
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1st Leela Sudarshan
Dept. of Electronics and Communication Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering Tirupati,India
4th Rohith Palleti
Dept. of Electronics and Communication, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Tirupati,India.
2nd G. Padma Priya Professor
Dept. of Electronics and Communication Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering Tirupati,India
5th Keerthi P
Dept. of Electronics and Communication Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering Tirupati,India
Abstract This paper states a remote gas monitoring and alert system designed for mining environments, where toxic gas causes severe risks to workers. The proposed system employs an IoT-based approach to detect, measure, and transmit gas concentration data in real-time while providing alerts through a webbased interface. The module integrates MQ-7 for detectingcarbonmonoxide(CO),MQ-135forhydrogen sulfide (H₂S), and MQ-4 for methane (CH₄), ensuring comprehensive environmental monitoring. The hardware architecture consists of an ESP32-CAM, which is for the rover’s control purpose and navigation, and an ESP32 responsible for gas data obtaining and transmission. Sensor readings are continuously sent to a web dashboard, enabling remote users to monitor hazardous gas levels and analyze trends. The web service is useful for data sharing and remote access, building situational awareness, and worker safety. Sensor readings are continuously sent to a web dashboard, enabling remote users to monitor hazardous gas levels and analyze trends. The system’s web interface allows for data sharing and remote accessibility, enhancing situational awareness and worker safety. The benefit of this prototype is being cost-effective, scalable, and real-time gas monitoring capability and alerting system, and hence an efficient solution for occupationalsafetyforundergroundmines
Keywords IoT, gas monitoring, mining safety, toxic gas detection, ESP32-CAM, real-time alert system, MQ-7, MQ135, MQ-4, occupational safety, environmental monitoring, web-based dashboard.
Miningremainsoneofthemosthazardousindustries,with exposure to toxic gases such as methane (CH₄), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) posing severe health risks to workers. These gases, often odorless and highly combustible, contribute to fatal accidents such as
3rd Noojilla Lahari
Dept. of Electronics and Communication Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering Tirupati,India
6th Muthukuru Sreedhar
Dept. of Electronics and Communication, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Tirupati,India.
explosions, suffocation, and long-term respiratory diseases. Traditional gas monitoring systems have fixed sensors,whichneedconstantmanualattentionandarenot useful in large-scale mining operations where gas accumulation may occur suddenly. Furthermore, limited accessibility to certain mining areas makes manual monitoringbothchallenginganddangerous.
AccidentsliketheChinacoalmineexplosionin2024,three peoplekilled inatMexicoincident in2024andtheOdisha mine gas leakage in 2023 have been fatal ones and these arethemainreasonstohavethesafetysysteminreal-time suchasintheundergroundminingarea.
Such calamities point to the drawbacks of traditional monitoring methods where one is likely to take time to detect the gas or where safety measures may not be effective enough to prevent an explosion. This is because there is no strong real-time alerting system that would warnminerswhenthereisanoccurrenceofgasleakageor anexplosion.
The conventional methods of monitoring gases have been enhancedwiththenewstrategiesintherecentpast.Oneof them is the Smart Safety Helmet which is a helmet containing microcontrollers like ESP32 along with the integrated sensors that help in detecting hazardous gases. These helmets offer monitoring and notification to the miners, which adds to the safety aspect due to response features.[1]Another essential development is the IoTBased Environmental Monitoring System that uses WSNs to monitor the gas concentrations in the mining areas. Thesesystemsofferinformationandalarms,whichenable timely action to be taken in the event of a leakage of gas [2].OpticalFibreSensorscanthereforebeconsideredasa reliable solution for the detection of hazardous gases in mines and tunnels. The sensors include the advantages of nonelectrical transmission of signal, electromagnetic interference, corrosion, and miniaturization, and these make them suitable for challenging underground conditions[3].

