
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1H.O.D. of Civil Dept., S.E.S Polytechnic College, Solapur, Maharashtra 413002
2Lecturer at Civil Dept., S.E.S Polytechnic College, Solapur, Maharashtra 413002
3Lecturer at Civil Dept., S.E.S Polytechnic College, Solapur, Maharashtra 413002
4Lecturer at Civil Dept., S.E.S Polytechnic College, Solapur, Maharashtra 413002
Abstract - In this study, Water is one of the world’s most valuable resources, yet it is under constant threat due to climate change and resulting drought, explosive population growth, and waste. One effective solutiontoaddress theglobal water shortage is the process of treating and reusing water from industries and cities, known as water reclamation and reuse. Water distribution network is complex when area to be covered is large and analysis and design need to be done by manual or tradition method, this problemmaybeovercome by using software for design and analysis. Thus this analysis was taken for research which includes the existing water distribution system network. The existing water distribution system was analyzed using software tools. This analysis revealed variations in materials, identified different network alternatives, enabled optimization of the distribution system, and provided a comparison based on various hydraulic parameters. This gives the economical alternative solution to the distribution system and payback period of project. After analysis it is found that the existing system may need some modification and therefore software based analysis may be utilized for complex distribution system to achieve economy and time saving.
Key Words: Distribution system, Analysis, material variation,optimization,paybackperiod.
Waterisessentialforhumansurvivalandhasalwaysplayed a vital role in daily life. In ancient times, people relied on naturalsourceslikeriversandwellsfordrinking,washing, and irrigation. As civilizations advanced, such as those in Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa, water was also used for religiouspurposesandwasconsideredsacred.Today,water use has expanded significantly through piped systems for activities like bathing, fire fighting, and agriculture. Managing and operating water distribution systems is crucialtoensuringsafedrinkingwaterreachesconsumers. While treatment at the source is important, maintaining waterqualitythroughoutthedistributionprocessisequally critical. Water can become contaminated due to poor treatment, reactions with pipes, leaks, and aging infrastructure.Furthermore,thequalitymaydegradeonce water enters household plumbing, which is beyond the
utility’scontrol.Modernwaterdistributionsystemsinclude pipes, pumps, valves, tanks, and more, forming the final barrier before water reaches consumers. Though these systemsaredurable,theyareoftenoverlookedinfunding andmaintenance,despiteneedingcontinuousinvestmentas populationsgrowandinfrastructureages.
The aim of this report is to evaluate the current water distributionsystemandexplorealternativenetworkdesigns tooptimizeitsperformanceintermsofefficiency,reliability, andwaterqualitydelivery
1. Tostudytheexistingwaterdistributionsystem.
2. To analyze various alternative networks to optimize system
Contributionsofresearchersarepresentedasfollows,
Radha Krishnamurthy (1996) [1] studiedthedistribution systeminthetimeofMohenjo-DaroandHarappacivilization. Mohenjo-DaroandHarappawereoldyetdevelopedcitiesin theancienttimes.Thesecitieswerewell-organizedandbuilt of brick and stone. Thedrainage systems, wells and water storage systems were ahead of its time. These organized systems set them apart from all other ancient civilization’s.Thepaperemphasisoncleanwatersupplyfor drinking,agriculturaloperations,cooking,washingandfor medicalpurposeatthatera.Thepure,divinewaterconveys offeringtogod.Peoplewereawareaboutqualityofwaterand itsproperuse.Paperdescribesclassificationofthewater& itsdifferentpropertieswhichwouldbesafeforthehealthof personbyprovidingdifferentSanskritstanzas.Itcoversuse of water for distribution system in the form of rain water, groundwater,andRiverwater.Byreferringthispaperwe come to know that our ancients knew many method of utilization of water. In thisproject I am using referenceof cleanandqualitywaterfordistributionsystemandresearch isextendeduptostorageofwaterbyundergroundmethod whichisliftedbypumptoreachuptoconsumer.