
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:04|Apr2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:04|Apr2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Dr. B. Satpute1 , D. Guru Venkata Vishnu Vardhan2 , B. Sai Praneetha3 , M. Deepika4 , K. Vighnesh5
1Professor, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Jain (Deemed-to-be University), Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
2,3,4,5 Students, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Jain (Deemed-to-be University),Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
Abstract- An powered by AI placement cell system that automates and improves the campus hiring processispresentedin this research. For academics and students,thesystemprovidesrole-based access, making it possible to manage resumes, job advertising, and application analysis with ease. The incorporation of an AI model (LLaMA), which dynamically matches student talents with employment requirements and extracts pertinent information from student resumes, is a crucial component. Resumes are saved in a binary state and only analyzed during login, in contrast to traditional systems, protecting data privacy while preserving performance. For the purpose of making hiring decisions, faculty users can create downloadable reports and assess skill compatibility. This system functions as an exhaustive instrument for automating the placement workflow in academic institutions, minimizes human workload, and maximizescandidate-jobmatching.
Key words: AI in Placement, Resume Parsing, WebBased Placement System, LLaMA Model, Campus Recruitment, Role-Based Dashboard, Skill Matching, StudentResumeAnalysis.
Campus recruitment is a crucial stage in students academic careers, and educational institutions face several difficulties in effectively handling it. Conventional placement procedures, which include gathering resumes in person, shortlisting them, and coordinating with instructors and students, are frequently laborious, time- consuming, and prone to errors. Systems that can automate these processes and offer useful insights are becoming more and more necessary as web technologies and artificial intelligence develop. This study presents a clever web-based framework designed to automate and integrate AI to expeditetheplacement process. By facilitating automated resume processing, AI-driven job matchmaking, and central accessibility for both academics and students, the suggested system overcomesthedrawbacksoftraditionalapproaches.
Recentresearchhasfocusedheavilyontheuseofdigital technologies to transform placement systems. A study developed a computer-human interface layout for a placement management system with the goal of streamlining user interaction and improving overall experience [1]. This system offers improved processes and organized modules to help both students and administratorswithplacement-relatedtasks.
Deeplearningtechniquesareroutinelyused to forecast student placement results. One study used numerous deep learning models to predict the placement of an individual based on educational institutions, demographic, and related to skill data [2]. The models predicted with great accuracy, proving the possibility of intelligentforecastingtechniques.
An integrated, a web-based platform was developed to enhanceplacementcoordinationandstudentinteraction in academic institutions [3]. This platform aimed to digitize every stage of the placement process, from registration for students to employer collaboration and interviewtracking,providingastandardized and flexible methodforplacementmanagement.
Using historical data, a data mining approach was created to forecast individual overall institutional placement percentages [4]. The study used machine learning as well as statistical tools to generate insights and illustrate placement trends, allowing educational institutionstomakedata-drivendecisions.
Another study presented an automated personnel recruitment management system based on artificial intelligence [5]. The technology enabled robotic candidate choosing, resume analysis, and ranking based on job descriptions, minimizing manual work and shorteningrecruitmenttimes.
Another placement prediction approach used machine learning to identify students based on their chance of placement,utilizingfeaturessuchasCGPA,knowledgeof technology, and extracurricular engagement [6]. The

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:04|Apr2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
study found that statistical techniques, particularly ensemble models, were useful in estimating placement probability.
Astudyonstudentplacementsforinternshipsexamined waystoimprovethevalueofinternshipprogramsinthe study of engineering [7]. The study emphasized systematiccoordination,industry-academiccooperation andandeffectivemonitoringofstudent development throughout internships. Effectivefeedbackandconstant monitoringarecrucialforinternshipsuccess.
This project's main goal is to do away with the delays and inefficiencies that come with using conventional campus placement methods. Faculty personnel at the majority of universities manually gather, examine, and shortlist student resumes for a variety of positions. In addition to taking a lot of time, this procedure does not have a consistent way to assess students' fit for particular job profiles. Additionally, it can be timeconsuming and prone to errors for students to fill out theirprofilesbyhand.
Byimplementingintelligentautomationatcrucialpoints inthehiringprocess,thePlacementCellSystemseeksto addresstheseissues. Themaingoalistocreateasystem that automatically extracts pertinent information from student resumes, including name, location, talents, and education, using artificial intelligence. The system may evaluate these abilities and compare them to the specifications of faculty-uploaded job descriptions by incorporating the LLaMA model. With distinct features and interfaces catered toindividual requirements, the system also guarantees role-based access control for instructorsandstudents.
