
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
D 1 , H.SAnuja ,M.E,2
1PG Scholar, BioMedical Engineering, Udaya school of engineering, Kanyakumari.
2Professor BioMedical department, Udaya school of engineering, Kanyakumari.
Abstract The heart is a vital organ in the human body because it acts as a pump, delivering nutrients and oxygen to the body while also transporting waste products from metabolism, including carbon dioxide, to the lungs. Therefore, the human body's heart health is extremely important. Surgical problems are more likely to occur in older patients with pre-existing heart conditions. It is essential to keep an eye on the heart to prevent this risk. Most of the previously developed heart issue monitoring systems are unable to identify environmental factors in real time and provide cost-effective real-time heart monitoring. An Internet of Things (IoT)-based real-time postoperative cardiac disease patient monitoring system was developed in order to address this issue. The designed device is portable, easy to use, and reasonably priced. The user will be able to test many heart parameter indices simultaneously, and the results will be shown in a mobile application. Anybody can use the system because of the way it is designed. The Arduino UNO is used in conjunction with a variety of analog sensors to monitor different aspects of the heart. In this system, the heart is monitored by the temperature, pressure, and heart rate sensors. To ascertain the ambient state, a temperature is used. Numerous people were used to test and validate the strategy. In order to evaluate and detect heart activity in real time, the system continuously monitors a large number of individuals. The data processing capabilities of the system may disclose cardiac activity in some of the people being watched, as well as the cause of heart disease. We may deliver cephalosporins in regular interval to the patients automatically by using parameters.
Keyword’s:MobileHealthApplication(mHealth), Automated Drug Administration, Cephalosporin Delivery, Wearable Medical Devices, Remote Patient Monitoring,SmartHealthcareSystem.
In recent years, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) have emerged as the primary cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The 12-lead electrocardiography (ECG), a non-invasive test, is frequently used to diagnose CVDs. Artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted automatic
diagnosis systems have garnered significant interest in clinical practice due to the swift advancements in deep learning and AI. The majority of these systems are made for a certain environment in which there are enough annotated samples that are evenly distributed and only belong to one class of CVDs. Unfortunately, this ideal environment is not always possible in the complex realworldsetting,whereitcanbedifficulttocollectannotated ECG segments and several CVDs can be recognized from each segment. Additionally, it is possible that the test and training data in the actual world are not drawn from the same distribution, which significantly impairs the model's performance. Current systems' clinical applications are limited by the gap between the ideal and real-world environments. In summary, the clinical implementation of autonomous diagnosis systems presents three challenges: 1) The issue of label scarcity. 2) Inadequate results on hidden datasets. 3) Multiple CVDs occurring at the same timeOneofthebiggestglobalconcernsfacinghumanityis health[1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) acknowledges that everyone has a basic right to optimal health.Heartdiseasecontinuestobeaglobalhealthcrisis, affecting millions of people and leading to high rates of morbidity and mortality. According to estimates from the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular illnesses account for 17.9 million deaths annually, or almost 31% of all fatalities worldwide. Heart disease continues to be a significant burden on society and the healthcare system despite improvements in medical technology and treatment modalities. An Internet of Things-based patient monitoring system for postoperative heart problems. They discovered an affordable, real-time IoT-based post-operative cardiac disease monitoring device. [2]. The Heart Aid, a commercially available AED produced by the Cardiac Resuscitator Corp. in Wilsonville, Oregon, was the specific AED examined in thisstudy.Thelogicparametersassessedinthisstudyand currentlyinwidespreadusagedifferfromthoseemployed in the prior experiments, despite the fact that there has been limited clinical use of this device previously documented. There were two phases to this assessment. validation of algorithms. A single unit was shown a set of 205 real patient rhythms that had previously been capturedaspartofastudy oncardiacarrestinruralIowa

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net
