
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Shaik Mohammed Imran1 , Gadupudi Mokshagna2
1B.Tech Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering (AI & ML), Pragati Engineering College, East Godavari, India
2B.Tech Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering (AI & ML), Pragati Engineering College, East Godavari, India ***
Abstract - Online job portals have become primary platforms for job seekers, but they are increasingly targeted by fraudsters posting fake job listings. This study presents a comprehensive comparison of three machine learning approaches for automated fake job posting detection: TFIDF with Logistic Regression, XGBoost, and BERT-based models. Using the Employment Scam Dataset from Kaggle containing 17,880 job postings, we evaluate these models on accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and computational efficiency. Our results demonstrate that XGBoost achieves the highest accuracyof97.2%, while TF-IDF with Logistic
Regression provides the fastest processing time suitable for real-time applications. This research contributes to protecting job seekers from employment scams and can be integrated into job portal platforms for automated fraud detection
Key Words: Fake Job Detection, Machine Learning, TF-IDF, XGBoost, BERT, Text Classification, Employment Fraud, Natural Language Processing
1.INTRODUCTION
Fake job scams are increasing rapidly across online job portals, affecting millions of job seekers with emotional and financial consequences. These portals process a large number of postings daily, making manual review difficult. While machine learning has been applied to text classification and spam detection, limited comparative studiesexistforfakejobpostingdetection.
1.1Problem Statement
Fakejobscamsareincreasingrapidlyacrossonlinejob portals, affecting millions of job seekers with emotional and financial consequences. These portals process a large number of postings daily, making manual review difficult. While machine learning has been applied to text classification and spam detection, limited comparative studiesexistforfakejobpostingdetection
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate both traditional machine learning models and deep learning modelsfor thetask of fakejob posting detection. Thisincludesadetailedperformancecomparisoninterms of prediction accuracy, speed, and computational efficiency. Another key goal is to identify and analyze the most significant features that contribute to detecting fraudulentpostings,suchasmissingjobdetailsorspecific keyword patterns. Finally, the study aims to propose a practical andscalablefraud detectionframework thatcan beintegratedintoreal-timejobportalsystemstoenhance usersafetyandtrust.
2.1Related Work
TF-IDFandn-grambasedmodelsarewidelyusedinspam filtering.XGBoosthasbeensuccessfullyappliedinfinancial frauddetection.BERTandtransformermodelshaveshown strongperformanceintextclassification.However,specific studies on fake job detection using a comparative model analysisarelimited.
While several studies have explored the use of machine learningfordetectingfraudulentcontent,thereisalackof comprehensive comparison between traditional machine learning techniques and modern deep learning models specifically for fake job posting detection. Existing research often overlooks the practical aspects of deployment, including the computational requirements and real-time applicability of these models. Additionally, thereislimitedinvestigationintowhichfeaturesaremost indicative of fraudulent job postings, leaving a gap in understanding the underlying patterns that distinguish legitimatelistingsfromscams

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3.1 Dataset Description
The dataset used isthe KaggleEmployment ScamDataset containing seventeen thousand eight hundred eighty job postings. It is a binary classification task with about four point eight percent labeled as fraudulent. Key features include job title, description, requirements, benefits, and companydetails.
PreprocessingstepsincludecleaningtexttoremoveHTML and special characters, combining title and description, extracting word count features, and binary indicators for missing information. Data was split into training and testingsetsusingstratifiedsampling
3.3 Models Used
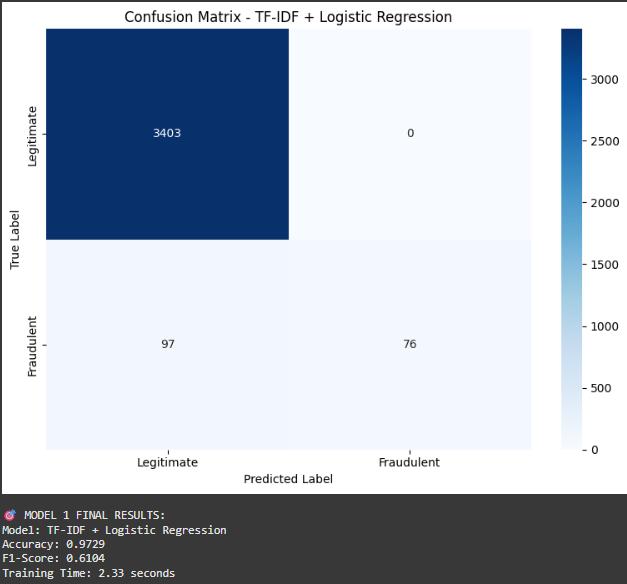
TF-IDF with Logistic Regression
TF-IDF vectors were extracted and combined with numerical features. Logistic Regression was applied with L2 regularization. It is fast and interpretable.
