduce.
This operator randomly flips some of the bits in a chromosome. For example, the string 0000 might be mutated in its first position to yield 1000.
3. SELECTION
2.2 Crossover
The operation selection is used to choose a list of individuals for reproduction, the so-called mating pool from a list of solution candidates. Selection may behave in a deterministic or in a randomized manner, according to its application- dependent implémentation.
This operator randomly chooses a locus and exchanges the sub sequences before and after that locus between two chromosomes to create two offspring. For example, the strings 10000100 and 11111111 could be crossed over after the third locus in each to produce the two offspring 10011111 and 11100100. Mostly the crossover is same as biological recombination between two single−chromosome (haploid) organisms.
© 2017, IRJET
|
Impact Factor value: 5.181
There exist two classes of selection algorithms: with replacement and without replacement. In a selection algorithm without replacement, each individual from the
|
ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
| Page 2453