Abstract

Abstract

2 Blood pyruvate and lactate levels are important bioindicators that can signify the onset of many different diseases. Current clinical work to quantify blood lactate and pyruvate uses HPLC and UPLC, with drawbacks such as long assay times and high sample volumes. This research project follows the development of high voltage capillary electrophoresis (CE) methods that use electrophoretically mediated microanalysis (EMMA) to quantify lactate and pyruvate concentrations via the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzymatic reaction. During the conversion of pyruvate to lactate, cofactor NADH is converted to NAD+. While lactate and pyruvate are not photoactive, NADH absorbs at 340 nm, and NAD+ absorbs at 260 nm. Basic CE instruments are equipped with UV-vis spectrophotometers and can monitor these absorbances. Two EMMA methods were developed.Along-contact method was developed where the capillary was filled with substrate, and a plug of enzyme was injected, facilitating a continuous reaction in the capillary. Second, a classical plug-plug mode was developed where a plug of substrate was injected before a plug of enzyme, with the electrophoresis causing mixing of the plugs in the capillary. Standards were prepared using three buffer systems: Tris Base at pH 7.5 for pyruvate assay and pH 9.5 for lactate assay, and a pH 8.8 glycylglycine buffer for both assays. Standards were diluted to favorable concentrations using tris buffer and were spiked with 3mM cofactor before injection. The long contact method was found to be applicable to pyruvate (R2 = 0.9992) and lactate (R= 0.9990). The plug-plug method was discovered to only be applicable to pyruvate (R2 = 0.9780).
ΔG =

In the body, lactate and pyruvate react via the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. The conversion of pyruvate to lactate is energetically favorable, with a G of -28.1kJ/mol. This reaction requires coordinating cofactor NADH. During this reaction, NADH is converted to NAD+ with a quantifiable change in absorbance at 260nm.
Conversion of lactate to pyruvate is not energetically favorable but occurs due to an equilibrium. During this reaction, NAD+ is converted to NADH with a quantifiable change in absorbance at 340nm.
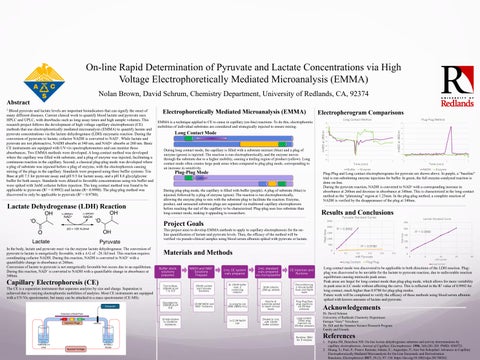
The CE is a separation instrument that separates analytes by size and charge. Separation is achieved due to varying electrophoretic mobilities of analytes. Most CE instruments are equipped with a UV-Vis spectrometer, but many can be attached to a mass spectrometer (CE-MS).
EMMAis a technique applied to CE to cause in capillary (on-line) reactions. To do this, electrophoretic mobilities of individual substrates are considered and strategically injected to ensure mixing.
Long Contact Mode




During long contact mode, the capillary is filled with a substrate mixture (blue) and a plug of enzyme (green) is injected. The reaction is run electrophoretically, and the enzyme moves through the substrate due to a higher mobility, causing a trailing region of product (yellow). Long contact mode often creates large peak areas when compared to plug-plug mode, corresponding to an increase in sensitivity.
Plug-Plug Mode






Plug-Plug and Long contact electropherograms for pyruvate are shown above. In purple, a ”baseline” trial is run substituting enzyme injections for buffer. In green, the full enzyme-catalyzed reaction is done on-line.
During the pyruvate reaction, NADH is converted to NAD+ with a corresponding increase in absorbance at 260nm and decrease in absorbance at 340nm. This is characterized in the long-contact method as the “plateauing” region at 1.25min. In the plug-plug method, a complete reaction of NADH is verified by the disappearance of the plug at 340nm.
This project aims to develop EMMAmethods to apply to capillary electrophoresis for the online quantification of lactate and pyruvate levels. Then, the efficacy of the method will be verified via pseudo-clinical samples using blood serum albumin spiked with pyruvate or lactate.
During plug-plug mode, the capillary is filled with buffer (purple).Aplug of substrate (blue) is injected, followed by a plug of enzyme (green). The reaction is run electrophoretically, allowing the enzyme plug to mix with the substrate plug to facilitate the reaction. Enzyme, product, and unreacted substrate plugs are separated via traditional capillary electrophoresis before reaching the end of the capillary to be characterized. Plug-plug uses less substrate than long-contact mode, making it appealing to researchers. Acknowledgements
Long contact mode was discovered to be applicable to both directions of the
Plugplug was discovered to be unviable for the lactate to pyruvate reaction, due to unfavorable reaction equilibrium causing miniscule peak areas.
Peak areas are larger for long contact mode than plug-plug mode, which allows for more variability in peak area in LC mode without affecting the curve. This is reflected in the R2 value of 0.9992 for long contact, much higher than 0.9780 for plug-plug modes.
Future work will be completed to verify the efficacy of these methods using blood serum albumin spiked with known amounts of lactate and pyruvate.