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thomas m Walski (2006) [2] American water world associationhadstudiedthatearlyhumanhastocarrywater fromsourcetopointofconsumptionwhichrequiredmore effortsandonlyminimalwaterfordrinkingandwashingwas available.Pipedwatersystemwasdiscoveredtwomillennia beforeChristwhichstillfunctioningtoday.Papershowedthe resultofmostextensivewaterdistributionsysteminancient time laid by Roman aqueduct which conveyed water by gravityandclosedconduits.Leadpressurepipewasinstalled first in Germany in 1455 for 25 Km pipe line. Wood Stave pipewereusedin1900whichremainsstrongwhenfullof waterrunsthroughpipe.Initiallypumpwasusedofsteam driven pumping system in 1869 later it was replaced by centrifugalpump.In1935undergroundtanksofsteelplate rivetedwereused.In1942pre-stressedconcretetankwas introducedandthenin1952to60castinsituconcretewere common practice for tank. By referring this paper in this project different pipe material and diameter are used and undergroundwatertanksforstorageofwaterhavinglarge capacity of water. For lifting same water pump system installationareconsidered
National research council of National Academy (2006) [3] StudiedthatWaterdistributionsystemscarrydrinkingwater from a centralized treat-ment plant or well supplies to consumers’ taps. These systems consist of pipes, pumps, valves,storagetanks,reservoirs,meters,fittings,andother hydraulicappurtenancesMorethan80percentofthewater suppliedtoresidencesisusedforactivitiesotherthanhuman consumption such as sanitary service and landscape irrigation.Mostwatersystemsanddistributionpipeswillbe reachingtheendoftheirexpectedlifespansinthenext30 years(althoughactuallifespansmaybelongerdependingon utilitypracticesandlocalconditions).Thereportfocuseson traditional distribution system design, in which water originatesfromacentralizedtreatmentplantorwellandis then distributed through one pipe network to consumers. Thelossofphysicalintegrityofthedistributionsystem in whichthesystemnolongeractsasa barrierthatprevents external contamination from deteriorating the internal, drinking water supply is brought about by physical and chemicaldeteriorationofmaterials,theabsenceorimproper installation of critical components, and the installation of alreadycontaminatedcomponents.Whenphysicalintegrityis compromised,thedrinkingwatersupplybecomesexposedto contamination that increases the risk of negative public healthoutcomes.Byreferringthispaperemphasisisgiven for the system which is installed is used water only for drinkingpurpose.Whileinstallingpipelineprecautiontobe takentoavoidcrossconnectionandsimplenetworkisused for the distribution system. The utilization of different materialforpipeanditslifeconsideration.
3.1
ExistingDistributionsystemisrequiredfortheanalysisby using software. The distribution system is situated at Indradhanu near, Damari nagar Solapur. By collecting information and input data in the form of drawings, and various design parameters. This information is utilized as inputforsoftwareandtheanalysisiscarriedouttogetthe outputfromsoftware.Heredifferentalternativesofanalysis forvariouspipematerial(DuctileIron(DI),CastIron(CI))is obtainedwithexistingwaterdistributionsystem.Thenthis system is optimized with two alternatives and the cost of each alternative is worked out to get best economical alternative. At last Payback period is worked out for optimized distribution system for the beneficiary to consumer
1.WaterGemssoftware.
2.Drawingofexistingdistributionsystem.
3.Lengthofpipesinstalled.
4.Diameterofpipes.
5.Pumpdetails.
6.Headattheconsumerend..
7.Materialofpipe
This chapter deals with the results obtained during the analysiswork.Thisstudywasdependsupontheanalysisof existingdistributionsystemandoptimizationofit.Results obtained during the research work are presented by the graphs and tables and analysis was done on the basis of theseresults.Thisstudywasveryimportantfortheanalysis ofdifferentmaterial(DIpipe,CIpipe).Byusingthisresults one can compare the system which gives economical alternative.
Resultsaretabulatedasbelow,
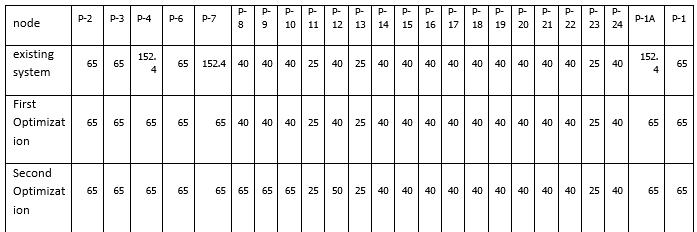
TableNo.4.1aDiameterforDIpipeandoptimization

