
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Pushkar Jawale1 , Rahul Gorana2 , Sunny Kevat3 , Dr. Nita Patil4
1,2,3Student, Department of Computer Engineering, K.C College of Engineering, Management Studies and Research, Maharashtra, India
4Professor, Department of Computer Engineering, K.C College of Engineering, Management Studies and Research, Maharashtra, India
Abstract - AI-powered personal assistants are revolutionizing how people handle everyday activities and increaseproductivityinthefast-paceddigitalsocietywelivein today. Neo: AI Personal Assistant is a smartphone application that surpassesconventionalvoice-command-drivensystemsby offering consumers a smooth, intelligent, and interactive experience. Neo offers a more comprehensive approach to personal help by integrating a number of AI-powered capabilities.
The app contains a sophisticated AI chatbot that can respond to user questions, fetch related information from places such as Wikipedia and YouTube, and have substantial conversations. It also has an AI-based image generator that enables users togenerateimagesfromtextualprompts,aswell as an image fetcher that fetches relevant images based on descriptions. It has anintegratedmultilingualtranslatorthat enables real-time speech-to-text input as well as effortless language switching.
Neoboosts productivity with note-takingfeaturesthatenable the creation, editing, pinning, and organization of notes in a convenient manner. The to-do list technology provides a calendar-based view for task organization, reminders, and deadlines with the support of subtasks. Additionally, Neo features an intelligent summarizer that can summarize lengthy articles or PDF material into simple and clear summaries, enabling users to save time and quickly understand vital insights.
Built withFlutter, Neoprovides a responsive andnaturaluser experienceona varietyof devices. Withlocalstoragebasedon Hive, the app provides offline capability, allowing for secure and quick access to notes, tasks, history, and preferences without reliance on the cloud. In general, Neo is a robust yet light AI personalassistant builttosimplifydailyactivitieswith intelligent, intuitive features.
Index Terms AI Chatbot, AI Image Generator, AI Personal Assistant, Flutter, Hive Storage, Language Translator, Mobile Application, Note Taking, Productivity Tool, Smart Summarizer, To-Do List, Virtual Assistant, Voice Interaction.
Key Words: AIChatbot,AIImageGenerator,AIPersonal Assistant,Flutter,HiveStorage,LanguageTranslator,Mobile Application, Note Taking, Productivity Tool, Smart Summarizer,To-DoList,VirtualAssistant,VoiceInteraction.
In today's fast-paced digital era, artificial intelligence (AI) has become the force behind several technological advancements, transforming the way individuals interact with technology, plan their lives, and boost efficiency. AIdrivenpersonalassistantsarenowanindispensablepartof one'slife,offeringsuchservicesasvoicerecognition,instant information access, and task automation. Popular choices like Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa are found everywhere for smart device control, web searches, and voicecommands.Thesepopularassistantsarecloud-based, however,andrequireongoinginternetconnectivityandare usuallydevelopedwithgeneral-purposeuseinmindrather than with deep personalization or premium productivity features.
With rising user expectations, there is a greater need for smarter, task-oriented, and context-aware personal assistantsbeyondvoice-basedcommands.Amajorityofthe current virtual assistants are poor in functionalities like offlineoperation,taskmanagement,contentgeneration,and wrappingupahostofAIfeatures.Thisopensthedoorfora single,comprehensiveAI-basedsolutionthatoffersaricher, standalone,andmulti-aspectuserexperience.
To bridge this gap, Neo: AI Personal Assistant has been createdasasmart,mobile-firstsolutionthatisaccompanied byanextensivearrayofAI-driventoolsaimedatenhancing organization, productivity, and digital interaction. Unlike traditionalvoice-onlyassistants,Neoprovidesafeature-rich settingwithsmartutilitiessuchasanAI-poweredchatbot, AI-driven image creation, multilingual translation, notetaking,tasktracking,anddocumentsummarization.