in order to verify the AED's diagnostic accuracy. During real resuscitations in the field, ambulance staff skilled in defibrillationdocumentedeveryrhythm.[3].Abhisheket.al proposed an estimated 17.9 million deaths annually, cardiovasculardiseaseisaseriousglobalhealthconcern.It includesavarietyofheartandbloodvesseldisorders,such as heart failure, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Numerous risk factors, both modifiable and nonmodifiable, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, sedentary lifestyles, obesity, diabetes, and genetic susceptibility, are frequently linked to these disorders. Machine learning and data analysis have become effective methods for identifying and averting cardiovascular disease. Researchers can find trends and risk factors linked to cardiovascular disease by analyzing sizable and intricate datasets of medical information. In ordertocreatepreciseandtrustworthypredictivemodels, machine learning algorithms can be utilized to find significant data elements that are predictive of the course of cardiac disease. Furthermore, biases and discrepancies in the outcomes of cardiovascular disease among various groupsandgeographicalareascanbefoundwiththeaidof data analysis. [4]. Sangeeta Kurundkar et.al This project suggested a Smart Helmet and Health Monitoring System for miners. Sensors including the DHT sensor, MQ-07 gas sensor, ultrasonic sensor, health-based oximeter, and temperature sensor are all included in the system. It uses thedatavisualizationandanalysisplatformThingSpeakto monitor and analyze collected data. The Smart Helmet's sensorsmonitorphysiologicalmarkersandenvironmental conditions, and ThingSpeak provides managers and safety personnel with remote access to real-time data visualization. Predictive maintenance, early health issue identification, and timely alarm production are made possible by data analysis employing machine learning algorithms. By improving safety and ongoing health monitoring, this device can alter mining safety rules and ensureworkerwell-being.Asmarthelmetsystemthatcan identify potentially hazardous conditions, monitor the surroundings,updateinformation(suchassensordataand GPS location) to the central console for convenient tracking, and supply air to stop toxic compounds from being inhaled.[5],[6]., System architecture is illustrated in Fig. 1. Therefore, A major cause of death in the United States and around the world, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) often go undiagnosed in their early stages, which lowers awareness and decreases the likelihood of controlling the condition. This study offers a viable athome monitoring solution by utilizing artificial intelligence's(AI) predictive capabilitiestocreatea fusion framework that integrates patient electrocardiograms (ECGs) and electronic medical records (EMRs) to identify CVDriskearlyon. [7],[8].Boththeheartandthebrainare
p-ISSN:2395-0072
essentialformaintainingbodilycoordination,buttheheart requiresmoreattentionandcaretofunctionproperlythan the brain. Therefore, the heart is vital to all living things. Our body functions properly when oxygenated blood is pumped and distributed to all organs in the right flow. Therefore, maintaining a healthy and disease-free heart is our top priority. Predicting the genesis of cardiovascular ailments will be a noteworthy endeavor in the healthcare industry becauseofthisproposal.Healthcarefacilitiescan treat diseases at their earliest stages by processing raw data using practical tools and techniques that make it significant for early disease prediction. Every day, vast amounts of patient data pertaining to illnesses are saved, whichcanbepreprocessedandusedtotraindeeplearning or machine learning models that aid in early disease prediction. In order to train and forecast the etiology of CVD so that patients can begin treatment as soon as possible,deeplearningalgorithmssuchasRNN(Recurrent Neural Network) with its type LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) are employed in this study. In the proposed work, a comparative analysis of previously utilized algorithms and the suggested functioning algorithms with precise prediction without delay is developed. The categorization technique, accuracy, and severity of causative characteristics are used to construct the diagnosis model's outcomes. [9]. Aleksey.et.al proposed. Both the heart and the brain are essential for maintaining bodilycoordination,buttheheartrequiresmoreattention and care to function properly than the brain. Therefore, the heart is vital to all living things. Our body functions properly when oxygenated blood is pumped and distributed to all organs in the right flow. Therefore, maintaining a healthy and disease-free heart is our top priority. Predicting the genesis of cardiovascular ailments will be a noteworthy endeavor in the healthcare industry because of this proposal. Healthcare facilities can treat diseases at their earliest stages by processing raw data using practical tools and techniques that make it significant for early disease prediction. Every day, vast amounts of patient data pertaining to illnesses are saved, whichcanbepreprocessedandusedtotraindeeplearning or machine learning models that aid in early disease prediction. In order to train and forecast the etiology of CVD so that patients can begin treatment as soon as possible,deeplearningalgorithmssuchasRNN(Recurrent Neural Network) with its type LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) are employed in this study. In the proposed work, a comparative analysis of previously utilized algorithms and the suggested functioning algorithms with precise prediction without delay is developed. The categorization technique, accuracy, and severity of causative characteristics are used to construct the diagnosismodel'soutcomes[10].

