
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sachin Srivastava1 , Prakhar Dwivedi2 , Ayush Kanoujia3 , Shivendra Singh4, Er. Anjali Tiwari5
1,2,3,4 B. Tech Students Department of Civil Engineering, Axis Institute of Technology and Management, RoomaKanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India
5Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Axis Institute of Technology and Management, RoomaKanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India ***
Abstract - The process of planning and crafting a structure is an artistic endeavor with the goal of ensuring safety, functionality, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Successful structural planning requires not only creativity and conceptual thinking but also a solid grasp of structural engineering principles, practical considerations, design codes, and building regulations based on hands-on experience. While architects typically address functional and aesthetic aspects, structural engineers concentrate on guaranteeing the safety, functionality, durability, and costeffectiveness of the structure.
In this specific project, a site has been chosen for an 2B+G+9 story building with four apartments on each floor, providing essential residential facilities. The primary focus is on analyzing and designing the apartment building, considering only dead load and live load for analysis and design. Dead loads are determined following IS-875 (Part 1), and live loads are based on IS-875 (Part 2). AutoCAD is used for creating the plan and elevation, with a focus on the exterior appearance.
For analysis, E-Tabs software is employed, while the manual design of structural elements such as slabs, beams, columns, and footings is undertaken. The project strictly adheres to building by-laws, and the design complies with specified codes, including IS:456-2000 for Plain and Reinforced Concrete and SP-16 for Design Aids for Reinforced Concrete. Additionally, the Code of Practice of Design Loads (IS: 875 Part 1 and Part 2) is applied throughout the design process.
Key Words: ETABS, WIND ANALYSIS, P-DELTA ANALYSIS, BUCKLING ANALYSIS, MODAL ANALYSIS
In the intricate process of planning, analyzing, and designing a 2B+G+9 residential building, a structured approach is imperative to ensure a seamless transition from conceptualization to execution. The initial planning phase involves meticulous site selection, taking into account factors such as accessibility, utility availability, and adherence to zoning regulations. Simultaneously, client requirements are carefully assessed, and project
goals are defined, forming the foundation for subsequent designdecisions.
The analysis phase, conducted using ETABS software, is a critical step in guaranteeing the structural integrity and safety of the building. Structural assessments are performed to understand the load-bearing requirements, followed by detailed load calculations encompassing live loads, dead loads, and other relevant factors. The utilization of ETABS for seismic analysis ensures that the structural design meets stringent safety standards, especially crucial for multi-story buildings. This phase is pivotalindeterminingtherobustnessandresilienceofthe structureinthefaceofpotentialenvironmentalchallenges.
Subsequently, the design phase unfolds, primarily orchestrated through AutoCAD software. This stage involves the creation of comprehensive architectural designs, including detailed floor plans and elevations. AutoCAD facilitates the integration of structural design elements, ensuring alignment with the analysis results obtained from ETABS. The software proves instrumental in developing construction drawings that provide precise dimensions and specifications, laying the groundwork for the physical realization of the residential building. The process is iterative, with constant refinements based on feedback and evaluations. Coordination between architectural and structural aspects is paramount, and AutoCAD becomes the tool of choice for revisions and updates, maintaining design consistency throughout the project's evolution. Collaboration among architects, structural engineers, and other stakeholders is fostered, ensuringaholisticandwell-coordinateddesignapproach.
A meticulous documentation process accompanies each phase, recording design decisions, calculations, and changes made during planning and design. This comprehensive set of construction documents serves as a blueprint for the construction team, ensuring that the envisioned 2B+G+9 residential building is executed precisely according to the design intent. In essence, the integration of ETABS and AutoCAD software in the planning, analysis, and design phases provides a robust frameworkfortheefficientandaccuratedevelopmentofa multi-storyresidentialstructure

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ApplyETABSsoftwareforthedesignandanalysis of a residential building encompassing two basements, a ground floor, and nine additional floors.
Evaluate the structure's stability and workability againstarangeofnaturalevents.
Confirmthestabilityofbeamsandcolumnsunder thespecifiedloadconditions.
Perform an analysis for shear and bending moments.
Conduct the analysis in accordance with all applicableIndianStandardCodesforbuildings.
