
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Er Mohd Altamash Khan1, Ar Rakesh Paijwar2
1PG Student (MURP), Faculty of Architecture & Planning, Dr A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow
2Assistant Professor, Faculty of Architecture & Planning, Dr A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow
Abstract - The rapid expansion of the Information Technology (IT) and IT-enabled Services (ITES) sector has significantly reshaped urban development, particularly influencing residential growth patterns. This study explores how the growth of IT infrastructure drives changes in housing typologies, real estate trends, and supporting urban infrastructure. As cities position themselves as IT hubs, the demand for housing near employment centers intensifies, resulting in varied residential developments and shifts in land use patterns. This research investigates spatial and economic impacts of IT sector expansion on surrounding residential areas,focusingonaffordability,accessibility, and infrastructure adequacy. By combining spatial analysis, secondary data review, and case-based observations, the study identifies emerging patterns of urban form and residential clustering around IT corridors. The results suggest that IT-driven development often leads to increased land values, shifts in housing demand, and infrastructural stress, thereby necessitating integrated urban planning approaches. The study concludes with recommendations for promoting balanced urban growth through policies that ensure affordable housing, enhance infrastructure capacity, and support sustainable development in IT-influenced regions.
Key Words: IT Sector, Residential Growth, Housing Typology, real estate dynamics, urban infrastructure, spatialpatterns,affordability,urbanplanning.
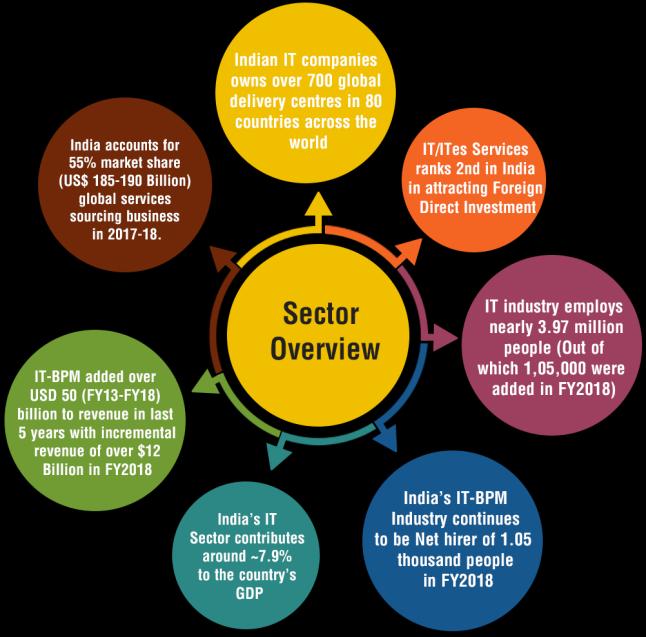
TheITsectorisadrivingforcebehindmodernresidential growth, influencing everything from smart infrastructure to decentralized living and data-driven planning. This interplay between IT and urban development creates smarter, more sustainable cities with a high demand for residential properties that meet the needs of the digital age.
Historically, industrialization has driven urbanization by creating jobs and economic opportunities. The industrial sector is sub categorized into many other sectors like mining & quarrying, Manufacturing, Software & hardware technologies(IT Sector) etc. As per the records, the industrialsectorholdsashareof24.2%intheIndianGDP, of which 11.3% is contributed by IT sector. This shows how crucial the IT sector is, not only to the national economybutalsotothetransformationofurbanspaces.
The IT sector has become a major driver of economic growth and urban development in many cities. As technology companies expand, they often influence patterns of residential development due to changes in employment,incomelevels,andurbaninfrastructure.
In summary, this study seeks to fill existing gaps in the literature regarding the direct impact of the IT sector on residentialhousingdemand.Italsoendeavorstoprovidea comprehensive framework for understanding the future trajectoryofurbandevelopmentinIT-centriccities.
Thisstudyaidsin the evaluationof the growth pattern and future development guidance for cities with comparable IT sector growth scenarios by policy makers andspatialplanners.
A thorough examination is necessary to determine its preciseeffectsonresidentialdevelopment,includingshifts in the demand for housing, property values, and urban growth.
Understanding the Dynamics of the Housing Market: I need to examine the ways in which the growth of the IT

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
sector affects land values, housing prices, and rental markets.
PolicyGuidance:Thestudyoffersinsightfulinformation to help policymakers and spatial planners direct future urban development and solve the issue of IT worker's homeaffordability.
