
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Atharva Kumtakar1 , Nishant Khandagale2, Amrish Karpe3, Narhari Joglekar4 , Prof. Pramila Chawan5
1 B. Tech Student, Dept of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
2 B. Tech Student, Dept of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
3 B. Tech Student, Dept of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
4 B. Tech Student, Dept of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
5 Associate Professor, Dept of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - In India's financial sector, customers face significantinefficiencieswhenverifyingtheiridentityacross multiple institutions, as the Know Your Customer (KYC) process requires repeated submission of identical personal information. This research proposes an innovative distributed ledger solution to address these redundancies. The system enables initial KYC verification data to be securely encoded on a blockchain network, allowing individuals to subsequently access their authenticated records through password verification for future identity requirements. After completing an initial verification with any financial institution, critical personal information including identity confirmation, residential details, and financial records becomes securely available on the distributed network. For subsequent verifications (such as new account establishment or credit applications), customerscanauthorizeaccesstotheirpreviouslyvalidated information without resubmitting documentation, dramatically improving processing efficiency. The distributedandpermanentnatureofblockchaintechnology provides enhanced security, transparency, and confidentiality while reducing vulnerability to information breaches. This approach offers financial organizations reduced operational expenses, stronger regulatory compliance,andaself-validatingsystemthatpreservesdata integritywhileenhancingcustomerexperience.
Key Words: Distributed Ledger, Decentralized Systems, Identity Validation, Efficiency Improvement, Financial Verification
The conventional method for issuing government documents in India is often plagued by inefficiencies and errors due to repetitive data entry. Citizens must repeatedly submit their personal information for each document application, leading to wasted time and an increasedriskofdatabreachesandinconsistencies.
To overcome these challenges, this paper introduces a blockchain-based decentralized document issuance system. By securely storing verified citizen data on a distributed ledger, the system seeks to streamline document issuance, enhance data security, and improve transparency.
The proposed system consists of the following key components:
Blockchain Network: A decentralized infrastructure that maintains a shared, tamperproofledgerofcitizenrecords.
Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements that automate document issuance and ensure data integrity.
Citizen Portal: A user-friendly platform enabling individuals to access their stored data and apply forgovernmentdocumentsseamlessly.
Furthermore, this paper explores different blockchain technologies to determine the most appropriate framework for implementing an efficient and secure decentralizeddocumentissuancesystem.
Hyperledger Fabric (HLF) is a permissioned blockchain frameworkthatisparticularlywell-suitedforgovernment applications involving multiple authorized entities. It enables government agencies to verify and issue documents while ensuring data privacy and controlled access. HLF supports private transactions and selective datasharing,allowinginstitutionstoregulateaccessbased on predefined roles. Key features include permissioned access, ensuring that only authorized entities participate

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
in the document issuance process, and private channels that securely share sensitive information among relevant parties. Its modular architecture allows seamless integrationwithexistinggovernmentsystems, simplifying thetransitionfromtraditionaldatabases.Smartcontracts, also known as chaincode, automate document issuance and verification, enabling citizens to retrieve their preverified data securely. The consensus mechanism, Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), ensures efficiency in networks where participants are already trustedentities.
ProofofAuthority(PoA)isaconsensusmechanismwhere transaction validation is handled by a predetermined set of trusted authorities. This approach is highly effective in government applications, as specific agencies can act as validators for official records. PoA balances decentralization with reliability, ensuring that only authenticated data is added to the blockchain.A key advantageofPoAisitsefficiency byeliminatingtheneed for extensive computational work, transactions are processed much faster than in Proof of Work (PoW) systems. This speed and efficiency make PoA an excellent choiceforlarge-scaledocumentissuance,wherereal-time processing is essential. Additionally, because validators are recognized government entities, security is enhanced, reducing the risk of unauthorized modifications while maintainingalightweightinfrastructure.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) offer a way to validate an individual’s credentials without revealing sensitive information. This is particularly useful in document issuance, where authorities need to confirm details like age or address without exposing additional private data.One of the major benefits of ZKP is its ability to upholdprivacywhileenablingefficientverification.Evenif parts of the blockchain network are compromised, ZKP ensures that raw data remains undisclosed, preserving system security. By implementing ZKP, governments can provide a privacy-centric approach to digital identity verification while maintaining the integrity of document issuanceprocesses.
Ethereumisawell-establisheddecentralizedplatformthat enables smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).Whileitspublicnatureandwidespreadadoption make it a promising technology, Ethereum's scalability limitations may pose challenges for large-scale document issuance systems requiring rapid processing.Despite this, Ethereum’s strong developer ecosystem and advanced contractfunctionalitiesmakeitasolidchoiceforproof-ofconcept projects and pilot programs. Its transparent and
secure nature ensures that document issuance processes can be automated while maintaining trust and accountability.
Corda is a distributed ledger platform designed specificallyforenterpriseuse,withafocuson privacyand controlled data access. Unlike traditional blockchains, Corda restricts access to transaction data, ensuring that only relevant participants can view specific records. This selective access makes Corda highly suitable for government document issuance, where confidentiality is paramount. Additionally, Corda’s support for smart contracts helps automate document verification, reducing manual intervention while ensuring compliance with regulatoryframeworks.Itsprivacy-firstapproachmakesit anexcellentoptionforsecuredocumentmanagement.