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
This project proposes to eliminate these drawbacks by implementinganautomatediot-basedroverthatcanmove through dangerous mining areas and simultaneously measuretheconcentrationofpoisonousgases.theroveris built around the esp32-cam module to provide live video feed and data visualization to the supervisors or safety officerswhoareawayfromtheworkingarea.thismakesit possible to prevent human involvement, and thus lessen the chances of worker exposure to fatal conditions. furthermore, due to the rovers’ capability of moving and performing scanning and mapping in complex and restricted mining areas, it is able to cover a larger area as comparedtofixedsensors
Apartfromsafety improvements,the OreHazardExplorer presents a versatile and inexpensive method for the detection of potentially lethal gaseous mixtures in mining environments and the prevention of such hazards. This project of integrating IoT and real-time analytics in the minespavesthewayforamuchsaferenvironmentforthe workerswherethepossiblerisksarereducedtothebarest minimumandtheirlivesvalued.Alltheseadvancementsin one way or the other mark significant progress in enhancing the safety of the workers in the mining sector eradicating the shortcomings that come with the conventionalmonitoringprocesses.
Much research has been conducted on the detection and monitoringofgasesinthe minesresultinginthedesignof sophisticatedmethodsthatincorporatesensortechnology, communication components, and alerts. They seek to reducetheriskofaccidentsattheworkplaceandfatalities in mining and provide continuous monitoring of the environmentinundergroundmining.
Smart mining to monitor dangerous gases such as (CH₄), (CO), and (H₂S) in the coal mine. This system uses gas sensors in conjunction with an MCU that collects data and transmitsittoaremoteserver.Alarmsareraisedwhenthe gas levels surpass certain set limits and send alerts to the supervisors using text messages and mobile applications Thesystemfocusesonthereal-timeacquisitionofdataand enhanced interaction between the miners and control rooms.[4]
Employing the environmental sensors to detect the concentrations of the gaseous components and the subsequent transmission of the data to a control center. The system is intended to give the readings in real time and also give an alarm in the instance of leakage or fire outbreak. Data collected is displayed on an LCD screen in the control room while information dissemination is done through wireless communication channels to those concerned[5].
Aproposedschemeformonitoringthegaslevelsinmining areas using the Bluetooth-based communication system. The system provides the miners with Bluetooth devices that sense toxic gases in the mining environment. These send information to a control station within theBluetooth range thus allowing the supervisors to monitor the safety ofeachminerinthemine.[6]
Incorporatingenvironmentalsensorstomonitorthelevels of toxic gases in the coal mines. There is a loud beeping sound and flashing light to warn of high-level dangerous gasespresentinthearea.Forthepurposeofdatatransfer, thesystemreliesonawirednetwork inordertoprovidea reliable connection in confined spaces such as undergroundenvironments.[7].
Lone worker protection, including the use of tracking and monitoring of the surrounding environment. It is used for monitoring the gas levels and sends signals to a control room incase ofthe existenceof dangerous levelsofgases. Intended for use in themobilesetting,thesystem ensures the safety of a person when working alone. Although suitable for individual employees, this system is only helpfulforpersonalprotectiontoolsandcannotcovervast mining space. This system provides a gas detection rover that can roam large areas and report visuals and environment data in real time to the supervisors. This increasesthesafetyoftheindividualandtheteamandalso providesaholisticcoverageofminingactivities.[8].
The proposed system brings forward the idea of a rover that will be able to move independently in dangerous zones instead of being immobile and having only sensors. This mobility also helps achieve wider coverage within difficult mining conditions where the formation of gas pockets can be unpredictable. Also, the integration of ESP32-CAMaugmentstheflowofreal-timevisualizationof thescenarioandevengraphical representationsofthegas concentrations.
This system has efficient data acquisition, the main disadvantage of this system is that it is highly dependent on the installation of the sensors, which can be difficult in somecircumstances.Thisisdoneawaywithinthissystem through the use of a mobile rover that can manoeuvre in confined and unstable areas for complete area coverage. TheESP32-CAMalsohelpsinstreamingvideoinareasthat canonlybemonitoredphysically,whichisquiterisky.The Bluetooth transmission is useful for short-range transmission, but it is not applicable to expansive mining areas.
Thisisachievedin thissystemthroughtheuseofa Wi-Fienabled ESP32-CAM for the transmission of data to a distant location. This makes it possible for data to be transmitted even in challenging environments such as

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
underground thus improving the flow of communication besides enhancing safety. Although the wired networks help a great deal in this case they are somewhat rigid, especiallyinlargeandunstableminingzones.Thissystem employs wireless communication technologies for the efficienttransferofdataoverlargeminingterrains.Italso has the capability of moving around independently, thus making it easier to collect data from areas that cannot be accessedbyfixedsensors.