The primary objective of structural design is to guarantee the strength, stability, and workability of the structure. The design must fulfill three key requirements: stability to prevent overturning, sliding, or buckling; strength to resist induced stress in various structural elements; and serviceability to ensure satisfactory performance under service load conditions, maintaining ample strength, stiffness, reinforcement, and limiting deflectionandvibrationwithinacceptablelimits
Examining the dynamic performance of a raft footing under different loads and investigating structural behavior concerning factors such as moments, punching shear, and deflection using SAFEsoftware
Nidhish Vijay Pawar et al. (2023)[1] design and analysis of a residential building comprising 22 floors (G+22) has been successfully completed. This software is characterized by user-friendly handling and a visually intuitiveinterface,enhancingefficiencyandsavingtime.It facilitates easy computation of required reinforcement in structures and provides a comprehensive 3D view of the structure.ETABS offers the capability to calculate wind loads and seismic loads acting on the structure, emphasizing its primary usage in the design and analysis offramedRCCstructures
U C Ahammed Kutty et al. (2022)[2] revealed challenges, and the structural engineer navigated constraints to align witharchitecturaldrawingsUtilizingETABS,thedesignof RCC frame components like beams and columns was meticulously undertaken, adhering to standard specifications as much as possible.The planning and design of a ten-story apartment building were executed, employing ETABS V15.2 software for thorough analysis. This software, renowned for its excellence, demonstrated remarkable efficacyinhandlingdiversestructural aspects Following the findings of the soil investigation report, an isolatedfootingwasimplemented
Dr. Alok Singh et al. (2019)[3]research, evaluation, and design process were undertaken for a multi-story residential building, consisting of ground plus 25 stories. The structure includes ground-floor parking and upperlevel apartments. AutoCAD was employed to design and detailallstructuralcomponents,whileanalysisanddesign utilized both STAAD and conventional criteria, making it an optimal choice for static and dynamic loads. Structural member sizes were calculated, incorporating dead, live, and seismic loads. Comprehensive deflection and shear tests were conducted on beams, columns, and slabs, confirming their safety. The project involved a blend of theoretical and practical work, ensuring a well-rounded completion
Manas Rathore et al. (2021) [4] focuses on the most economical column method, aiming to achieve this by reducingsectionsizes.Giventhattheloadisgreateratthe bottom than the top, it's unnecessary to provide a larger column size at the top. By adhering to IS Codes, we can optimizecolumndesignbyprovidingtherequiredamount specified.Typically,theminimumpercentageofsteelarea is 0.8% of the Gross cross-sectional area, while the maximum is set at 6% according to IS code.With increasing structure height, the slenderness effect or long column effect becomes significant. Utilizing ETABS software not only saves working time but also facilitates accuratestructuredesign
Harendra Nath Pandey et al. (2020) [5] is modeledafter E-Tabs,ensuringoptimalserviceability,strength,andcosteffectiveness. Utilizing ETABS software not only saves time but also enhances the precision of structural design. Structural elements were devised through both manual methods and software assistance. Urban areas, constrained by limited land, prompt the construction of multi-story buildings to maximize vertical space utilization. Instead of clearing forests and swamps for housing, shopping centers, and factories, placing them in verticaltowersisasustainableapproachtoenvironmental preservation.
Dr.G.D.Awchat et al. (2021)[6] The utilization of ETABS software not only streamlines the analysis and design processes, significantly reducing time, but also ensures high accuracy. This software facilitates the easy retrieval ofstructurevalues,accommodatingdiversezonesandsoil types. The values vary based on soil conditions; for instance, soil 1 yields lower values, while soil 3 presents higher values. This observation indicates that soil 1 has a lowerbaseshearcomparedtosoil2andsoil3.
Dr. Yusuf et al (2021)[7] - analysis results align with geotechnical and structural engineering codes, aiding in predicting natural threats, preventing issues, and comprehending soil foundation behavior over time.Some

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
researchers have explored soil profiles like Aeolian and black cotton, directly impacting the Safe Bearing Capacity (SBC) and the structures built on them.Enhanced bearing capacity during compaction is a key feature in the soft foundation during the subclass filling stage. Laboratory studies in soil mechanics contribute to precise soil foundation design, improving failure mitigation. Soil mixing designs have been utilized in geotechnical engineering to enhance soil properties. Emphasizing the importance of studying foundation design concerning soil conditions is crucial for achieving stable and secure designs for high-rise and multi-storey buildings. Evaluation of earthquake-resistant buildings, considering foundation depth, can be conducted manually or through software, utilizing both linear and non-linear approaches for structural analysis. Assessment of bearing capacity, employing manual methods and tests such as Standard Penetration Test (SPT) and Core test, is essential before constructing building designs. The study explores various software applications for analysis, including Plaxis, FEM, ABACUS, ETABS, incorporating 3D Finite Element Method (FEM) analysis. Some researchers base their studies on testing approaches to analyze soil, foundation, and failure mechanisms
Zia-abe Deen. S. Punekar et at. (2017) [8] concludesthat the analysis and design of the Raft footing focus on the critical envelope combination, particularly for dynamic scenarios. Regarding moment considerations, the study indicates that the steel area obtained from the SAFE software's envelope combination matches that obtained fromstrips,affirmingthedesignprocess'svalidityforthis combination. Additionally, the study finds the mat/raft foundation to be safe against punching shear or two-way shear, with a punching shear ratio below 1. Observations on deflection reveal a slight hogging deflection in the raft footing, deemed within acceptable limits and not detrimental to the building. The detailing and casting processforraftfootingsissimplifiedcomparedtoisolated footings,withexcavationandconcretepouringcompleted simultaneously,leadingtocostandtimesavings.
The methodology for planning, analyzing, and designing a residential building with two basements, a ground floor, and nine additional levels using ETABS and AutoCAD comprisesseveralsequentialsteps:
Project Initiation:
Definetheproject'sgoals,limitations,andscope. Collect information on the site, including geography, soil conditions,andlocalregulations.
Architectural Planning:
Collaborate with architects to devise the building layout, considering functional needs, aesthetics, and local zoning regulations.
Utilize AutoCAD for detailed structural drafting, creating construction drawings with precise measurements and requirements.
Ensure synchronization between structural and architecturaldrawings.
Structural Conceptualization:
Createan initial structural concept based on architectural plans.
Identify load-bearing elements, lateral force-resisting systems,andpreliminarymembersizes.
ETABS Modeling:
Generate a comprehensive 3D model of the structure in ETABSbyinputtingsectionandmaterialinformation. Assign names to the model's supports, loads, and constraints.
Structural Analysis:
Conduct structural analysis in ETABS to assess the building'sresponsetovariousloads,suchasgravity,wind, andseismicforces.
Evaluatestability,deflections,andmemberforces.
Design Optimization:
Refine thestructural design based on the analysisresults, ensuringcompliancewithsafetyandcodestandards. Repeattheprocessasneededforoptimization.
Detailing and Drafting:
Use AutoCAD for detailed structural drafting, producing construction drawings with precise dimensions and specifications.
Maintain coordination between architectural and structuraldrawings.
Foundation Design:
Consider structural requirements and soil conditions in designingthefoundationsystem.