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net
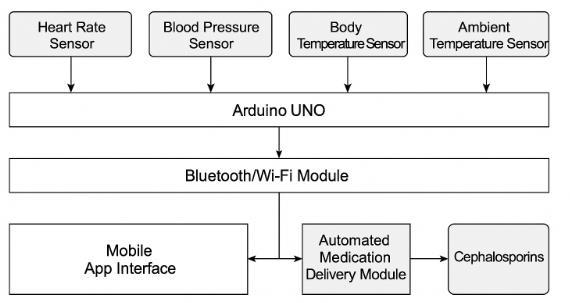
The proposed IoT-based real-time post-operative heart disease patient monitoring system integrates multiple biomedical sensors to continuously measure critical vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure (BP), and body temperature. These sensors are connected to a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino), which collects and transmitsthedataforfurtherprocessing.
The collected data is analyzed in real-time using embedded algorithms designed for the early detection of heart-related abnormalities. These algorithms can detect deviations from normal physiological ranges, potentially indicating the onset or progression of heart disease. Upon detection of such anomalies, the system immediately notifies healthcare providers and patients through a mobile application, ensuring timely medical intervention. For system validation, rigorous testing is conducted to evaluatetheaccuracyandreliabilityofthesensorreadings and the detection algorithms. Validation ensures that the system effectively supports clinical decision-making and improves patient outcomes. Real-time data and analysis results are displayed on both the Arduino serial monitor andthemobileapplicationinterface,providingcontinuous feedback to both patients and caregivers. In advanced implementations, the system is equipped with a relaycontrolled pump motor to automate the administration of medications such as cephalosporins at regular intervals. This feature supports adherence to prescribed treatment schedules and enhances patient care, especially during post-operativerecovery. Thesesensorsareconnectedtoa microcontroller, such as an Arduino, which collects the physiological data and processes it using embedded algorithms designed to detect early signs of heart-related abnormalities. The system enables real-time monitoring, with alerts sent to both healthcare providers and patients via a mobile application whenever irregularities are detected, allowing for timely medical intervention. To ensure the system’s effectiveness, validation procedures
p-ISSN:2395-0072
are carried out to confirm the accuracy and reliability of both the sensor readings and the analytical algorithms. ThemonitoringresultsaredisplayedontheArduinoserial monitor as well as on the mobile app for continuous visibility.Furthermore,thesystemcanincorporatearelayoperated pump motor to automatically administer medications such as cephalosporins at predefined intervals, supporting consistent post-operative care and improvingpatientoutcomes.