FillinguptheResearchGapsFewresearchhavelooked at how the expansion of the IT sector directly affects the demand for residential housing, specifically if IT workers aredrivingthisneed.Thegoalofthisstudyistoclosethat gap.
Tostudy the relationship betweenthe growth of theIT sectorandresidentialdevelopment.
IdentifychangesinhousingtypologiesresultingfromIT workforcedemand.
To evaluate impacts on real estate markets and urban infrastructure.
Scope- TheconnectionbetweentheriseoftheITindustry and the urbanization of residential regions. It examines changes in housing typologies, built-up areas, land, properties, and rental values with an emphasis on the spatialandstructuralchangesinhousingthatoccurinthe 200,300,and400-meterrangesurroundingITbusinesses. The study also evaluates housing availability and affordability for IT workers and investigates the broader effects of IT-driven economic activity on residential development.
Limitation- The study does not take into consideration the impact of other businesses and is restricted to a particularregionwithaconcentrationofITcompanies. In addition, subjectivity could be introduced by the study's dependenceonsurveydata,andlong-termeffectsofurban designmightbemissed.
The Urban development, especially residential growth around IT hubs, has been a topic of increasing academic interest. This review summarizes key contributions that informthisstudy.
R.B. Andrews (1942) in his work Elements in the UrbanFringe Pattern highlights the urban fringe as a dynamic growth zone characterized by mixed-use developments and unregulated land use. Economic shifts, decentralization, and employment hubs drive this expansion, while speculative land development and infrastructure deficiencies pose challenges. This work
underscores the importance of land-use planning and infrastructuredevelopmentforsustainableurbangrowth.
Dr.ShobhaM.N,Dr.KrishneGowda,andProf.SridharaM. V(2016),inCitiesinTransition,analyzetheimpactofthe IT industry in Bangalore, identifying how IT-driven growth influences spatial, social, and economic aspects of cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad, and Pune. Key issues include rising land values and housing affordability, making a strong case for strategic housing and urban planningnearITcorridors.
Anand, Rashmi Rani (2022), in her study Issues and Challenges of Real Estate Sector in Urban India, explores the effects of IT sector expansion and foreign direct investmentonrealestate.Despitegovernmenteffortslike the Real Estate Bill and increased FDI, persistent issues such as delayed possession and inadequate infrastructure continue to hinder sustainable housing growth in urban regions.
Juha Talvitie (2003) in The Impact of ICT on Urban and Regional Planning emphasizes the transformative role of ICT on spatial development. Changing work practices and location dynamics necessitate updated education and planning policies, highlighting the need for adaptive planningapproachesintheinformationsociety.
M.R. Narayana (2010) in his work on Bangalore's economic globalization finds that the ICT sector has propelled Bangalore’s urban and economic growth. The study calls for future infrastructure improvements to sustain this development, noting the need for inclusive policiesthatalsoaddressinformalICTsectors.
Christine Whitehead et al. (2005) in their pilot study Understanding the Local Impact of New Residential Development reveal that new housing initially disrupts local property values but ultimately contributes to price growth and market integration. Factors like site location, development scale, and land-use history are critical in shapingthelong-termimpact.
These studies collectively underline the multidimensional influence of the IT sector on urban form, housing dynamics,andplanningstrategies.Theyalsopointtoward thenecessityofaffordablehousingpolicies,infrastructure planning, and regulatory frameworks to manage ITinducedurbantransformationeffectively.
The IT sector has emerged as a major driver of urban growth, shaping the spatial organization of cities through thedevelopmentofITparksandassociatedinfrastructure. Kumar et al. (2021) note that cities like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune have become IT hubs, attracting a

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
growing workforce and necessitating integrated residential and commercial zones. McKinsey Global Institute (2016) highlights that this sector-led urbanization often results in mixed-use developments designedtoimprovelivabilitybyreducingcommutetimes.
IT sector expansion has significantly altered housing markets. Knight Frank (2023) reports a sharp rise in property values near IT parks, often pricing out middleincome households. In Hyderabad, luxury housing dominates areas like HITEC City, while affordable options are pushed to peripheral zones such as Kompally and Medchal. According to JLL (2022), there is a growing preference for gated communities and mid-to-high-end residential developments, leading to a decline in affordablehousingsupply.
InfrastructuredevelopmentiscriticaltosupportIT-driven urbanization.PatelandSingh(2020)emphasizetheroleof transport networks like the Outer Ring Road and HyderabadMetroinlinkingIThubswithresidentialareas, facilitating real estate growth in outer zones. Eco-friendly ITdevelopmentssuchasAscendasinHITECCityshowcase sustainable planning practices that cater to both global firmsandgreen-consciousresidents.
