
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Arun
Soni1 , Isha Tiwari2 , Ashutosh Gautam3 Arihant Jain4
1,2,3,4 4th Year, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Laksmi Narain College of Technology, Bhopal
Abstract - Attendance tracking is a fundamental aspect of administrative operations in educational institutions and workplaces, yet traditional manual systems are timeconsuming, error-prone, and susceptible to proxy entries. To address these challenges, this paper presents a low-cost, IoT-enabled RFID-Based Attendance Management System utilizing an ESP8266microcontroller, MFRC522 RFID reader, LCD display, and buzzer module to automateanddigitizethe attendanceprocess.
Each user is issued a unique RFID tag embedded with a digital identifier. When scanned, the RFID reader captures the tag’s UID, which is processed by the ESP8266 and transmitted via Wi-Fi to a cloud database such as Google Firebase or Google Sheets. The system records the attendance along with timestamps and provides instant feedback through an LCD display and audible alerts. This ensures real-time data logging, enhances transparency, andeliminatesthe needfor manual intervention.
The system’s compact architecture, wireless communication, and web-based interface make it easily deployable in schools, colleges, offices, and industrial settings. Experimental testing under various conditions demonstrated high accuracy, consistent data transmission, and real-time accessibility, validating the system’s effectiveness and reliability. Its open-source nature allows for further customization, such as integration with biometric systems, automated notifications, and analytics dashboards.
This project demonstrates the potential of combining RFID and IoT to modernize attendance systems, offering a scalable, efficient, and user-friendly alternative to conventional methods. Future enhancements may include face recognition, AI-based behavior tracking, and mobile app integration, enabling a holistic smart attendance ecosystem.
Key Words: MFRC522RFID,ESP8266,LCD.
1. Introduction
The integration of automation in administrative operations has become a necessity in today’s digital age. Attendance management, one of the most routine and time-consuming tasks in academic and organizational environments, is prone to human errors and manipulation. To address these inefficiencies, Radio
FrequencyIdentification(RFID)offersaviablesolutionfor secure,fast,andaccurateattendancetracking.
This project proposes an RFID-Based Attendance Management System using the ESP8266 microcontroller and MFRC522 RFID reader, which digitizes and automates the process of attendance recording. Each user is issued an RFID tag or card embedded with a unique identifier. Upon scanning, the systemcapturesthecarddataanduploadsitwirelesslyto a clouddatabaseinreal time.A16x2I2C LCDmoduleand buzzermoduleprovideimmediatefeedbackforbothusers andadministrators.
Compared to manual entry or biometric scanners, RFIDbased systems offer speed, affordability, and scalability. Moreover, real-time accessibility via cloud platforms enhances transparency and convenience for monitoring attendance. This system also improves security by reducingtheriskofproxyattendance.
The proposed system is adaptable and customizable for use in schools, universities, offices, and industrial setups. With the increasing demand for smart and connected solutions, this project provides a robust foundation for futureIoT-basedattendancetrackingapplications.
2. Literature review
Automatedattendancesystemshavebecomeavitalareaof research and development due to the increasing demand forefficiency,accuracy,andtransparencyinacademicand professional environments. Traditional attendance methods whether manual or biometric suffer from significantdrawbacks,includingtimeconsumption,human error,proxyattendance,anddifficultyinmaintaininglongtermrecords.Asaresult,researchersandinstitutionshave turned to more advanced technologies such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Internet of Things (IoT), andcloud-basedsystemstoaddresstheselimitations.
RFID technology enables wireless, contactless identification of individuals using electromagnetic fields, offeringacost-effectiveandpracticalsolutionforreal-time tracking. According to Aysha Qaiser and Shoab A. Khan (2006), RFID-based systems significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of time and attendance management, particularly in institutional settings. These systems eliminate manual data entry and facilitate rapid,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
automated record-keeping, improving overall operationalefficiency.