Thechatbotalsoaccommodatesconversationalsearchesand integrateswithservicessuchasWikipediaandYouTubeto retrieve appropriate content and respond in a thoughtful manner. Neo'sAIimagecreatorenablesusersto generate visualsbasedontextinput,whileanimageretrieverenables userstosearchanddownloadappropriateimages.Language translatorfeaturestwo-waytranslationandspeech-to-text inputaswellaslanguagetogglinginsimplelanguage.They alsogetaccesstoanintegratednote-takingsystemtotake chargeofandkeepnotesandancalendar-integratedto-do listforplanningactivitywithremindersandsubtasks.There isalsoanintelligentsummarizerfacilitywhereintheusers

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
can summarize long text or PDF content into brief summariesbyemployingsophisticatedAI.
Designed using Flutter, Neo provides a smooth, crossplatform experience with a responsive UI. In contrast to cloud-based assistants, Neo takes advantage of local data storage via Hive, so users can access their notes, tasks, translations, and history offline without authentication, cloudsync,orthird-partyreliance.
By integrating multiple smart tools into a single unified mobile platform, Neo reengineers the paradigm of digital assistants.Itevolvesfromaninferiorcommandexecutortoa genuinely personal productivity assistant versatile, streamlined,anduser-centeredinitsreal-worldpriorities.
While studying the field of artificial intelligence, Many research papers highlight the development of AI systems that support voice interaction, task automation, language translation,andevencontentcreation.However,duringour literature review, wefound thatthesesystemsare mostly designedtoserveonespecificpurpose.Thereisverylittle integration among features, which limits the overall productivityandintelligenceoftheassistant.
Dharmanietal.[1]andGargetal.[5]focusedonvoice-based virtual assistants that help with reminders, alarms, and simpleinteractionsusingnaturallanguageprocessing(NLP). Their systems were effective for basic use cases, but they lackedcontextualunderstandingandmultitasking.
We also studied works that focused on improving the intelligence of chatbots. For instance, Shazhaev et al. [3] integrated ChatGPT into voice assistants to improve the qualityofresponses.Verșebeniucetal.[4]usedatechnique called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to improve the accuracy of chatbot replies by pulling relevant information from sources like Wikipedia. While these projectsshowedimprovedaccuracy,theystillfocusedonly onthechatbotmodule.
Intermsofcreativitytools,Suryadevara[2]andYadavetal. [6]usedgenerativeAItoconverttextintoimages.Theyused advancedAImodelslikediffusionto producehigh-quality outputs.PatiandPaul[7]combinedbothchatbotandimage generationfeaturesintoonemobileappusingFlutter,which inspired us to work with similar technologies in our own mobile-basedassistant.
Apartfromconversationandcreativity,note-takingandtask management are important areas in personal assistant systems.WereviewedtheworkofPitura[8],whodiscussed howdigitalnote-takinghelpswithlearningandorganization. Santhosh et al. [9] introduced “Todify,” a smart to-do list applicationwithreminderfunctionality,andSravanthand Dhanush [11] developed a real-time task management
system.Despitetheirusefulness,thesesystemsarestandalonetoolsthataren'tintegratedwithotherAImoduleslike chatorsummarization.
Inlanguagetranslation,KolharandAlameen[13]developed an AI-based translation platform for basic sentence conversion.Mohamedet al.[14]focusedmore oncultural context and improving translation quality using AI. These systemswerehelpfulbutlackedfeatureslikespeechinputor output,andweren’tpartofafullassistantplatform.
Finally,weexploredsystemdesignapproaches.Bhudhiraja andSharma[12]proposedamodularAIassistantthatcould switchbetweenfeatures,andSangeethaetal.[10]surveyed differentchatbotmodelsandtheirlimitations.Thesestudies helped us understand how important it is to keep the assistantmodularandcontext-aware.
Existing systems have the following drawbacks, despite improvementsinspecificmodulessuchaschatbots,image generation,translation,andtaskscheduling:
- Lack of integration: The majority of works concentrate on a single feature and do not communicate across modules (for example, a chatbotcannotcreatetasks).
