
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Shreyash S. Chavan1 , Prof. P. V. Muley2
1PG Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Datta Meghe College of Engineering (DMCE), Airoli, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
2 Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Datta Meghe College of Engineering (DMCE), Airoli, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - This study provides a comparative analysis of various structural systems, includingReinforcedConcrete (RC) frames, shear walls, bracing systems, andoutrigger systems, to assess their seismic performance as per IS 1893: 2016. The evaluation is conducted across seismic zones II, III, IV, andV to determine the efficiency of these systems in resisting earthquake-induced forces. Key parameters such as base shear, inter-story drift, and lateral displacement are analyzed using static and dynamic methods to assess the behavior of each structural system under different seismic intensities. The findings highlight the strengths andlimitations ofeachsystem, offering critical insights to aid in selecting appropriate structural solutions for enhanced seismic safety and performance across varying zones
Key Words: Seismic performance, structural systems, RC frames,shearwalls,bracingsystems,lateraldisplacement, earthquakeresistance
Seismicdesignhasevolvedsignificantlyovertime,driven byadeeperunderstandingofearthquakedynamicsandthe need for resilient structures. In India, traditional constructionmethodsprovidedsomeresistancetoseismic forces, but modern approaches have brought systematic improvements.Historicalarchitecture,suchastemplesand forts, showcased durability through massive and solid designs, albeit without explicit seismic principles. Early construction relied on empirical methods until modernizationhighlightedtheneedforstructuredseismic design, leading to the adoption of global standards and localizedstrategies.
Major earthquakeshave been pivotal inshapingIndia's seismicdesignpractices.The1934Bihar-NepalEarthquake (magnitude 8.0) underscored the need for robust engineering in vulnerable regions. The 1967 Shillong Earthquake (magnitude 6.7) emphasized seismic considerationsinnortheasternIndia.Thedevastating2001 Gujarat Earthquake (magnitude 7.7) spurred a comprehensiveoverhaulofdesigncodes,includingstricter enforcementofregulationsandupdatestostandardslikeIS 1893. These events have driven the evolution of seismic
design,ensuringsaferandmoreresilientstructuresacross thecountry.
Moment-Resisting Frames: Moment-ResistingFrames are structural systems that rely on rigid beam-column connectionstoresistlateralforcesthroughbending,offering significantductilitytoabsorbseismic energy.Theyenable openfloorplans,providingflexibilityinarchitecturaldesign. ClassifiedintoOrdinary,Intermediate,andSpecialMoment Framesbasedonductilityandseismicperformance,theyare widely used in earthquake-prone regions. However, these frames can be costly and complex to construct and may sustain damage during severe earthquakes. Modern advancementslikeseismicisolationanddampingsystems areincreasinglyintegratedtoenhancetheirresilienceand efficiency.