UtilizeETABSforfoundationanalysisanddetailing.
Seismic Design:
Enhance the building's seismic performance through a thoroughseismicstudyinETABS,incorporatingnecessary designelements.
The architectural plan, section, and elevation of the building were drafted in AutoCAD 2021. Dead loads were derived from material unit weights specified in IS 875 (Part I): 1987. Live loads were determined based on IS 875 (Part II: 1987. Preliminary dimensions of beams and slabsconformedtoIS456-2000.Loadcalculationsforonewayandtwo-waycontinuousslabswereperformedusing Excel Sheets. Universal Excel sheets were prepared for designing one-way continuous slabs and two-way continuousslabs.Earthquakeloadwascalculatedusing IS 1893(PartI):2016.Buildinganalysiswasconductedusing

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ETABS 2021, and moments, shear forces, and axial forces were obtained. Structural element design, including beams, columns, and foundations, was carried out using theobtainedresults.
Design codes:
Thestructuraldesigniscarriedoutwiththeconsideration of latest Indian codes and standards, the codes are which arereferredforthisprojectareshownbelow
ISCODE DESCRIPTION
IS456:2000 PLAIN AND REINFORCEMENT CONCRETE
IS875(PART1):1987 DEADLOAD
IS875(PART2):1987 LIVELOAD
IS875(PART3):1987 WINDANALYSIS
IS1893:2016 SEISMICANALYSIS
Table1; DESIGNCODES
Fig1:FramingStructure
4. STRUCTURE DATA
4.1. STORY DATA
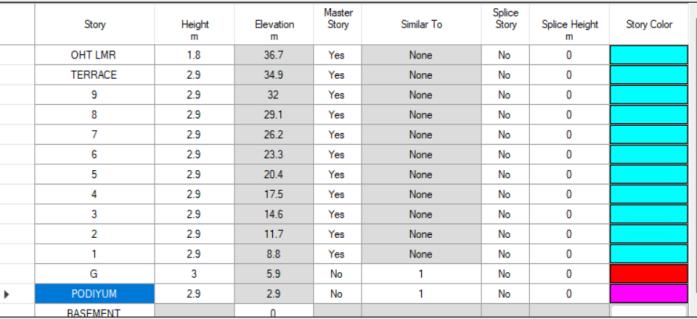
FIG2:STOREYDATA
4.2. SECTION PROPERTIES
DESCRIPTIO N SIZE
FE500 FE415
200 M35 FE500 FE415
Table2:SectionProperties

4.3.
Table5:LoadPattern
5. ANALYSIS IN ETABS
51. SEISMIC ANALYSIS
Fortheanalysispurposeweconsidertwotypesofanalysis Static analysis and Dynamic analysis both analysis have theirownsignificance.
Mass source
Seismicweightofthestructure–itisthesumofdeadload andspecifiedamountofimposedloadsonthestructure. D=1&L=0.25ifimposedloadlessthan3kN/m2.
D=1 & L=0.25 , L>3=0.5 if imposed load greater than 3kN/m2.
ReferIS1893:2016Part1Table-10Clause7.3.1
SeismicZone III
Seismic Zone Factor(Z) 0.1
SiteType TypeII
Importance Factor(I) 1.2
Response Reduction Factor (R) 3
Table 3 (clause 6.4.2)
Table 3 (clause 6.4.2)
Table 4 (clause 6.4.2.1)
Table 8 (Clause 7.2.3)
Table 9 (clause 7.2.6)
DampingRatio 0.05 (Clause7.2.4)
SoilProfile Aspersoilreport Type2
Table6:GeneralDesignParameter
CALCULATED BASE SHEAR
Table7:BaseShear
5.2. WIND ANALYSIS
Computation of Wind analysis parameter is done by referring IS 875 Part 3 1987
Class of the Structure General Clause 5.3.1 table 1
Probable Design Life(Years) 50 Basic Wind Speed,(Vb) 47m/s
5.2 AppendixA Risk Co-efficient, K1 1.0
Table8:WindAnalysisParameter

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The P-Delta analysis isa type of Geometric nonlinearity, which accounts for secondary structural behaviour when axial and transverse loads are simultaneously applied to beam or wall elements.P-Delta effect usually becomes prevalent in a tall structure that is experiencing gravity loadsand large lateral displacement due to wind or other forces.If the lateral displacement or the vertical axial loads are significant, P-Delta analysis should be performed.
Thisanalysisisperformedtillthetolerancelimitof0.0001 D=1.5or(D=1.2+L=1.2)whicheverisMore(IS456:Table 18).
InalltypesofanalysisP-deltaeffectisconsidered.
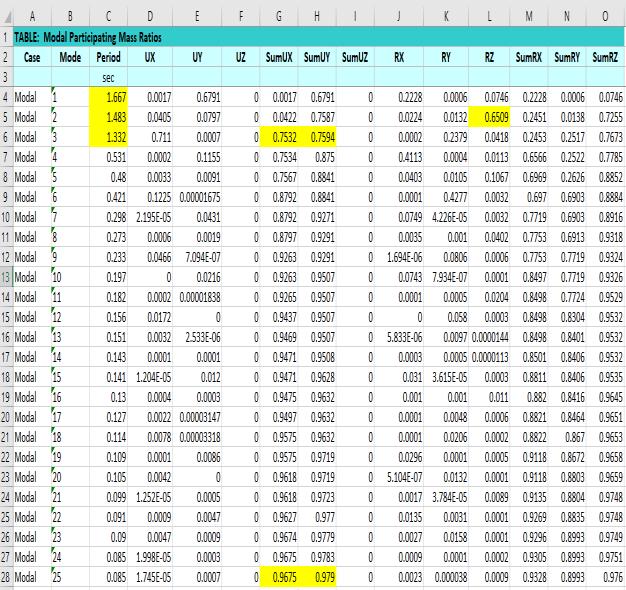
5.4. MODAL ANALYSIS
Firstthreemodesshouldcontributemorethan65%mass participation.