Microcontroller-based platforms, such as Arduino and ESP8266, have further enhanced RFID system capabilities. The ESP8266 Wi-Fi-enabled module, widely adoptedinembeddedIoTsystems,enablesseamlessdata transmission to cloud databases like Google Firebase or Google Sheets. This facilitates real-time access to attendance records from any remote location. As described by M.K. Yeop Sabri et al. (2007), such architectures are particularly effective in building scalableattendanceframeworksforlargeorganizations.
Research also explores the integration of front-end interfaces, such as web portals or mobile applications, allowing administrators to view, analyze, and export attendance reports. Lightweight cloud solutions have provensuperiorintermsofcostandsimplicitycompared to local server-based systems, particularly for educational institutions that lack dedicated IT infrastructure.
While biometric solutions (e.g., fingerprint and facial recognition) offer high levels of security, they require more expensive hardware and are often sensitive to environmental factors like dirt, moisture, or lighting. In contrast,RFID-basedsystemsaremoreresilientandnonintrusive,makingthembettersuitedforhigh-throughput scenariossuchasschoolsorcorporateentrances.
Recent developments have introduced hybrid models, combining RFID with biometric verification or facial recognition to prevent impersonation and improve system security. Machine learning and artificial intelligence are also being explored to detect anomalies in attendance patterns and generate intelligent insights. However,theincreasedcomputationalrequirementsand data privacy concerns associated with such models presentongoingchallenges.
In summary, the literature supports RFID-based attendance systems as a highly effective and scalable alternative to conventional methods. Their integration with IoT components, cloud services, and real-time data processing tools positions them as a cornerstone of modernsmartadministrationsystems.Futureresearchis expected to focus on personalization, energy efficiency, AI-enhancedanalytics,and advanceduserauthentication mechanisms.
The proposed RFID-Based Attendance Management Systemisdesignedtoautomatetheprocessofattendance tracking using RFID technology integrated with IoT infrastructure. The system utilizes the MFRC522 RFID readertodetectRFIDcardsortagsassignedtoindividual
users. Upon scanning, the tag’s unique identifier (UID) is captured and processed by the ESP8266 microcontroller, whichtransmitsthedataviaWi-Fitoacloud-basedserver (such as Google Sheets or Firebase) for storage and visualization. To enhance user interaction, the system incorporatesa16x2I2CLCDdisplayforreal-timefeedback andabuzzermoduleforaudiblealerts.
This design offers a compact, cost-effective, and scalable solution for educational institutions, workplaces, and secure facilities. The use of contactless RFID technology ensures quick and hygienic attendance marking, while real-time cloud integration allows for centralized access and data transparency. The system’s modular design supports easy integration with existing infrastructure and offers potential for future upgrades, such as biometric integration, facial recognition, mobile alerts, and analytics dashboards.
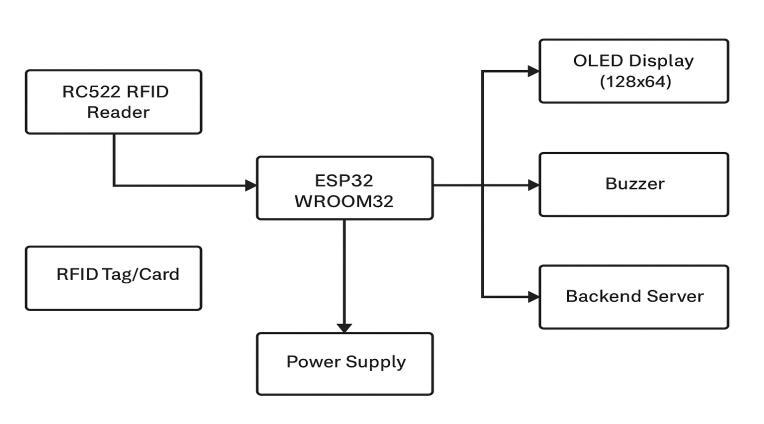
Fig.1.A
ESP8266 Microcontroller – A low-cost, Wi-Fi-enabled microcontroller that processes data received from the RFID reader. It handles real-time communication with the cloud server and controls output peripherals such as the LCDdisplayandbuzzer.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
MFRC522 RFID Reader – A compact and energyefficient RFID module operating at 13.56 MHz. It reads passive RFID cards and tags by emitting an electromagnetic field and capturing the UID of any tag presentedwithinrange.