- Cloud dependence: A lot of assistants don't supportofflinestorageorretrievalandmainlyrely oninternetconnectivity.
- Limited feedback adaptation: Notmanysystems support interaction-based reformatting or userdirectedformatting(suchas"bulletpoints").
- Poor contextual memory: Systemsareunableto rememberpastinteractionsorpreferences.
- Limited cross-platform usability: Notallsystems have a seamless user interface and offline capabilitiesbecausetheyarenotmadeformobilefirstenvironments.
- Underutilized STT/TTS integration: Although voice input and output are widespread, few effectively integrate them with response or translation.
- Lack of intelligent data persistence: Tasks and notesarefrequentlynotkeptlocallyorintelligently linkedtoothermodules.
These studies collectively address individual needs communication, translation, productivity, creativity but rarely combine them into one AI-powered, context-aware assistant.Thisformsthekeymotivationforthedevelopment ofNeo:AIPersonalAssistant.
Inthissection,wedescribeinextremetechnicaldepth the methodologyusedtodevelopNeo,ourintelligentAI-based multimodalassistant.Thissystemhasbeenarchitectedfrom scratchusingamodularandlayereddesignwhereeachlayer

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
playsauniqueroleinthequeryprocessingpipeline.Unlike traditional implementations that depend on pre-built services, our project assumes that the Primary LLM (Neo LLM),whichorchestratesthelogic,taskrouting,andmodel interaction,is entirelydeveloped byus. Itissupported by various independently connected services like image generation,translation,andvideoretrieval.
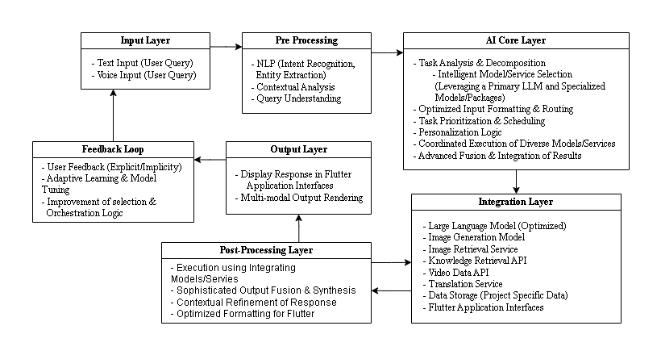
3.1 Input Layer
TheInputLayeristhefirstinteractionpointbetweenthe user and Neo. It captures queries either in text or speech format. Our system includes full support for textual commands across all modules and voice input for select featureslikechatbotinteractionandtranslation.
When text is provided, it undergoes a preprocessing pipelinebeginningwithlexicalsanitization,whereweapply regular expression-based cleaning to remove trailing whitespace, special characters, repeated punctuation, and HTML encoding issues. Next, case folding is performed throughUnicode-standardtoLowerCase()transformations toensureconsistentdownstreamtokenization.Wefurther applyUnicodeNormalizationFormC(NFC)usingtheICU4C librarytoharmonizemulti-characterrepresentationssuchas accented letters. In the final canonicalization step, contractions and common grammatical variants are expandedusingarule-basedlexiconmatcher e.g.,“I’m”is convertedto“Iam,”and“don’t”becomes“donot.”
For voice input, our system includes a built-in STT (Speech-to-Text)modulepoweredbyahybridmodel.First, theaudiowaveformiswindowedinto25-millisecondframes usingaHannfunctionwitha10-millisecondstride.Then,we extract 13 Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) alongwiththeirfirst-andsecond-orderderivativestoforma 39-dimensionalfeaturevectorperframe.Thesevectorsare passedintoaDeepNeuralNetwork(DNN)thatactsasthe AcousticModel,trainedontheLibriSpeechdataset.Phoneme outputsarethenfedintoaWFST-baseddecoder,integrated with a tri-gram language model that assigns word-level likelihoods. The output word sequence is post-processed using a beam search decoder with a spell-corrector to generatethefinaltextualstring.