Thefundamentalnaturaltimeperiodofthebuildinginthe two principal plan directions are more than 10% difference and for principal plan directions to rotational mode10%timeperiodismandatory For N’th mode should contribute more than 90% mass participation.
IS 1893: table-6(vii) IS 1893 2016: clause 7.7.5.2
5.5. BUCKLING ANALYSIS:
Whenevertheelevationaspectratioisgreaterthan4then thebuildingisgovernbybucklinganalysis Itisglobalanalysis
Heightratio(H/W)=1.66
Inthisprojectbucklinganalysisisnotgovern
6.ANALYSIS RESULTS
The structure underwent ordinary momemt resisting frame analysis utilizing the joint coordinate command to define joint coordinates and initiate structural specifications. The member incidence command was
employed to establish connectivity between joints, modeling columns and beams with beam elements. Specific member properties were designated for each member. The analysis provided maximum design loads, moments, and shear for each member, guiding the subsequentstructuraldesignprocess.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
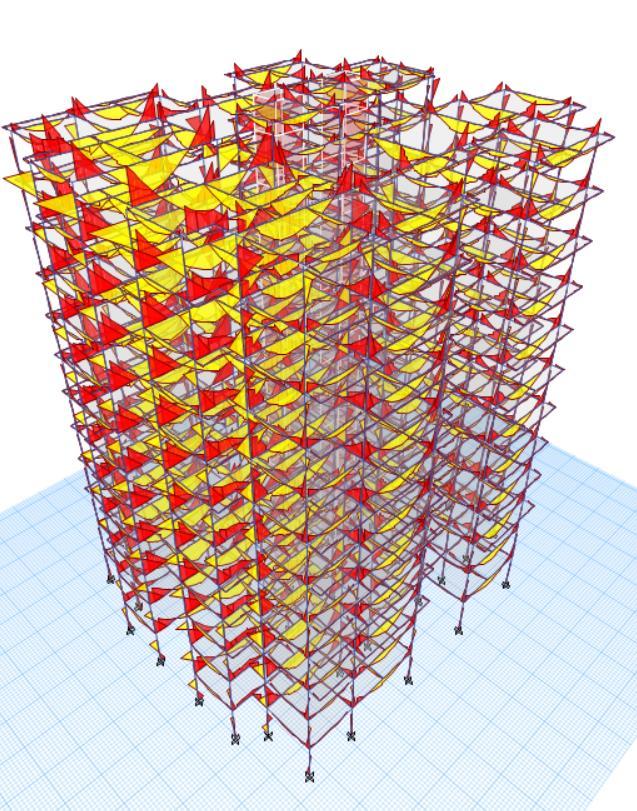