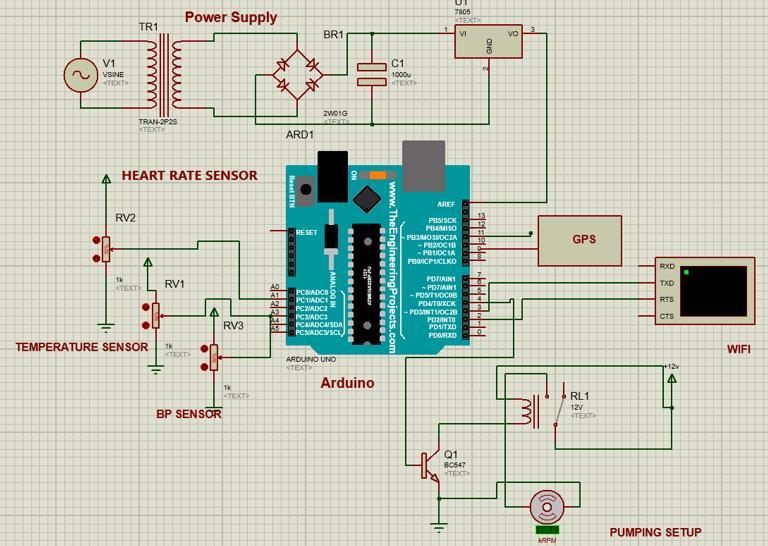
Infig2thecircuitdiagramconsists ofseveral key components interconnected to monitor and process the patient'svitalsignseffectively.Atthecoreofthesystemis an Arduino microcontroller, which serves as the central processing unit. Multiple biomedical sensors are connected to the Arduino, including a heart rate sensor, a blood pressure (BP) sensor, and a temperature sensor. These sensors measure the patient's physiological parameters in real time. Each sensor outputs analog or digital signals corresponding to the measured vital signs. Thesesignalsarefedintotheappropriateanalogordigital inputpinsoftheArduino.TheArduinocontinuouslyreads thesesignalsandprocessesthedatausingembedded logic to identify any abnormalities. For real-time data visualization and alert generation, the Arduino is connected to a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi module (such as HC-05 or ESP8266), which transmits the processed data to a mobile application. This enables both patients and healthcare providers to receive instant updates on the patient's condition remotely. Additionally, a relay module is connected to one of the Arduino's digital output pins. Thisrelaycontrolsapumpmotor,whichisresponsiblefor the automatic administration of medication (e.g., cephalosporins) at scheduled intervals. When a specific condition is met or a timer triggers, the Arduino sends a signal to the relay to activate the pump motor, ensuring timely drug delivery. Power is supplied to the system

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net
through a regulated power supply unit (battery or adapter), ensuring stable operation of both the sensors and the microcontroller. Pull-up or pull-down resistors may also be used where necessary to stabilize sensor readings. The circuit is designed to be compact and energy-efficient, ensuring it can be reliably used in a clinicalorhome-basedpost-operativecaresetting.
2.1
The proposed system utilizes a variety of hardware modules working in coordination to ensure continuousandreliablemonitoringofpost-operativeheart disease patients.At theheartof thesystemistheArduino microcontroller(Uno,Nano,orMega),whichservesasthe central control unit responsible for reading sensor data, processing inputs, executing algorithms, and managing communicationbetweenmodules.
2.2
Vital physiological parameters are captured throughseveral biomedical sensors. Theheartrate sensor detects thepatient'spulseinbeatsperminute(BPM) and, in some cases, also measures blood oxygen saturation (SpO₂), which is crucial for identifying oxygen-related complications. A blood pressure sensor is employed to monitor systolic and diastolic pressure levels, which are especially important for post-surgery heart patients. This may involve a cuff-based analog sensor or a digital BP sensor module interfaced via analog pins. To track body temperatureakeyindicatorofpotentialinfectionsorpostoperativeinflammationatemperaturesensorlikeLM35 is includedinthecircuit.
2.3
All these sensor readings are collected and processed by the Arduino in real time. For data communication and remote monitoring, the system can useeithera wireless moduleforshort-rangetransmission to a smartphone or a Wi-Fi module (like ESP8266) for long-range, internet-based data transfer to a mobile application or cloud platform. In systems that prioritize scalability and remote access, ESP32 can serve as both a microcontroller and a Wi-Fi-enabled processing unit, makingthedesignmorecompactandefficient.
Anessentialcomponentforautomateddrugdeliveryisthe relay module, which functions as an electronic switch controlledbytheArduino.Therelaygovernstheoperation of a pump motor, typically a peristaltic or DC mini pump,
p-ISSN:2395-0072
which is responsible for delivering medications such as cephalosporins at regular intervals. This feature ensures that critical drugs are administered automatically without manual intervention, enhancing treatment reliability and patientsafety.
