
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
OmkarDhongade
E&TC Engineering
MVPS’s KBTCOE Nashik,India omkardhongade23@gmail.com
Mandar Lohare
E&TC Engineering
MVPS’s KBTCOE Nashik,India mandarlohare73@gmail.com
Abstract This project presents the development and implementation of an RFID-Based Appointment Calling System integrated with queue management and administrative control functionalities. The system is designed to streamline the user check-in and appointment-handling process in high-traffic environments such as hospitals, banks, and government offices.By utilizing RFID technology, users can effortlessly register and check in using RFID cards, which are then assigned a unique queue number.Atokencallingmechanismensuresthatusersarecalledin afairand sequential manner, while real-time monitoring prevents queuejumpsandunauthorizedaccess.
The system features an intuitive user interface with an I2C LCD display and a 4×4 keypad for direct interactions, including secure administrator access. Admins can configure system set- tings, assignmastercardsforimmediateaccess,resetqueues,andmodify PIN credentials using a dedicated admin menu. Addition- ally, the integration of ESP-NOW wireless communication allows remote token calling via a secondary ESP32 module, enhancing accessibilityforoperators.
This intelligent queue system reduces manual intervention, minimizes waiting time confusion, and ensures orderly management of user flow. It is scalable, cost-effective, and adaptable to various organizational needs, making it a practical solution for improvingcustomerserviceandoperationalefficiency.
Keywords RFID, Token System, ESP32, Admin Control,Access Control,Real-Time Monitoring, I2C LCD Display,Keypad Interface.
In today’s fast-paced world, managing queues and streamliningaccesscontrolareessentialcomponentsofefficientservice delivery, particularly in healthcare, government offices, and customer service environments. Long wait times, manual appointment tracking, and inefficient calling systems not only lead to customer dissatisfaction but also increase administrative overhead. To address these challenges, automation and smart technologies are being increasingly integrated into appointmentandqueuemanagementsystems.
This paper presents the design and development of a smart RFID-based appointment calling system that integrates queue management and centralized admin control. The system leverages Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) for user identification,akeypadforadministrativeandemergencyinteractions,an I2C-based LCD for real-time feedback, and ESP-NOW
Jagdish Mutadak
E&TC Engineering
MVPS’s KBTCOE
Nashik,India jagdishmutadak03@gmail.com
communication to wirelessly call the next token using a remote ESP32-basedbuttonunit.
Unlike conventional queue systems, this model ensures contactless check-ins and structured token issuance upon card tapping. It allows administrators to manage registered users, resetqueues,andcontrolaccessthroughasecureadmin menu. An emergency access PIN and master card functionality further improve operational flexibility. The system is robust, low-cost, and scalable, making it suitable for a wide range of real-world applications.
By automating the check-in and token-calling process and providing secure admin-level controls, the proposed system enhances both user convenience and administrative efficiency. The integration of wireless communication ensures ease of operation without reliance on traditional button interfaces, enablingatrulymodernandresponsivequeueenvironment.
A. ProblemStatement
In many publicand private service centers, managing queues and appointments is still done manually or with limited automation. This often leads to long waiting times, inefficient service delivery, and user dissatisfaction. Additionally, lack of a systematic way to track and call users results in confusion, overcrowding, and operational delays. There is a need for a smart, automated system that can register users, assign tokens, managequeuesefficiently,andprovidesecure,contactlessaccess while minimizing human intervention and errors. The solution mustalsoofferadministrativecontrolsandreal-timemonitoring to ensure flexibility, reliability, and scalability for various environments.
• Develop a Secure Access Control System – Implement an RFID-based authentication system to allow only authorizeduserstoaccessarestrictedarea.
• Automate Token-Based Queue Management – Introduce a systematic approach for handling multiple users by assigningandmanagingtokensfororderlyaccess.
• Easy to Use for Everyone The system will be simpleto useforbothcustomersandstaff,makingiteasyforanyone tooperatewithoutconfusion

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
• Enhance Security and Efficiency – Reduce unauthorized access and manual intervention by automating the access controlprocess.
• EnsureReliableand ScalableDesign – Createa systemthat can be expanded for use in various applications such as offices,hospitals,andrestrictedfacilities.
In many public and private institutions, managing access and controlling queues is often inefficient, leading to delays, overcrowding, and potential security risks. Traditional manual systemsarepronetoerrorsandunauthorizedaccess,especiallyin high-traffic environments such as hospitals, government offices, andcorporatebuildings.Thisprojectismotivatedbytheneedto design an intelligent, secure, and user-friendly system that automates access control and queue management using RFID technology. By integrating features like token generation, an adminmenu,andimmediateaccessoptions, thesystemaimsto streamline operations, reduce human effort, and enhance the overalluserexperience.Furthermore,theuseofreal-time token validation and timeout features improves responsiveness. The flexibilityofthesystemmakesitadapt-abletodifferentsectors, promotingscalabilityandlong-termusability.