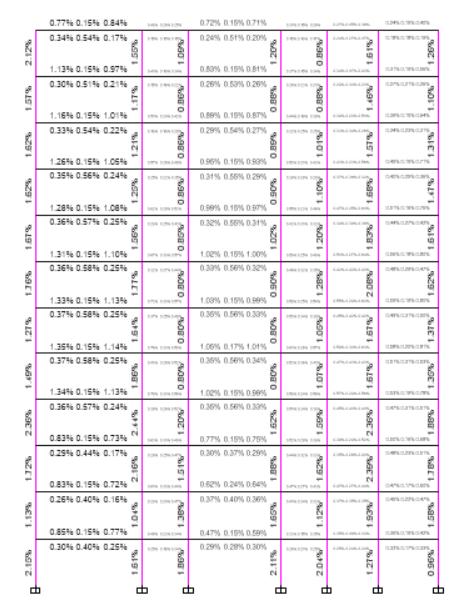
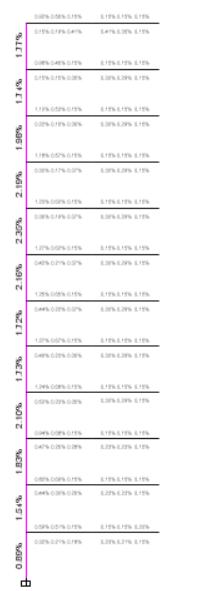
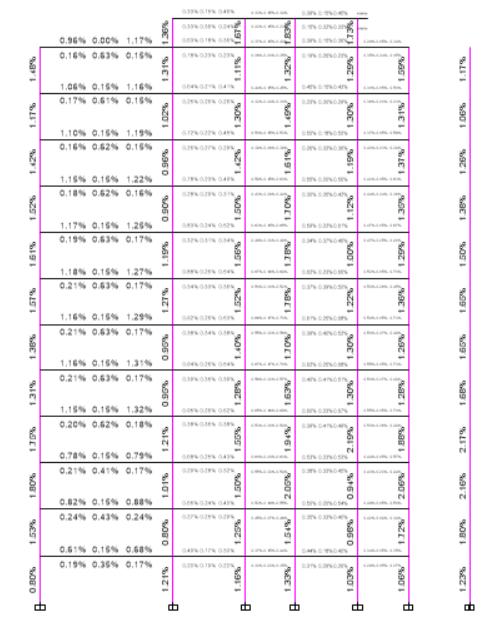
FIG6:BENDINGMOMENTDIAGRAM(IN3-3DIRECTION)
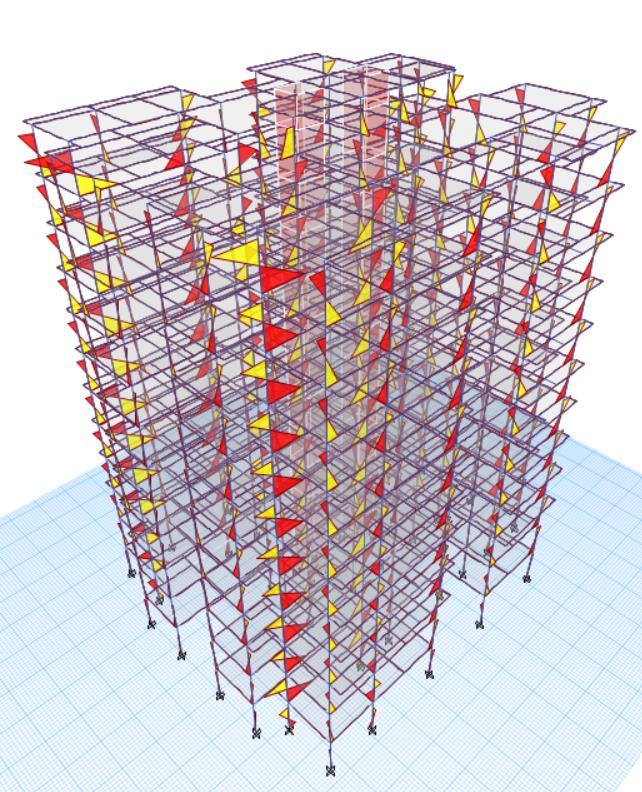
FIG7:BENDINGMOMENTDIAGRAM(IN2-2DIRECTION)
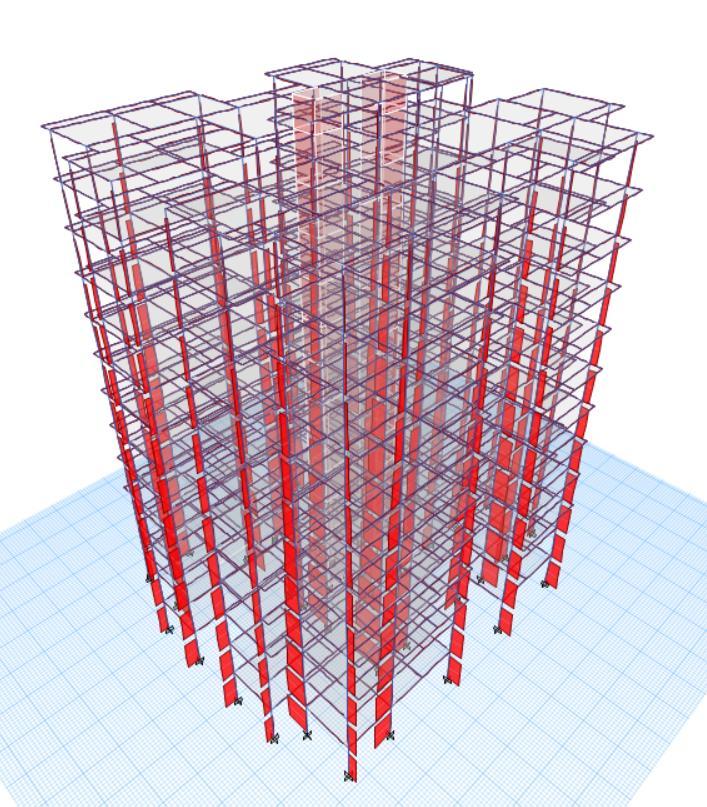
FIG8:AXIALFORCEDIAGRAM
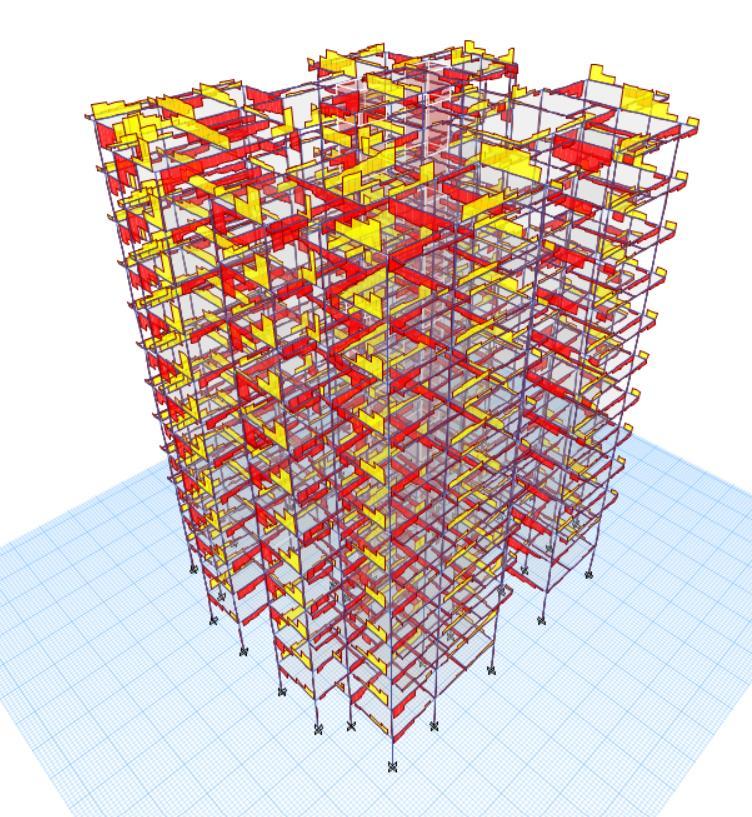
FIG9:TORSIONDIAGRAM(DEAD+LIVE)
7.CONCRETE FRAME DESIGN:
7.1.DESIGN LOAD COMBINATIONS:
Designing structures would become prohibitively expensiveifalltypesofforceswereappliedatalltimesfor maintaining serviceability and safety. To address this, the
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page131

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net
concept of characteristic loads has been embraced, ensuring that in at least 95 percent of cases, these loads are calculated based on the average or mean load from logical combinations of all mentioned loads. Standards such as IS 456:2000, IS 875:1987 (Part-V), and IS 1893 (Part-I):2002 specify the load combinations to be consideredinstructuraldesign.