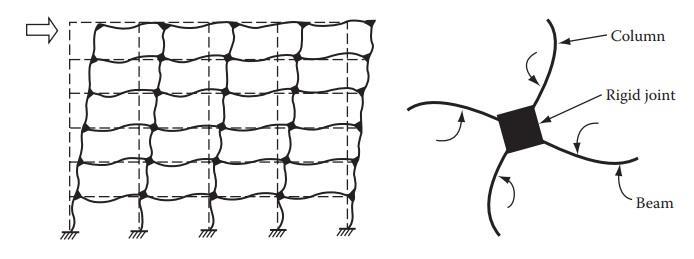
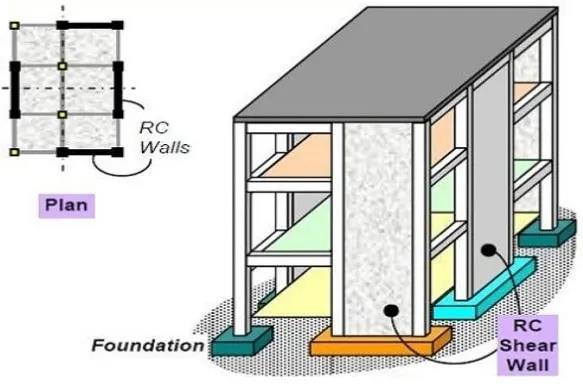
Shear walls: Shearwallsareverticalstructuralelements designedtoresistlateralforcesthroughshearandstiffness, commonly placed in building cores for stability. They are categorized into reinforced concrete, masonry, and compositeshearwalls.Renownedfortheirexcellentlateral stability and efficiency in tall buildings, they offer a costeffectivesolutionwhendesignedproperly.However,shear walls can limit floor plan flexibility and demand precise constructiontechniques.Moderninnovationsemphasizethe useofhigh-performancematerialsandadvanceddesignsto enhancetheirstrengthandadaptability.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
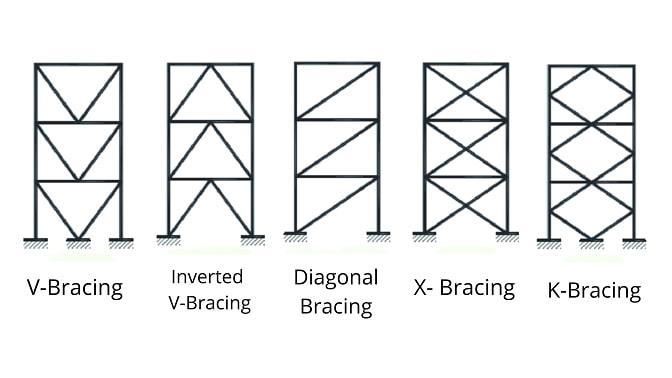
Bracing: Bracing systems use diagonal elements to resist lateralforcesbyconvertingthemintoaxialloads,providing enhanced stability and reducing building sway. Common types include X-Bracing, K-Bracing, Chevron Bracing, EccentricBracing,andKneeBracing.Thesesystemsarecostefficient and space-saving but may limit architectural flexibilityandposechallengesinaestheticsandconstruction. Modern trends focus on incorporating smart sensors and hybrid designs with damping systems to optimize performanceandresilience
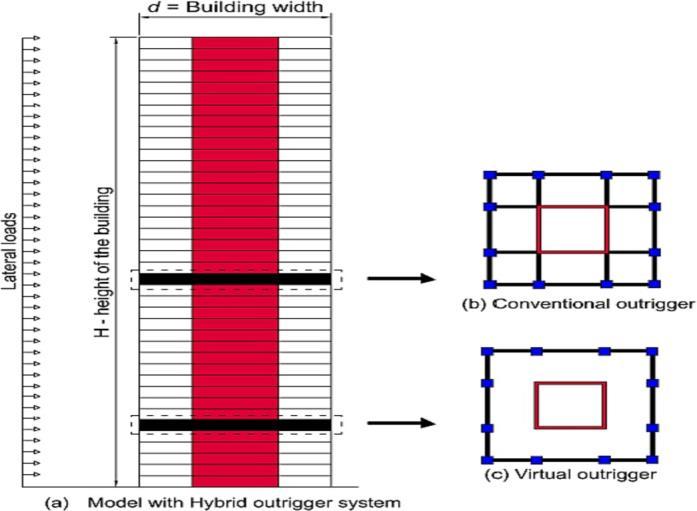
Outrigger: Outriggersystemsarestructuralsolutionsthat connectabuilding’scoretoexteriorcolumnsusinghorizontal beams,significantlyenhancingstabilityandreducinglateral swayfromwindorseismicforces.Byefficientlydistributing loads, they enable taller, more resilient structures with reduced material usage, contributing to cost and resource efficiency. Configurations include single, multi-outriggers, outriggers with belt trusses, and hybrid designs, offering flexibility for various architectural and structural needs. However,theyinvolvecomplexdesigns,highinitialcosts,and potential impacts on floor layouts and interior spaces. Modernadvancements,suchassmartmonitoringsystems, ultra-high-performanceconcrete(UHPC),andhybriddesigns withdampingsystems,addressthesechallengeseffectively,
optimizingperformanceandadaptabilityformodernhighrisestructures.
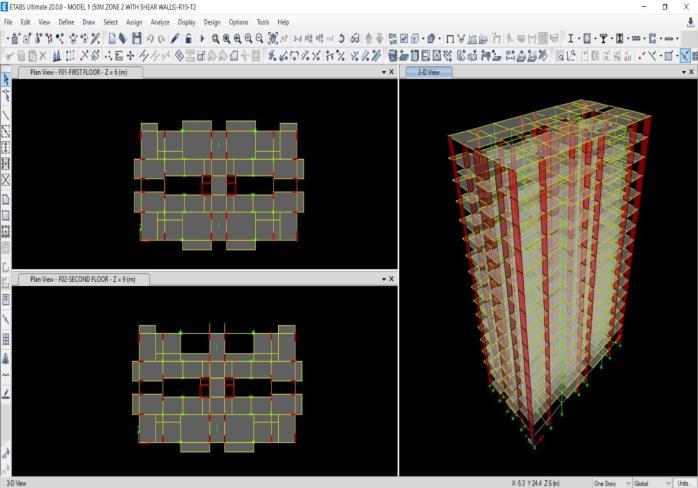
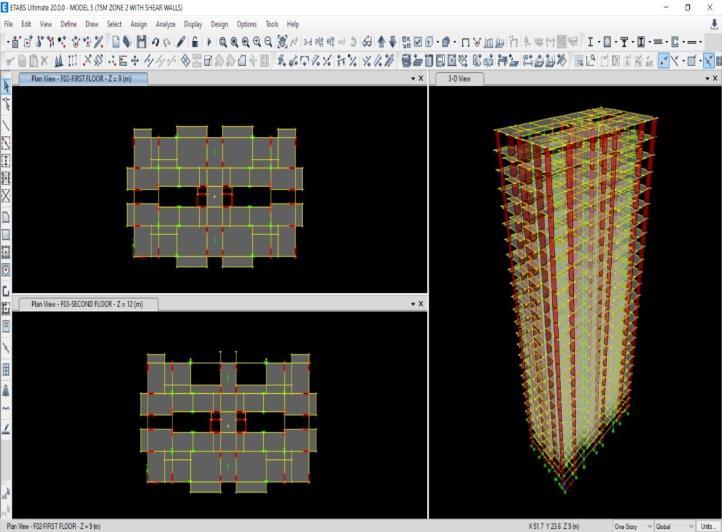
1. TomodelandanalyseG+15andG+25multistorey RC buildings using ETABS 2021 software with actualbuildingplandimensions.
2. To perform both equivalent static analysis and responsespectrumanalysisfortallbuildingmodels subjectedtoseismicloads.
3. To investigate the effects of various structural systemsinseismiczonesII,III,IV,andVasperIS 1893:2016.
4. To evaluate performance based on key response parameters,includingstoreydisplacement,storey drift,baseshear,andfundamentaltimeperiod.
5. Tocompare theseismicperformanceof buildings with shear walls, bracing systems, outrigger systems,andmoment-resistingframes.
