
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Ms. Sayali A. Kore1, Prof. A. B. Patil2 ,
1PG Student, Civil (Construction Management), Tatyasaheb Kore Institute of Engineering and Technology, Warananagar, Pin – 416113, Maharashtra, India
2Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Tatyasaheb Kore Institute of Engineering and Technology, Warananagar, Pin – 416113, Maharashtra, India
Abstract - Maharashtra,astatewithsignificantagricultural output, faces severe challenges due to its vulnerability to drought. In Western Maharashtra, several districts are particularly vulnerable to drought includes Pune, Satara, Sangali, Solapur and Ahmadnagar districts. Several water supply schemes and initiatives have been implemented in Maharashtratoaddresswaterscarcity,particularly indroughtprone areas Krishna-Koyna Lift Irrigation Scheme plays vital role in solving these water scarcity issue. Water from Krishna River at Mhaishal KT weir (A/p- Mhaishal, Tal- Miraj, DistSangali) lifted to irrigate 81697 Ha area in Sangali & Solapur district. Water lifted from krishna river at mhaishal KT Weir is distributedthroughsystemof CanalDistributionNetwork(CDN) & Pipe Distribution Network (PDN). The conventional Canal distribution systems, are less expensive and easier to maintain than Pipe Distribution System, but have some drawbacks. To overcome this drawback and meet the demands of modern irrigation there is need of Pipe distribution system for water supply. The main aim of this project is to find the causes and effects of delay in Pipe Distribution Network System (on the basis case study on of Mhaishal LIS scheme, Maharashtra, India) and suggestion of remedial measures for these factors contributing to delay. This study is not only crucial for the PDN system of Mhaishal LIS, but it also has significant implications for equivalent irrigation projects internationally.
Key Words: Pipe Distribution Network (PDN), Canal DistributionNetwork(CDN).
1. INTRODUCTION:
Water is one of the most essential resources for human survival, economic development, and environmental sustainability. In Maharashtra due to geographical and climaticdiversity,hasseveralregionsthatareaparticularly prone to drought. Drought prone areas in Maharashtra experience a range of issue that impact agriculture, water resource and rural live hood. Drought poses a significant challenge to Maharashtra like reduced agricultural Productivity water scarcity, Economic strain soil degradation, migration health issue etc. Water Supply
Scheme plays a crucial role in managing water resources, ensuring that both urban and rural areas have access to clean and sufficient water. The Water Supply Scheme involvesthecollection,storage,treatment,anddistribution ofwatertothepublic.Itisdesignedtocatertotheneedsof domestic, industrial, and agricultural sectors while maintaining sustainability and minimizing wastage. The water supply scheme ensures a more reliable and sustainablewatersupplyforMaharashtra’sdrought-prone areas.Oneofthecriticalaspectsofanywatersupplyscheme is its design to meet the needs of the population, both in termsofquantityandquality.Thisrequirescarefulplanning, data analysis, and long-term forecasting to ensure that future growth, climate variability, and changing consumption patterns are accounted for. Several water supply schemes and initiatives have been implemented in Maharashtra to address water scarcity, particularly in drought-proneareas.Thewatersupplyschemesinclude,
JalJeevanMission(JJM)
MahatmaGandhiNationalRuralEmploymentGuarantee Act(MGNREGA)WaterSchemes
IntegratedWatershedManagementProgramme(IWMP)
National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP) etc.
TheseWaterSupplySchemealsoplaysanessentialrole inpublichealthbyensuringthatpeoplehaveaccesstosafe drinkingwater.
In Western Maharashtra, several districts are particularly vulnerabletodroughtincludesPune,Satara,Sangali,Solapur andAhmadnagardistrictsetc.facingchallengeslikeerratic monsoon rainfall, over-reliance on groundwater, and inadequate water conservation measures. Krishna-Koyna LiftIrrigationSchemeplaysvitalroleinsolvingthesewater scarcity issue. Tembhu dam isconcrete gravity dam on KrishnaRiverlocatedinSataradistrict.Ithascapacityof3.5 TMC and was built in 1984. The dam provides irrigation watertotheMhaishalliftirrigationprojectsandTakarilift

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
irrigationprojects WaterfromKrishnaRiveratMhaishalKT weir (A/p- Mhaishal, Tal- Miraj, Dist-Sangali) lifted to irrigate 81697 Ha area in Miraj, Kavathemhankal, Jath, TasgaontahsilsofSangalidistrictandSangola,Mangalvedha tahsilsofSolapurdistrict
WaterliftedfromKrishnariveratmhaishalktweir isdistributethroughsystemof,
CanalDistributionNetwork
PipeDistributionNetwork
TheconventionalCanaldistributionsystems,areless expensive and easier to maintain than Pipe Distribution System, buthavesomedrawbackslikewatertheft,lossof water parameters, water pollution, water seepage, land required for service road etc. To overcome this drawback andmeetthedemandsofmodernirrigationthereisneedof Pipedistributionsystemforwatersupply.Pipesdistribution systemgivesbenefitslikereductioninwaterlossandhaving capability of greater precise water distribution. However thissystemcomeswithsomedrawbackslike,Higherinitial cost, complex selection of material of pipe to be used, handling of heavy pipes, corrosion, failures due to design, Theft,complexityindesign,etc.,whichwillresultinproject delay.