Inadditiontoautomation,thesystemoffersfeatureslike real-time resume parsing without saving extracted data in the database, downloadable analysis results in CSV format, and a clear, responsive online interface that enhance overall usability and transparency. In addition to digitizing the hiring process, the goal is to improve decision-making, decrease manual work, and make the placement process more intelligent, dependable, and quick.
Thesystemwasdevelopedutilizingamodular,full-stack web building methodology with MongoDB as the database, Node.js and Express.js for the backend, and React.js for the frontend. Teachers and students use differentloginsitestoaccessthesystem.
Students submit their resumes when they register, and the database stores them as binary data in PDF format.
The resume is retrieved from a database and instantly parsed utilizing PDF parsing tools when students log in. The LLaMA language model receives the extracted text and returns structured data like name, email, location, andskills. Withoutstoringtheparsedinformationinthe database, this data is subsequently used to dynamically fillthestudent'sprofileonthefrontend.
A special faculty code that verifies their position is used by faculty users to register. By providing employment specifics, such as necessary skills, they can publish new job openings. These job openings are displayed in a specialareawhereacademicscanrevieweachone.When the "Analyze" button is clicked, the system uses the LLaMA model to compare the parsed skills from all student resumes with the skills needed for the position. Faculty can clearly see which candidates are the best fit thanks to the calculation and sorting of match percentages in ascending order. For offline reference, a CSVfilecontainingtheanalysiscanalsobedownloaded.
Through RESTful APIs, the system guarantees secure data processing, real-time interactions, and smooth frontend-backend communication. Below is the workflowoftheapplication.

The LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) model powers the fundamental AI features. The algorithm operatesinthesubsequentstages:
ResumeParsing:Aparser(suchaspdf-parse)is used to extract text from the uploaded resume PDF.
Text Analysis: The LLaMA model receives the extracted material, processes it, and extracts pertinent fields like name, location, contact information,education,andskills.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:04|Apr2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Skill Matching: The student's extracted skill set is comparedtothe necessary skills for each job posting.
To assess appropriateness, the overlap % is calculated.
Sorting of Results: To facilitate evaluation and decision-making, the results are sorted by matchpercentage.
In addition to improving student-job matching accuracy and doing away with manual evaluation, this AI-driven process is scalable and flexible enough to accommodate variousjobprofiles.
A full-stack online application, the Placement Cell System facilitates smooth communication between instructors and students. React.js is used in the development of the frontend, which offers a role-based and dynamic user experience. The backend, which was constructed using Node.js and Express.js, uses RESTful APIs to manage data routing, resume uploads, job postings,andauthentication. ThedatabaseisMongoDB, which stores resumes and user credentials in a binary format(ArrayBuffer).
A student submits their resume in PDF format when they register. This resume's text is not extracted or stored; instead, it is safely kept in the database. Following a student's login, the backend retrieves the binary data, uses a PDF parser to transform it into legibletext,andthentransmitsittotheLLaMAAImodel.
The student's profile is shown in real-time on the frontend once the model processes the data and produces structured JSON with personal information andcompetencies.
Duringregistration,facultyusers'accessisverifiedwith a pre-established faculty code. Faculty can add new job listings with pertinent information, like necessary abilities,afterloggingin. Facultycaninitiateanalysisfor each of these positions, which are displayed in a panel of job listings. The system determines a match percentage for each student after comparing the parsed student skills with the needed abilities using LLaMA when the "Analyze" button is clicked. In order to assist faculty in making data- driven judgments when shortlisting candidates, the findings are sorted and suppliedinadownloadableCSVformat.
To guarantee a seamless user experience, role-based navigation, variable side generating, secure session management,andreal-timedatafetchingareallhandled effectively. Future expansion and scalability are also madesimplebythesystem'smodulardesign.
The findings of the intelligent web-based placement management system show that AI-driven elements that improve the placement process for professors and students have been successfully integrated. The overall placing process was enhanced by the LLaMA model's promising accuracy in analyzing student resumes and matching them with pertinent job advertisements. Additionally, the faculty and student role- based dashboards showed smooth communication, enabling faculty to post job openings and evaluate skill matches while students uploaded resumes, applied for positions, andtrackedtheirapplications.
