
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Robin Nadar1 , Saveena Nadar2
1M.Tech. Student, Electronics and Telecommunication, SunRise University, Alwar, Rajasthan, INDIA.
2M.Sc. IT, Information Technology, Nagindas Khandwala College, Malad, Mumbai, INDIA. ***
Abstract - The Face Emotion Recognition and Analysis system is a real-time application designed to detect human emotions from facial expressions using deep learning. It leverages the FER-2013 dataset and a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture with 13 layers for accurate classification of seven emotion categories: happy, sad, angry, fear, surprise, disgust, and neutral. A unique feature of the system is its ability to log recognized emotions with timestamps and categorize them into specific time slots (morning,afternoon,evening,night),enablinginsightfultrend analysis through visualization. The system is implemented using Python, TensorFlow, and Streamlit, achieving an accuracy of 74.62% over 50 epochs. Applications spanacross healthcare, security, customer service, and user experience evaluation.
Key Words: Face, Emotion, Recognition, Analysis, CNN, Convolutional Neural Network, Neural Network, FER, Face Emotion Recognition and Analysis.
Theintegrationofartificialintelligence(AI)intobehavioural analysishasrevolutionizedthewaymachinesperceiveand respond to human emotions. Among various biometric indicators, facial expressions are considered the most intuitive and immediate means of non-verbal communication.Inrecentyears,facialemotionrecognition (FER) systems have evolved significantly with the advancement of deep learning techniques and the availabilityoflarge-scaleannotateddatasets.
Fromanengineeringperspective,facialemotionrecognition presents a complex, multi-stage problem involving image acquisition,pre-processing,featureextraction,classification, andpost-processing.Eachstagerequiresrobustalgorithmic frameworks and optimized implementations to ensure system accuracy, speed, and real-time operability. Traditional emotion detection systems often relied on handcrafted features (like Local Binary Patterns or Gabor filters), shallow classifiers (like SVM or k-NN), and offline static image analysis. These approaches suffered from limitations such as sensitivity to lighting conditions, poor generalization across diverse populations, and lack of temporalorcontextualemotiontracking.
Toaddressthesechallenges,thisstudyproposesareal-time, deeplearning-basedFaceEmotionRecognitionandAnalysis system that leverages Convolutional Neural Networks
(CNNs) for automatic hierarchical feature extraction. The modelistrainedontheFER-2013dataset,awell-established benchmarkinthedomain,whichenablestherecognitionof seven key emotions: happy, sad, anger, surprise, fear, disgust,andneutral.TheCNNarchitectureemployedinthis workisengineeredwithmultipleconvolutionalandpooling layers, dropout regularization, and optimized using the Adamalgorithm,ensuringbothdepthandgeneralization.
A distinct engineering enhancement introduced in this systemisthetemporalemotionloggingmechanism,which records each recognized emotion with a timestamp and categorizes it into defined time slots, morning, afternoon, evening, and night. This time-aware design allows behavioural trend analysis, providing an additional dimension of emotion interpretation not present in most existingmodels.Theloggeddataisfurthervisualizedusing dynamicbargraphsandpiecharts,enablingbothqualitative andquantitativeanalysis.
Another critical advancement is the system’s ability to function with low-latency on resource-constrained environmentsusingoptimizedlibrariessuchasTensorFlow andOpenCV,makingitdeployableonembeddedplatforms or edge devices (e.g., Raspberry Pi, Jetson Nano). Unlike conventionalFERsystemsthatoperateonlyonsingleface detectionorrequirecloudbackends,thissystemperforms multi-face real-time detection and emotion prediction directlyonthehostmachine,therebypreservingprivacyand reducingprocessingdelay.
TheproposedmodelisalsointegratedwithaGraphicalUser Interface (GUI) built using Streamlit, allowing interactive visualization and user engagement without the need for programming knowledge. All detections are stored in a structuredCSVformat,and theinterfaceincludeseasy-tounderstandanalytics,makingitaccessibletobothengineers andnon-technicalusers.
