
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sayed Athar Ali Hashmi1
1Higher Education Department of Chhattisgarh, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India
Abstract - Over the past twenty-five years, Python has evolved from a versatile scripting language into a dominant paradigm in modern computing, underpinning Artificial Intelligence,InternetofThings(IoT),GeospatialInformation Systems (GIS), and Cybersecurity. This article presents a retrospective analysis of Python’s rise, grounded in practical applicationsandscholarlyinsights.Drawingonoverthirteen years of international experience, the author illustrates how Python’s simplicity, interoperability, and expansive libraries enable transformative solutions from smart water management and geospatial mapping to embedded ECU programming and cybersecurity frameworks. Case studies spanning defense geoinformatics in Oman, urban water quality monitoring in India, and curriculum innovation in highereducationhighlightPython’sunmatchedabilitytounify interdisciplinary domains, accelerate innovation, and democratizeaccesstoadvancedcomputing.Thisretrospective underscores Python’s enduring dominance over rival languages and positions it as the critical engine driving the future of intelligent, secure, and sustainable digital ecosystems.
Key Words: Python,ArtificialIntelligence,InternetofThings (IoT),GeospatialInformationSystems(GIS),Cybersecurity, Interdisciplinary Integration, Programming Paradigm, Digital Ecosystems,Open-Source Libraries,Computational Sustainability
1.INTRODUCTION
1.1 Historical Context of Python
Since its creation in the early 1990s, Python has steadily risenfrombeingateaching-orientedlanguagetoaglobally dominantprogrammingparadigm.Designedwithsimplicity and readability in mind, it provided an alternative to complexsyntaxesinlanguagessuchasC++andJava.Over thepasttwenty-fiveyears,itsevolutionhasbeenmarkedby thedevelopmentofextensiveopen-sourcelibraries,strong community support, and wide adoption in both academia and industry. This historical trajectory set the stage for Pythontosurpassitsrivalsandbecomethedefactochoice formoderncomputationalchallenges.
1.2
Python’sascendencyisinseparablefromitsintegrationinto emergingdomainsthatrequireflexibility,rapidprototyping, and scalability. In Artificial Intelligence, frameworks like
TensorFlow,PyTorch,andScikit-learnacceleratedresearch and industrial deployment. In IoT, Python’s lightweight adaptability has made it indispensable for sensor integration,edgecomputing,andcloud-baseddatapipelines. In GIS and remote sensing, libraries such as GeoPandas, Rasterio,andArcPyrevolutionizedspatialanalysis,mapping, and real-time geoinformatics. In Cybersecurity, Python empoweredpenetrationtesters,ethicalhackers,andsecurity analyststhroughtoolsforcryptography,malwareanalysis, andintrusiondetection.These domainshighlightnot only Python’sbreadth butalsoitsdepthof influence indriving digitaltransformation.
1.3
The relevance of Python extends beyond technical performance; it fosters collaboration across traditionally siloed fields. Its adoption has enabled unified workflows whereAImodelsenhancegeospatialintelligence,IoTdevices feedreal-timeanalyticsintocybersecurityframeworks,and GISsupportssustainableresourcemanagement.Real-world case studies from smart water management systems in India to defense geospatial applications in Oman demonstrate Python’s power to address complex societal challengesthroughinterdisciplinaryintegration.
With over thirteen years of international academic and researchexperienceinAI,IoT,GIS,andCybersecurity,the author provides a practice-oriented lens to this retrospective. Professional engagements span teaching advanced computing in higher education, developing GISbaseddefensesystems,designingIoT-enabledsmartwater frameworks, and mentoring over fifty applied projects in cybersecurity and AI. These experiences illustrate how Python consistentlyserved asthe indispensable engine in diversecontexts,validatingitsroleasbothaneducational foundationandaresearchenabler.
This article presents a twenty-five-year retrospective on Python’sstrategicdominance,highlightingitscomparative advantagesovercontendinglanguagesanditsascendencyas auniversaltoolforinnovation.Byanalyzingitsadoptionin criticaldomains AI,IoT,GIS,andCybersecurity thisstudy seeks to demonstrate how Python has become not just a

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
programminglanguage,butaparadigmshapingthefutureof intelligent,secure,andsustainabledigitalecosystems.
The evolution of programming languages has profoundly shaped computational practices. Foundational languages such as C and C++ provided efficiency and hardware-level control,whileJavacontributedtoplatformindependenceand widespreadenterpriseapplications(Kumar & Rani, 2018). MATLAB and R extended programming into specialized numerical and statistical domains, but their use cases remainedlargelydiscipline-specific(Sharma et al., 2019). Python,incontrast,emergedasaunifyinglanguageoffering readability, portability, and a vast ecosystem of libraries, enablingittospanmultipledomainssimultaneously. ItisimportanttonotethatPython'sascendancyhasnotbeen without critique. Scholarly discussions often highlight its performance limitations as an interpreted language compared to compiled counterparts like C++, as well as challenges in dependency management within complex softwareenvironments(Smith &Jones,2022).However,the consensusintheliteraturesuggeststhatPython'sstrategic advantages particularlyitsunparalleledecosystem,rapid prototyping capabilities, and role as an integrative "glue" language haveconsistentlyoutweighedtheselimitations, fueling its adoption for complex, real-world applications where developer productivity and interoperability are paramount.