Themainaimofthisprojectistofindthecausesand effectsofdelayinPipeDistributionNetworkSystem(onthe basis case study on of Mhaishal LIS scheme, Maharashtra, India)andsuggestionofremedialmeasuresforthesefactors contributingtodelay.Thisstudyisnotonlycrucialforthe PDN system of Mhaishal LIS, but it also has significant implications for equivalent irrigation projects internationally.
PDN system useful for large-scale irrigation projects, especially in regions with sufficient water sources. These system use pipelines to transport water They are more expensive to construct but are more efficient than open canals.PDNsystemCansupplywatertomultiplefarmsand agricultural regions simultaneously. PDN system covers drawbacksofconventionalCDNsystemandresultsinHigher water use efficiency, Reduced evaporation losses, Lower Maintenance cost, Reduced land acquisition and displacement, Minimized water contamination, Reduced floodingrisketc.
TheMhaisalLiftIrrigationScheme(MLIS)isasignificant irrigation project located in the Sangli district of Maharashtra, designed to combat water scarcity in the regionandimproveagriculturalproductivity. TheMhaisal Lift Irrigation Scheme is a vital project aimed at ensuring
sustainable agricultural practices in Maharashtra’s waterscarceregions.Byleveraginginnovativetechnologiessuchas solar power, energy-efficient systems, and advanced monitoring, MLIS has the potential to transform the agriculturallandscapeoftheregionandimprovethequality of life for farmers. With the ongoing investments in infrastructure and technology, this project represents a modelforfutureirrigationschemesinIndiaandbeyond.
Table -1: Salient Features of Mhaishal LIS
Sr no Attribute Particulars
1 Projectname MhaishalLiftIrrigation,Project
2 Purposeofproject ToliftwaterfromMhaishalKTweir on Krisha River to irrigate drought proneAreasinSangli&Solapur
3 Irrigation command area (ICA)inHA 81697Ha
4 ICAONPDN 33300Ha
5 Total Length of PDN 710Km
Hasibullha Mohaseni, Hawna Sahay[1](2021) Describe the pervasive issue of construction delays in Afghanistan, specificallyfocusingontheBistHazerwatersupplyproject. The authors conducted a comprehensive survey involving contractors,clients,consultants,andworkerstoidentifyand categorize the causes of delays. Their findings categorize delays into compensable, excusable, and non-excusable types. The study identifies 83 distinct causes of delay, grouped into project-related, owner-related, contractorrelated,design-related,material-related,equipment-related, and labor-related categories The analysis utilized the ImportanceIndexformulaandSpearman’sRankCorrelation to assess the relationships and strength of agreement betweenvariouspartiesinvolved.Keyfindingsindicatethat projectswithdurationsshorterthan12monthsarehighly susceptible to delays, with the first six months being particularlyproblematic.
M.M.Satpute,P.V.Khandve,M.L.Gulhane[8](2012) informas theglobalpopulationgrowsrapidly,thedemandfornatural resources like water and food increases, creating a significantchallenge.TraditionalirrigationmethodsinIndia, whichrelyonopenchannels,sufferfromhighwaterloss about50%ofwateriswastedduetoinefficienciesinstorage and distribution. To address these issues, adopting Pipe Distribution Networks (PDN) offers a promising solution. PDNutilizesHDPEpipestodeliverwaterundergravityflow, which significantly improves the efficiency of irrigation systems. This method minimizes water loss, reduces

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
maintenance problems, and increases the overall project efficiency (OPE). The Nagthana-2 project in Maharashtra exemplifiesthebenefitsofPDN,showcasingimprovements in water application efficiency and the ability to irrigate a largerareacomparedtotraditionalsystems.Implementing PDN requires careful planning and adherence to specific guidelines, but it has the potential to enhance food production while conserving valuable water resources. Embracing PDN could lead to more sustainable and productive agricultural practices, making it a valuable solution for modern water management and food production.