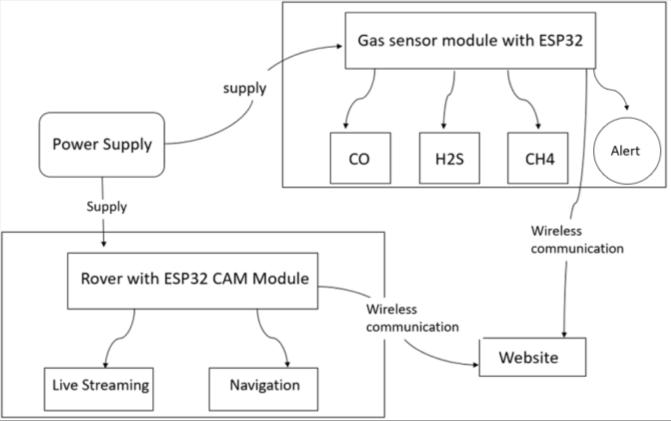
A. ROVERMODULE:
The rover module is the traveling and observation componentoftheOreHazardExplorersystem.Itismeant to be used in some dangerous areas, asit hasthe function of video streaming, remote control for the robot, and gas concentration measurement. The ESP32-CAM is mainly responsibleforcontrollingthelivevideostreamaswellas serial communication with the motor driver board. The real-timevideostreamisprovidedthroughawebinterface whichcanbeusedtocontroltheroverandtomonitorthe conditions below the ground. This is safe for operation sinceitcanbedonewithouttheneedforahumantobein thevicinityofthedangerzone.
Its mobility is attributed to four DC motors that are operated by an L298N motor driver. The ESP32-CAM receives directional commands through Wi-Fi and relays the commands to the motor driver to control the voltage signal to the motors so as to achieve the desired movements in different terrains. This makes the web interface enable real-time movement commands such as forward,backward,left,and rightthrougha control panel. Thisisbecausethecommunicationbetweentheroverand the web application is very low latency hence making it suitable for applications such as mining, industrial inspections,andenvironmentalmonitoring.
Thehardwarecomponentsoftherovermoduleinclude:
Live video streaming comes with the help of ESP32-CAMandwirelesscommunication.
L298N motor driver to control the rover movement based on input signals given through Website.
FourDCmotorsforpropulsion,providingmobility inruggedenvironments.
Rechargeable power supply through Lithium Batteries for uninterrupted operation in remote locations.
Wheels are designed for stability and adaptability tounevensurfaces.
With Wi-Fi connectivity incorporated in it, the rover does not need close physical interaction and is very useful in exploration and monitoring. This capability is useful in safety assessments in mines, during disasters, and in monitoring hazardous areas where human intervention is dangerous.
The sensor module of the Ore Hazard Explorer system is part of the system that monitors hazardous gases in real time. This module involves MQ-4, MQ-7, and MQ-135 sensorswhichareconnectedtotheESP32microcontroller for monitoring air quality on a continuous basis. The collecteddataisthenprocessedanalyzedandpresentedon a web-based application interface as graphs to help the users to make an interpretation of the environmental gas concentrations.AndcancreateaBuzzeralert.
Thegassensorsusedinthemoduleare:
•MQ-4 (Methane Sensor): Designed to sense methane (CH₄),whichisusuallypresent inundergroundminesand confined areas. Methane is highly combustible, and early detectionisrequiredtopreventexplosionsand causeskin irritationtotheworkers.
• MQ-7 (Carbon Monoxide Detector): Designed for the detection of carbon monoxide (CO), an odorless and colorlessgasthatispoisonoustohumans.Exposureathigh concentrations results in serious poisoning and fatal mishaps so CO monitoring under steady conditions becomesimperative.