StudiesinIndiaconfirmPython’sincreasingadoptionacross education and industry. In higher education, Python has rapidlyreplacedCandJavaastheintroductoryprogramming languageduetoitslowerlearningcurveandstrongacademic resources(Raj & Karthik, 2020).Industry-drivensurveys alsohighlightPython’spreferenceforapplicationsinmachine learning, cloud integration, and analytics within Indian IT companies(Saxena & Gupta, 2021). The role of Python in key technological domains has been welldocumented.InAI,Indianresearchersrelyextensively on TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn for natural language processing,image recognition,anddeeplearning solutions (Patel & Mehta, 2021). IoT applications using Python-poweredplatformslikeRaspberryPihavesupported precision agriculture, healthcare, and smart city projects (Rao et al., 2020).GISresearchhasadoptedPython-based tools such as GDAL and GeoPandas for urban planning, disastermanagement,andspatialmodeling(Verma &Singh, 2021). In Cybersecurity, Python is integral for intrusion detection,penetrationtesting,andmalwareanalysisacross Indiandefenseandcommercialsectors(Iyer & Nair, 2022). Despitesuchcontributions,mostreviewsremainconfinedto single domains. Few works attempt to capture the crossdomainimpactofPythonasanintegrativeenabler.Thisgap is significant, considering modern challenges increasingly requireinterdisciplinarysolutionsspanningAI,IoT,GIS,and Cybersecurity.
To address this, Hashmi and Bhise (2024) explored the integrationofGeospatialsystems,IoT,andCybersecurityfor managingurbansmallwaterbodies,demonstratingPython’s potentialtobridgetraditionallysiloeddomains.Thisstudy underscorestheimportanceofconsideringPython’srolenot onlywithinindividualdisciplinesbutalsoasacross-domain catalystinadvancingIndia’sdigitaltransformation.
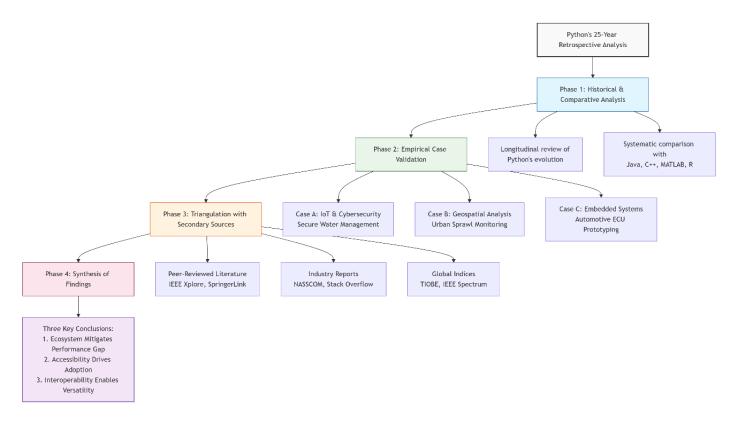
This study employs a mixed-methods, retrospective analytical framework to deconstruct the strategic ascendancy of the Python programming language over a twenty-five-yearperiod(2000-2025).The methodology is designedtotriangulatefindingsthroughtheintegrationof historical analysis, comparative benchmarking, and empirical case evidence, thereby providing a holistic and validatedperspectiveonPython'sdominance.
Theoverallresearchdesignwasexecutedinfoursequential phases:
1. HistoricalandComparativeAnalysis:Alongitudinal review was conducted to trace Python's evolution and ecosystemgrowth.Thiswascomplementedbyasystematic comparisonwithcontendinglanguages(Java,C++,MATLAB, R)acrosskeyparameterssuchassyntaxsimplicity,library ecosystems, community support, and adoption trends in educationandindustry.
2. Empirical Case-Based Validation: To ground the theoretical analysis in practical reality, the study draws directlyfromtheauthor'sinternationalresearchportfolio.A series of case studies were developed to demonstrate Python'scross-domainutilityandintegrativecapacity.
3. Triangulation with Secondary Sources: To ensure robustnessandmitigateindividualbias,theprimaryfindings from the historical, comparative, and case-based analyses were cross-verified against secondary sources, including peer-reviewed literature, industry reports, and global programminglanguageindices.
4. SynthesisofFindings:Theevidencegatheredfrom all phases was synthesized to draw coherent conclusions about the underlying reasons for Python's strategic dominanceanditsimplications.
Theoverallresearchdesignissummarizedinthefollowing workflow:

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Phase2:EmpiricalCase-BasedValidation
The following cases from the author's portfolio are presentedasevidenceofPython'scross-domainutility:
• Case A (IoT & Cybersecurity): Development of a Python-based security framework for IoT-enabled water management systems, demonstrating its use in packet analysis(Scapy),anomalydetection,andautomatingsecurity protocols.