This study aims to analyse the seismic performance of G+15 and G+25 RC buildings with different structural systemssuchasRCframe,shearwall,bracing,andoutrigger. The buildings are modeled in ETABS 2021 as per IS 1893:2016,consideringseismiczonesII,III,IV,andV.Both equivalentstaticandresponsespectrummethodsareusedto evaluatetheirresponseunderearthquakeloads.Theanalysis focuses on key parameters including storey displacement, storey drift, base shear, and time period. The results are comparedtoidentifythemostefficientsystemforimproving stabilityandseismicresistanceoftallbuildings

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
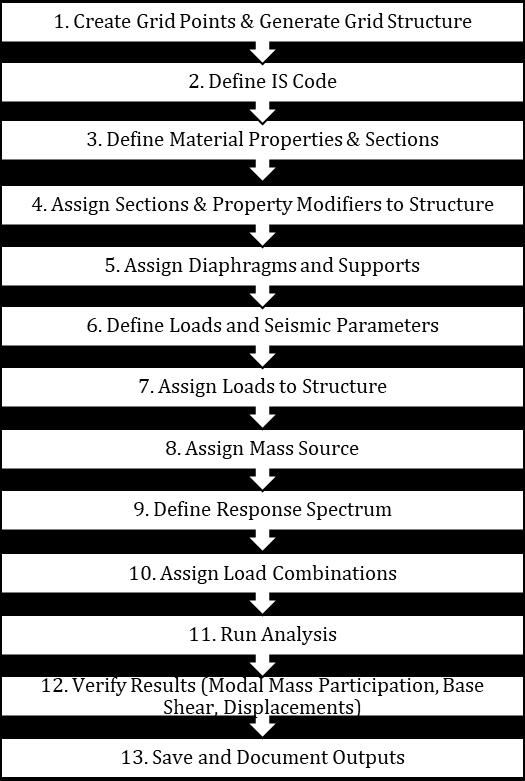
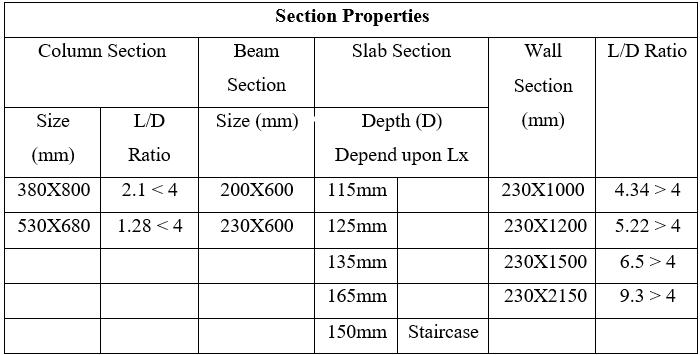
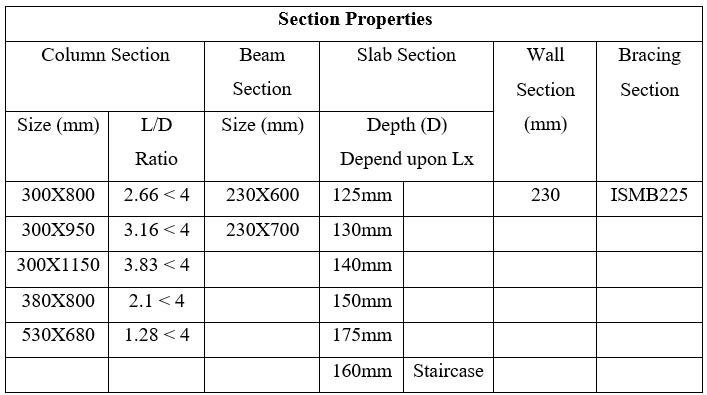
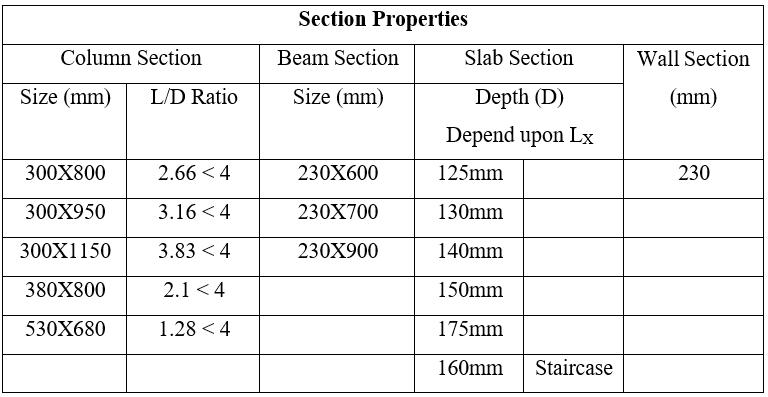
3.2 Model data
No.offloors-15&25floors
Groundstoryheight-3m
Floortofloorheight-3m
PlandimensionalalongX-33.07m
PlandimensionalalongY-17.59m
Shearwallthickness-230mm
Bracing-ISMB225
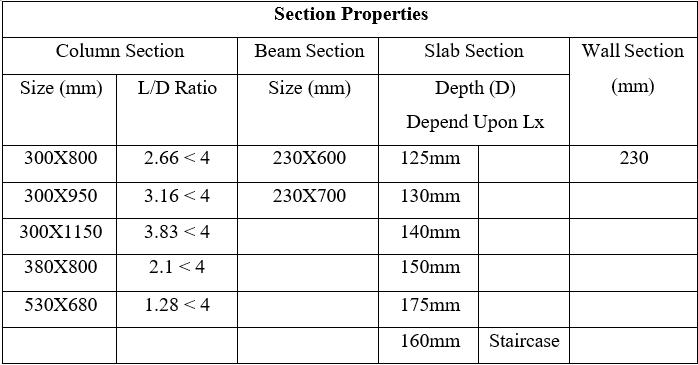
Slabthickness-dependonL/Dratioasper IS456:2000
Sizeofbeam-230mmX600mm
Gradeofconcrete-M40forcolumn,M30for slabandbeam