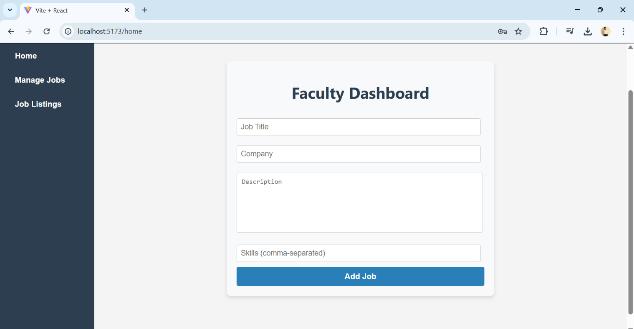
Fig5.1Facutlyviewtoaddjobs
After registering using a secure faculty code, users gain access to a personalized dashboard (Figure 5.1), which includesfeaturessuchasHome,AddJob,andJobListings. Facultymemberscanpostjobopportunities.
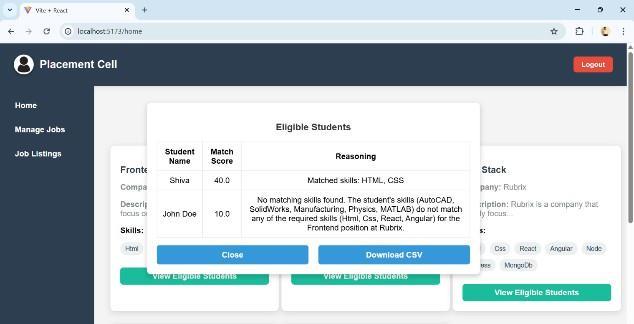
Fig5.2Facultyviewtodownloadeligiblestudentlist
Examine every listing that has been added in the past using a structured interface (Figure 5.2). The AI-based resume analysis utilizing the LLaMA model, which creates accurate skill match percentages by comparing student talents with job requirements, is a crucial feature. Faculty members can also download these analytical findings as CSV reports, which enables offline evaluationandbetterhiringdecisions.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:04|Apr2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
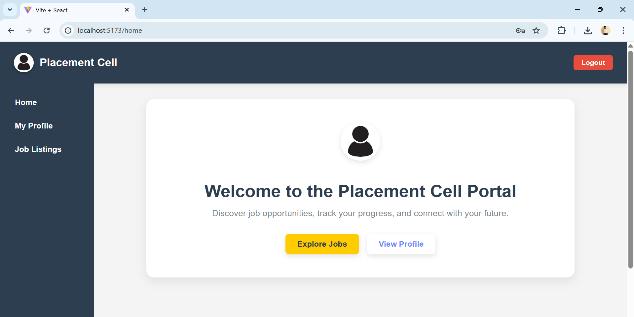
Fig5.3Studentview
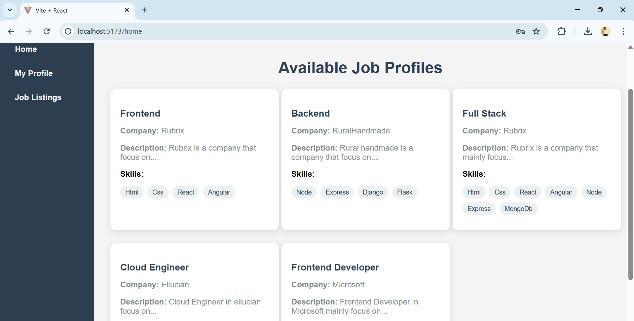
Fig5.4Displaysavailablejobstostudents
Students are greeted by a tidy dashboard (Figure 5.3) whentheylogin,whichallowsthemtoreadtheirprofile, apply for jobs, and investigate employment openings. Using real-time parsing with the LLaMA model, the Profilesectionisdynamicallycreatedfromthestudent's uploaded resume. Students are shown the available job area(Figure5.4).
An inventive and perceptive method of overseeing the campushiringprocedureisprovidedbythepoweredby AIPlacementCellSystemdescribedinthisresearch. The solution effectively automates resume processing, allows for real-time student profile development, and supports data- driven choices through AI-based talent matching by fusing artificial intelligence with contemporary online technologies. By eliminating the storage of resume material that has been removed, the role-based architecture preserves data privacy while guaranteeing a customized experience for both professorsandstudents. Thetimeandeffortrequiredto shortlist candidates is greatly decreased since faculty members are equipped with the means to evaluate applicants'suitabilityandobtainorganizedreports.The solutionoffersascalablefoundationthatcanbeadjusted to changing recruitment needs in addition to improving operational efficiency. This study lays the groundwork for future smarter, more transparent placement algorithms while showcasing the useful effects of AI in educationalinstitutions.