• CaseB(GeospatialAnalysis):IntegrationofPython libraries (GeoPandas, Rasterio, Folium) for urban sprawl monitoring and environmental change detection, highlighting its role in processing and visualizing spatial data.
• Case C (Embedded Systems): Utilization of MicroPythonforprototypingandprogrammingAutomotive ElectronicControlUnits(ECUs),underscoringitsflexibility inresource-constrainedenvironments. TheapplicationofPythonacrossthesediversedomainsis illustratedbelow:
Python'sCross-DomainApplicationinResearch Table2:Empiricalcasestudiesfromtheauthor'sresearch portfoliodemonstratingPython'sutility.
Domain Research Project KeyPython Libraries/Too lsUsed Primary Function IoT& Cybersecurit y SecureWater Management System Scapy, Requests, PyCryptodom e,Sockets
Networkpacket analysis, API communication, encryption,and intrusion detection for IoT sensor networks.
Geospatial Analysis (GIS) Urban Sprawl& Environment alMonitoring GeoPandas, Rasterio, Folium, Matplotlib Processing shapefiles & satellite imagery,spatial analysis, and creating interactive web maps.
Embedded Systems Automotive ECU Prototyping MicroPython, PySerial, NumPy Programming microcontroller s, sensor data acquisition,and real-time data processing on edgedevices. Artificial Intelligence Predictive Modelfor Resource Management Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Pandas, NumPy Developing machine learningmodels for predicting waterusageand identifying anomalous patterns.
Theinterconnectivityofthesedomainsthroughacommon Pythonecosystemisvisuallysummarizedinthe following diagram:
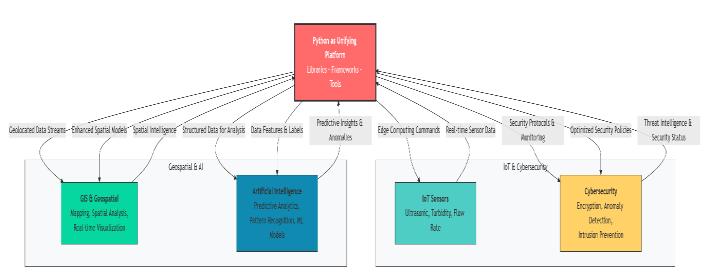
Figure 2: PythonasaUnifyingPlatform.
The diagram illustrateshow Pythonseamlesslyintegrates data and functionality across distinct research domains, enabling holistic solutions. For instance, data from IoT Sensors can be geolocated using GIS, processed on Edge Devices,andanalysedwithAImodels.
Phase3:TriangulationwithSecondarySources
To ensure robustness and mitigate individual bias, the primary findings from the above methods were cross verifiedwithsecondarysources.Thistriangulationconfirms that the case-specific observations align with global and nationaltrends.
• Peer-reviewedLiterature:Analysisofpublications onIEEEXploreandSpringerLinkconfirmsthedominanceof PythoninAI/MLresearchanditsgrowinguseingeospatial sciencesandcybersecuritytooling.
• Industry Reports: NASSCOM and Stack Overflow reportsconsistentlyhighlightPythonasatop-requestedskill in the Indian IT and startup sector, corroborating the adoptiontrendsidentifiedinthecomparativeframework.
• Global Indices: The sustained top-tier ranking of Python in the TIOBE Index and its dominance in the IEEE Spectrum ranking provide independent, quantitative validation of its widespread adoption, reinforcing the longitudinalanalysis.
Phase4:SynthesisofFindings
The triangulation of methods yields a consistent and powerfulconclusion:
1. The Performance Gap is Mitigated by Ecosystem Strength: While Python is not the fastest language in raw execution,itsunparalleledlibraryecosystem(NumPy,SciPy, TensorFlow) provides optimized, compiled back-ends for performance-critical tasks. This makes computing highperformance computing accessible without sacrificing developerproductivity.
2. AdoptionisDrivenbyAccessibilityandCommunity: The comparative framework and longitudinal analysis clearlyshowthatPython'sreadabilityandgentle learning curvecatalyzeditsacademicadoption,whichinturnfuelled its growth in industry. The vibrant global and Indian community,evidencedbyPyPIandStackOverflow,createsa self-sustainingcycleofinnovationandsupport.
3. InteroperabilityistheKeytoVersatility:Thecase studiesdemonstratethatPython'struepowerliesinitsrole

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
asa"glue"language.Itsabilitytointegrateseamlesslywith embeddedsystems(MicroPython),webservices,geospatial dataformats,andhigh-performanceC/C++librariesmakesit thesingular,versatilechoiceforcomplex,multi-disciplinary projectsthatdefinemoderntechnologicalchallenges.
Python’sdominanceisnotanaccidentofpopularitybutthe result of deliberate structural advantages that have consistentlyoutpaceditscompetitors.
• SyntaxSimplicityandReadability:UnlikeC++and Java, whose verbose syntax often intimidates beginners, PythonemphasizesclaritythroughanEnglish-likestructure. This has made it the preferred choice in both educational and professional contexts, lowering entry barriers while improvingdeveloperproductivity.