Gradeofrebar-Fe500formain&Fe415for shear
Gradeofsteel-Fe250

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3.2.3

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4.1 Modal Mass Participation
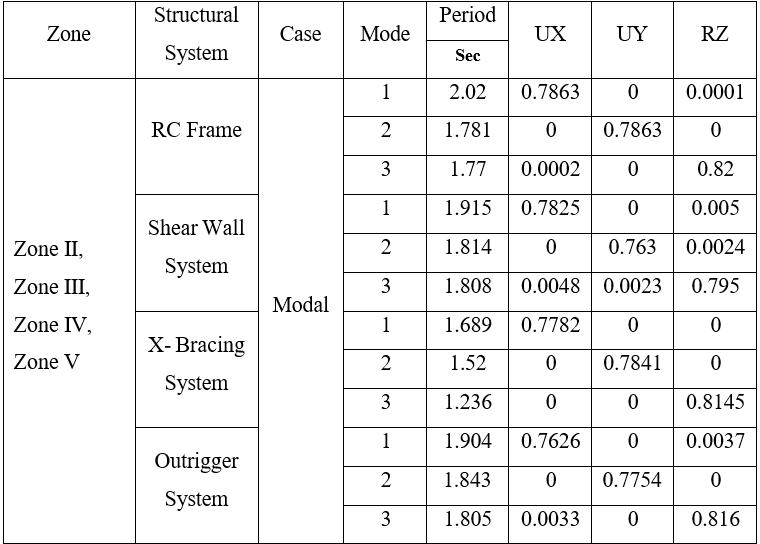
Table 5: ModalMassParticipatingRatioandTimePeriod for45mHeight
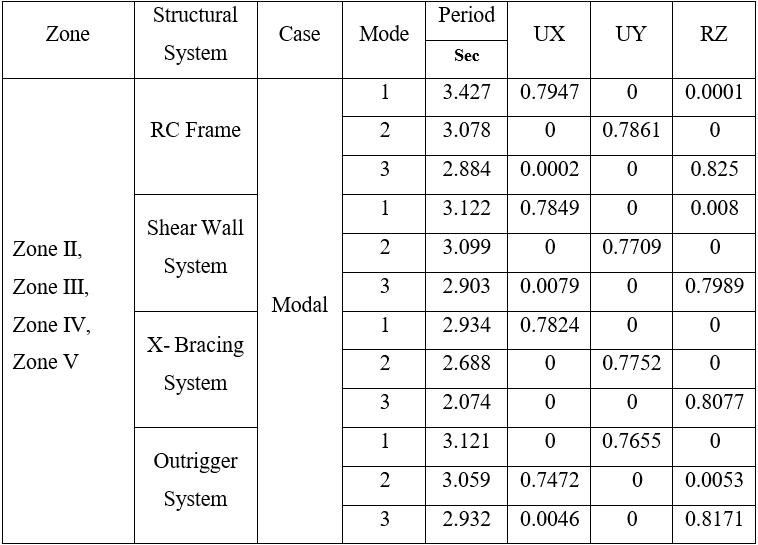
Table 6: ModalMassParticipatingRatioandTimePeriod for75mHeight
Note-ThemodalanalysisresultsindicatethattheRCframe structure exhibits the highest fundamental time period, followedbytheshearwallandoutriggersystems,whilethe X-bracingsystemshowsthelowestperiodamongall.This demonstrates that the inclusion of bracing and outrigger systems enhances the overall stiffness of the structure, thereby reducing the fundamental period and improving resistanceagainstlateralloads

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
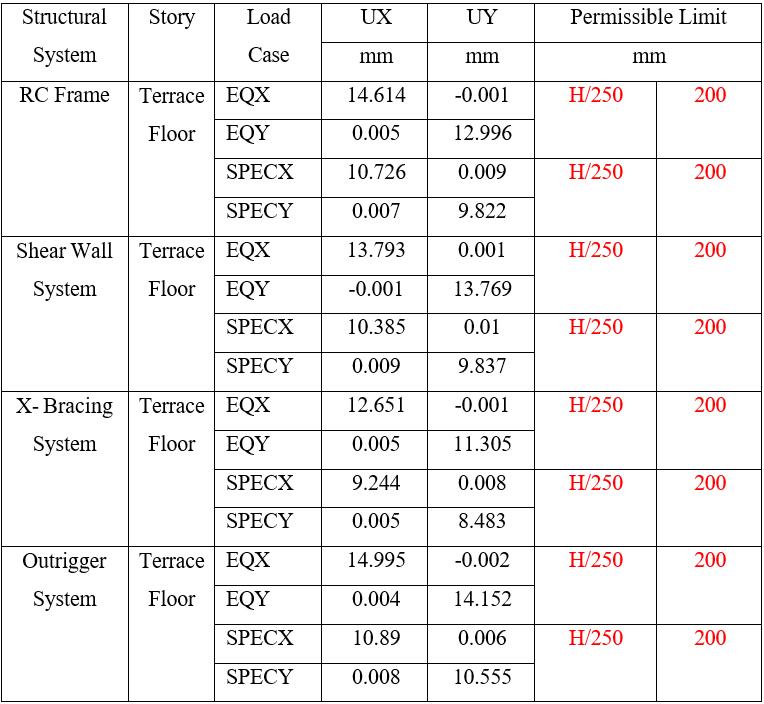
Table 7: DisplacementinZoneIIfor45mHeightofBuilding
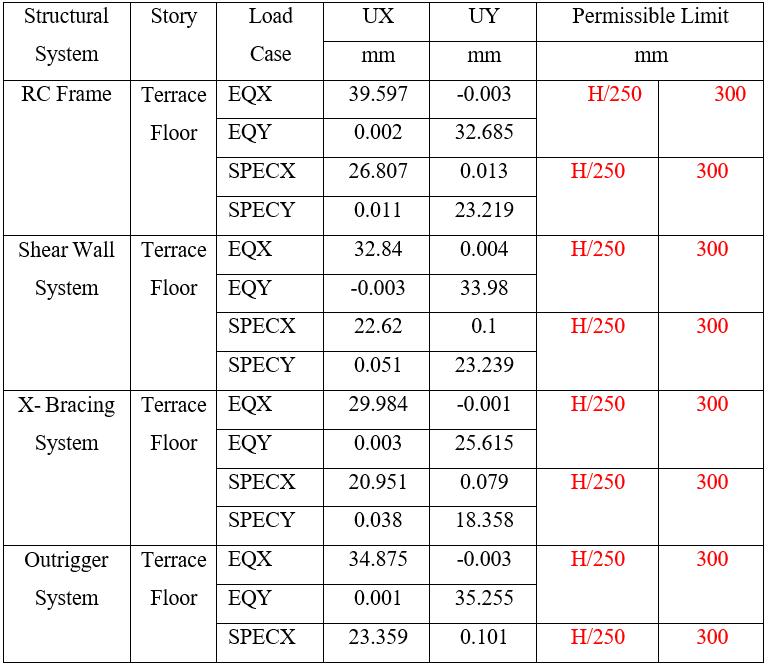
Table 8: DisplacementinZoneIIfor75mHeightofBuilding