OncetextualinputisreceivedfromtheInputLayer,the PreprocessingLayerbeginsitsoperationbyidentifyingthe user’sintentandtheentitiesembeddedinthequery.
Intent Recognition is conducted using a BERT-based transformer fine-tuned on a domain-specific corpus of labeled queries. Tokenization is done using WordPiece encoding, and classification is achieved through a dense layerappendedtothe[CLS]token’sfinalhiddenstate.We trainedthemodelusingcategoricalcross-entropylosswith an AdamW optimizer (learning rate = 3e-5), achieving a classification F1-score of 94.1% across 10 intent classes including translate_text, generate_image, get_info, and set_alarm.
Entity Extraction is managed through a BiLSTM-CRF sequence tagging model. The BiLSTM layer captures both forward and backward dependencies across the token streamusingGloVeembeddingsasinput.Thefinaloutput layerisa Conditional RandomField(CRF),whichdecodes theoptimalsequencepathovertheBIO-taggingformat.This hybridmodeloutperformsvanillaNERmodels,achievinga token-levelF1-scoreof92.6%onourtestset.
ContextualAnalysisisperformedtopreservemulti-turn conversational continuity. This includes a custom-built DialogueStateTracker(DST)thatrepresentsthestateasa dynamickey-valuedictionarymappingslots(e.g.,location, time,object)tovaluesextractedfromthecurrentandprior queries.Slotupdatingdecisionsaremadeusingatree-based decision model trained on slot-fill confidence scores. Additionally, coreference resolution is achieved through SpanBERT,fine-tunedontheOntoNotesdataset.Themodel uses span-scoring and antecedent prediction to resolve anaphoraandpronounslike“he”or“that.”Toselectrelevant history, we use Sentence-BERT to embed the user’s past interactionsandcomparecosinesimilarityscoreswiththe currentinput.Thecontextwiththehighestscoreisretained forcontinuity.
TheAICoreLayeristhecentralintelligenceengineofNeo. It orchestrates all downstream processing, including task analysis, model selection, routing, personalization, and executioncoordination.
TaskAnalysisandDecompositionishandledbyasemantic parser that first generates a dependency parse tree using spaCy’s syntactic analyzer. We then apply Semantic Role Labeling(SRL)toextractpredicatesandargumentsfromthe sentence.Tasksarebrokendownand storedinaDirected Acyclic Graph (DAG) where each node corresponds to a subtask (e.g., translation, retrieval) and edges represent execution dependencies. Topological sorting ensures that prerequisitetasksareexecutedfirst.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Model and Service Selection relies on a reinforcement learning-based agent trained using a Dueling Deep QNetwork(DQN).Thisagentselectsthemostsuitableservice for each subtask based on a scoring function: Score = w1*Confidence + w2*Latency + w3*Reliability + w4*UserPreferenceMatch. These scores are precomputed andstoredinametadataregistryYAMLfile,whichtheagent accessesduringdecision-making.
InputFormattingandRoutingutilizesaSchemaMapperto convert internal task objects into API-specific payload formats. For LLM-based prompts, we employ a Few-Shot Prompt Builder that generates structured input using an indexed prompt repository. Task execution is dispatched usinganevent-drivencoroutinehandlerthatsupportsretryon-failureandtimeoutsafeguards.
Task Prioritization and Scheduling is achieved using a priorityqueuethatassignsscoresbasedontheurgencyand criticality of each task. When multiple subtasks exist, a topologicalsortisperformedontheDAGtodeterminethe correct execution sequence. We also implement a fallback planfornon-deterministicfailures.
PersonalizationLogicoperatesonvectorizeduserprofiles generated via Matrix Factorization. Each user interaction contributes to a latent feature matrix, which adjusts generation parameters (e.g., temperature, max_tokens) in real-timeto reflect personal preferencessuchastoneand verbosity.
CoordinatedExecutionofServicesistrackedviaaFinite StateMachine(FSM),whichlogsthestatetransitionsofeach task from idle → running → complete → error. In case of failure,aFallbackControlleristriggeredtoroutethetaskto asecondaryservice.