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

GraphNo 4.1chartshowingthediameterforDIpipeand optimization
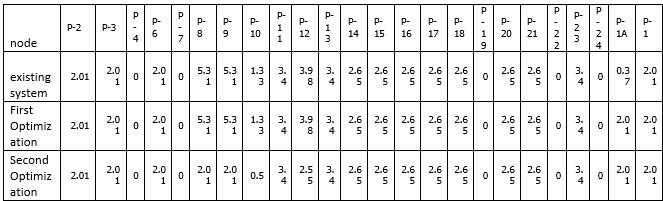
TableNo.BvelocityforDIpipeandoptimization
Followingchart(fig.4.2)showsthattheparametersVelocity forDIpipe.Chartisplottedonthebasisofdatatabulatedin thetableno.B

GraphNo 4.2chartshowingthevelocityforDIpipeand optimization
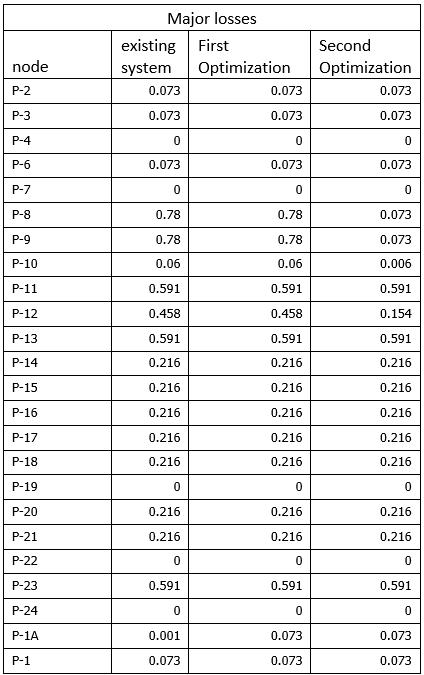
TableNo.CMajorlossesforDIpipeandoptimization
Followingchart(fig.4.3)showsthattheparametersVelocity forDIpipe.Chartisplottedonthebasisofdatatabulatedin thetableno.C.

GraphNo 4.3chartshowingtheMajorlossesforDIpipe andoptimization

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
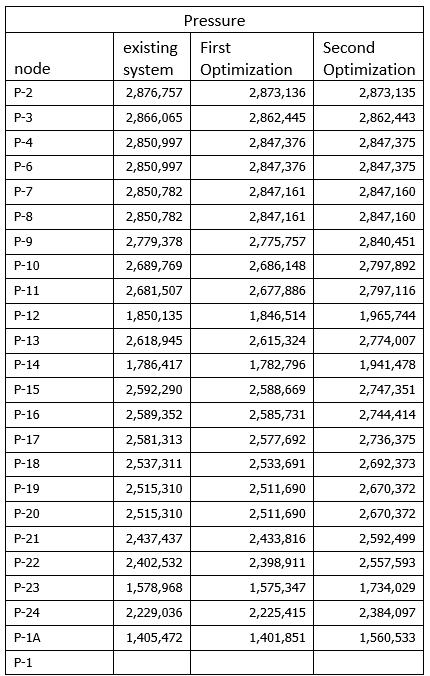
TableNo.D Pressure forDIpipeandoptimization
Following chart (fig. 4.4) shows that the parameters Pressure for DI pipe. Chart is plotted on the basis of data tabulatedinthetableno.D
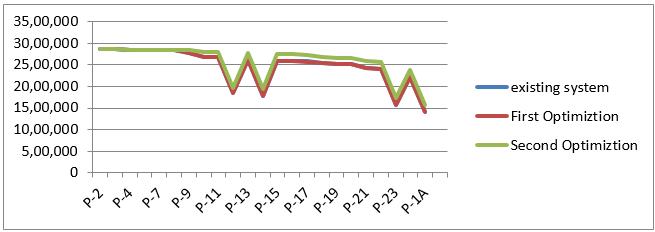
GraphNo 4.4chartshowingthePressureforDIpipeand optimization