The IT sector’s expansion has deepened socio-economic divides.ChakrabortyandGupta(2018)observethatrising property prices displace lower-income populations, contributing to urban polarization. In Hyderabad, luxury housing supply continues to grow while demand-supply mismatches persist in the affordable segment, often forcing low-income households to relocate to distant suburbslackingessentialurbanservices.
Basedonthecomprehensiveliteraturereview,severalkey inferences have been drawn that illustrate the multifacetedimpactofITsectorgrowthonurbanhousing anddevelopment:
TheestablishmentofIThubshasadirectcorrelationwith the transformation of urban housing typologies. The demand from IT professionals has led to the proliferation ofmixed-usedevelopments,gatedcommunities,andhighdensity residential zones in close proximity to IT corridors.
Proximity to IT parks significantly escalates land and property values due to the desire for reduced commute times and access to modern amenities. Case studies from HITEC City (Hyderabad) and Whitefield (Bengaluru) exemplify how IT presence stimulates exponential real estategrowth.
WhiletheITsectorfosterseconomicdevelopment,itoften exacerbates housing affordability issues. The surge in property prices within IT-centric regions contributes to the displacement of middle- and lower-income groups, pushingthemtolessaccessibleperipheralzones.
3.4
UrbanareaslikeHyderabad,Bengaluru,andPuneprovide successful examples ofhow strategic planning and zoning can integrate IT and residential growth. These cases underscore the role of proactive governance in achieving balancedandsustainableurbandevelopment.
3.5
Rapid, IT-induced urbanization can result in unregulated expansion, infrastructure overload, and environmental degradation. Literature emphasizes the necessity for sustainable and resilient planning approaches that mitigatetheserisks.
3.6 Socio-Cultural Transformation
The influx of a cosmopolitan IT workforce reshapes the socio-cultural fabric of cities. While this transition promotesmodernlifestyles,itcanalsoleadtotheerosion of traditional housing forms and the displacement of culturalheritage.
4. CASE STUDY: BENGALURU – THE IT HUB AND ITS URBAN TRANSFORMATION
4.1 Introduction
Bengaluru, India's "Silicon Valley," exemplifies how rapid ITsectorgrowthtransformsurbanhousingdynamics.The city's evolution into a leading tech hub has significantly influenced its spatial structure, residential development, and affordability, offering a valuable case for examining theinterplaybetweenITexpansionandurbangrowth.
4.2
Bengaluru's rise as an IT powerhouse began in the 1990s withfirmslikeInfosys,Wipro,andIBMestablishingmajor

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
operations. The subsequent emergence of tech clusters such as Electronic City and Whitefield led to an influx of skilled professionals, driving demand for housing and catalyzinglarge-scaleurbanexpansion.
The demand for proximity to workplaces has spurred the development of new residential nodes around IT hubs. AreaslikeWhitefield, Sarjapur,andOuterRingRoadhave experiencedsignificantrealestategrowth,hostingamixof luxury apartments and mid-income housing. This shift reflects a response to the evolving preferences of the IT workforce.
Proximity to Employment Nodes: Preference for reduced commute times has fueled the growth of gatedcommunitiesandintegratedtownshipsnearIT parks.
Infrastructure Development: Roadnetworks,metro connectivity, and public utilities have supported the expansionofsuburbsintolivableurbanzones.
Land Price Escalation: Increaseddemandhasledto rising land and property values, especially near tech corridors, contributing to gentrification and reduced affordability.
Shift in Housing Typology: Developers are increasingly delivering high-rise apartments with modern amenities to cater to upwardly mobile IT professionals.
4.5 ITPL Whitefield: An IT Park as a SelfContained City
The International Tech Park Bangalore (ITPL), located in Whitefield, represents a microcosm of integrated development. Originally a small settlement, Whitefield transformed into a vibrant tech district, highlighting the self-sustainingnatureofmajorITparks.ITPLincorporates workspaces, housing, retail, and recreational facilities, reflectinghowsuchparksinfluenceurbanecosystemsand catalyzeplannedurbanization.
Housing Affordability: Escalating property prices around IT hubs have marginalized low-income populations, pushing them to peripheral locations with limited infrastructure.
Infrastructure Stress: Rapid development has strained existing infrastructure, leading to congestion, waste managementissues,andunevenservicedelivery.