Note: Tables7and8presentthedisplacementforZoneII. Theresultsshowthatdisplacementsincreasewithheight, while all systems remain within the permissible limit of H/250. Among them, shear wall and X-bracing systems exhibitcomparativelylowerlateraldisplacements,indicating betterstiffnessandcontrolagainstlateralloads
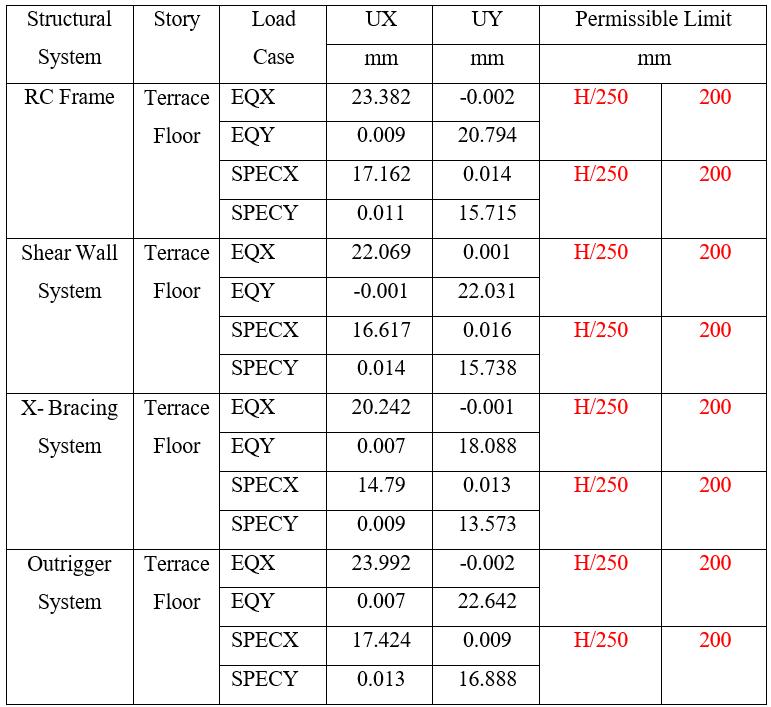
Table 9: DisplacementinZoneIIIfor45mHeightofBuilding
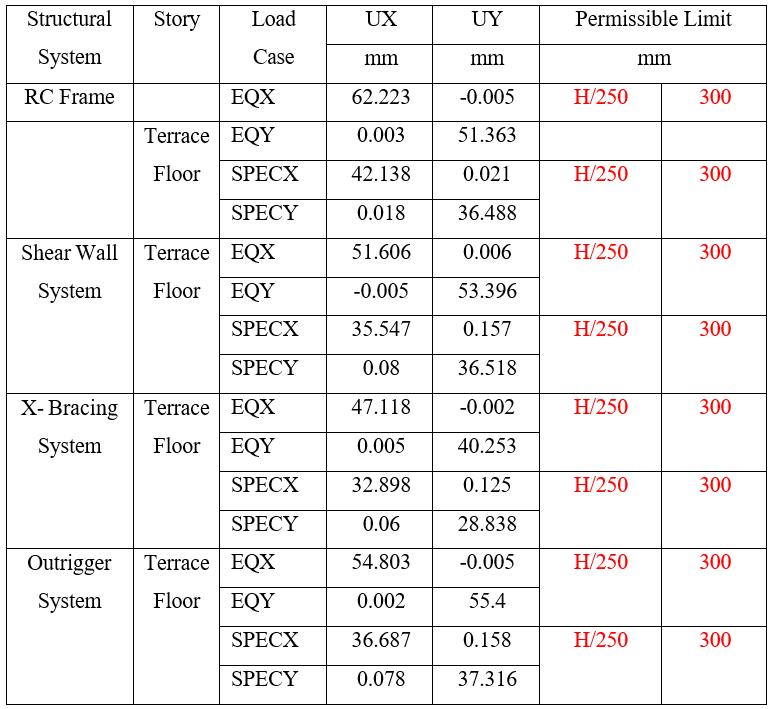
Table 10: DisplacementinZoneIIIfor75mHeightof Building
Note: Tables9and10presentthedisplacementforZoneIII. Theresultsshowsthatdisplacementsincreasewithheight, while all systems remain within the permissible limit of H/250. Among the systems, the X-Bracing System consistently exhibits the lowest lateral displacements, indicatingsuperiorstiffnessandcontrolagainstlateralloads.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
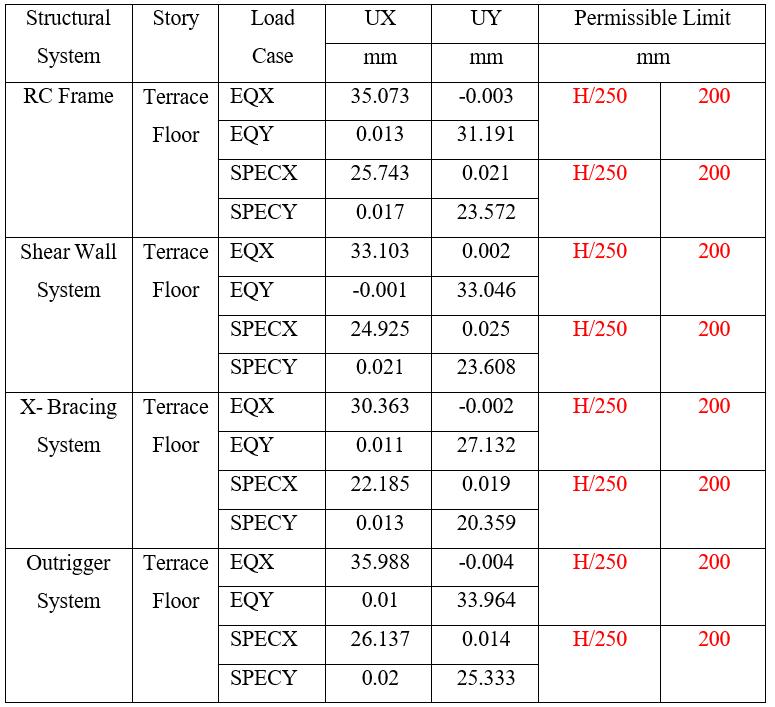
11: DisplacementinZoneIVfor45mHeightof Building
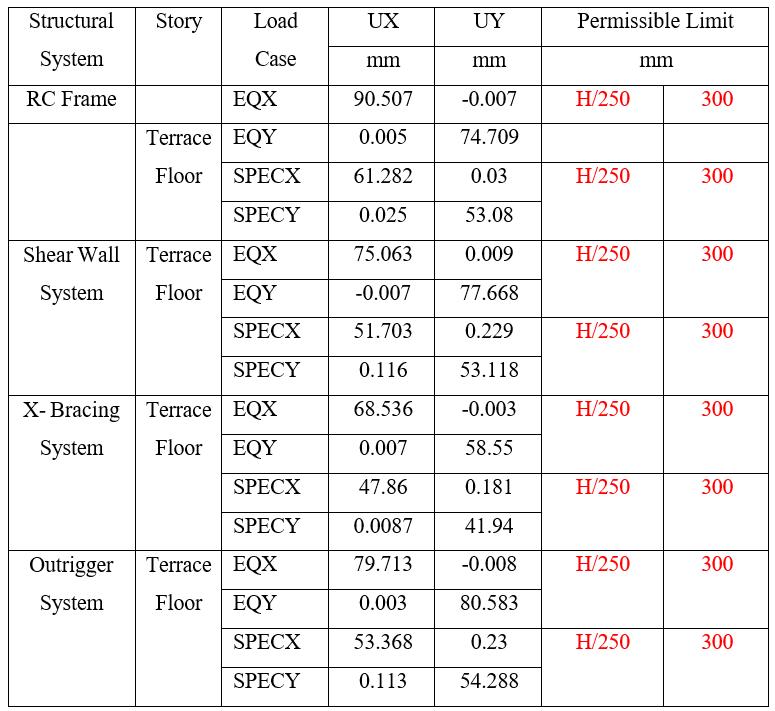
Table 12: DisplacementinZoneIVfor75mHeightof Building