ExistingliteratureonRFID-basedaccess control,smartqueue management, and user authentication has influenced the design ofthissystem.Notablecontributionsinclude:
Patil and Pawar (2018) proposed an RFID-based access controlmodelforsecureofficeentry,emphasizingthesimplicityand low cost of RFID tags for identity verification. Their work highlights the technology’s effectiveness in minimizing unauthorizedaccess.
Jadhav et al. (2019) explored a hospital queue management system using RFID and GSM modules. Their implementation reduced wait times and enhanced patient flow, demonstrating howautomationcanimproveserviceefficiency.
Singh and Sharma (2020) developed a smart queue token system integrated with a real-time display. Their study shows how such systems reduce human intervention and increase transparencyinpublicservicecounters.
Kumar et al. (2021) discussed RFID-based attendance and access monitoring in educational institutions. Their research supports the importance of secure data logging and administrativecontrolformanaginghighvolumesofusers.
Gupta and Yadav (2022) implemented a multi-user RFID access system with an admin interface, enabling dynamic user registration and monitoring. This system laidthe foundation for combining user authentication with backend administrative controlforreal-timedecision-making.
Sahu et al. (2023) integrated RFID with IoT for smart queue management in clinics. Their use of cloud-based analytics showcases the growing trend toward connected systems for optimizingqueuehandlingandresourceallocation.
Together, these studies offer a foundation for designing a robust, scalable, and secure appointment calling system with integratedRFIDandadministrativefeatures,aligningcloselywith thegoalsofthisproject.
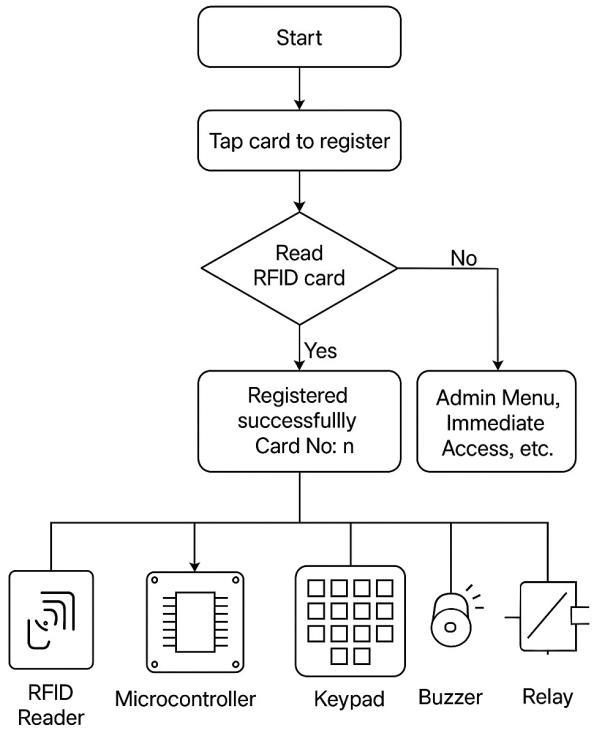
Fig.1.RFID-Based AppointmentCallingSystemAr-chitecture
This system integrates RFID technology with a microcontrollerbased decision unit to manage secure access, user registration, and queue-based appointment calling. Unlike purely web-based or biometric systems, this design prioritizes contactless cardbasedauthentication,token-basedqueueas-signment,andrealtimeLCDfeedbackforaseamlessandefficientuserexperience.
System Components and Data Paths:
• RFID Reader Module:Actsastheprimaryinputsensorfor detectingand authenticatinguseridentityviapassive RFID cards. Each card has a unique UIDthat isprocessed by the systemtograntaccessorperformregistration.
• Microcontroller Unit Functions as the system’s control hub.ItreceivesinputfromtheRFIDreader,maintainsuser registration records, processes access logic, gener- ates queuetokens,andhandlesadminfunctionssuchasviewing orresettingdata.
• LCD Display Module: Provides real-time user feedback. Displays initialization status, prompts for card tapping, successful registration messages, assigned token numbers, andqueuestatus.

Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
• Admin Access Interface: Enabled through a master RFID card. When tapped, this card bypasses standard user flow and opens the admin menu, allowing actions like clearing userdata,viewingregisteredusers,orsystem maintenance withoutinterferingwiththeregularqueue.
• EEPROMStorage:Non-volatilememoryisusedtostoreuser registrationdataandqueuestate,ensuringdatapersistence evenduringpowerloss.
SystemWorkflowOverview:
• On startup, the LCD displays “System Initializing...” for 5 seconds.