•MQ-135 (Hydrogen Sulphide Sensor): Industrial multigas sensor capable of sensing ammonia, benzene, smoke, andotheraircontaminants.Thisprovidesthesystemwith greater flexibility to be used for industrial safety, environmentalmonitoring,andpollution.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
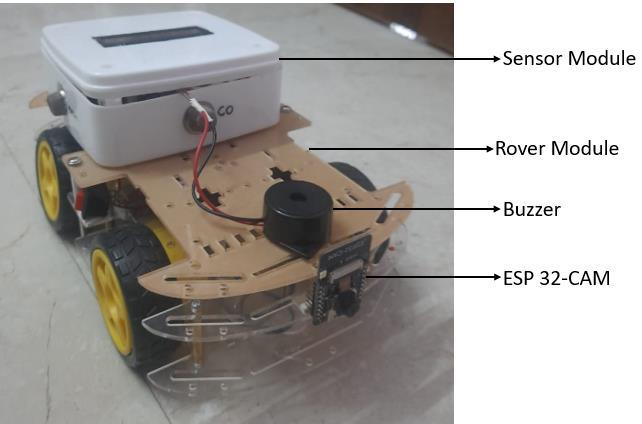
2. Prototype Overview
Each sensor transmits analog data to the ESP32 microcontroller, which processes the readings using predefined threshold values. If the concentration of any detectedgasexceedssafetylimits,thesystem:
User Activates buzzer alarms integrated to provideimmediateon-sitewarnings.
The web-based dashboard presents sensor data using interactive elements, such as gauge meters, real-time graphs, and color-coded alerts, making the system userfriendly and easy to interpret. This feature ensures that miners, supervisors, or remote operators can quickly assessrisksandtakeprecautionarymeasures.
Moreover, through ESP32 the data transmission is done throughWi-Fiandsothesensormodulecanbecontrolled evenwhenitisphysicallydisconnectedfromtheroverbut can be accessed remotely. This capability makes the system ideal for long-term monitoring of the environment in underground mines, tunnels, and other industrial structureswithhazardousgasesthatendangerthelivesof workers.
C. WEBSITE:
TheOreHazardExplorerhasawebapplicationthatisused for monitoring gas concentration data, rover position, and video stream. It is made simple, interactive, and available from any location to allow for remote operation and constantenvironmentalmonitoring. The Website link is https://orehazardexplorer4.netlify.app/
KeyFeaturesoftheWebInterface
1. Real-TimeGasMonitoringDashboard
o Displays live data from MQ-4, MQ-7, and MQ-135sensors.
o Representation of gas concentration for detailedanalysis.
o LivevideofeedstreamedfromtheESP32CAM.
o Directional control buttons for navigating theroverremotely.
o Speed adjustment and movement logs for improvedmaneuverability.
3. AlertsandNotifications
o Sound alarms are triggered by a switch buttononthewebsite.
The backend system, powered by , guarantees the continuous data transmission and processing. The web server is designed to be lightweight so as to minimise latency and to provide communication between the sensors,theroverandtheusers.
Thisapproach of integratingthe Ore Hazard Explorerinto aweb-basedsystemmeansitcanbeeffectivelyusedasan industrial safety tool and in disaster management as well asforautonomousmonitoringoftheenvironment.Remote evaluation of dangerous conditions and the ability to control robotic modules also minimise the risk levels for peoplewhileincreasingproductivity.
TheOreHazardExplorerwebsitewasthereforedeveloped as an easy to use and fully equipped tool that improves user safety, rover control and system management. Realtime monitoring of the gas situation, remote control of rovers, and available maintenance resources make the work of the website fast, problem-oriented, and safe. It is self-explanatory,allowingprofessionalsandresearchersto control the environment and make decisions from a distancebasedontheinformationreceived.
TheprimaryfocusoftheOreHazardExploreristhesafety ofthepeopleworkingintheminingindustry,duetowhich

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
the platform is equipped with MQ-4, MQ-7, and MQ-135 sensorstomonitorhazardousgasesconstantly.Inorderto monitorthetoxicgaslevelsintheatmosphere,thesystem alerts the users when the concentration of the toxic gases is high. The system detects and alerts users to toxic gas accumulations before they reach dangerous levels. In case of elevated gas concentrations, can we trigger an alarms fromthewebinterface,allowingforswiftintervention.

Also, for safety, the platform includes a safety guideline section that outlines the emergency response procedures, gas concentrations, and suggested evacuation procedures to enhance the user’s ability to take action in the event of an emergency. The system’s data also allows for the storageofhistoricaldataontheconcentrationofthegasin order to determine trends and make maintenance and safetyprecautionsinadvance.