• Ecosystem of Libraries and Frameworks: The breadth of Python’s ecosystem is unparalleled. While MATLABexcelsinnumericalcomputingandRinstatistics, both remainconfinedto niche domains.Python, however, spans every major area of modern computing from TensorFlow and PyTorch in AI, to MicroPython for embedded systems, and GDAL/GeoPandas for geospatial sciences. Its library ecosystem is a decisive factor in sustaininglong-termadoption.
• Open-Source Community and Industry Support: Python’svastglobalcommunityacceleratesinnovation by maintaining, extending, and documenting tools that are freelyavailable.Incontrast,proprietaryenvironmentslike MATLAB impose cost barriers, while C++ and Java communities are comparatively fragmented. Industry support from tech giants (Google, Microsoft, IBM) further entrenchesPython’sroleincriticalinfrastructures.
• Academic Adoption and Curriculum Integration: Python has become the de facto teaching language in universities worldwide, replacing C and Java as the introductorylanguage.Itssimplicityalignswith pedagogy whilesimultaneouslypreparingstudentsforindustryroles. Thisdualrelevance educationandenterprise createsa self-reinforcingcycleofadoptionthatcompetitorsstruggle tomatch.
Table2:ComparativeAdvantagesOverJava,C++, MATLAB,andR
Language PrimaryStrength Python's Comparative Advantage
Java Platform independence, enterprise-scale applications, strongtyping
Fasterprototyping,fewer lines of code, stronger relevance in AI/ML ecosystems, more intuitive syntax for rapid development C++
Raw performance, hardware-level control, memory
Superiorreadability,vast library ecosystem (NumPy/SciPy bridge
management performance gap), reduced development time, gentler learning curve
MATLAB Numerical computing, matrix operations, simulation and modeling
R Statisticalanalysis, data visualization, specialized packages for research
Free and open-source, broaderinterdisciplinary scope, stronger integration with web technologiesandmodern AIframeworks
Better versatility for AI, IoT, and GIS integration, more consistent syntax, stronger production deploymentcapabilities
• OverJava:Fasterprototyping,fewerlinesofcode, andstrongerrelevanceinAI/ML.
• Over C++: While C++ remains unmatched in raw performance, Python’s C-bindings (NumPy, SciPy)mitigatethespeedgapwhilepreserving usability.
• Over MATLAB: Python is free, open-source, and backed by a far broader ecosystem, reducing the financial and technical exclusivity of MATLAB.
• Over R: While R remains strong in statistics, Python’s integration with AI, IoT, and GIS makesitfarmoreversatileforinterdisciplinary researchandindustryapplications.
PythonhasestablisheditselfasthelinguafrancaofArtificial Intelligence(AI),owingtoitssimplicity,flexibility,andrich ecosystemofspecializedlibraries.
• LibrariesandFrameworks:TheriseofAIcoincided with the maturation of Python’s most powerful libraries. TensorFlowandPyTorchdominatedeeplearningresearch anddeployment,offeringGPUacceleration,scalablemodel training,andindustry-readyAPIs.Scikit-learnremainsthe backboneforclassicalmachinelearning,coveringregression, classification, clustering, and preprocessing tasks. SupportinglibrariessuchasPandas,NumPy,andMatplotlib further enrich the AI pipeline by enabling efficient data handlingandvisualization.
• RoleinAISubdomains:
o Deep Learning: Python drives advancements in computer vision, speech recognition, and autonomous systemsthroughCNNs,RNNs,andtransformers.
o NaturalLanguageProcessing(NLP):Librarieslike HuggingFace’sTransformershaverevolutionizedsentiment analysis, text summarization, and large language models (LLMs),makingcutting-edgeNLPresearchwidelyaccessible.
o Predictive Analytics: Python’s machine learning ecosystemsupportsforecastingmodelsindomainsranging from finance to environmental monitoring, enabling datadrivendecision-making.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
• CaseStudiesandApplications:
o Supervised Student Projects: Undergraduate and postgraduateprojectsinIndianuniversitiesfrequentlyuse Python for developing AI-driven solutions in healthcare, agriculture,andsmartcityinitiatives.
o AcademicTeaching:Pythonhasbecomethedefault medium for teaching AI and ML courses worldwide, replacinglanguagessuchasJavaandMATLABincurricula. This facilitates rapid prototyping while ensuring learners cantransitionseamlesslyintoresearchandindustryroles.
o PublishedWorksandResearch:Numerousscholarly contributions from predictive healthcare analytics to defensegeoinformatics demonstratePython’scentralityin appliedAIresearch.Theauthor’sownexperienceincludes mentoring over fifty applied projectsin AIand publishing researchthatintegratespredictivemodelswithgeospatial andIoTdatasets,underscoringPython’sversatilityincrossdomainapplications.
Python has emerged as a cornerstone in the Internet of Things(IoT)ecosystemduetoitslightweightdeployment, rapid prototyping capability, and cross-platform interoperability.Itsadaptabilityallowsdeveloperstobridge low-levelhardwareinteractionswithhigh-levelcloud-based analyticsseamlessly.