TheIntegrationLayeractsastheinterfacebetweentheAI Coreandallexternaltools.Thesetoolsareabstractedusing customconnectorstoensuremodularity.
The Text Generation module is our custom-built LLM consistingofa24-layerdecoder-onlyTransformer.Ituses rotarypositionalembeddings,GELUactivations,andacausal masktopreventinformationleakageduringdecoding.The tokenizerisSentencePiece-based(32kvocab).Inferenceis handled using beam search (beam width = 5), with top_k, top_p,andrepetitionpenaltiesconfiguredfornaturalness.
TheImageGenerationModelisbasedonLatentDiffusion Models(LDMs).Thetextpromptisencodedintolatentspace usingCLIP,whichguidesaU-Netthroughareverse-diffusion processtodenoisealatentGaussiandistribution.Theoutput isdecodedbacktopixelspaceusingaVQGANdecoder.
TheImageRetrievalServiceisaccessedthroughaREST API. Retrieved results are ranked based on semantic similarity, where the input query is expanded using synonymsfromWordNetandmatchedagainstimagetags.
The Videa Data API is queried using the search list endpoint with parameters like q, order=viewCount, and maxResults=3.Videosarefilteredthrougharelevancescore computed using engagement metrics (likes/views/comments).
For Knowledge Retrieval is accessed with action=query andprop=extracts.ResultsaresummarizedusingTextRank, anunsupervisedgraph-basedrankingalgorithmappliedto theparagraphstructure.
TheTranslationModule,whichisinternallybuiltontopof Google’s Neural Machine Translation (NMT) engine. It follows an encoder-decoder architecture with global attention and beam search decoding. Translations are rankedbasedonBLEUscoreandeditdistancefromknown samples.
All system data, including task logs and saved items, is storedinHive,akey-valuestoreoptimizedforlow-latency mobile access. Data is serialized into binary using Hive Adaptersandencryptedforprivacy.
This layer prepares final outputs from the Integration Layerintoasinglecohesiveresponse.
We first use a Task Execution Monitor to execute all pending calls via a coroutine handler with event-loop scheduling. Timeouts and failures are recorded in an executionlogforretryorfallbackresolution.
The Contextual Fusion Module merges responses from variousservices.WeapplyNaturalLanguageInference(NLI) usingaBERT-basedclassifiertodetectcontradictions.For coherence,outputsareparaphrasedusingaT5-smallmodel trainedtopreservefactualcontentwhileimprovingfluency.
AFusionScorerassignsfinalqualityscorestoeachfused responseusingtheformula:
Score = α * ContextMatch + β * Coherence + γ * EntityCoverage
Theseweightsarefine-tunedthroughgridsearchbased onhumanevaluation.
The Output Layer assembles the final user-visible response.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
We create a structured response schema consisting of type, payload, and metadata fields. Each modality (text, image,video)isinsertedbasedonamodalclassifiertrained usingsoftmaxprobabilitiesovercontentembeddings.
AMultimodalResponseSynthesizerrewritestransitional phrases and combines outputs into grammatically correct compound responses. Linguistic coherence is optimized usingaGPT-2modelfine-tunedonassistant-styledialogues.
TheFeedbackLoopallowsNeotoevolvebylearningfrom real-worldusage.
Feedback data is logged into a time-series database (InfluxDB) that records session ID, user actions, response time,andsatisfactionmetrics.
A Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) layer is trained periodically on failed or rephrased queries to tune the primaryLLM.
Prompt templates are adapted using a meta-learning algorithm(MAML)tominimizegeneralizationerroracross tasks.
Finally,theorchestrationlogicisoptimizedusingamultiarmed bandit strategy (UCB-1) that dynamically adjusts serviceweightsinthetoolregistrybasedonexplorationvs. exploitationtrade-offs.