[1.] R. K. Kousik and G. Nagappan, "Computer Human Interface for Placement Management System," 2024 IEEEInternationalConferenceonComputing,Power and Communication Technologies (IC2PCT), Greater Noida, India, 2024, pp. 1245–1248,doi:Student Placement Prediction," 2022 2nd 10.1109/IC2PCT60090.2024.10486671.
[2.] T. Maragatham, P. Yuvarani, S. Harishri and R. Swetha, "Student Placement Prediction using Deep Learning Techniques," 2024 8th International Conference on Electronics, CommunicationandAerospaceTechnology(ICECA), Coimbatore,India,2024, pp. 620–626,10.1109/ICECA63461.2024.10800998.
doi:
[3.] D. S. Prakash, S. KM, D. R, S. S. R and P. M. B, "An Integrated Web-Based Platform for Enhanced College Placement Management and Student Engagement," 2024 10th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 2024, pp. 26242628, doi:10.1109/ICACCS60874.2024.10717061.
[4.]AshokMVandApoorvaA,"Dataminingapproachfor predicting student and institution's placement percentage," Conference 2016 International on Computation System and Information Technology forSustainable Solutions(CSITSS),Bengaluru,India, 2016, pp. 336340, doi: 10.1109 /CSITSS.2016.7779381.
[5.]G.L.L.SilvaI,T.L.Jayasinghe,R.H.M.Rangalla,W.K. L. Gunarathna and W. Tissera, "An Automated System for Employee Recruitment Management," 2022 4th International Conference on Advancements in Computing (ICAC), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2022, pp. 346–351, 10.1109/ICAC57685.2022.10025159.
doi:
[6.]M.Manike,P.Singh,P.S.Madala,S.A.VargheseandS. Sumalatha, "Student Placement Chance Prediction Model using Machine Learning Techniques," 2021 5th Conference on Information and Communication Technology (CICT), Kurnool, India, 2021, pp. 1–5,10.1109/CICT53865.2020.9672372.
doi:
[7.]R.GarciaandJ.Puig,"StudentInternshipPlacements: Improving the quality of engineering internship programmes," IEEE EDUCON 2010 Conference, Madrid, Spain, 2010, pp. 91–98, doi: 10.1109/EDUCON.2010.5492592.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:04|Apr2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
[8.] C. S. K and K. S. Kumar, "Data Preprocessing and Visualizations Using Machine Learning for International Advancements Conference in Computational on Technological Sciences (ICTACS), Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 2022, pp. 386 391, doi: 10.1109/ICTACS56270.2022.9988247
[9.]G.M.SpandanaandL.Pallavi,"PlacementPrediction System using Machine Learning," 2023 2nd International Conference on Edge Computing and Applications (ICECAA), Namakkal, India, 2023, pp. 903–907,10.1109/ICECAA58104.2023.10212409 doi:
[10.]M. S. Surya, M. S. Kumar and D. Gandhimathi, "Student Placement Prediction Using Supervised MachineLearning," 2022 2nd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 2022, pp. 3521355,doi:10.1109/ICACITE53722.2022.982364
[11.]T.Varsha,Y.C.Shekar,S.P.Shankar, A. Bharadwaj, D. Varadam and M. S. Supriya, "On Campus Student Recruitment Analysis using Machine Learning techniques," 2023 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India, 2023, pp. 1–6, doi: 10.1109/CONECCT57959.2023.10234797.
[12.] C. Cai, K. Yan, H. Lu and M. Ye, "Intelligent Placement Model Based on Decision Tree," 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Hangzhou, China, 2018, pp. 837–841, doi: 10.1109/ITME.2018.00188.
[13.] S. K. Thangavel, P. D. Bkaratki and A. Sankar, "Student placement analyzer: A recommendation system using machine learning," 2017 4th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 2017, pp. 1–5, doi: 10.1109/ICACCS.2017.8014632.
[14.] P. Pathak, N. Bansal and S. Singh, "Mulyankan: A prediction for student's performance using Neural Network," 2015 2nd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom),NewDelhi,India,2015,pp.46–49.
[15.] D. R. Ramani, B. Rajalakshmi, S. K. B. V,R. Sarkar, S. Das and V. Dadyala, "DreamCraft: A Captivating Web Oasis for Seamless Job Placements," 2024 International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Security, Communication and Sustainable Development
(CISCSD),PortBlair,India,2024,pp.67–71,
doi:10.1109/CISCSD63381.2024.00027.