Note: Tables11and12presentthedisplacementforZone IV The results shows that displacements increase with buildingheightandseismiczone,whileallsystemsremain withinthepermissiblelimitofH/250 Amongthesystems, theX-BracingSystemconsistentlyexhibitsthelowestlateral displacements, indicating superior stiffness and control againsthighlateralloads.
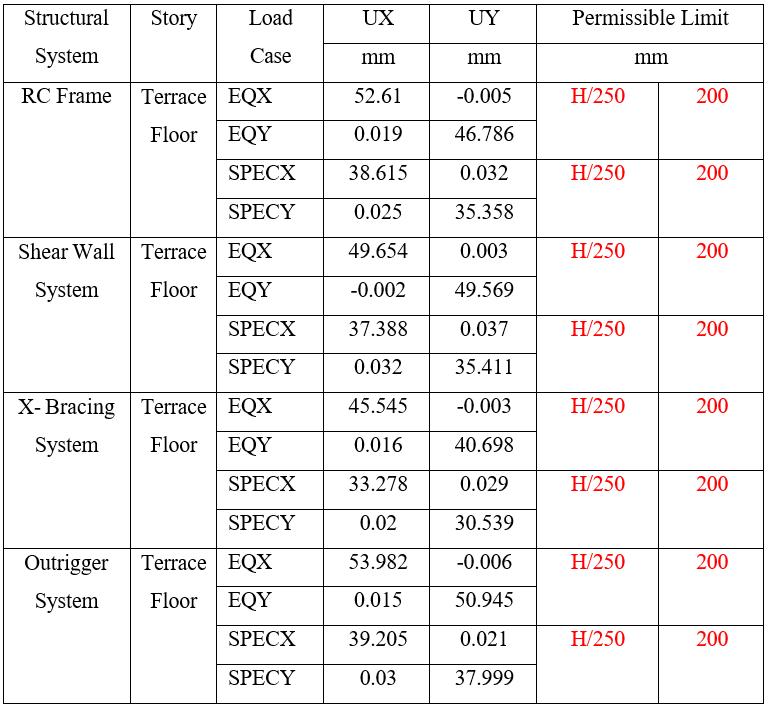
Table 13: DisplacementinZoneVfor45mHeightof Building
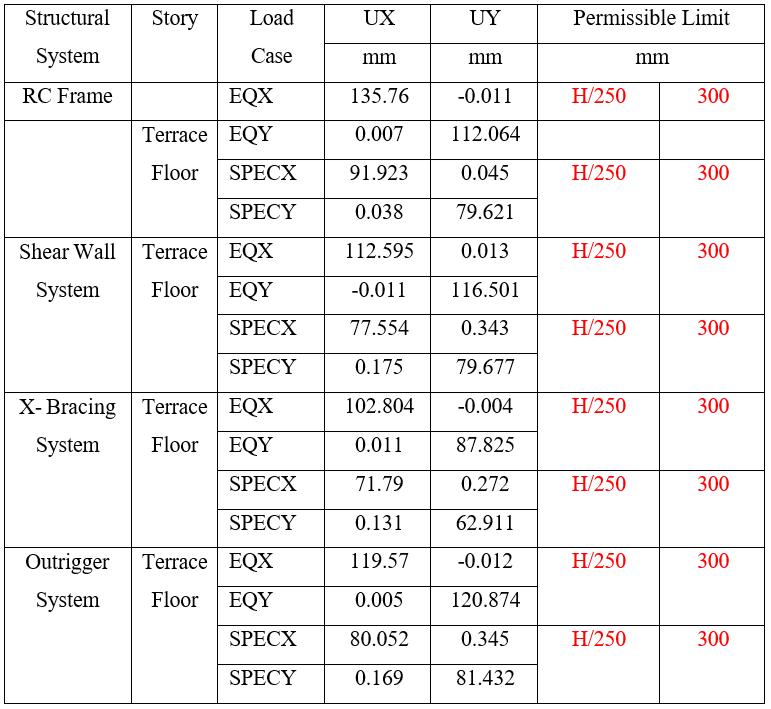
Table 14: DisplacementinZoneVfor75mHeightof Building
Note: Tables13and14presentthedisplacementforZoneV Theresultsshowsthatdisplacementsincreasewithbuilding heightandseismiczone,whileallsystemsremainwithinthe permissible limit of H/250. Among the systems, the XBracing System consistently exhibits the lowest lateral displacements, indicating superior stiffness and control againsthighlateralloads.
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page255

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
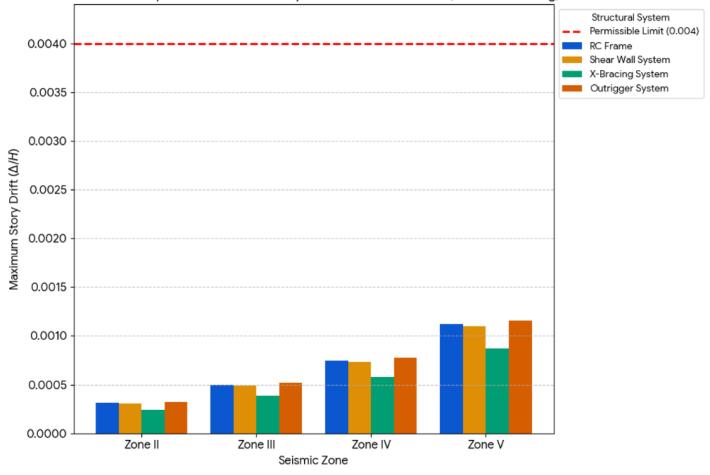
1: StoryDriftVsPermissibleLimitfor45mHeight ofBuilding.
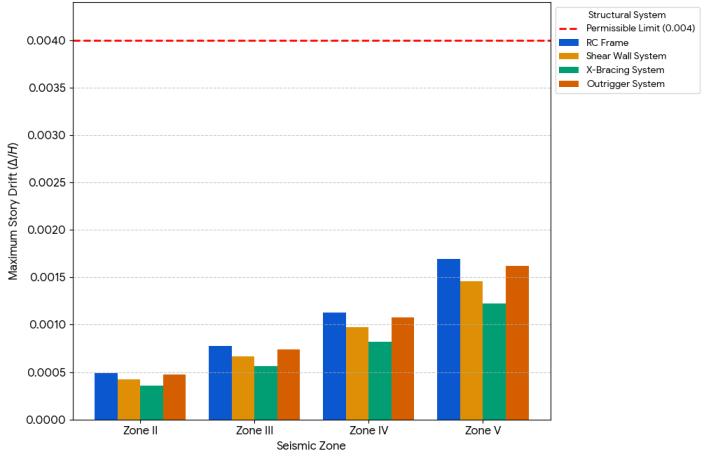
Graph 2: StoryDriftVsPermissibleLimitfor75mHeight ofBuilding.