DESIGN
LoadCombinations
Theprimarygoalofstructuraldesignistoensurethatthe designed structure can effectively fulfill its intended function and safely endure the various influences it will encounter throughout its useful life. These influences mainly include loads and other forces exerted upon the structure. Additionally, considerations should be given to factors like temperature fluctuations and foundation settlements. Thedesign methods employed for reinforced concrete structures encompass the working stress method, ultimate load method, and limit state method. In this context, the limit state method has been chosen for
thedesignofslabs,beams,columns,andstairs.Inthelimit state method, the structure is engineered to safely withstand all foreseeable loads during its lifespan while meeting serviceability requirements such as limiting deflection and preventing cracking. The acceptable safety and serviceability limits before failure are termed limit states. To ensure an adequate level of safety and serviceability, all relevant limit states must be taken into account during the design process. The structure should be designed based on the most critical state and subsequentlyverifiedagainstotherlimitstates.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ELEVATION3
ELEVATION4
ELEVATION5
ELEVATION7

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

FIG15:ELEVATION6

FIG16:ELEVATION8
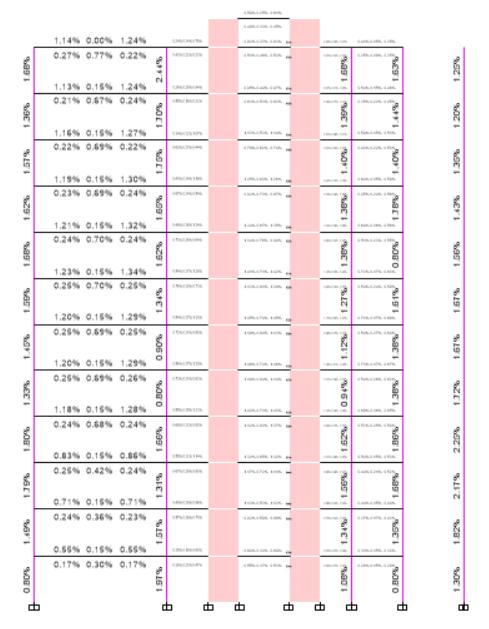
FIG17:ELEVATION9
FIG18:MathematicalModal
Foundation is a part of astructural systemthat supports and anchors the superstructure of abuildingand transfersitsloadsdirectlytotheearth.
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page134

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
In this project we have considered isolated footing based ongeotechnicalreport.
The SBC of the soil is 250 kN/m2 based on geotechnical report.
Theallowablesettlementforisolatedfootingis50mm. We have used M40 concrete grade, Fe500 & Fe 415 steel grade
9.1. Load combinations used for analysis and design of foundation
STRENGTH LOAD COMBINATION SERVICE LOAD COMBINATION
1.5D+1.5L 1D+1L
1.5D+1.5SPECX 1D+1SPECX
1.5D+1.5SPECY 1D+1SPECY
1.5D+1.5W0 1D+1W0 1.5D–1.5W0 1D–1W0
1.5D+1.5W90 1D+1W90
1.5D–1.5W90 1D–1W90
1.2D+1.2L+1.2W0
1.2D+1.2L+1.2W90 1D+0.8L+0.8W0
1.2D+1.2L–1.2W90 1D+0.8L–0.8W0
1.2D+1.2L+1.2SPECX 1D+0.8L+0.8W90
1.2D+1.2L+1.2SPECY 1D+0.8L–0.8W90
0.9D+1.5W0
0.9D–1.5W0
0.9D+1.5W90
0.9D–1.5W90
0.9D+1.5SPECX
0.9 D+1.5SPECY
Table10:LoadCombination
9.2.Material properties
Raftsize–28.95mX24.25mX0.6m.
Dropsize
Table11:DropSize
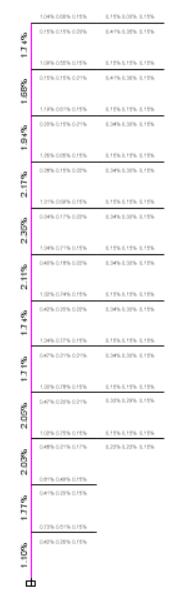
9.3.Ground Bearing pressure check (GBP)
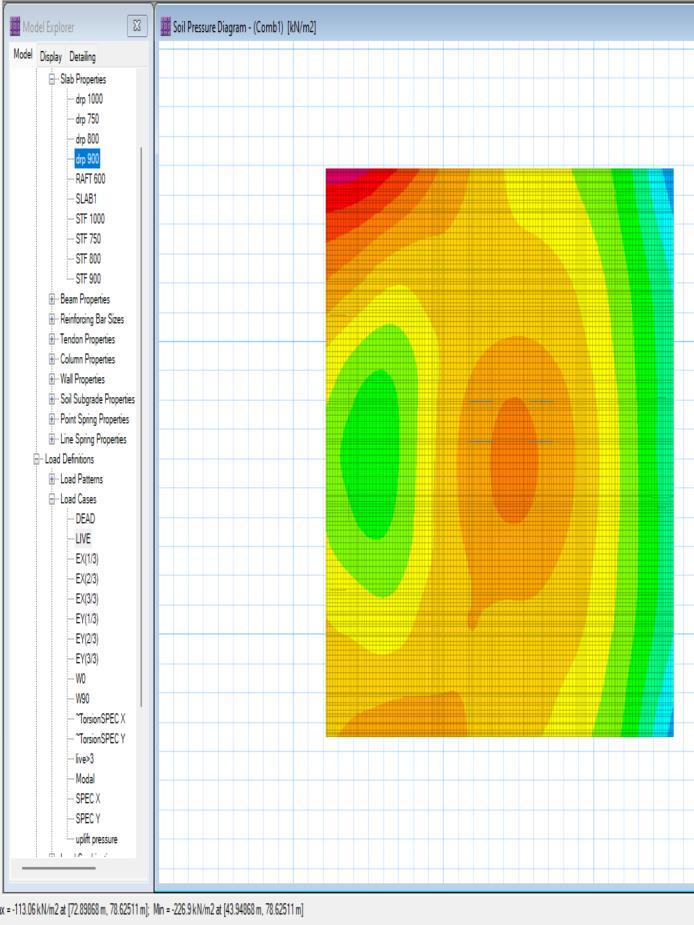
Fig19:GROUNDBEARINGPRESSURE

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The ground bearing pressure should be less than SBC giveningeotechnicalreport.