• After initialization, the message changes to “Tap Card to Register.”
• WhenanewusertapstheirRFIDcard,thesystemregisters themandassignsaqueuenumber.
• The LCD displays “Card Registered Successfully” and “Your No.is:X”for3secondsbeforereturningtotheregistration prompt.
• The admin can access backend controls instantly viathe master card, enabling secure and efficient system maintenance.
Error Handling and Duplicate Detection:
To maintain queue integrity and prevent misuse, the microcontrollerchecksifanRFIDcardisalreadyregistered.IfthecardUID existsinEEPROM,itisnotassignedanewtokenandappropriate feedbackisshown.Thispreventsduplicateentriesandconserves memory.
Admin Control Logic and Security:
The master card is hardcoded in the system, and its UID is matched before triggering administrative functions. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing the control menu. Adminactionsincludeclearingallrecords,reviewingregis-tered users,andresettingthetokencounter.
LCD Display Interface for Real-Time Feedback:
A16x2or20x4LCDmoduledisplayssystemstatusmessageslike ”System Initializing...”, ”Tap Card to Register”, ”Reg- istration Successful”, and ”Your Token Number is X”. This provides clear guidance and feedback to users at every step without requiring humansupervision.
A. How Our Work Differs From Previous Approaches
1) DualFunctionality: AccessControlandQueueManagement: Unlikesystemsfocusedsolelyonaccessortokengeneration,this system combines both to streamline user flow in secure and service-drivenenvironments.
2) Immediate Admin Override:: The admin card enables instant entry into backend settings without disrupting ongoing useroperations,maintainingbothsecurityandcontinuity.
3) Offline Capability with Local Persistence:: No internet or cloud connectivity is required. All data is stored locally via EEPROM, ensuring reliability and functionality in environments withlimitedconnectivity.
4) User-Centric Design with Feedback Loop:: Real-time LCD feedback, buzzers, and token tracking enhance the user experience, ensuring clarity and minimizing confusion during interaction.
5) Scalable and Modular Architecture:: The design can be expanded to accommodate multiple RFID readers or display systems and can be integrated with GSM, IoT modules, or databaseloggingasfutureupgrades.
Thissectionoutlinesthestep-by-stepdevelopmentprocessof theaccesscontrolsystem,detailingbothhardwareandsoftware design choices. Additionally, it highlights the security measures integrated to ensure data privacy, prevent unauthorized access, andprotectusercredentials.
A. Methodology:
The development of the RFID-based Appointment Calling Systemfollowedastructured,modularapproachthatinte-grated hardwareselection,softwaredesign,andaccesslogic toensurea seamlessandreliableuserexperience.Theprocessisoutlinedas follows:
1) Hardware Selection: The core components were chosen based on system requirements, real-time response capabilities, andeaseofintegration:
• ESP32 Microcontroller: Selected for its dual-core performance,built-inWi-FiandBluetooth,andsufficientGPIOs, making it ideal for controlling multiple peripher- als and handlingcomplexlogic.
• RC522 RFID Reader: This module was used to detect and readRFIDtags.ItcommunicatesviaSPIwiththeESP32and readsuniquecardUIDsforuseridentification.
• Solenoid Lock: A 12V solenoid was used as the phys- ical barrier mechanism to allow or deny access. It was controlledviaarelaymoduleinterfacedwiththeESP32.
• LCD Display (16x2 or I2C): Provided user-friendly realtime feedback, including system status, prompts, and successfulregistrations.
• Relay Module: Actedastheswitchtoactivatethesolenoid, providingelectricalisolationbetweenthemi-crocontroller andthehigh-currentsolenoid.
2) SoftwareFlow: Thesoftwarewasdesignedarounda statemachineapproachwithclearlydefinedstates:
• Initialization State: Upon startup, the system displayed a ”System Initializing. ” message for 5 seconds while the hardwaresetuproutineswerecompleted

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
• Idle/Registration State: The system entered a standby mode waiting for card input. It displayed ”Tap Card to Register”.
• Card Detection and Validation: Upon reading a card UID, thesystemcheckedagainststoredUIDsinmemory.Ifitwas new, it registered the card and displayed a confirmation messagealongwithitsqueuenumber(e.g.,“YouareNo.1”).
• Confirmation Delay: After successful registration, the messagepersistedfor3secondsbeforereturningtotheidle state.
• Admin Mode: A special RFID card or long press button sequence granted access to the admin menu. This section allowed tasks like resetting the system, viewing current queuestatus,orclearingEEPROM.
B. Security Implementation:
Since the system deals with access control and user-specific identification via RFID, certain security and privacy protocols wereintegratedtoensuredataintegrityandpreventmisuse.