E. ServicePage:
TheServicePageisaseparatesectionthatprovidesallthe necessary information on how to maintain, repair, and improve the rover and its sensor units. It also provides step by step procedures on how to perform some of the basic maintenance including sensor calibration, motor cheque, connexion cheque, and software update to enhancethefunctionalityanddurabilityofthesystem.
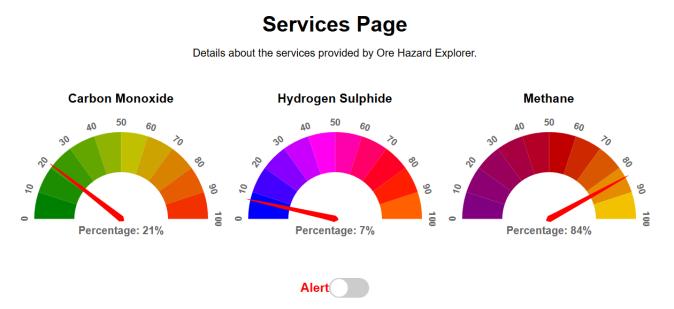
The service section outlines the different calibration processes that would be used to make sure that the gas
sensorsgiveaccurateandreliablereadingshencereducing the number of errors that might be present within the system. Through these guidelines, the users can maintain the Ore Hazard Explorer in its best condition and performanceinhazardousareas.
The Rover Control Page can be described as a web-based interface that provides easy and efficient means for controlling the rover and viewing its data feeds. It has a control panel that includes directional controls that will help the user maneuver the rover in any terrain including undergroundmines,tunnels,andindustrialareas.Also,the control panel includes the data obtained from the gas detection module and the state of the environment, to enabletheuserstomakerationaldecisionsconcerningthe route.Thesystemalsoincludesoptionsforautomatedpath planning and avoidance of various obstacles, thereby minimizing the number of instances that require human intervention during exploration. Also, the page has data logging and history where the users can monitor the movements of the rover, the readings of the sensors, and theconcentrationofthegasestoimprovetheevaluationof theareaandresearch.
These critical features incorporated in the Ore Hazard Explorerwebsiteenabletheusertomonitorthehazardous conditions,controltherover,andmanagethesystemwith maximum efficiency, and least possible downtime. Connectivity, easily navigable interface, and strong safety features make it an essential tool in mining and industrial safetyandenvironmentalthreatidentificationforthemore effective and safer means of gas detection and remote exploration.
The source code for the implementation presented in this paperismadeavailableatthefollowingGitHubrepository https://github.com/leelasudarshan-git.
TheOreHazardExploreristestedtocheckitseffectiveness inidentifyingtoxic gases,mobilityindifficultterrains,and data relaying in real-time. It was used to assess the performance of the MQ-7, MQ-136, and MQ-4 sensors in detectingdesiredmine-likeconcentrationsofCO,H₂S,and CH₄,respectively.Also,theESP32-CAMmoduleallowedfor continualdatatransmissionandlivestreamingthroughthe rover-remote monitoring system interface. Gas Detection AccuracyandSensorValidation
In order to determine the efficiency of the gas detection, specific amounts of toxic gases were introduced into a chamber that simulated the conditions of underground mining. This showed that the MQ-7, MQ-136, and MQ-4 sensors were sensitive and had a quick response in detectinghazardousgasesinanaverageof5seconds. The

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
recorded gas concentration levels were then compared withthereadingsofcommercialgasdetectiondevicesand it was found that the difference was less than 5% of the actual reading proving the efficiency and reliability of the system. It was also effective in raising alerts when the concentrations of the gases were beyond the permitted levelshenceunderliningthesystem’sefficiencyasahazard preventiontool.
The mobility of the rover was tested in a scenario that depictedaminingenvironmentthatentailsroughsurfaces, low light conditions, and many barriers. The results indicateda92%passrateonobstacleavoidanceindicating the efficiency of the rover in manoeuvring through complexterrains.Itprovedtohaveasteadymovementon gravel, sand, and rocky terrains to guarantee its functionality in a real mining environment. Also, the experiment involved using the web interface to take manual control of the rover in case it was needed to override the autonomous mode of the rover. This allows theOreHazardExplorertohavebothautonomousmotion and the ability for manual control in case of encountering unexpectedandpotentiallydangerousconditions.