TheSBCis300kN/m2 >GBP226kN/m2.Henceitissafe.
9.4. Settlement check
The maximumallowable settlement forRaft foundation is 50mmfor(D+L)combination. The allowable settlement (50mm) > the settlement occurring (45mm),Hencesafe
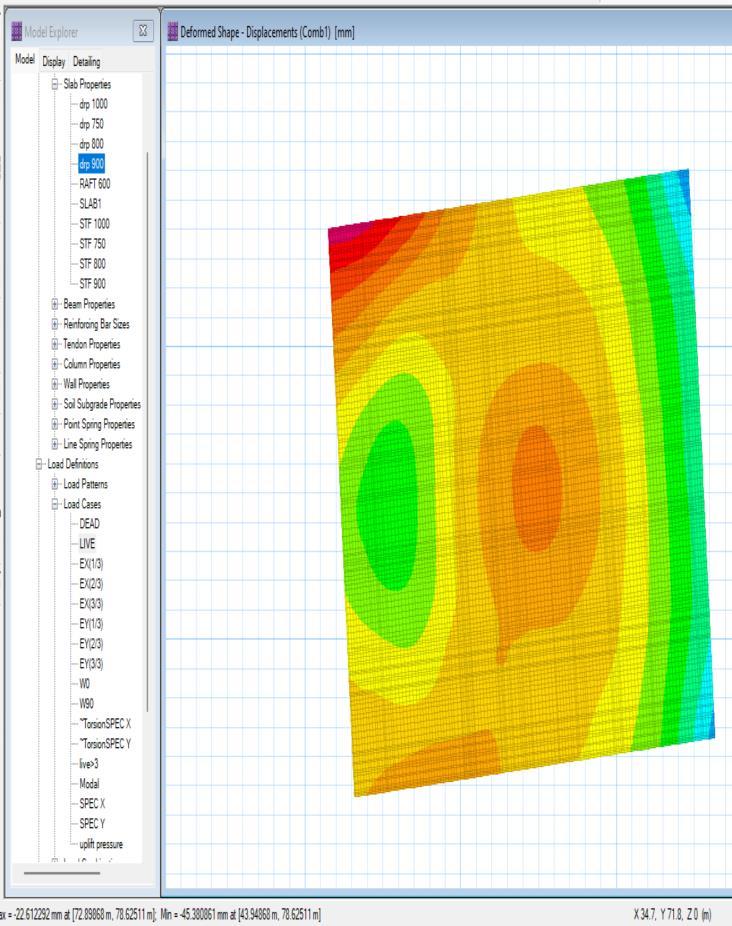
9.5. Punching shear check
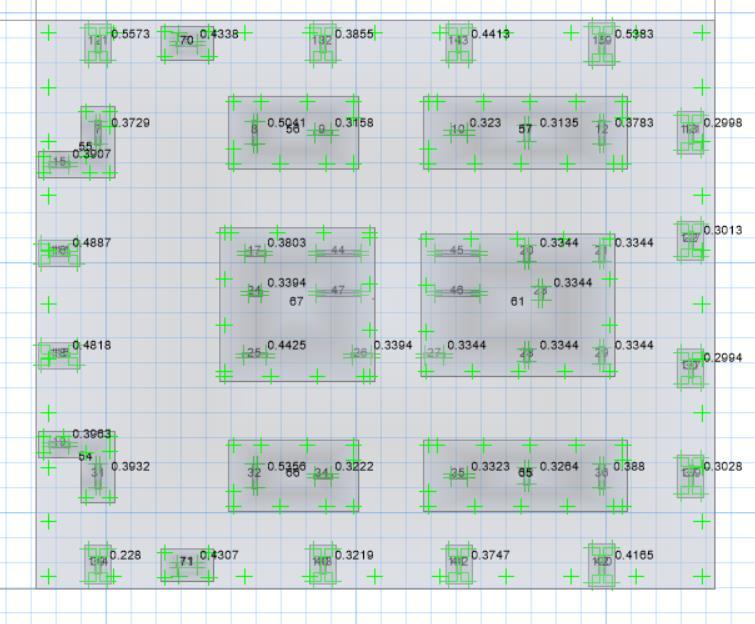
Punchingisaservicecriteriasothepunchingischeckedin serviceloadcombination.
Thepunchingratioshouldbelessthan1.
Thepunchingratioisnotdisplayedforshearwallitshould bemanuallychecked.