To power the entire setup, a regulated power supply is used often in the form of a rechargeable battery or adapter connected to a voltage regulator to ensure consistent 5V or 3.3V output, depending on the modules used. Optionally, a display module such as a 16x2 LCD or an OLED screen can be connected to the system for local displayofreal-timesensordata.
Furthermore,amobileapplication,eithercustomdeveloped or using platforms like Blynk, ThingSpeak, or Firebase, provides a user-friendly interface for patients and doctors to view live data, receive alerts, and maintain logs for future reference. This interconnected module design forms a robust, scalable, and intelligent system capable of improving the quality of post-operative care through real-time monitoring, early diagnosis, and automatedintervention.
The implemented system successfully achieved real-time monitoring of critical vital signs heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature using integrated biomedical sensors connected to an Arduino-based platform. Sensor data was accurately read, processed, and displayed on both the Arduino serial monitor and the accompanying mobile application. The mobile interface provided real-time access to patient data, allowing both patientsandhealthcareproviderstoobservephysiological changes instantly. Alerts were effectively triggered when vital parameters exceeded predefined thresholds, demonstratingthesystem’spotentialforearlydetectionof post-operative complications such as arrhythmias, hypotension,orfever.
In testing environments, the heart rate sensor produced consistent readings within ±3 BPM of standard medical-grade devices, while the temperature and blood pressure sensors showed acceptable accuracy levels for non-clinical monitoring. The system maintained stable performanceacrossvarioustestcases,includingsimulated abnormal conditions, which validated the reliability of the anomaly detection algorithm. Additionally, the real-time data transmission via Bluetooth/Wi-Fi remained

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net
consistent, with minimal latency observed between the sensorinputanddatadisplayonthemobileapplication.
A significant feature of the system the automated drug delivery mechanism was validated by simulating the timed administration of cephalosporins using a relay-controlled pump motor. The relay reliably activated the pump at scheduled intervals, demonstrating the system’s capacity to integrate treatment protocols along with monitoring. This function is particularly useful for patients requiring regular doses of post-operative antibiotics, reducing dependency on manual administration and ensuring adherence to treatment schedules.
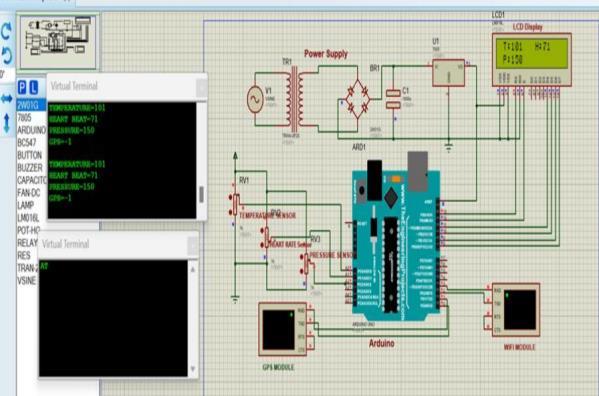
As shown in Fig.3, IoT-based real-time post-operative heart disease patient monitoring system was successfully carriedoutusingProteusDesignSuite,apowerfultoolfor simulating embedded systems. In this simulation, an Arduino Uno microcontroller was used as the central processing unit, with various biomedical sensors connected toittosimulatethemeasurementofvital signs The Arduino code written in the Arduino IDE was compiled and exported as a .hex file, which was then uploaded to the simulated Arduino in Proteus. During simulation, real-time adjustments were made to the input sensors using potentiometers and signal generators to observe how the system responded to various health conditions. The LCD output, motor actuation, and serial terminal messages verified that the system was functioning as expected. Overall, the Proteus simulation effectively demonstrated the core functionalities of the system, including real-time monitoring, data processing, alert generation, and automated intervention, validating the feasibility of the proposed design before hardware implementation.