• LightweightDeploymentonEdgeDevices: PythonsupportsIoTdevelopmentacrossplatformsranging from Raspberry Pi and Arduino to specialized microcontrollers running MicroPython or CircuitPython. Theseenvironmentsenabledeveloperstoprogramsensors, actuators, and edge devices using simplified Python code withoutcompromisingfunctionality.ComparedtoCorC++, Python drastically reduces development time while still enablingreal-timeresponsivenessinresource-constrained settings.
• Real-TimeDataCollectionandCloudIntegration: IoT relies heavily on data acquisition, transmission, and remoteprocessing.Pythonlibrariessuchaspaho-mqttand aiocoapenablesecure,lightweightcommunicationthrough protocolslikeMQTTandCoAP,whileRequestsandSockets libraries facilitate HTTP-based integration. This makes Pythonapowerfulmiddlewarelanguageforconnectingedge devicestocloudservicessuchasAWSIoT,AzureIoTHub,or open-source platforms like ThingsBoard. Its ability to combinelocaledgeanalytics(viaNumPy,Pandas)withcloud pipelinescreatesrobustend-to-endIoTarchitectures.
• CaseStudy:SmartWaterReportingSystem(IoT+ GIS):
A practical demonstration of Python’s IoT capabilities is foundinthedesignofaSmartWaterReportingSystemthat integratesIoTsensornetworkswithgeospatialmapping.In thissystem:
o IoT-enabledsensors(ultrasonic,turbidity,flowrate) deployed in reservoirs and canals collect real-time water levelandqualitydata.
o PythonscriptsmanageMQTT-baseddatatransfer, ensuringsecureandefficientcommunicationbetweenedge devicesandacentralserver.
o The incoming data is geolocated and visualized through Python-based GIS libraries (GeoPandas, Folium), enabling authorities to monitor resource availability and leakage/seepagepatternsinreal-time.
o Theauthor’sresearchdemonstratedhowthisIoT+ GIS integration supports sustainable urban water management, offering predictive analytics for reservoir control while maintaining cybersecurity through Pythondrivenencryptionframeworks.
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) have undergone a paradigm shift with the integration of Python, which has become the primary scripting language for spatial data analysis,visualization,andautomation.
Libraries and Frameworks: Python supports geospatial workflows through an extensive ecosystem. GeoPandas extends the power of Pandas to handle geospatial data structures, enabling vector-based spatial operations. Rasteriosimplifiesrasterdatasetmanipulationforsatellite imageryandlanduse/landcover(LULC)mapping.ArcPy,an ESRI-supportedPythonmodule,automatescomplexArcGIS tasks such as geoprocessing, cartographic rendering, and network analysis. Complementary libraries like Shapely, Folium,andPyProjexpandcapabilitiesforspatialgeometry, webmapping,andcoordinatetransformations.
Applications in Spatial Analysis: Python streamlines tasks likespatialinterpolation,overlayanalysis,terrainmodeling, andremotesensingworkflows.Inenvironmentalstudies,it supportsLULCmappingandchangedetectionusingLandsat and Sentinel imagery. In urban contexts, Python enables real-time geoinformatics, such as monitoring air quality sensors, tracking transportation systems, and modeling urbansprawldynamics.
CaseStudy:NationalSurveyAuthority,Oman DefenseGIS Applications:
During collaborative projects with the National Survey Authority in Oman, Python was used to enhance defense geoinformatics.LibrariessuchasArcPyandRasteriowere applied to automate geoprocessing tasks for topographic mapping and defense terrain analysis. Python-driven workflowsenabledtheintegrationofsatelliteimagerywith GISdatabasestoprovidereal-timegeospatialintelligencefor surveillance,bordermonitoring,andmissionplanning.This caseillustrateshowPythonstrengthensdefensereadiness by combining automation, accuracy, and real-time intelligenceingeospatialapplications.
Pythonhasbecomeanindispensabletoolincybersecurity, serving as the preferred language for security analysts, penetration testers, and digital forensic investigators. Its

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
strengthliesinrapidscripting,cross-platformcompatibility, and the availability of specialized libraries for security operations.
LibrariesandTools:Pythonpowersnumeroustoolsusedin penetrationtestingandethicalhacking.Scapyallowspacket crafting and network sniffing, while Paramiko supports secureSSHautomation.Forforensicanalysis,librarieslike Volatility (memory forensics) and PyExifTool (metadata extraction) play a key role. Python’s open-source tools integrateseamlesslywithpopularcybersecurityframeworks such as Metasploit and Wireshark, enhancing analyst productivity.
ApplicationsinCryptography,MalwareAnalysis,andThreat Intelligence:
Cryptography: Python libraries like PyCryptodome and Hashlib provide secure encryption, hashing, and digital signaturefunctionalities.
MalwareAnalysis:SecurityresearchersusePythonscriptsto decompilebinaries,analyzeobfuscatedcode,andautomate sandboxtestingofmalicioussoftware.
ThreatIntelligence:Python-basedautomationpipelineshelp collect,normalize,andanalyzethreatfeeds,integratingdata fromAPIs,firewalls,andintrusiondetectionsystems.