Insummary,thisresearchaimstobuildatechnicallysound, scalable,anduser-friendlyemotionrecognitionframework. Thesystemnotonlyoutperformstraditionalapproachesin terms of real-time capability, contextual analysis, and engineering efficiency, but also opens new possibilities in fieldssuchasadaptivelearning,mentalhealthmonitoring, smartsurveillance,andemotion-awareAIagents.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Deeplearningisasubsetofmachinelearningthatemploys multi-layered artificial neural networks to learn complex representations from large volumes of data. Unlike traditional algorithms that rely heavily on manual feature engineering,deeplearningmodelscanautomaticallydiscover spatialhierarchiesoffeaturesindataespeciallybeneficialfor imageclassificationtasks.
In the context of face emotion recognition, deep learning excelsincapturingsubtlenuancesinfacialexpressions.This projectusesa superviseddeeplearning approachwherea CNNistrainedusingtheFER-2013datasettoclassifyhuman facial emotions. The network is optimizedusing the Adam optimizer and trained over multiple epochs to reduce categorical cross-entropy loss, improving its classification performancethroughbackpropagationandgradientdescent.
[1] [4] [5]
A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a deep neural networkarchitectureparticularlyeffectiveforimage-based tasks. CNNs are built using three main types of layers: convolutional layers, pooling layers, and fully connected layers.Convolutionallayersapplylearnablefilterstoinput imagestoextractfeaturemapsrepresentingedges,contours, and shapes. Pooling layers down-sample these maps, preservingessentialfeatureswhilereducingcomputational load.
Inthisproject,theCNNarchitectureconsistsof:
Inputlayeraccepting48x48grayscalefacialimages.
Multiple convolutional layers with ReLUactivation to extractspatialfeatures.
MaxPoolinglayersfordimensionalityreduction.
Dropoutlayerstopreventoverfitting.
Dense layers followed by a final Softmax layer for classifyingemotions.
The trained model outputs one of the seven emotion categories: Happy, Sad, Angry, Fear, Surprise, Disgust, and Neutral.
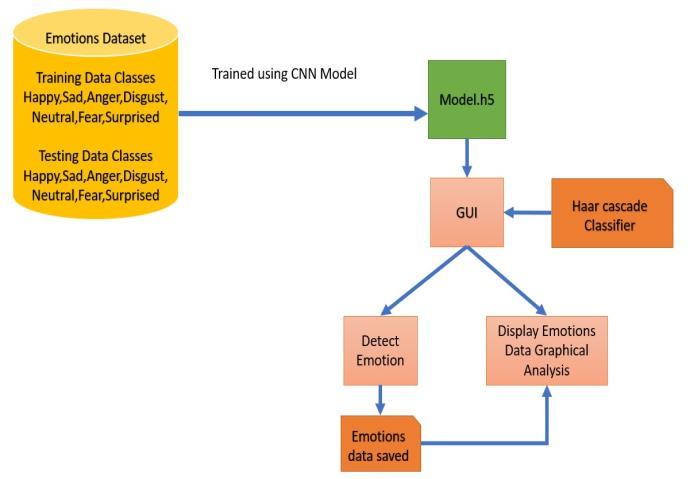
Theblockdiagramrepresentsthecompletearchitectureof the proposed Face Emotion Recognition and Analysis System,clearlyoutliningthedataflowfrominputtooutput andtheinteractionbetweenvariouscomponents.
ThesystemistrainedusingtheFER-2013dataset,whichis dividedintotwoparts:
Training Data: Includes35,887grayscalefacialimages labeled with seven emotions: Happy, Sad, Angry, Disgust,Neutral,Fear,andSurprise.
Testing Data: A subset used to validate the model’s performanceaftertraining.
The Convolutional Neural Network is trained using the labeledtrainingdata.Oncethetrainingprocessiscomplete, themodelissavedinaserializedformatasmodel.h5,which can be loaded into the GUI for real-time prediction. This modelperformsfeatureextractionandclassification.
Beforeemotionprediction,thesystemmustfirstdetectfaces fromthevideostream.Forthis,theHaarCascadeClassifier,a classicalobjectdetectionmethodinOpenCV,isusedtolocate thefaceregionineachframe.