RFID Tag – Eachuserisassigneda passiveRFIDcardor tag with a unique identifier. When scanned, the UID is read by the MFRC522 module and transmitted for identificationandattendancelogging.

16x2 I2C LCD Display – A liquid crystal display used to provide real-time visual feedback to users. It displays messagessuchassuccessfulscanconfirmations,userIDs, andsystemstatus.ControlledviaI2Cprotocol,itreduces wiringcomplexity.

Buzzer Module – Generates an audible tone to alert the userofsuccessfulRFIDscansoranysystemstatuschange.
Cloud Database (Google Sheets/Firebase) – The backend cloud platform receives attendance data sent by the ESP8266. It logs each scan with a timestamp and unique UID, making it accessible for real-time monitoring, historicalanalysis,andreporting.
Web or App Interface (Frontend) – A lightweight dashboard or Google Sheets interface where administrators can view, organize, and export attendance records. It simplifies record-keeping and enables remote accesstoattendancedata.
Power Supply – A stable and regulated power source is used to operate the ESP8266 and other peripheral components, ensuring consistent system performance duringcontinuoususe.
Wires & Connectors – Standard jumper wires and durableconnectorslinkvariouscomponentsofthesystem. Proper connections are essential for signal integrity and long-termreliabilityoftheembeddedhardware.
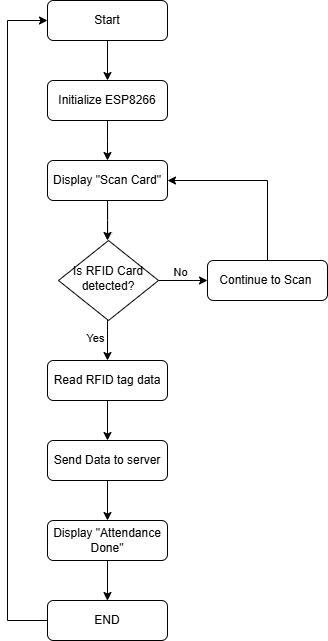
The flowchart represents the operational workflow of an RFID-Based Attendance Management System integrated with IoT, designed to automate the attendance process, enhance data accuracy, and reduce the burden of manual record-keeping. The workflow begins with the initializationoftheESP8266microcontroller,whichserves asthecentralprocessingunitofthesystem.Uponstartup, the ESP8266 establishes a Wi-Fi connection using preconfigured credentials and simultaneously initializes all connectedperipheralcomponents,includingtheMFRC522 RFIDreader,16x2I2CLCDdisplay,andthebuzzermodule.
Once the system is fully operational, it transitions into standby mode, where it displays an idle message such as “Scan your Card” on the LCD screen to prompt user interaction. During this state, the RFID reader remains active and continuously polls for the presence of RFID cards or tags within its detection range. If no card is detected,thesystemmaintainsitsstandbystatus,ensuring lowpowerconsumptionwhileawaitingavalidinput.
When a registered user places their RFID card near the MFRC522 reader, the module detects the card and captures its unique identification number (UID). This UID is then passed to the ESP8266 microcontroller for processing.Uponsuccessfuldetection,themicrocontroller performsaseriesofsequentialoperations.First,itdisplays the UID or the corresponding user name, if stored, on the LCD display along with a friendly personalized message suchas"Hey[Name]!" toconfirma successful scan.Atthe same moment, the buzzer module emits a brief audible

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
beep to provide auditory confirmation of the system’s response.