This comprehensive methodology represents the full technicalblueprintofNeo.FromsignalprocessingandNLU toorchestration,multimodalfusion,andadaptivelearning, every module is built to maximize intelligence and personalizedinteraction.
The creation and launch of Neo: AI Personal Assistant created a highly interactive and functional AI system that integratesnumerousintelligentcapabilitiesintoonemobile app.Throughextensivetestingandassessment,thesystem turnedouttobeextremelycompetentinAI-drivenchatbot conversation, real-time language translation, AI-driven image creation, smart note-taking, task management and summarization. Each module was tested separately and integratedwiththeotherfunctionalitiessuchthatitwould functionperfectlyandhaveaneasy-to-useinterface.

The AI chatbot, implemented through cloud APIs, was tested for its capacity to provide accurate, relevant, and context-sensitive responses. In testing, the chatbot consistentlyreturnedsuitableanswerstoabroadspectrum ofuserquestionsrangingfromgeneralknowledge,technical information,andeverydayconversation.Itcouldsustaina naturalflowofconversationwithoutsuddeninterruptions, enhancinguserinteractionandusability.
Afurtherstrengthwasitsabilitytopullinformationfrom otherplatformssuchasWikipediaandYouTube,providingit withaccesstoup-to-dateinformation.Thechatbotwasalso abletoincorporateafeedbackloop,wherebyuserscouldask foranswerstobereturnedinaparticularformate.g.,bullet points or paragraphs enhancing readability and customization. STT and TTS integration allowed voice interaction and accessibility, while key answers could be storeddirectlyintonotesforfutureaccess.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

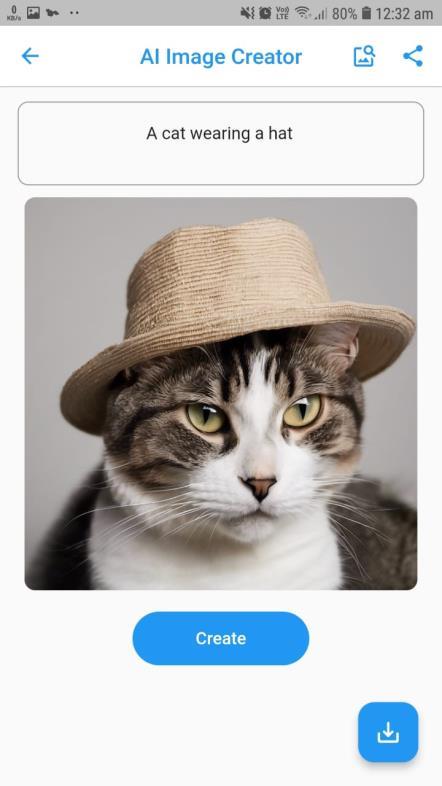
Neo'simagecreationabilityalloweduserstocreategoodqualityimagesbasedonnaturallanguageinputs.Byusingan AI-driven image creation API, the system successfully mapped user input to corresponding images. The output presented good visual coherence with the inputs and was diverseenoughtoenablecreativeexplorationfordifferent usecases.
Moreover,userswereabletoretrievereal-worldimages based on keywords. Retrieved images were appropriate, high-resolution, and could be previewed, downloaded, or shared within the app. The testing affirmed stable performance,correctimagerendering,andfastfetchtimes, providing users with flexibility in both generating and acquiringvisualcontent.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thelanguagetranslationmodulewasevaluatedforrealtime performance, language richness, and user interface design. Neo could translate text into the selected target language,anddeliverresultsinminimallatency.Thesystem had multiple language pairs supported and exhibited excellentperformancewithidiomaticphrases,fullsentences, andlongerinput.
Key features like text input and audio output through speech-to-text input and text-to-speech playback helped towardahands-free,audio-orientedtranslationexperience. Userswerealsoabletoreversetranslationdirectionthrough theswapfunctionforgreaterusability.Testsconfirmedhigh accuracyinfrequentlyusedlanguagesanduniformoffline availabilityofpriortranslationhistorythroughlocalstorage.