TheGUIistheinteractivefront-endlayerofthesystembuilt usingStreamlit.Itperformsthreecriticaltasks:
Accepts real-time webcam input and integrates with theHaarCascadetodetectfaces.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Passes the cropped face image to the CNN model for emotionclassification.
Displaystheoutput(predictedemotion)totheuserin realtime.
4.5 Output Processes:
Detect Emotion: Eachdetectedfaceisclassifiedinto one of the seven emotion categories by the trained CNN.
Emotions Data Saved: Thepredictedemotionisstored inaCSVfilealongwithatimestamp.
Display Emotions Data - Graphical Analysis: The stored emotion data is later visualized using charts suchasbargraphsandpiechartstoanalyzeemotional patternsoverdifferenttimesoftheday.
This modular design allows easy integration, low latency, andtheabilitytoexpandthesystemforadditionalinputs
5. METHODOLOGY [1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
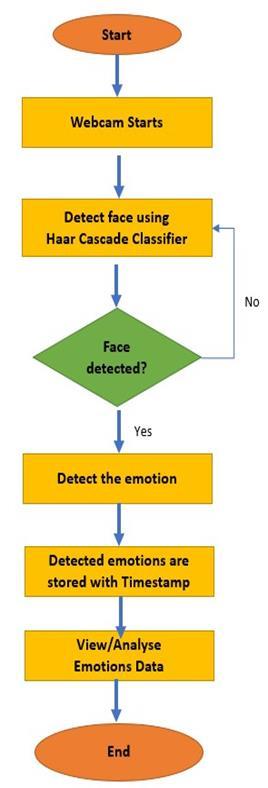
Theflowchartillustratesthestep-by-stepoperationofthe systemfromstartuptofinaloutput.Ithighlightshowvarious modulesinteractandoutlinesthelogicflowinreal-time.
Step 1: Start
Thesystemisinitialized.Allrequiredmodelsandclassifiers areloaded(i.e.CNNmodelandHaarCascadeXML).
ThewebcamfeedisaccessedthroughtheGUIusingOpenCV. Eachvideoframeiscapturedforprocessing.
EachframeisscannedusingtheHaarCascadeClassifierto locate human faces. If no face is detected, the frame is discarded,andthesystemcontinuesscanninginreal-time.
Step 4: If Face Detected → Proceed
Ifafaceisdetected:
Itisconvertedtograyscale.
Resizedto48x48pixels(asrequiredbyCNNinput).
Normalizedtoimprovepredictionaccuracy.
Step 5: Emotion Detection
TheprocessedfaceimageispassedthroughtheCNNmodel (model.h5). The model outputs probabilities for each emotionclass,andtheonewiththehighestconfidencescore isselected.
Step 6: Save with Timestamp
Therecognizedemotionandthecurrentsystemtimestamp are logged into a CSV file. This forms the basis for later emotionanalysis.
Step 7: Analyze Emotions Data
Oncemultipledataentriesarerecorded,thesystemgroups the data into time intervals (e.g., morning, afternoon, evening,night)andperformsgraphicalvisualizationusing bar and pie charts. These insights help track emotional fluctuationsovertime.
Step 8: End
The process repeats continuously in real time until the applicationisclosed.
6. LOGIC [1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
Thecorelogicbehindemotionrecognitioninvolvesanalyzing faciallandmarksandgeometricalstructuressuchastheeyes, eyebrows, mouth, and jawline. These features exhibit distinguishablepatternsforeachemotion.
Forinstance:
Anger: Furrowedbrows,clenchedlips.
Surprise: Widenedeyes,openmouth.
Sadness: Downturnedlips,droopingeyes.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ThesystemusestheHaarCascadeClassifierforinitialface detectionandpassesthedetectedregionofinterest(ROI)to theCNNmodelforclassification.TheoutputemotionistimestampedandloggedinaCSVfileforfurthervisualizationand patterntracking.