Thepunchingratioislessthan1,Hencesafe
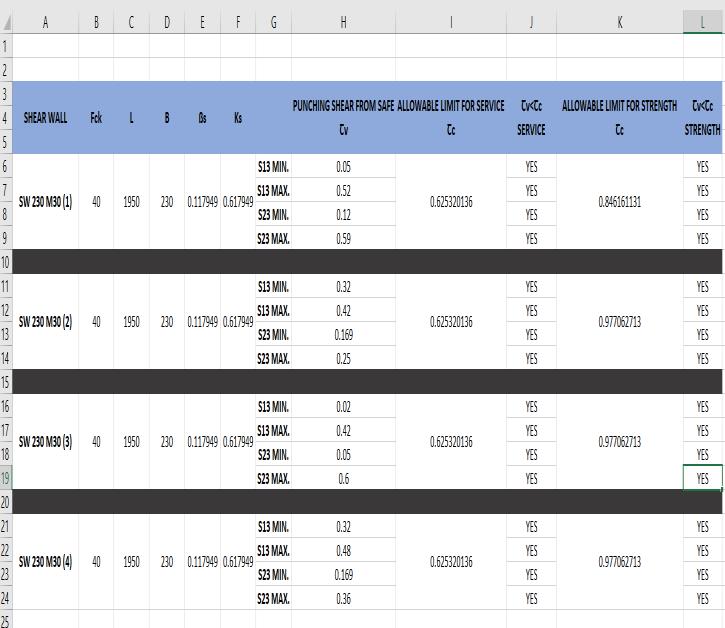
9.6. Punching check for shear wall

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Punchingstressesatthedistance d/2 fromtheedgeofthe columnshouldbelessthan 0.25 (β+0.5) forstrengthenvelope.
The stressSW1 & SW2and SW Combined foting are< Tc, hencesafe
Slab reinforcement design & Crack width check
The design and analysis tasks performed using ETABS can also be replicated in Staad Pro for resultcomparison.
In addition to designing, attention must be given to the provision of foundations and tanks within theprojectscope.
Dynamicanalysisisa crucial aspectthat needsto be conducted to assess the structural response effectively.
Diverseoptionsforslabs,columns,variousfooting types, and foundation designs can be explored and applied as part of the project's flexibility and adaptability.
Table12:SlabReinforcementDetail
Crackwidthisperformedinnon-lineartypeofanalysisin strengthloadcombination.
Themoment(m11)indirection1andthemoment (m22) indirection2iscalculatedusingserviceenvelope. Theareaofsteelrequired(ast)iscalculatedusingstrength combination in both direction 1& 2.For isolated footing only bottom reinforcement is given & for combined footing both top and bottom is given. Maximum crack widthallowedis0.2mm.
10. Conclusion
ThedesignbasedonE-Tabsensurestheadequacy of the structure concerning serviceability, strength,andcost-effectiveness.
The use of ETABS software not only saves time but also improves the precision of structural design.
Structural elements underwent design using a combination of manual methods and software assistance. Urban areas, dealing with limited available land, choose multi-storey constructions tomaximizetheutilizationofverticalspace.
Instead of clearing forests and swamps for construction, vertical towers can accommodate residences, shopping centers, and factories, contributing to the preservation of the environment.
Utilizing both software and manual analysis methods, providing comprehensive details on various depth cases, assessing the number of floors needed based on the soil's safe bearing capacity, presenting a case study demonstrating plate load test execution, illustrating the subsurface strata profile in a specific research location, and conducting foundation analysis usingsoftwaremechanismsfordifferenttypes.
[1] Nidhish Vijay Pawar, Neel Sanjay Patel, Rajan Mayaram Verma, Qureshi Mohammed Naved, (2023) “Design and Analysis of G+22 Residential Building Using ETABS journal (IJAEM) Volume 5, Issue 4 April 2023,pp:1604-1612ISSN:2395-5252”
[2] FathimaShalbana,NibaE,FarsanaCV,AthulyaVijay N,(2022)“AnalysisandDesignofMultistoreyBuilding usingETABS journal (IJERT)ISSN: 2278-0181 Vol.11 Issue05“
[3] Anjum Asfi, Vikash Kumar Badal, Dr. Alok Singh, (2022) “ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF MULTISTORIED EARTHQUAKE RESISTANT BUILDING G+25 journal (IRJET)e-ISSN:2395-0056Volume:09Issue:02”
[4] Ayush Chandrakar, Manas Rathore, (2021) “257 Design of Multistoried Residential Building (G+5) UsingETABSsoftwarejournalIJSDRVolume6Issue5 ISSN:2455-2631”
[5] Abhishek Kumar Ranjan1 , Aditya Pratap Singh2 , Harendra Nath Pandey, (2022) “Analysis and Design of G+21 Building using ETABS journal (IJRASET) Volume10IssueIIIISSN:2321-9653”

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
[6] Shubham Borkar, Dr.G.D.Awchat , (2021) “ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF G+6 BUILDING IN DIFFERENT SEISMICZONES BY USING SOFTWARE journal (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 Volume: 06 Issue:05 p-ISSN:23950072”
[7] Mr.PiyushKumarTripathi,Dr.Yusuf,Mr.Arvind Vishwakarma, (2021) “A Review on Analysis of Foundation & its Super Structure under the SBC ConditionofSoilSBCjournal(IJCET)E-ISSN2277 –4106,P-ISSN2347–5161”
[8] Zia-abe Deen. S. Punekar, M H Kolhar , Anjum Algur , Kushappa M K, (2017) ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF RAFT FONDATION JOURNAL IJRET eISSN: 2319-1163 |pISSN:2321-7308”
[9] CSIUSERGUIDE
Volume: 11 Issue: 02 | Feb 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified
|