Note: The graphs compare story drift values of different structural systems (RC Frame, Shear Wall, X-Bracing, Outrigger) across seismic Zones II to V in both X and Y directions.Allsystemsstaywithinthepermissibledriftlimit of 0.004, with X-Bracing consistently showing the lowest drift.ZoneVexhibitsthehighestdriftvalues,especiallyforRC FrameandShearWallsystems,indicatingincreasedlateral displacementunderstrongerseismicforces.
5. CONCLUSIONS
Following are the conclusions obtained from these studies:
• X-Bracingsystemiseffectiveinalltheseismiczones ofIndia.
• X-Bracingsystemhaslessertimeperiodof1.689sec and2.934secfor50mand75mheightofbuilding.
• X- Bracing has a minimum displacement of 12.651mm,20.24mm,30.363mmand45.545mmin zoneII,zoneIII,zoneIVandzoneVrespectivelyfor 50mheightofbuildingascomparetoothersystem.
• X- Bracing has a minimum displacement of 29.984mm,47.118mm,68.536mmand102.804mm inzoneII,zoneIII,zoneIVandzoneVrespectively for 75m height of building as compare to other system.
• X-Bracinghasaminimumstorydriftof0.726mm, 1.161mm,1.743mmand2.613mminzoneII,zone III,zoneIVandzoneVrespectivelyfor50mheightof buildingascomparetoothersystem.