TableNo.E Diameter forCIpipeandoptimization
Following chart (fig. 4.5) shows that the parameters Pressure for CI pipe. Chart is plotted on the basis of data tabulatedinthetableno.E

GraphNo.4.5 chartshowingtheDiameterforCIpipeand optimization

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

TableNo.F Velocity forCIpipeandoptimization
Followingchart(fig.4.6)showsthattheparametersVelocity forCIpipe.Chartisplottedonthebasisofdatatabulatedin thetableno.E
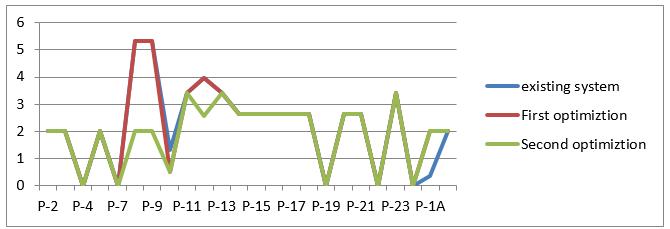
Graph No 4.6 chart showing the Velocity for CI pipe and optimization
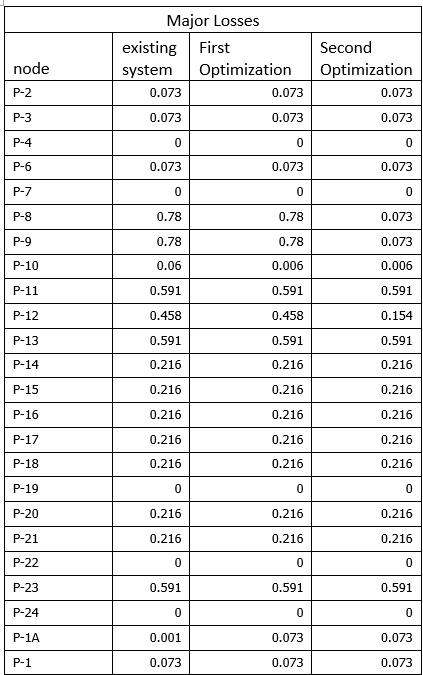
TableNo.G majorlosses forCIpipeandoptimization
Followingchart(fig.4.7)showsthattheparametersVelocity forCIpipe.Chartisplottedonthebasisofdatatabulatedin thetableno.G

GraphNo.4.7 chartshowingthemajorlosses forCIpipe andoptimization
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page874

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

TableNo.H pressure forCIpipeandoptimization
Following chart (fig. 4.8) shows that the parameters pressure for CI pipe. Chart is plotted on the basis of data tabulatedinthetableno.H
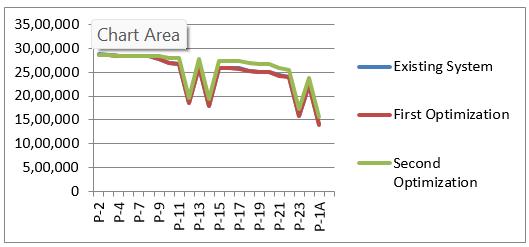
GraphNo 4.8 chartshowingpressure forCIpipeand optimization
REFERENCES
[1] RadhaKrishnamurthy,“WaterinAncientIndia”,Indian JournalofhistoryandSciences,31(4),1996
[2] Mahendra Pratap Singh, Gopinath S, Satish Goud, Abhilakhkumar Singh and Vijay Kumar P (2017) “Analysis and Design of Residential Building with TransferSlab”,JournalofIndustrialPollutionControl, ISSN(0970-2083)
[3] Thomas. M Walski, “A History of water distribution System” Journal AWWA Volume 98 No. 3 WALSKI MARCH2006.
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page875