The ESP32-CAM was tested to check the capability to stream live using data transmitted from the rover to a remotemonitoring center. Thesystem wasableto display the monitor's high-quality image and the real-time gas concentration with very low delay in order for constant environmental monitoring to take place. In terms of the efficiencyofthecommunicationmodule,thedataloss rate waslessthan3%eveninthezoneswithlowdensityofWiFi signals. For improved performance in low signal areas, the system is capable of data buffering and retransmissions thus minimizing on data loss of crucial information. It also had a very effective interface for presenting sensor data and data logs as well as live streaming video for giving users a real-time awareness of thesituation.

The results of the experiment also supported the hypothesis of the proposed system that is efficient for monitoring and exploration of the gases and for detecting toxic gases, avoiding errors in navigation through terrains and transmitting data in real time. Some of the future advancements may include the incorporation of 5G for better data transfer, AI for real-time hazard identification and better battery management for longer use. All these improvements will bolster the Ore Hazard Explorer’s position as a premier solution for mining safety and hazardousenvironmentdetection.
The experimental values confirm that the Ore Hazard Explorer is an effective low-cost and safe tool for the detection of toxic gases and environment analysis in dangerous and hard-to-reach areas. Through the use of real-time gas detection, obstacle avoidance, and remote monitoring,thesystemimprovessafetymeasuresinmines and offers a technological advantage in industrial risk management. It has also been able to identify toxic gases withahighlevelofprecision,avoidobstaclesonitspathon its own, and send relevant information about the surroundingstothecontrolcenterwithlittledelaythrough its wireless connections. This makes it easier for mine workers, researchers, and safety personnel to make fast decisions on whether or not the environment is safe to ventureinto,orwhethertheidentifieddangersaresafeto approach.
The mobility in any environment allows the rover to be usedinhazardousareaswheretheinvolvementofhumans is either risky or inconceivable. Its portable and portable structure makes it suitable for use in industrial, scientific, and even exploration such as mining, disaster management, and environmental studies. The inclusion of wireless communication modules as a part of the device enables real-time hazard evaluation and monitoring, and themeasurestobetakenintheeventofanemergencycan betakenwithoutdelay.Unlikeothergasdetectionsystems that are immovable, expensive, and fixed, the Ore Hazard Explorerismovableandcheaperandcanbetakentoareas withhighrisksforimprovedsafetyandproductivity.
The rover’s greatest asset is that it is highly flexible, with the ability to be built to order, and can be designed and built to suit the needs of a particular operation. The platformcanbeexpandedwithmoresensorsforadditional purposes, AI analysis, and new forms of communication, which makes it a future-oriented solution for the development of the industry. In the future, more efforts will be made to enhance the performance of the sensors, increase the battery capacity to support the longer operation time and develop an AI-based decision-making systemformoreintelligentnavigationinvariousterrains.
Possible advancements may include the use of 5G to ensureconstantdatatransmissionbymeansofconnexion,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
the enhancement of the precision of the sensors through sensor fusion and the application of machine learning algorithms that could predict future leakage or hazardous conditions before they occur. When it comes to ensuring safeworkingconditions,minimizingthehumanfactor,and popularising hazardous environment navigation, the Ore Hazard Explorer has the potential to become an indispensable tool due to its constant development in terms of functionality, accuracy, and real-time response systems.
[1] C. P. Chirag, Gurudeep, P. Alva, S. S. M., and S. A. B., “Advanced Mine Helmet with Real-Time Gas MonitoringandAutomatic Oxygen Supply,” Proc.IEEE Conf.onIndustrialSafetyTechnologies,2024.
[2] T. Manasa, J. Kadali, N. Syed, G. S. V. S. K. Raju, and K. Jamal, “IoT-Based Coal Mine Safety Monitoring and Warning System,” Proc. IEEE Conf. on Smart Mining Solutions,2023.
[3] T. He, W. Wang, B.-G. He, and J. Chen, “Review on OpticalFiberSensorsforHazardous-GasMonitoringin Mines and Tunnels,” IEEE Trans. on Environmental Safety,2022.
[4] D. Nagadevi, B. Mukesh, E. Sai Teja Goud, and J. Sai Ganesh, “Prototype of Coal Mines Safety Monitoring and Alerting System Using IoT,” Proc. IEEE Conf. on Industrial Safety and IoT Applications,2024
[5] P. Hazarika, “Implementation of Smart Safety Helmet for Coal Mine Workers,” IEEE Conf. on Power Electronics&IntelligentControl,2016.