Followingthislocalfeedback,theESP8266constructsan HTTP request containing the UID and the current timestamp and sends it to a pre-configured cloud-based serverusingHTTPSprotocol.Thiscloudservermaybea Google Apps Script endpoint linked to a Google Sheets documentoraFirebaseRealtimeDatabase,dependingon the implementation. Once the data is successfully received and logged in the cloud backend, the system displays a confirmation message on the LCD screen such as“DataRecorded”toinformtheuserthattheattendance hasbeenmarked.
In the event of network failure or if the cloud server is unreachable, the system displays an error message, and the data transmission is retried after a short delay. This ensures data integrity and reliability in various operationalenvironments.
After completing the data logging and feedback process, the system automatically resets to its initial standby state, ready to process the next RFID scan. This entire loop is designed to function autonomously and continuously, requiring minimal to no human intervention.Themodularandevent-drivennatureofthe systemallowsittohandlemultiplescanswithconsistent performanceandhighreliability.
This methodology ensures secure, real-time attendance recording with immediate user feedback and centralized datastorageaccessiblefromremotedevices.
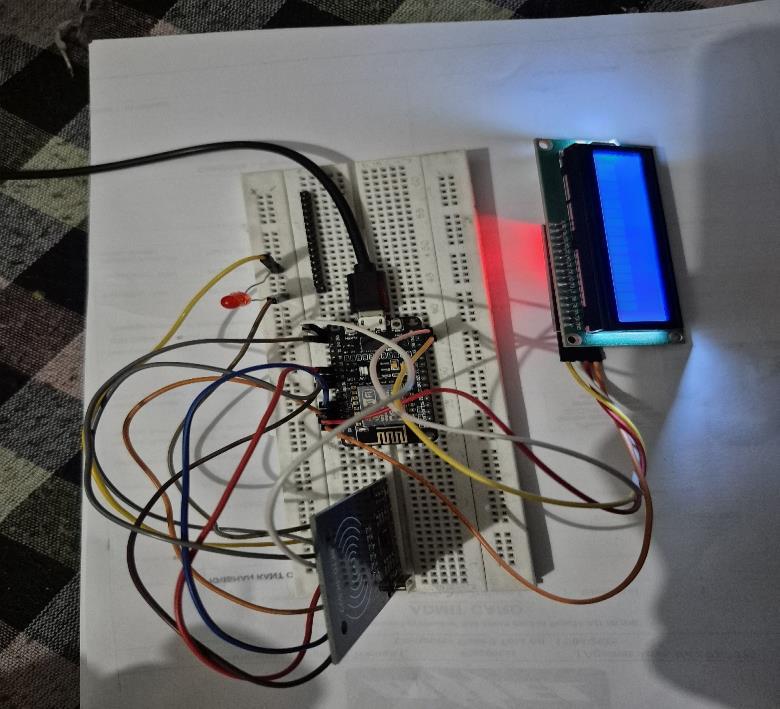
The implementation of the RFID-Based Attendance Management System involved both hardware assembly and software development to enable real-time attendance trackingandcloudintegration.Theprojectwasbuiltusing the ESP8266 microcontroller as the core processing unit due to its built-in Wi-Fi capabilities, compact form factor, andcompatibilitywithArduinoIDE.
The hardware setup included the MFRC522 RFID reader module, which was interfaced with the ESP8266 via SPI (SerialPeripheralInterface).Thismodulewasresponsible for reading passive RFID cards or tags assigned to each user. A 16x2 I2C LCD display was connected to the microcontroller to provide immediate visual feedback suchasprompts,UID display,andconfirmationmessages. A buzzer module was also integrated to generate brief audible alerts when an RFID scan was successful. The entire setup was powered using a regulated 5V power supplytoensureconsistentoperation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Onthesoftwareside,thesystemwasprogrammedusing the Arduino IDE, with supporting libraries such as ESP8266WiFi, MFRC522, LiquidCrystal_I2C, and HTTP Client. Upon boot-up, the ESP8266 connects to a predefined Wi-Fi network and initializes all connected components.WhenauserscanstheirRFIDcard,theUID isextracted,displayedontheLCD,andtransmittedviaan HTTPSGETrequesttoaGoogleAppsScriptURLlinkedto aGoogleSheetsdocument,whichlogstheUIDalongwith thecurrenttimestamp.