• X-Bracinghasamaximumstorydriftof1.074mm, 1.680mm,2.451mmand3.678mminzoneII,zone III,zoneIVandzoneVrespectivelyfor75mheightof buildingascomparetoothersystem.
• Time period, displacement and storey drift of xbracingsystemislessinallthezonesascomparedto shearwallandoutriggersystem.
• Outrigger System has minimum base shear coefficientascomparetoshearwallandx-bracing System.
• CombineShearwallandx-bracingsystemhasless displacementof40.089mmand60.134mminzone IV and zone V respectively for 75m height of building.
[1] Pramod Kumar Lodhi, Professor Dr. Rajeev Chandak (2024)AResearchonComparativeSeismicAnalysisof RCCBuildingwithandWithoutBracingUsingETABS–“International Journal of Scientific Research & Engineering Trends Engineering (IJSERT), Volume 10, Issue 04, Aug 2024”
[2] Mr.MukeshR.Zambre,Prof.Y.R.Suryawanshi,Prof.V. P. Bhusare, Dr. N. V. Khadake (2022) Seismic PerformanceofRCCIrregularBuildingwithShapeand Stiffness– “InternationalResearchJournalofEngineering and Technology (IRJET), Volume 09, Issue 05, May 2022”
[3] Dr.VijayaG.S,VinodhiniS(2021)AnalysisofHigh-Rise Building with Dual Systems – “ADBU-Journal of Engineering Technology, Volume 10, Issue 04, December 2021”
[4] Nilendu Chakrabortty, Akshit Lamba (2020) Analysis andDesignofG+3BuildinginDifferentSeismicZones using E-tabs – “International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), Volume 07, Issue 08, Aug 2020”
[5] KNJeevanKumar,SabyathPShetty(2020)Behaviorof Multi-Storey R.C.C Structure with Different Types of

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Bracing against Earthquake Forces – “International Research Journal of EngineeringandTechnology, (IRJET), Volume 07, Issue 07, July 2020”
[6] P. Gwalani, Y. Singh, H. Varum (2020) Seismic PerformanceofRCDualSystemBuildingsDesignedfor IndianCode– “The 17th World Conference onEarthquake Engineering, (17WCEE), September 13th to 18th 2020”
[7] Han-Soo Kim, Yi-Tao Huang and Hui-Jing Jin (2019) InfluenceofMultipleOpeningsonReinforcedConcrete Outrigger Walls in a Tall Building– “Multidisciplinary DigitalPublishingInstitute(MDPIAPPLIEDSCIENCES), 15Nov2019”
[8] Yuhong Ling, Anqi Li, Rui Liu (2019) Analysis of performance-based seismic design method for super high-riseframe-supportedshearwallstructure–“IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 304(2019)042071”
[9] E.DileepKumar,Dr.N.VictorBabu(2018)Comparative Analysis of Earth Quake Resistant Building Design by Consider Bracings and Shear Wall System in ETABS Software– “InternationalJournalofEngineeringResearch and Application, (IJERA), Volume 09, Issue 08, Aug 2019, pp. 40-47”
[10] Abdul Halim Etemad, Aditya Kumar Tiwary (2019) ComparisonofTubular,OutriggerandBracingSystem forStabilizationofHigh-RiseBuildings– “International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), Volume 10, Issue 03, March 2019, pp. 1968-1977”
[11] Harshitha M K, Vasudev M V (2018) Analysis of RC Framed Structure with Structural Steel Braces Using ETABS– “International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), Volume 05, Issue 01, Jan 2018”
[12] Dharanya,Gayathri,Deepika(2017)ComparisonStudy of Shear Wall and Bracings under Seismic Loading in Multi- Storey Residential Building – “International Journal of ChemTech Research (CHEMTECH), Volume 10, Issue 08, Oct 2017, pp. 417-424”
[13] Narla Mohan, A. Mounika Vardhan (2017) Analysis of G+20 RC Building in Different Zones using ETABS –“International JournalofProfessionalEngineeringStudies (IJPRES), Volume VIII, Issue 03, March 2017”
[14] S Monish, S Karuna (2015) A Study on Seismic Performance of High-Rise Irregular RC Framed Buildings – “International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), Volume 04, Issue 05, May 2015”
[15] Abdul Karim Mulla, Srinivas B. N (2015) A Study on Outrigger System in a Tall R.C Structure with Steel
Bracing– “International Journal of EngineeringResearch & Technology (IJERT), Volume 04, Issue 07, July 2015”
[16] P.M.B. Raj Kiran Nanduri, B. Suresh, MD. Ihtesham Hussain(2013)OptimumPositionofOutriggerSystem for High-Rise Reinforced Concrete Buildings Under WindandEarthquakeLoadings– “American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER), Volume 02, Issue 08, 2013, pp-76-89”
[17] KiranKamath,N.Divya,AshaURao(2013)AStudyon Static and Dynamic Behavior of Outrigger Structural System for Tall Buildings – “Bonfring International Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management Science (BIJIEMS), Volume 02, Issue 04, Dec 2012, ISSN 2277-5056”
[18] P.M.B. Raj Kiran Nanduri, B. Suresh, MD. Ihtesham Hussain(2013)OptimumPositionofOutriggerSystem for High-Rise Reinforced Concrete Buildings Under WindandEarthquakeLoadings– “American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER), Volume 02, Issue 08, 2013, pp-76-89”
[19] HiSunChoi,LeonardJoseph(2012)OutriggerSystem DesignConsiderations–“InternationalJournalofHighRiseBuildings(CTUBH),Volume01,Issue03,Sep2012”
[20] Z. Bayati, M. Mahdikhani and A. Rahaei (2008) OptimizedUseofMulti-OutriggersSystemtoStiffenTall Buildings–“The14thWorldConferenceonEarthquake Engineering(14WCEE),Oct12-17,2008”