Case Study: Academic Cybersecurity Teaching and Surveillance Systems Consultancy: In higher education, Python has been central to teaching cybersecurity fundamentals, allowing students to design intrusiondetectionsystems,simulateattacks,andautomate loganalysis.Beyondacademia,Pythonhasbeenappliedin consultancyprojectsforsurveillancesystems,whereitwas used to develop security scripts for real-time monitoring, anomalydetection,anddataencryptioninIoT-basedcamera networks.TheseexperienceshighlightPython’srolenotonly as a teaching tool but also as a professional enabler for buildingresilientcyberdefenseinfrastructures.
OneofPython’smostdefiningstrengthsliesnotonlyinits impact within individual domains but also in its ability to integrate multiple technological paradigms into cohesive, interdisciplinary solutions. By acting as a unifying layer across Artificial Intelligence (AI),Internet of Things(IoT), Geospatial Information Systems (GIS), and Cybersecurity, Python enables the creation of complex, intelligent, and securedigitalecosystems.
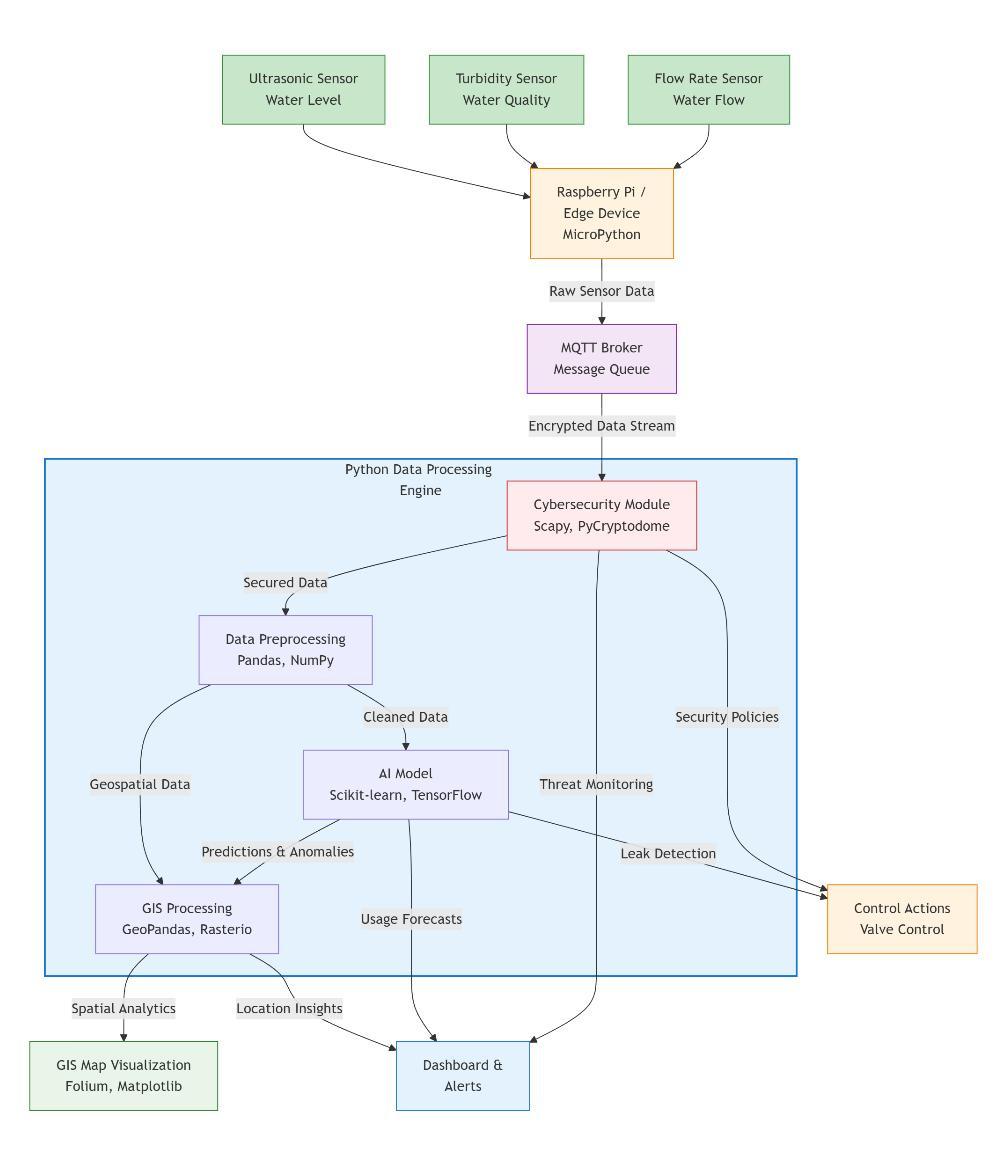
Figure 3: SmartWaterManagementSystemArchitecturePythonasIntegrativePlatform
Integration Across Domains: Python’s flexibility allows AI modelstodirectlyconsumereal-timedatafromIoTsensors, geolocate it using GIS libraries, and secure the resulting workflows through cryptographic and intrusion-detection modules. This seamless interoperability is unmatched by other programming languages, many of which remain limitedtodomain-specificapplications.