Mr.Sandesh,B.Kulavmode,Dr.S.S.Valunjkar[5](2017)provides detailed guidelines for designing and constructing pipe distribution networks (PDN) for irrigation systems. It highlights the inefficiencies of traditional canal-based irrigation methods and advocates for PDN systems due to theirhigherapplicationefficiency.Thepaperoutlinesdesign requirements for PDN, including pipe material selection, flow velocity, and control mechanisms. The study emphasizesthebenefitsofPDN,suchasreducedwaterloss, lowermaintenancecosts,andcompatibilitywithadvanced irrigationmethods.Theguidelinesaimtoenhanceproject efficiency and reduce overall costs by adopting modern irrigationpractices.
Tostudythepresentstatusofselectedprojectand collecttheinformationaboutworkprogresstilldate.
Toidentifyfactorscontributingtodelayandeffects ofdelayofselectedongoingproject.
To carry out analysis of various responses obtainedthroughselectedPDNwatersupplyproject.
To recommend best suggestive measures for causesofdelay.
To improve productivity of work by minimizing timeandcostofproject.
3. METHODOLOGY:
Thefollowingmethodologywillbeadopted:
Gathering preliminarydata aboutPDN forwater supplyschemethroughreviewofexistingliterature.
Collection of information about Mhaishal Lift IrrigationScheme.
SelectionofongoingPDNprojectofwatersupply schemeforstudy.
Studyofpresentstatusofselectedproject.
Gathering necessary data by conducting
Questionerssurvey,
Sitevisit
Checklist
Analysisofcollecteddata
Findingcausesofdelay
Effectofdelay
Conduction of awareness program on site in order to improve productivity of work.
Suggestionofremedialmeasurestoavoidcauses ofdelay
ResultsandConclusions.
Flow Chart:
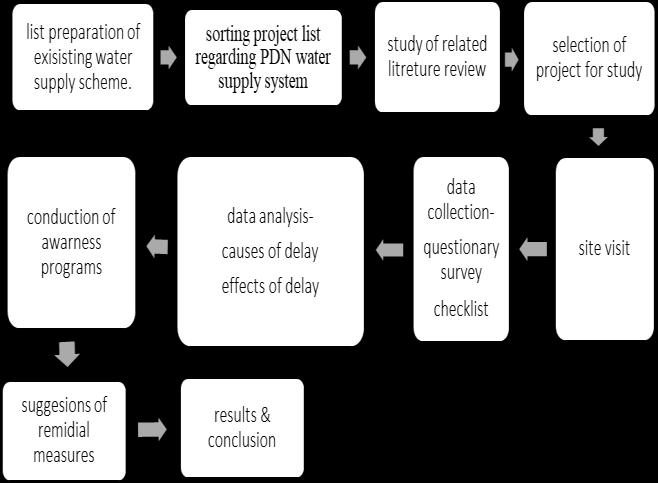
4.
Thisstudyinvolvesmainlythefollowingprocess:
Determinationofobjectiveandscopeofstudywork.
Reviewoftheliterature.
Datacollectionsusingthequestionnairesurvey,site visit.
Analysisofcausesandeffectsofdelayonselected ongoingproject
Suggestionsofremedialmeasure.
Resultsandconclusions.
5. OUTLINE OF THESIS:
ThisthesisconsistsofthefollowingChapters:
The first chapter explains the essential role of water supply schemes in ensuring the availability and

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
equitabledistributionofwater.Ithighlightshowwater issourced,treated,anddistributedtomeettheneedsof domestic, industrial, and agricultural sectors while maintainingsustainability.
The Second Chapter explains literature review examines various studies on delays in irrigation and water supply projects.Keyfindingsincludetheidentificationofmultiple delaycauses, suchas poor planning, financial stability, and external factors like community unrest or pandemics.
Chapter three explains The Mhaishal Lift Irrigation Scheme(LIS)inMaharashtrautilizesaPipeDistribution Network (PDN) to improve irrigation efficiency in drought-prone areas. The project highlights the potential of PDN systems but also reflects ongoing hurdles in project execution and efficiency improvement.
The fourth chapter contains questionnaire survey for the PDN work will aim to gather insights from key stakeholders, including contractors, site engineers, and laborers, to identify the main causes of delays in the Mhaishal Lift Irrigation Scheme. It will focus on factors such as project planning, resource availability, material procurement, and labor management.
The fifth chapter include data analysis using the Relative Importance Index (RII) method to rank and assess the significance of various delay factors identified in the survey. The RII will be calculated for each factor based on responsesfromstakeholders,suchascontractors,engineers, and laborers, to determine their impact on project delays.
Sixth chapter include an awareness program. This will be conducted at the project site to educate workers, contractors, and engineers about the causes ofdelays in the PDN system and the importance of efficient project management.