International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

4.7
IT sector growth has directly driven residential development,especiallyinEastandSouthBengaluru.
ProximitytoIThubsremainsaprimaryfactorinfluencing housingdemandandpricing.
The emergence of premium residential segments reflects theincreasingaffluenceofthetechworkforce.
Infrastructure investments, such as metro expansions, reinforce the interdependence between IT-driven employmentnodesandresidentialchoice.
Table -1: ComponentandParameters
Component Parameters
Urban Growth
Social Sustainabili ty
Economic Factors
IncreaseinlandvalueduetoproximitytoITparks
Expansionofhousingandcommercialproperties
Developmentofrelatedindustries(e.g.,realestate ,retail)
“Walk-to-work”infrastructure
Availabilityoflocalamenities(schools,healthcen ters)
Communityintegrationandqualityoflife
Impactonlocalandregionaleconomy(GDP,empl oyment)
Attractionofinvestmentandtechnologicalinnova tion
Developmentofsupportingindustries
Governmen tPoliciesan dPlanning
Governmentincentives(subsidies,taxbreaks)
Urbanzoningregulations
Long-termsustainabilitygoalsinurbanplanning
UrbanInfra structure Developmentoftransportnetworks(roads,public transit)
Housingdevelopmentandutilitiesprovision
IntegrationofITparksintourbaninfrastructure
Bengaluru’strajectoryunderscorestheneedforintegrated urbanplanningapproachesthatbalanceeconomicgrowth withhousinginclusivity.Futurepoliciesmustprioritize:
Affordablehousingnearemploymenthubs.
Phasedinfrastructuredevelopment.
Strategiczoningtomanagelandvalueescalation.
Inclusionary housing to mitigate socio-spatial segregation.
The case of Bengaluru illustrates both the positive and negativeimpactsofIT-drivenurbangrowthonresidential development. On the one hand, the IT sector has driven economicgrowthandinfrastructuredevelopment,leading to more housing opportunities. On the other hand, it has exacerbated affordability issues for lower-income groups. Future urban planning policies in Bengaluru should focus on creating affordable housing options and improving infrastructure to accommodate the growing population while maintaining a balance between economic growth andsocialequity.
Hyderabad, particularly HITEC City and the Financial District, exemplifies how IT sector development can drastically alter urban form and residential growth. With theestablishmentoflarge-scaleITparkssuchasAscendas ITPark,DLFCyberCity,andRahejaMindspace,Hyderabad has emerged as a premier IT destination in India. These developments have significantly contributed to the city’s realestateboom,particularlyinWestHyderabad.
AttributesoftheCaseStudyArea:
Location: HITEC City and Financial District (West Hyderabad)
Key IT Parks: HITEC City, housing IT giants such as Infosys,Wipro,Deloitte,andMicrosoft

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Residential Growth Hotspots: Gachibowli, Kondapur, Manikonda,Tellapur
5.2 Background: Growth of the IT Sector in Hyderabad
Once known for its cultural and historical heritage, Hyderabad has redefined its urban identity over the past two decades. The development of HITEC City (Hyderabad Information Technology Engineering Consultancy City), along with other IT parks such as Ascendas IT Park, DLF Cyber City, and Raheja Mindspace, has positioned the city asaglobalITdestination.HITECCityhousesfirmssuchas Microsoft, Google, Infosys, Wipro, and Amazon. Its rise catalyzed urban expansion into previously peripheral areaslikeGachibowli,Kondapur,andManikonda.
Table -2: Top10fastest-growingcitiesintheworld,201935

5.3 Impact of the IT Sector on Residential Development
a. Residential Demand Surge: The influx of professionals seeking proximity to workplaces significantly increased housing demand within 5–10 kmofHITECCityandtheFinancialDistrict.
b. Emergence of New Residential Nodes: Neighborhoods like Gachibowli, Tellapur, and Madhapur have become prime real estate destinations,attractingbothpremiumandaffordable housingdevelopers.
c. Luxury Housing Proliferation: Developerslaunched gatedcommunitiesandhigh-riseapartmentsoffering amenitiestargetedathigh-incomeITprofessionals.
d. Affordable Housing Trends: Peripheral zones such as Narsingi and Kompally have witnessed growth in budget housing to serve lower and middle-income groups.
a. Predominantly High-Rise Living: Residential construction is characterized by vertical development gated communities, apartments, and townships.
b. Luxury Segment Growth: Homes priced above INR 10millionaccountedfor62%oftotalhousingsalesin Q22024,upfrom45%inH12023.
c. Affordable Housing Gap: Thoughaffordablehousing exists, rising land values are pushing such developments further from IT zones, increasing commutetimes.
d. Real Estate Trends: The real estate market in West Hyderabad remains robust, with year-on-year (YoY) residential sales increasing by 21% in H1 2024 and by 28% in Q2 2024. West Hyderabad alone accounts for62%oftotalcitywidesales.