Smart Water Systems as a Case Example: A clear demonstrationofPython’sintegrativecapacityisevidentin smartwatermanagementsystems:
IoT Sensors: Python scripts manage data acquisitionfrom ultrasonic, turbidity, and flow sensors embedded in reservoirsandcanals.
AI Analytics: Using Scikit-learn or TensorFlow, Pythondrivenmodelspredictwaterdemand,detectanomaliessuch asleaks,andoptimizedistribution.
GISMapping:LibrarieslikeGeoPandasandFoliumtransform raw sensor data into interactive spatial visualizations, enabling decision-makers to monitor water distribution geographically.
CybersecurityProtection:Python-basedframeworkssecure IoT communication through packet analysis (Scapy), encryption (PyCryptodome), and anomaly detection, ensuringresilienceagainstcyberthreats.
Interdisciplinary Innovation: The convergence of these domains’ highlights Python’s unique role as an enabler of interdisciplinary innovation. For example, in urban management,AI-poweredanalyticsintegratedwithGIScan guideinfrastructureplanning,whileIoTdevicesprovidelive

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
datastreams,allunderpinnedbycybersecurityframeworks tosafeguardcriticalsystems.Thiscross-domainsynergynot onlyaddressesisolatedtechnicalchallengesbutalsofosters holistic, sustainable, and secure solutions to societal problems.
Discussion
The sustained dominance of Python reflects not only its technical merits but also the strategic ways in which it evolved to meet the demands of academia, industry, and research. Unlike many of its predecessors and contemporaries,Pythoncombinedsimplicity,accessibility, and community-driven growth into a formula that encouraged adoption across disciplines. Where languages such as Java and C++ stagnated within enterprise and system-levelniches,Pythonexpandedbybecominga“glue language”thatintegratesseamlesslywithothertechnologies. Itssuccessisthereforenotrootedsolelyinperformance,but initsecosystemandadaptability,whichallowedittobridge AI,IoT,GIS,andCybersecurityinwaysotherlanguagescould not.
Analysis of Python’s Dominance: The reasons behind Python’ssuccesslieinitsclarityofsyntax,vastopen-source libraries,andinteroperability.Itsdesignphilosophylowered barriers for students and non-specialists, ensuring widespreadadoptionineducation.Therobustcommunity support system fueled iterative improvement and a rapid expansionofdomain-specificlibraries.Thisecosystemeffect created a positive feedback loop: the more Python was adopted,thefasteritevolved,ensuringitremainedrelevant incutting-edgefieldslikedeeplearning,geospatialanalytics, anddigitalsecurity.
ChallengesandLimitations:Despiteitsstrengths,Pythonis not without weaknesses. Itsperformance limitations, stemming from being an interpreted language make it slowerthancompiledlanguagessuchasC++orRust.While thisgapisoftenmitigatedbyoptimizedback-ends(NumPy, TensorFlow),real-timeorresource-constrainedapplications still face constraints. Additionally,dependency managementin large projects can create conflicts (“dependency hell”), though tools like pipenv, Poetry, and Conda are improving this situation. Python also facesemergingcompetition: Julia offershigh-performance numerical computing with Python-like syntax, while Rust emphasizes safety and concurrency for systems programming.Bothpresentcrediblealternativesindomains wherePythonhashistoricallythrived.However,thePython community has demonstrated a remarkable capacity for managedevolution,asevidencedbythesuccessful,though challenging,multi-yeartransitionfromPython2toPython3. This large-scale coordinated effort underscores the language'slong-termresilienceanditscommunity'sability to navigate significant technological shifts, which bolsters confidenceinitsfuturesustainability.
Long-TermSustainability:ThesustainabilityofPythonwill depend on its ability to evolve alongside technological
frontiers.Intheeraofquantumcomputing,Pythonisalready extendingitsreachthroughframeworkssuchasQiskitand Cirq, demonstrating adaptability to new paradigms. Similarly,inedge AIandIoT,lightweight versionssuch as MicroPython and CircuitPython expand Python’s utility in constrainedenvironments.Itscontinuedsurvivalwillhinge on its flexibility to interoperate with future technologies ratherthancompetesolelywithrawperformance.
Thefindingsofthisstudycarrysignificantimplicationsfor academia, industry, and society. For academia, Python’s versatility across artificial intelligence, IoT, GIS, and cybersecurityunderscorestheneedtodevelopcurriculathat align with evolving industry requirements and emphasize interdisciplinary,hands-onlearning.Integratingcasestudies suchasthe real-timewaterqualitymappingsystemusing IoTandGISwithenhancedcybersecurity(Hashmi&Bhise, 2024) ensures students gain practical experience with technologiesthatmirrorreal-worldapplications. Forindustry,Pythonenablesrapidprototyping,accelerates innovationcycles,andstrengthenscybersecurityreadiness. Tools and frameworks developed in studies like Water ReservoirControlUsingIoTinCyber-SecuredEnvironment (Hashmi,2025)demonstratehowsecure,automatedcontrol systemscanbedeployedefficientlyinresource-constrained environments,supportingwiderIoTadoptionacrosscritical infrastructureandindustrialprocesses.