The implementation was thoroughly tested under realworld conditions, simulating classroom or office attendance scenarios. The system consistently demonstrated high-speed response, accuracy in UID detection, and reliable data upload to the cloud. The modular design allows for easy maintenance, scalability, and further enhancement such as user name mapping, mobileintegration,orSMSalerts.
This successful implementation validates the effectivenessofcombiningRFIDandIoTforstreamlining attendance systems while offering real-time monitoring andremoteaccessibility.
The implementation of the RFID-Based Attendance Management System proved to be highly efficient, accurate, and responsive. Upon testing, the system successfully detected and read RFID cards within a fraction of a second, with immediate feedback through both the LCD display and buzzer. Attendance data was reliably transmitted to the cloud server (Google Sheets/Firebase)viatheESP8266’sWi-Fimodule,andall records were logged with precise timestamps. The system demonstrated stable performance in both indoor and semi-outdoor environments, maintaining consistent connectivity and reliable data capture. Overall, the project achieved its goal of automating attendance trackinginreal-timewhileminimizingmanualerrorsand simplifyingadministrativeworkload.
7. Conclusion
The RFID-Based Attendance Management System using IoTrepresentsasignificantsteptowardmodernizingand automating attendance tracking in educational, corporate, and industrial environments. By integrating the ESP8266 microcontroller, MFRC522 RFID reader, cloud databases, and real-time feedback mechanisms such as LCD displays and buzzers, the system delivers a reliable, fast, and contactless solution for recording user attendancewithenhancedaccuracyandefficiency.
This system leverages IoT capabilities to eliminate the limitationsoftraditionalmanualorbiometricattendance methods, such as time consumption, proxy entries, and
data inconsistency. Real-time data logging into platforms like Google Sheets or Firebase ensures transparency and remote accessibility, allowing administrators to monitor recordseffortlesslyfromanylocation.
The project’s architecture is compact, cost-effective, and highly adaptable for diverse deployment scenarios. It requires minimal infrastructure modification and is built on open-source components, enabling easy customization and scalability. Whether deployed in schools, colleges, offices, or event venues, the system ensures streamlined attendance management and reduces administrative workload.
Lookingahead,thesystemholdsvastpotential forfurther enhancement. Possible future developments include the integration of facial recognition for dual authentication, mobile application support, real-time alerts via SMS or email, and analytics dashboards for attendance pattern tracking and behavioral insights. These improvements wouldmakethesystemevenmoreintelligent,secure,and user-centric.
In conclusion, the RFID-based attendance system demonstrates how emerging IoT technologies can be harnessed to transform routine administrative functions. Itspracticality,scalability,andreal-timecapabilities make it a viable and valuable solution in the move toward smarter,moreconnectedinstitutionalenvironments.
References:
1. Aysha Qaiser and Shoab A. Khan, “AutomationofTime andAttendanceUsingRFIDSystem,” Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), IEEE,2006. (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4095461)
2. Grant Hornback et al., “Automatic Attendance System,” RFIDSensNet Lab, Texas A&M University, 2001.(http://www.rfic.ece.tamu.edu/rfidsensnet)
3. Sato DCS & Labeling Worldwide, “TheRFIDGuidebook (Revision 8),” Sato Corporation, 2004. (https://www.satoglobal.com/pdf/rfid_guidebook.pdf)
4. M. K. Yeop Sabri, M. Z. A. Abdul Aziz, M. F. Abd Kadir, “Smart Attendance System Using RFID,” Asia Pacific Conference on Applied Electromagnetics Proceedings (APACE),IEEE,2007. (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4603713)
5. Claudio Talarico et al., Embedded System Engineering Using C/C++ IEEE ECBS Conference Paper (2005): (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1421732)