p-ISSN:2395-0072
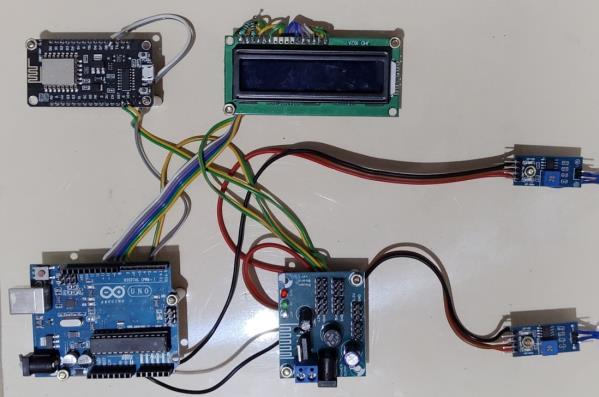
In Fig.4, The Hardware Implementation of. A temperature sensor (LM35) was connected to analog pin A0, providing real-timeanalogtemperaturedata.Aheartratesensorwas simulated using a pulse generator or variable voltage sourceconnectedtoanalog pinA1 to mimicthe heartbeat signal. Similarly, a blood pressure sensor was modeled using a potentiometer on analog pin A2 to represent varying pressure levels. The sensor outputs were displayed on a 16x2 LCD connected to the digital pins of theArduinotoprovideinstantfeedbacktotheuser.
For wireless communication, a virtual terminal was used to represent the serial monitor or a Bluetooth terminal, allowing for simulated data transmission to a mobile application. To demonstrate the automatic drug delivery feature, a relaymodule wasconnected to digital pin D8 of the Arduino, which controlled a DC motor acting as a pump.Whencertainhealthconditionsweredetected such as a high heart rate or elevated temperature the Arduino triggered the relay to switch on the motor, simulating the deliveryofmedicationlikecephalosporins.
In conclusion, the development and simulation of the IoT-based real-time post-operative heart disease patient monitoring system have demonstrated the potential of integrating embedded systems and IoT technologiesforenhancedhealthcaredelivery.Thesystem effectively monitors vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature in real-time using biomedical sensors connected to an Arduino microcontroller. The incorporation of wireless communication enables healthcare providers and patients toaccesscriticalhealthdatathroughamobileapplication, promoting continuous monitoring even outside the hospital environment. This project not only demonstrates technical feasibility but also highlights the importance of

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
low-cost, portable, and intelligent healthcare systems. While the system is currently best suited for home or transitional care, future improvements such as cloud integration,enhanceddataanalytics,andwearabledesigns can make it suitable for broader clinical applications. Overall, the project contributes to the growing field of smart healthcare and provides a scalable solution for improvingpost-operativecareandpatientoutcomes.
[1] Srivathsan et al. Ventricular tachycardia and ventricularfibrillation,Expertreviews,2009.
[2] Roy M. John et al. Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiacdeath,LancetVol.380,October27,2012.
[3] Gavin D. Perkins et al. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines for Resuscitation 2015 Section 2. Adult basic life support and automated external defibrillation, EuropeanResuscitationCouncil,2015.
[4] BRUCE A. KOPLAN et al. Ventricular Tachycardia and Sudden Cardiac Death, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, March 2009.
[5] The Brussels Time. Belgians ‘less likely’ to survive cardiacarrest,https://www.brusselstimes.com/news/belgi um-all-news/health/56765/ belgians-less-likely-survivecardiac-arrest-rates/,2019.
[6] Philippe Kolh, ANATOMIE ET PHYSIOLOGIE DU SYSTEMECARDIOVASCULAIRE.
[7]BenoitPlourdeetal.Suddencardiacdeathandobesity, 2014.
[8] Abdennasser Bardai et al. Epilepsy Is a Risk Factor for Sudden Cardiac Arrest in the General Population, PLOS ONE,2012.
[9] Ann-Sofie Forslund et al. Risk factors among people survivingout-of-hospital cardiac arrestandtheirthoughts about what lifestyle means to them: a mixed methods study,BMCCardiovasculardisorders,2013.
[10]BostonScientific.CausesandRiskFactorsforSudden Cardiac Arrest, https://www.sicdsystem.com/enUS/sudden-cardiac-arrest/causes-risk-factors.html,2021.