Table -3: Hyderabad'sResidentialMarketandthe InfluenceofITSectorGrowth

a. Connectivity Enhancements: ProximitytotheOuter Ring Road (ORR), ongoing metro rail expansion, and improved arterial roads have supported urban expansion.
b. Planned Development: Upcoming projects like the RegionalRingRoadaimtointegrateperipheralareas, allowing more organized growth and better housing distribution.
c. Lifestyle Urbanism: The rise in disposable income among IT professionals has spurred demand for lifestyle-centric housing with features like clubhouses, co-working spaces, and recreational amenities.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
a. Affordability Issues: Rising property prices have made housing in central IT districts inaccessible to non-IT workers and lower-income households, increasingsocio-spatialsegregation.
b. Gentrification: Traditional communities in proximity to HITECCityare being displaced byhighincomeearners.
c. Infrastructure Strain: Overburdened transport systemsandutilitiesreflectalagbetweenresidential growthandinfrastructureprovisioning.
d. Environmental Concerns: Rapid development has contributedtotheloss ofgreencoverandchallenges insolidwastemanagementandwatersupply.



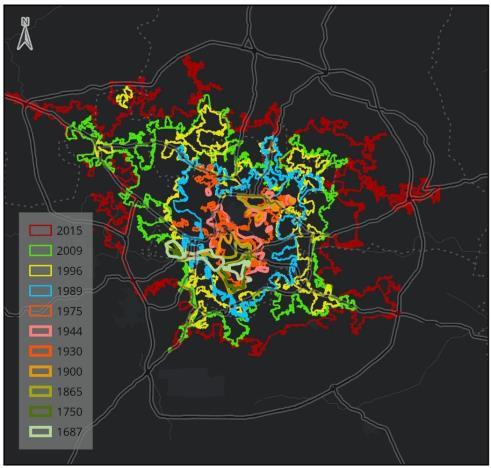
a. Unplanned Sprawl: Weak enforcement of the 2020HyderabadMasterPlanhasledtoirregular urban expansion without integrated infrastructure.
b. Affordable Housing Deficit: There remains limited emphasis on affordable housing, despite strong demand from service workers and middle-incomehouseholds.
c. Unsold Inventory: The premium housing segment continues to expand, while unsold inventory builds up in the affordable segment duetolocationandaccessissues.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
a. The IT sector has been the principal driver of residential development in West Hyderabad, with direct influence on location, typology, and pricing of housing.
b. There is a clear shift toward premium housing, reflectingthefinancialcapacityoftheITworkforce.
c. While robust infrastructure has enabled rapid urban growth, housing affordability and sustainability remainpressingchallenges.
d. Real estate markets in West Hyderabad exhibit high correlation with the concentration of IT firms, indicatingaspatialdependencyofhousinggrowthon ITcorridors.
Table -4: ResidentialGrowthAnalysis2018-23

Table -5: Prameters&impact Parameters
Demographic and Socioeco
Workforce Landconversion
ResidentialDemand Buildingheightincreases
Occupationalstructure Encroachments
Housingprofile Illegalconstructions
Spatial Economy
Landusechange Demandofland
Directionofgrowth Speculationoflandvalue
Built-upchange Neweconomicactivities
Landvaluechange Infrastructure
Physicalinfrastructure Infrastructureoflandincreases
Socialinfrastructure Waterlogging
Landholdingsize Gapsininfrastructurefacility
ThecaseofHyderabaddemonstratesthattheITsectorisa powerful force shaping urban growth. IT hubs like HITEC Cityhavesignificantlyinfluencedresidentialdevelopment, pushing up demand and reshaping housing typologies. However, the growth is uneven, with luxury housing dominatingandaffordablesegmentslaggingbehind.
While Hyderabad has witnessed improvements in infrastructure and economic growth, challenges such as socio-spatial segregation, environmental degradation, and unsustainableurbanexpansionpersist.
Forsustainableurbangrowth,itisessentialto:
a. Strengthenaffordablehousinginitiatives
b. Promotesustainableurbaninfrastructure
c. Integrate IT parks within broader city development frameworks
d. These efforts will ensure that the benefits of IT-led urbanizationareequitable,inclusive,andsustainable, aligningwithlong-termurbanplanninggoals.