[6] C. Qiang, S. Ji-ping, Z. Zhe, and Z. Fan, “ZigBee-Based Intelligent Helmet for Coal Miners,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf.onCommunicationSystems,2009.
[7] T. J. Davidson and P. M. Sanderson, “A Review of the Effects of Head-Worn Displays on Teamwork for Emergency Response,” IEEE Trans. on HumanMachineInteraction,2022.
[8] S. R. Deokar and J. S. Wakode, “Coal Mine Safety Monitoring and Alerting System,” Research J. of EngineeringandTechnology,2017.
[9] K. Mukhopadhyaya, S. Kiran, M. Chaturvedi, M. A, and M. V, “Detection of Toxic Gases and Temperature Sensing for Miners using IoT-Based Intelligent Helmet,” IEEE,on 2022
[10] S.M. Sakthimohan,A.S.Abiksha,D.S.Dharani,E.R.G. Elizabeth,andL.V.Logasarathy,“PioneeringSolutions for Advanced Gas Leak Detection in Hazardous Industrial and Mine Environments,” Proc. IEEE Symp. on Safety Technologies,2024.
[11] A.Choquehuanca,K.Quiñones,D.Rondon,andR.León, “FormalSpecificationandValidationofaGasDetection SystemintheIndustrialSector,” IEEE Access,2020.
[12] K. Cekova, C. M. Bande, A. Velkova, and N. Stojkovich, “MobileSensor Systemfor Detection of ToxicGases in Mines,” Proc. IEEE Conf. on Environmental Monitoring and Safety
[13] S.Matloob,Y.Li,andK.Z.Khan,“SafetyMeasurements and Risk Assessment of Coal Mining Industry Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning,” Proc. IEEE Conf. on AI and Industrial Safety
[14] B. Liu, X. Yang, Z. Chen, J. Liao, and H. Zhao, “The Internet of Things (IoT) System for Bolt Looseness Detection in Coal Mines,” Proc. IEEE Conf. on Smart MiningSystems,2023.
[15] S.D.Damayanti,M.Suryanegara,I.K.A.Enriko,andM. I. Nashiruddin, “Designing a LoRa-Based Panic Button forBaliSmartIslandProject,”IEEETrans.onWireless IoTNetworks,2022.
[16] J. Sai Ganesh and E. Sai Teja Goud, “Wireless Sensor NetworksforGasLeak Detection in Coal Mines,” Proc. IEEEConf.onSensorNetworks,2023.
[17] A. J. Pudke and S. Banger, “Coal Mine Monitoring and Alert System with Data Acquisition,” IEEE Trans. on IndustrialIoT,2017.
[18] M. Dhame and R. Qureshi, “Smart Helmet for Coal Miners Using ZigBee Technology,” IEEE J. on Wireless SafetySystems,2016.
[19] Y.Wu,G.Feng,andM.Zhang,“TheStudyonCoalMine Safety Using Bluetooth Wireless Transmission,” Proc. IEEEWorkshoponElectronicsandApplications,2014.
[20] D. Kock and J. W. Oberholzer, “The Development and Application of Electronic Technology to Increase SafetyintheSouthAfricanCoalMiningIndustry,”IEEE Trans.onIndustrialApplications,1997.
[21] S. Srivastava, “Real-Time Monitoring System for Mine Safety Using Wireless Sensor Networks,” Proc. IEEE Conf.onSmartMiningandSafety,2015.
[22] G. E. M. Abro and S. A. Shaikh, “IoT-Based Smart Wearable JacketforCoal Miners,”Proc.IEEEInt.Conf. onComputing,Electronics&Communications,2018.
[23] C. M. Sebillo, M. Vitiello, and G. Battistoni, “An IoTBased Mobile System for Safety Monitoring of Lone Workers,”IoTJ.,vol.2,pp.476-497,2021.
Cheng Qiang, Sun Ji-ping, Zhang Zhe, and Zhang Fan, “Wireless IoT-Based Communication System for Coal Miners,” Proc. IEEE Conf. on Wireless Sensor Networks,2019.