Neo'snote-takingmodulewastestedforspeed,flexibility, and offline persistence. Users could create, edit, pin, and deletenotesseamlessly.Notescouldbeviewedeitheringrid or list view depending on the user, and toggling worked without a hitch. All the notes were stored in Hive for referenceevenwhentheinternetwasnotavailable.
The incorporation of the chatbot enabled immediate saving of important responses in notes without manual copyingofreplies.Therewerenoissuesduringtheretrieval tests,withsavednotesstillbeingvalidacrosssessionsand
quick loading with no corruption of data.Thefeature was usefulforuserswhohadtosavedataimmediatelyandcould quicklyretrieveitatanytime.

Thetaskmanagementmoduleprovidedastructuredand easy-to-useinterfacefortaskcreation,editing,andtracking. Userscouldassignduedates,settimes,andsubtaskswith checkboxesfor better task breakdown. The calendar view gaveagraphicalrepresentationofupcomingtasks,making planningandmanagingdailyworkflowefficient.
Reminder messages were sent punctually via the local notificationframework.Hivewasusedtostorealltaskdata, keepingthedataavailableduringofflinescenariosaswell. Testing ensured task persistence reliability, punctual alertness, and simplicity of navigating tasks overall. The userswerealsoabletodeleteormodifytaskswitheaseto provideahassle-freeproductivityexperience.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Thesummarizationfeaturewasalsoattemptedwithlong contentandscholarlyPDFs.Itsummarizedlongmaterialinto short, accurate summaries without losing important meaning.Summariescouldbecopiedorsavedinthenotes moduletoreuse.TheAI-generatedsummarieswereshort, clear, and most importantly useful in understanding key ideasfromlongcontentquickly.
This module proved to be particularly useful for both students and working professionals dealing with large amountsoftext.Integratingitwiththenote-takingmodule created seamless flow from extracting information to arrangingcontent,bolsteringtheworkflowasawhole.

Toquantifytheperformanceoftheentiresystemandthe userinterface,Neoexperiencedrepeatedcyclesoffunctional testing, usability testing, and performance benchmarking. Theappdemonstrated:
- ResponsivenessofallfeaturespoweredbyAI.
- Seamlessswitchingbetweenfeatures.
- Improved offline storage of tasks and notes, with accessavailablealways.
Inusertesting,usersalsoreferredtotheinterfaceaseasy andsimplewithfeaturesthatwerewellorganizedandhada low learning curve. The inclusion of voice interaction (STT/TTS)alsofacilitatedaccessibilitysinceitenabledNeo tobeaccessedbyalargebaseofusers.
Overall,thefindingsshowthatNeo:AIPersonalAssistant deliversonitspromisewithseamless,AI-poweredpersonal assistant experience with strong features, real-time AI support,andsecurelocalstorageforofflineaccess.
The creation and release of Neo: AI Personal Assistant represent an important milestone toward developing an intelligent,multi-purposeAIassistantthatintegratesvarious intelligentcapabilitiesunderonemobileplatform.Withthe incorporation of an AI chatbot, real-time language translation,AIimagecreation,intelligentnote-taking,task

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
scheduling, and document summarization, Neo offers an end-to-end,easy-to-useproductivityexperience.Thesystem has been rigorously tested and has exhibited stability, responsiveness, and usability hence a trustworthy instrumentforoptimallymaintainingday-to-dayoperations.
One of the strongest abilities of Neo is its capability to providereal-time,interactive,andmultimodalsupport.The AIchatbotcananswerwithrelevantandcontext-dependent replies, complemented with live content fetching from YouTubeand Wikipedia.Thelanguagetranslationmodule supports two-way communication with speech and text, letting users translate, listen to, and speak without any inconvenience. The image generation and image retrieval featuresenableuserstogenerateorfetchvisualcontentat their command. While the to-do and note-taking modules assist users in information organization, reminders, and tracking, the functionality is complemented by offline capability.