TheexpansionoftheITsectorincitieslikeBangaloreand Hyderabad has significantly reshaped urban development patterns, particularly influencing residential growth near IThubs.ProximitytoITparkshasledtoincreasedhousing demand, spurring the rise of high-rise apartments, gated communities, and premium housing typologies, while pushing affordable housing to peripheral zones, causing socio-spatial divides. Real estate prices have surged, driven by the affluence of IT professionals, resulting in urban gentrification and affordability concerns for non-IT workers.Additionally,infrastructuredevelopmentsuchas metronetworksandroadwayshassupportedthisgrowth, thoughoftenstrainedbyrapidurbanization.Theresultant socio-economic polarization and environmental impacts highlight the urgent need for policy interventions promoting affordable housing, balanced growth, and sustainableurbanplanning.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The IT sector has emerged as a major driver of urban transformation, reshaping residential growth and socioeconomic structures in cities like Bangalore and Hyderabad. The proliferation of IT hubs has fueled demandforhigh-endhousingnearworkplaces,increasing property values and displacing affordable housing to peripheral areas, thus creating socio-spatial disparities. While infrastructure improvements like metro connectivity and road networks have supported this growth, they also face strain due to rapid urbanization. Environmentaldegradationandresourcepressurefurther underline the need for sustainable urban planning. To ensure inclusive and balanced development, comprehensive policy frameworks must prioritize affordable housing, infrastructure resilience, and ecological sustainability. This study underscores the pivotal role of IT in urban dynamics and offers valuable insightsforfutureplanninginemergingtech-drivenurban centers.
[1] Andrews, R. B. (1942). Elements in the Urban-Fringe Pattern. Discusses urban fringe growth driven by economicshiftsanditsimpactonresidentialpatterns.
[2] Chakraborty, A., & Gupta, R. (2018). Socio-economic Polarization Caused by IT Sector Growth. Analyzes socio-economic challenges of urbanization near IT hubs.
[3] Cote,R.,&Rosenthal,S.(1998).IndustrialEcologyand Sustainable Urban Development. Journal of Urban Development.
[4] Shobha, M. N., Krishne Gowda, & Sridhara, M. V. (2016). Cities in Transition: Impact of Information TechnologyIndustriesinBangalore.
[5] Talvitie, J. (2003). The Impact of Information and Communication Technology on Urban and Regional Planning.
[6] Knight Frank Research. (2023). IT Parks and Their ImpactonRealEstateDevelopment.
[7] LiveMint. (2021). Hyderabad’s Transformation into a PremierITDestination.
[8] McKinsey Global Institute. (2016). IT-Driven UrbanizationinEmergingEconomies.
[9] Narayana, M. R. (2010). Sector, Globalization and UrbanEconomicGrowth:EvidencefromBangalore.
[10] Patel, A., & Singh, R. (2020). Infrastructure InvestmentsandUrbanDevelopmentNearITHubs.
[11] Pellenbarg, P. (2002). Eco-Industrial Parksand Urban Planning.Springer.
[12] Poulomi Real Estate. (n.d.). Ready-to-Move-in Apartments in Hyderabad: Hyderabad's IT Parks and Their Impact on Real Estate Development. Retrieved from https://www.poulomi.in/realestate/ready-tomove-in-apartments-in-hyderabad-hyderabads-itparks-and-their-impact-on-real-estate-development/
[13] Roberts, P. (2004). Assessing Urban Growth Through IndustrialParkManagement.UrbanPlanningReview.
[14] ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Articles on Urban Development and IT Sector. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/ pii/S0160791X22001038
[15] Tech Park Housing. (n.d.). Housing Trends Near Ascendas IT Park, Hyderabad. Retrieved from https://techparkhousing.com/ascendas-it-parkhyderabad/
[16] The Hindu BusinessLine. (2022). The Impact of IT ParksonRealEstateDevelopmentinHyderabad.
[17] Wood, R. (2018). World's Fastest-Growing Cities, 2019–35.
[18] JLL.(2022).RealEstateTrendsinITHubsofIndia.
[19] Bhuvan. (n.d.). National Remote Sensing Centre Data for Urban Growth Mapping. Retrieved from https://bhuvan.nrsc.gov.in/
[20] Whitehead,C.,Sagor,E.,Edge,A.,&Walker,B.(2005). Understanding the Local Impact of New Residential Development:APilotStudy.