For society, Python-driven solutions contribute to sustainableresourcemanagement,improvedigitalsecurity, and democratize access to AI-enabled services. Initiatives suchasSecuringUrbanSmallWaterBodieswithGeospatial, IoT, and Cybersecurity (Hashmi & Bhise, 2024) and ReportingGeographicalReservoirLevelChangestoHigher Authority Using IoT (Hashmi, 2024) illustrate how integratedtechnologiescanprovidereal-timeenvironmental monitoring, public safety enhancements, and equitable access to data for informed decision-making. Collectively, these implications highlight Python’s role as a unifying technology that fosters interdisciplinary innovation and societaladvancement.
Python has evolved far beyond the boundaries of a traditional programming language, establishing itself as a paradigm for interdisciplinary innovation. Its simplicity, readability, and extensive ecosystem have enabled transformative applications across Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, Geospatial Information Systems, and Cybersecurity,fosteringintegrationthatbridgespreviously siloed domains. Python’s strategic adoption has not only accelerated research and industrial development but also democratized access to advanced computational tools, makingcutting-edgetechnologymoreaccessibletostudents, researchers,andpractitionersalike.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Lookingforward,Pythoniswell-positionedtomaintainits central role in emerging technological landscapes. Its adaptabilitypromisesseamlessintegrationwithblockchain frameworks for secure decentralized systems, edge AI for intelligentprocessinginresource-constrainedenvironments, andquantumcomputingfornext-generationcomputational challenges. Collectively, these trajectories underscore Python’senduringrelevance,highlightingitspotentialasthe engine powering the future of intelligent, secure, and sustainabledigitalecosystems.
[1]S.A.Hashmi,“Cybersecuritychallengesinlivestreaming: Protectingdigitalanchorsfromdeepfakeandidentitytheft,” Zenodo,2024,doi:10.5281/zenodo.17085678.
[2]S.A.Hashmi,“Impactofdigitalgovernanceoneconomic policy implementation,” Zenodo, 2024, doi:10.5281/zenodo.17085702.
[3] S. A. Hashmi, “Reporting geographical reservoir level changes to higher authority using IoT,” Zenodo, 2024, doi:10.5281/zenodo.17084697.
[4] S. A. Hashmi and A. Bhise, “Real-time water quality mapping and reporting system using IoT and GIS with enhanced cybersecurity,” Zenodo, 2024, doi:10.5281/zenodo.17085627.
[5]S.A.HashmiandA.Bhise,“Securingurbansmallwater bodies with geospatial, IOT, and cybersecurity,” Zenodo, 2024,doi:10.5281/zenodo.16790152.
[6] V. Iyer and S. Nair, “Python in Indian cybersecurity: A reviewofpenetrationtestingandmalwareanalysistools,” JournalofCyberSecurityTechnology,vol.6, no.2,pp.89105,2022.
[7] R. Kumar and P. Rani, Evolution of programming paradigms:FromCtoPython,Springer,2018.
[8] A. Patel and S. Mehta, “Adoption of TensorFlow and PyTorch in Indian AI research: A bibliometric analysis,” InternationalJournalofArtificialIntelligenceResearch,vol. 15,no.2,pp.112-128,2021.
[9] S. Raj and V. Karthik, “Python as a gateway language: Replacing C and Java in the Indian computer science curriculum,”JournalofComputinginHigherEducation,vol. 32,no.1,pp.78-95,2020,doi:10.1007/s12528-019-092369.
[10] K. Rao, M. Gupta, and L. Iyer, “IoT-enabled precision agricultureinIndia:APython-basedapproachonRaspberry Pi,”IEEEInternetofThingsJournal,vol.7,no.10,pp.1023410242,2020,doi:10.1109/JIOT.2020.3004567.
[11]A.SaxenaandN.Gupta,Industry4.0skillsinIndia:A survey of Python's demand in machine learning and analytics,NASSCOM,2021.
[12]P.Sharma,K.Verma,andN.Desai,“Acomparativestudy of MATLAB, R, and Python for statistical computing,” in Proceedingsofthe2019InternationalConferenceonData Science and Communication (IconDSC), 2019, pp. 1-6, doi:10.1109/IconDSC.2019.8816889.
[13]T.SmithandL.Joneās,“Performanceanddependency challengesininterpretedlanguages:AcasestudyofPython,” Software: Practice and Experience, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 891907,2022,doi:10.1002/spe.3056.
[14] R. Verma and A. Singh, “Leveraging GeoPandas and GDALforurbanplanninganddisastermanagementinIndia,” GeospatialTechnologyandApplications,vol.5,no.2,pp.2340,2021.

Sayed Athar Ali Hashmi isaGuest Lecturer at the Higher Education Department of Chhattisgarh, Raipur,India.Hisresearchfocuses onIoT-basedwatermanagement, cybersecurity, and geospatial technologies.