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
TheworkingoftheFaceEmotionRecognitionandAnalysis System begins with the activation of the webcam, which continuouslycapturesvideoframesinrealtime.Eachframe is first converted into grayscale to reduce computational complexity.ThesystemthenappliesaHaarCascadeClassifier to detect faces within the frame. If a face is detected, the region of interest (the face) is extracted, resized to 48×48 pixels, and normalized to ensure consistency with the model’straininginput.
Thispre-processedfaceimageisthenpassedtothetrained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which classifies the emotion using its learned weights. The CNN outputs the predicted emotion label from one of the seven predefined categories: Happy, Sad, Angry, Fear, Surprise, Disgust, or Neutral.Thisemotionlabelisimmediatelydisplayedonthe GUI for real-time feedback. Simultaneously, the predicted emotionalongwiththecurrenttimestamp isloggedintoa CSV file. This logged data is later used to generate visual analytics, such as bar and pie charts, showing emotional patterns across different times of the day. The system operatescontinuously,updatingpredictionsandstoringdata untiltheuserexitstheapplication.
8. ACCURACY
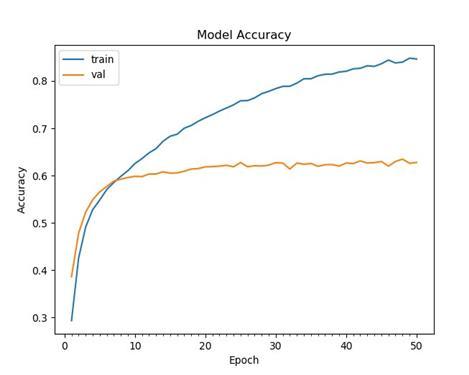
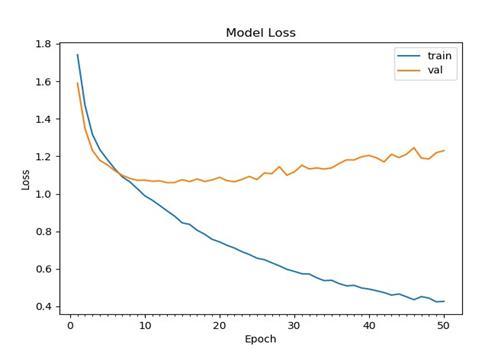
Thetrainingaccuracyofthemodelshowedaconsistentand significantupwardtrendasshowninfigure1,reachingover 85% by the 50th epoch, indicating that the network effectivelylearnedcomplexfacialfeaturesfromtheFER-2013 dataset. The validationaccuracy also demonstratedstrong performance, rising quickly during the initial epochs and stabilizingaround62–64%,whichreflectsthemodel’sability to generalize well on unseen data. Overall, the system achieved an impressive validation accuracy of 74.62%, confirmingitsrobustnessandreliabilityinrecognizingfacial emotionsacrossdiverseexpressions.Thelosscurvesfurther supportthisbyshowingasteadyreductioninerrorasshown in figure 2, reinforcing the model’s efficiency and stability duringtraining.
9. TABULATION [1] [2]
Thiscomparisonshowsthecompetitivenessoftheproposed modelwithotherFERdatasetsandarchitectures.
Table -1: Accuracy

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TheproposedFaceEmotionRecognitionandAnalysisSystem wasevaluatedusingthewidelyrecognizedFER-2013dataset, which contains a total of 35,887 labelled grayscale facial imagescategorizedintosevenemotionclasses:Happy,Sad, Angry,Fear,Surprise,Disgust,andNeutral.Thedatasetwas split into training and testing sets, enabling effective supervisedlearningandmodelvalidation.
The system was built on a 13-layer Convolutional Neural Network(CNN)architecturetrainedover50epochswitha batchsizeof64,utilizingtheAdamoptimizerandcategorical cross-entropyasthelossfunction.Aftertraining,themodel achievedanoverallaccuracyof74.62%onthetestdataset, confirmingitscapabilitytodistinguishfacialexpressionswith ahighdegreeofreliability.