Neo has been tested thoroughly and proved itself to be a reliable,user-focusedtool.OfflinestoragewithHiveallows uninterrupted access to notes, tasks, and other important information even when there is no internet connection. Voicesupport(STT/TTS)andasimpleuserinterfacemakeit accessible for more people, including voice users or those whoarelessdigitallyliterate.
ThoughNeohasachieveditsmaingoals,futuredevelopment caninvolvemorepersonalization,highercontextawareness, andhigherAI-basedautomationtomaketheassistanteven moreuser-responsive.
[1] A.Dharmani,M.Khatpe,P.Gayake,andS.Sharma,“AIBasedVirtualAssistant,” Int. Res.J.Modern.Eng.Technol. Sci.,vol.6,no.3,pp.251–256,Mar.2024.
[2] C. K. Suryadevara, “Generating Free Images with OpenAI’s Generative Models,” Int. J. Innov. Eng. Res. Technol. (IJIERT),vol.7,no.3,pp.112–116,2024.
[3] I.Shazhaev,A.Tularov,D.Mikhaylov,I.Shazhaev,andA. Shafeeg, “Voice Assistant Integrated with Chat GPT,” Indones. J. Comput. Sci., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 39–45, Feb. 2023.
[4] D.Verșebeniuc,M.Elands,S.Falahatkar,C.Magrone,M. Falah, M. Boussé, and A. Härmä, “Generative AI-based VirtualAssistantusingRetrievalAugmentedGeneration: An Evaluation Study for Bachelor Projects,” in Proc. BNAIC,2024.
[5] M. Garg, K. Bala, and S. Sharma, “Virtual Personal AssistantUsingArtificialIntelligence,” Int.J.CreativeRes. Thoughts (IJCRT),vol.10,no.12,pp.327–334,Dec.2022.
[6] N. Yadav, A. Sinha, M. Jain, A. Agrawal, and S. Francis, “Generation ofImages from TextUsingAI,” Int. J. Eng. Manuf.,vol.14,no.1,pp.21–27,Feb.2024.
[7] A.K.PatiandS.K.Paul,“SMARTCHAT:AReal-TimeChat ApplicationwithAI-BasedChatbotandImageGenerator usingFlutterandOpenAI,” Int. J. Creative Res. Thoughts (IJCRT),vol.12,no.4,pp.487–493,Apr.2024.
[8] J. Pitura, “Digital Note-Taking for Writing,” in Innovations and Challenges in Language and Literature, Springer,2023,pp.77–90.
[9] J.Santhosh,K.P.S,andM.VijayaKumar,“AI-BasedToDoAssist-Todify,” Int. J. Creative Res. Thoughts (IJCRT), vol.13,no.1,pp.160–166,Jan.2025.
[10] S. G. Sangeetha, P. L. B, and V. V., “A Survey on WebBasedIntelligentChatBot,” Int. J. Creative Res. Thoughts (IJCRT),vol.6,no.1,pp.421–427,Feb.2018.
[11] M. Sravanth and R. Dhanush, “Intelligent Task Management System,” Int. J. Creative Res. Thoughts (IJCRT),vol.11,no.12,pp.210–215,Dec.2023.
[12] H. Bhudhiraja and N. Sharma, “IntelliAssistant – AI BasedPersonalAssistant,” SSRN Electron. J.,May2021, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3847275.
[13] M.KolharandA.Alameen,“ArtificialIntelligence-Based Language Translation Platform,” Intell. Autom. Soft Comput.,vol.28,no.1,pp.145–157,Jan.2021.
[14] Y. A. Mohamed, A. Khanan, M. Bashir, A. H. H. M. Mohamed,M.A.E.Adiel,andM.A.Elsadig,“TheImpact of Artificial Intelligence on Language Translation: A Review,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 22245–22258, Feb. 2024.
[15] A.C.Jacob,S.G.Reji,H.Manoj,J.Joseph,andM.Nikhil, “AI Based Virtual Personal Assistant,” Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol.,vol.9,no.6,pp.143–147,Jun.2024.