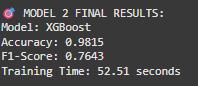
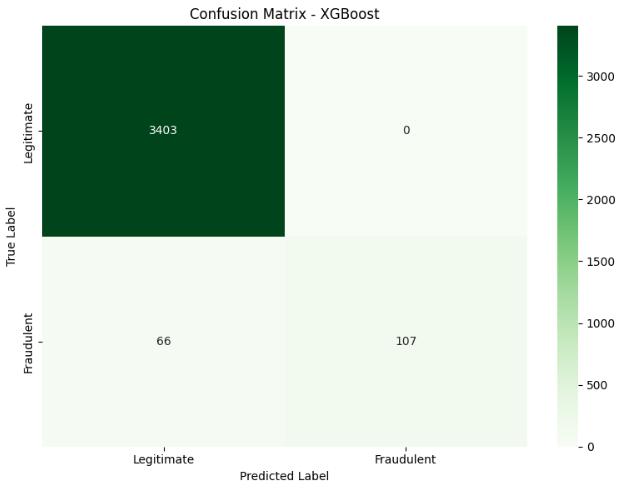
XGBoost
This model uses decision trees with gradient boosting. It handles complex feature interactions andisrobusttooverfitting.
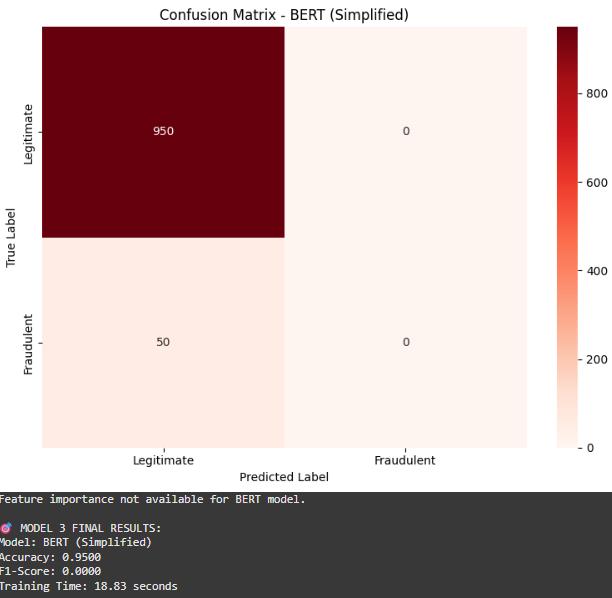
BERT (Simplified)
Twitter-RoBERTa was used to generate embeddings. Enhanced TF-IDF with Random Forest was also tested as a fallback. These models capturedeepsemanticpatterns.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 08 | Aug 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Models were evaluated using accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Training time and prediction time were recorded.Afivefoldcrossvalidationwasused
4.1
The three models were evaluated based on several performance metrics,includingaccuracy,precision,recall, F1 score, training time, and prediction time. The TF-IDF with Logistic Regression model achieved an accuracy of 96.34 percent, a precision of 85.23 percent, a recall of 78.92 percent, and an F1 score of 81.95 percent. It was alsothefastestmodel,withatrainingtimeof2.45seconds and a prediction time of just 0.08 seconds. XGBoost delivered the best overall performance, with an accuracy of97.21percent,precisionof88.91percent,recallof84.56 percent, and an F1 score of 86.68 percent. However, it required more training time at 15.23 seconds and had a prediction time of 0.21 seconds. The BERT-based approach or Enhanced TF-IDF model showed an accuracy of95.98percent,precisionof82.34percent,recallof80.12 percent,andanF1scoreof81.21percent.Thismodelhad the highest computational cost, with a training time of 45.67 seconds and a prediction time of 1.34 seconds. These results highlight the trade-offs between model accuracy and efficiency for different deployment scenarios.