• UID Storage and Access Each RFID tag has a unique identifier (UID), which was used as a digital signature for each user.These UIDs werestored inthe ESP32’s EEPROM in a structured format. The system accessed these entries via indexing, ensuring fast lookup and write operations. Accesstothisdatawascontrolledthroughtheadminmenu, andnosensitivepersonalinformationwasstoredalongside theUID,maintaininguseranonymity.
• Prevention of Duplicate or Spoofed Entries: To prevent registrationofduplicatecards,everyincomingUIDwasfirst checked against the existing list in EEPROM. Only unique UIDs were allowed to register, and repeated cards were rejectedwithamessagesuchas“CardAlreadyRegistered.” Spoofing attacks were minimized by using only officially issuedRFIDtags.AlthoughbasicRFIDcardsarein-herently vulnerable to cloning, the system is suitable for controlled environmentssuchaslabsorclinicswherecarddistribution istightlymanaged.
For higher security in future implementations, encrypted RFID protocols (e.g., MIFARE DESFire) or dualauthenticationmethodscouldbeadopted.
• Admin Access Security Administrative access was restrictedusingatwo-stepauthenticationmechanism:
1.MasterRFIDCard:Onlyapre-configuredUIDwasgranted admin-level access. This UID was hardcoded or securely stored.
2.Password Prompt: Upon accessing the admin panel, a password entry screen was displayed. The correct PIN had tobeenteredviaakeypadorsoftwareinterfacetoproceed
TheRFID-BasedAppointmentCallingSystemwithQueue Management and Admin Control successfully addresses the
commonissuesinmanualappointmenthandling.Byinte-grating RFID technology, real-time display, and admin-level control, the system ensures smooth, secure, and efficient user registration and queue management. Its modular design, low power requirements, and ease of use make it ideal for clinics, offices, and institutions aiming to digitize and streamline their appointmentprocesses.Futurescopeincludescloudintegra-tion andmulti-locationsupportforbroaderapplication.
[1] S. Patil and P. Pawar, “Design of RFID Based Access Control System for Office,” Int. J. Adv. Res. Electr. Electron. Instrum. Eng.,vol.7,no. 5,pp.2321–2325,May2018.
[2] A. Jadhav, P. Patil, S. Shinde, and A. Jagtap, “Smart Queue Management System Using RFID and GSM,” Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol.,vol.8,no. 6,pp.528–532,Jun.2019.
[3] R. Singh and M. Sharma, “Implementation of Smart Queue Management SystemwithReal-TimeDisplay,” Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput.Sci.Eng.Inf. Technol.,vol.5,no.3,pp.345–350,Mar. 2020.
[4] A. Kumar, R. Verma, and V. Bansal, “RFID Based Attendance and Access Monitoring System in Educational Institutions,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 183, no. 45, pp. 21–25, Sep. 2021, doi:10.5120/ijca2021921577.
[5] A. Gupta and D. Yadav, “Multi-User RFID Access Control Systemwith DynamicAdminPanel,” Int. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. Res.,vol.11,no.2, pp.67–72,Feb.2022.
[6] S.Sahu,M.Pati,andS.R.Panda,“IoT-IntegratedRFIDBased Smart Queue Management System for Clinics,” Int. J. Sci. Technol.Res.,vol. 12,no.1,pp.104–109,Jan.2023.
[7] A.MishraandR.Mehta, “DevelopmentofContactlessToken System using RFID and LCD Interface,” Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol., vol. 69, no. 8, pp. 135–139, Aug. 2021, doi:10.14445/22315381/IJETT-V69I8P221.
[8] S. Kulkarni and V. Patil, “Admin Controlled Queue Management System Using RFID,” Int. J. Innov. Res. Electr. Electron. Instrum. Control Eng., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 201–206, Apr.2022.
[9] M. Rathod and S. Jain, “RFID and Microcontroller Based Access Control and Monitoring System,” Int. J. Adv. Res. Electr. Electron. Instrum. Eng.,vol.6,no.12,pp.8900–8905, Dec.2017.
[10] N. R. Chauhan, H. Shah, and J. Mehta, “Wireless Queue Man- agement Using ESP32 and Cloud Integration,” Int. Conf. Elec- tron. Commun. Comput. Eng. (ICECCE),pp.32–36, Jul.2022, doi:10.1109/ICECCE56124.2022.9944293.
[11] A.F.NajarandM.Qureshi,“SmartQueueTokenSystemusing ESP- NOW Communication,” Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. Res.,vol.11,no. 2,pp.17–22,Feb.2023.
[12] M. Sharma and R. B. Patel, “Real-Time Embedded Queue Monitoring Using ESP32 and I2C Interface,” Int. J. Embed. Syst. Appl., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 12–18, Jan. 2024, doi:10.5121/ijesa.2024.13102.