The fifth chapter includes the data collection and analysis of sites by the green building rating system's criteriaalongwiththemethodologyadoptedtoachieve theobjectivesofthedissertation.
In seventh chapter remedial measures will be suggested to address the key causes of delay in the PDN project, focusing on improving planning, resource allocation, and communication among stakeholders.
Inseventhchaptertheresultswillhighlightthekey findings from the analysis of delay factors in the PDN project,includingtheirimpactontime,cost,andquality. Theconclusionwillofferactionablerecommendations tomitigatedelays,enhanceproductivity,andensurethe successful completion of future PDN water supply projects.
Chapter no eight Represent references used for the project work. And deals with the listing of Publications.
The analysis of delay factors in the PDN (Pipe Distribution Network) project across all key stakeholders Owner/Department, Contractors and Sub-contractors, and Manufacturers and Suppliers reveal that delays are a result of both internal inefficienciesandexternaldisruptions
FromtheOwner'sside, DelayedPaymentsemergedas themostcriticalfactor,severelyimpactingcontractors’ cash flow, procurement, and resource mobilization. Additionally,NaturalDisastersandLateApprovalsalso contribute to significant time losses, emphasizing the need for improved financial management, quicker decision-making, and risk preparedness within the department.
For Contractors and Sub-contractors, the delays are largely caused by Local Public and Political Issues, Shortage of Skilled Workforce, Subcontractor inefficiencies, and Inadequate Tools and Equipment These findings indicate poor planning, resource constraints, and lack of coordination as the primary causesofprojectslowdownsandcostoverruns.
On the Manufacturer and Supplier side, the most pressingdelayfactorsincludeProductionDelays, Supply Chain Disruptions, Equipment Shortages, and again, LocalPoliticalInterference. Theseaffecttimelymaterial deliveryandoverallsupplyreliability,directlyimpacting site work and leading to rework, increased cost, and timelineextensions
The Factor Natural Disaster which is common for all stockholders is not avoidable factor because it is unpredictable factor so sometimes we are unable to controlitseffectsduetounplannedchangeinweather condition.Sowecanonlygowithassumptiononly.
Local Public and Political Problems are major factors which is sometimes completely depends on their mentality. Because of demand of money, to show politicalpower,oldandtraditionalmindsetandlackof knowledgeoftheprojectSoit’sverydifficulttocontrol thisfactors.Sometimesthisdelayfactoriscompletely stoptheprojectforlongtim
[1] HasibullhaMohaseni,HawnaSahay,“CausesofDelay in Bist Hazer Water Supply Construction Project, KabulAfghanistan,”InternationalJournalofCreative ResearchThoughts(IJCRT),Volume9,Issue-9.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[2] Mr. Sandesh B. Kulavmode, Dr. S.S. Valunjkar, “Guidelines for Construction of Pipe Distribution Network (PDN) for Irrigation,” IRJET, Volume 04, Issue3
[3] N.A. Ngubane, M.A. Phiri, L.N. Kunene, “Cause and Effects of Delay in the Implementation Phase of Infrastructure Construction Project,” School of Management, IT and Governance, University of KwaZulu-Natal,SouthAfrica.
[4] Shreyansh Singhal, Dr. Rajeev Kansal, “Delay Analysis in Water Supply Project,” IRISRT, Volume 08,Issue9.
[5] Snehankita A. Karande, Amarsinh Landage, “Comparative Study of Pipe Distribution Network and Canal Distribution Network of Tembhu Lift IrrigationScheme,”JETIR,Volume11,Issue6.
[6] VidyaPurandare,Dr.V.H.Bajaj,“EconomicAppraisal of Lift Irrigation Scheme Benefit-Cost Ratio and InternalRateofReturn:CaseStudyofMhaishalLift IrrigationScheme,”IOSR-JHSS,Volume22,Issue1.
[7] W.D.A.Perera,R.U.Halwatura,“CausesandEffectsof Delay in Construction of Medium-Scale Drinking WaterSupplyProjectinSriLanka,”TheInstituteof Engineers,SriLanka
[8] Distribution Network: Analysis and Design, Handbook
[9] Report of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India onManagement oIrrigation Projects,Report No.-32014GOM.
[10] Land Acquisition and Resettlement Plan, Project No.-45371-007,WRDMadhyaPradesh&Contractor (L&T).
[11] Project Management Handbook, Department of EnvironmentHealthServices.
[12] PipeDistributionNetworkforIrrigation,Handbook, Volume-1,GOM-WRD
[13] PipeDistributionSystemforIrrigation,Handbook by Indian National Committee on Irrigation and Drainage-GOI