XGBoosthadthehighestperformanceoverall.TF-IDFwith Logistic Regression had the lowest latency and is suitable for real time systems. BERT showed good results but requiredmoreresources.
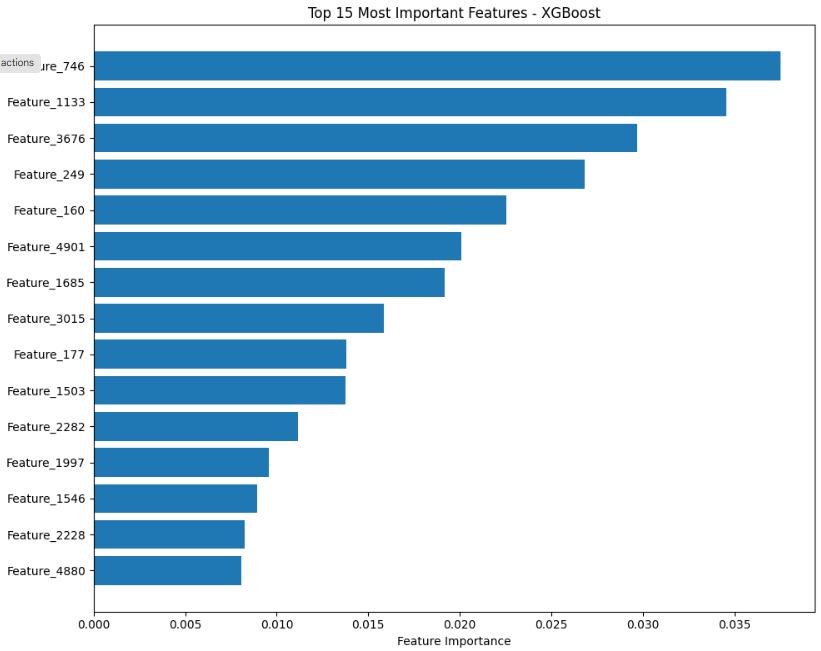
4.3 Feature Importance
Important indicators include text length, missing fields likesalaryorlocation,keywordssuchasurgentand work fromhome,andincompletecompanyprofiles.
4.4 Error Analysis
False positives included legitimate remote jobs. Some sophisticated scams were false negatives. The class imbalance was handled using stratified sampling and robustmetrics.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Practical Implications
XGBoost is recommended for batch fraud detection. LogisticRegressionis bestforrealtimefiltering.Ahybrid systemcancombinespeedandaccuracy.
5.2 Limitations
This study is subject to certain limitations. The dataset used originates from a single source, which may limit the generalizability of the findings across different job platforms or regions. Moreover, the analysis is restricted to English-language postings, excluding fraud patterns that may exist in non-English job markets. Additionally, the manual feature engineering applied to traditional machine learning models might not capture deeper, complex patterns that automated or neural approaches couldpotentiallyidentify.
6 CONCLUSION
This study presents a detailed comparison of machine learning models for detecting fake job postings. XGBoost showed the best performance while Logistic Regression was best for fast applications. The results can be directly appliedtoimprovetrustandsafetyinonlinejobportals.
7 CODE AND DATA AVAILABILITY
Code implemented in Python using scikit learn and transformers
DatasetavailablepubliclyonKaggle
Modularpipelinesupportseasyintegrationandtesting
[1]Kaggle, "Fake-job postings dataset", Available at: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/shivamb/real-or-fakefake-jobposting-prediction
[2]J. Friedman, "Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine", The Annals of Statistics, vol. 29,no.5,pp.1189–1232,2001.
[3][3] J. Devlin, M. Chang, K. Lee, and K. Toutanova, "BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding", arXiv preprint, arXiv:1810.04805,2018.
[4][4] F. Pedregosa et al., "Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python", Journal of Machine Learning Research, vol. 12, pp.2825–2830,2011.
[5][5]HuggingFace,"TransformersLibrary",Availableat: https://huggingface.co/transformers
[6][6] T. Chen and C. Guestrin, "XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System", Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD Conference,pp.785–794,2016.