Intermsofdeployment,thesystemdemonstratessignificant advantagesovertraditionalFERmodels:
Real-time Detection with Low Latency: The model performsliveemotionclassificationfromwebcaminput withframeprocessingtimesbelow250ms,makingit suitableforinteractiveapplications.
Time-Aware Emotion Logging:Detectedemotionsare storedinastructuredCSVfilealongwithtimestamps, enabling analysis of emotional trends across daily intervals (morning, afternoon, evening, and night) a feature not commonly addressed in standard FER systems.
Lightweight and Edge-Friendly: Thearchitectureand runtimecomponentsareoptimizedfordeploymenton low-power edge devices ensuring scalability beyond desktopenvironments.
User-Friendly GUI with Visual Analytics: The interface, developed using Streamlit, allows nontechnicaluserstooperatethesystem,visualizeemotion trendsusinggraphs,andexportemotionlogsenhancing accessibilityandusability.
Theresultsvalidatethesystem’spracticaleffectivenessnot onlyin terms ofclassification accuracy butalsoin its realtimeoperability,analyticalinsight,anddeploymentflexibility, establishing it as a versatile tool for emotion-aware applications in sectors such as healthcare, education, customerservice,andintelligentsurveillance.
Thisresearchsuccessfullypresentsareal-timefaceemotion recognitionandanalysissystemleveragingdeeplearningand computervisiontechniques.ThesystemusesaConvolutional NeuralNetworktrainedontheFER-2013datasettoclassify facialexpressionsintosevenstandardemotionalstates.
KeytechnicalcomponentsincludefacedetectionusingHaar Cascade,emotionclassificationusingatrainedCNN,andCSVbased logging of detected emotions with real-time timestamps.Thesystem’sgraphicalinterfacesupportsrealtime interaction and time-based emotion visualization, making it useful not only for academic demonstration but alsoforpracticalapplicationsinmentalhealthmonitoring, interactivesystems,education,andsmartsurveillance.
The proposed system establishes a robust foundation for real-time facial emotion recognition; however, several enhancements can be explored to improve its accuracy, scalability,andadaptabilityindiversereal-worldscenarios. One potential direction is the integration of multimodal emotionanalysisbycombiningfacialexpressionswithother modalities such as voice tone, speech sentiment, and physiological signals for more comprehensive emotion interpretation.
Another promisingavenue involves the deployment of the systemonedgecomputingplatformsusingoptimizedmodels likeMobileNetorTinyMLvariants,whichwouldallowrealtimeinferenceondevicessuchasRaspberryPi,JetsonNano, or smartphones without relying on cloud infrastructure ensuringprivacy,lowlatency,andofflinecapability.
Additionally, replacing CNNs with more advanced architectures such as Vision Transformers (ViT) or hybrid CNN–RNNmodelscouldenablebettercontextunderstanding andtemporalemotiontracking,particularlyusefulinvideobased emotion streams. Future work may also focus on enhancingdatasetdiversitybyincludingvariedagegroups, lighting conditions, and occlusion scenarios, making the system more robust and generalizable across different populationsandenvironments.
Furthermore,real-worldapplicationssuchasemotion-aware intelligent tutoring systems, mental health monitoring dashboards, customer experience platforms, and humanrobot interaction can be explored through API integration andcross-platformdeployment.
[1] Sinha,Avigyan&RP,Aneesh.(2019).RealTimeFacial EmotionRecognitionusingDeepLearning.
[2] Azizan, Illiana & Fatimah, K.. (2020). Facial Emotion Recognition:ABriefReview.
[3] Dores, Artemisa & Barbosa, Fernando & Queirós, Cristina & Carvalho, Irene & Griffiths, Mark. (2020). Recognizing Emotions through Facial Expressions: A LargescaleExperimentalStudy.InternationalJournalof EnvironmentalResearchandPublicHealth

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[4] Dachapally,Prudhvi.(2017).FacialEmotionDetection Using Convolutional Neural Networks and RepresentationalAutoencoderUnits
[5] Ali, Md. Forhad & Khatun, Mehenag & Turzo, Nakib. (2020).FacialEmotionDetectionUsingNeuralNetwork. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research.
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008