EOSIO is recognized for its scalability and flexibility, making it a strong candidate for decentralized document issuance systems. With its ability to handle high transactionvolumesandsupportcomplexsmartcontracts, EOSIO is well-equipped to manage large-scale governmental operations.By prioritizing speed and efficiency, EOSIO can help minimize processing delays, ensuring that citizens receive their documents in a timely manner. Its architecture allows for rapid transaction finalization, which is critical for maintaining smooth governmentservices.
Algorand operates on a Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS) mechanism, designed for high-speed and cost-efficient transactions. This blockchain framework is particularly advantageous for government applications that require quick response times, such as issuing identity documents and permits.By reducing transaction costs and enhancing processing efficiency, Algorand ensures a seamless document issuance experience. Its ability to finalize transactions quickly enables government institutions to provide faster access to verified citizen data, improving overallservicedelivery.
Tezos is a self-evolving blockchain that enables secure smart contracts while allowing for continuous improvements through community-driven governance. This adaptability is especially beneficial for government systems, which must evolve in response to regulatory changes and technological advancements.Tezos’ selfamending capabilities make it a forward-thinking choice for decentralized document issuance. With its robust infrastructureandfocusonlong-termsustainability,Tezos

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
provides a reliable foundation for building a secure and adaptablegovernmentdocumentissuancesystem.
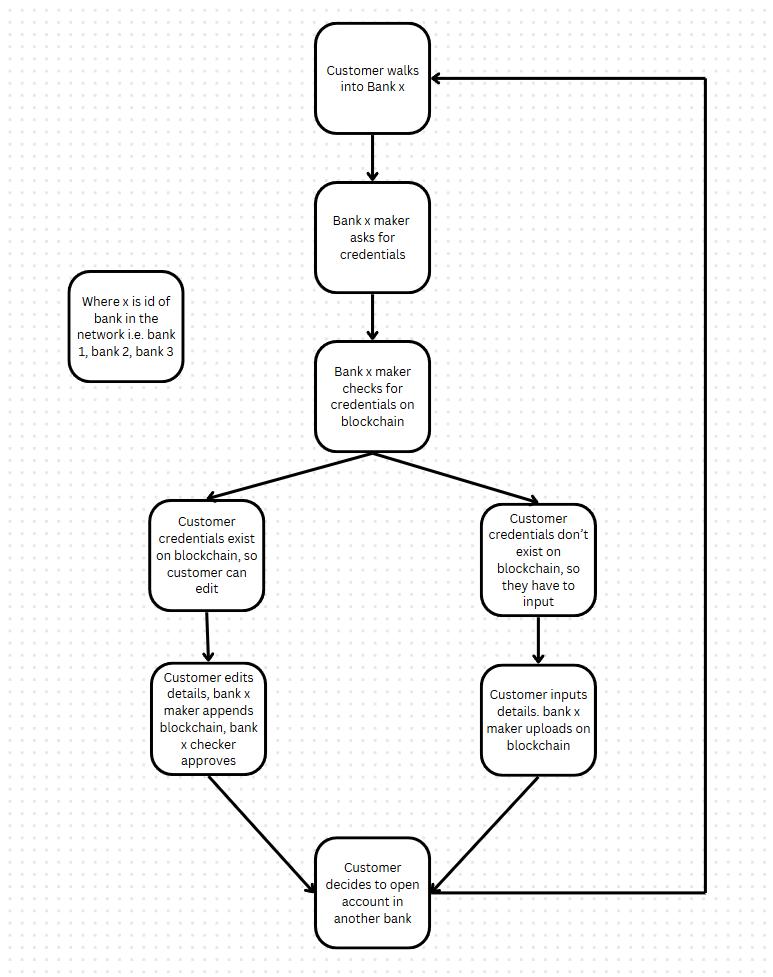
Here, 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3 are deemed suitable for usage. Anoverallviewoftheschemaisshownbelow(seeFig.1).
3.1 Problem Statement
The current centralized system for issuing government documents in India faces significant challenges, including redundant data entry, data security risks, and a lack of transparency. Citizens are forced to repeatedly provide personal information for each document application, leadingtotime-consumingprocessesandpotentialerrors. Centralized systems are vulnerable to data breaches, compromising sensitive personal information. Additionally, the lack of transparency in the traditional system hinders the tracking of document processing and identificationofpotentialbottlenecks.
Our solution is a blockchain-based decentralized document issuance system to mitigate the challenges and improve the overall efficiency and security of the documentissuanceprocess.
3.2 Problem Elaboration
The current KYC (Know Your Customer) verification process in financial institutions is plagued by inefficiencies,redundancies,andsecurityrisks.Customers are often required to submit the same personal information multiple times when opening bank accounts, applying for loans, or using other financial services. This repetitive data submission not only frustrates users but also increases the likelihood of errors, leading to delays and complications in financial transactions. These inefficiencies hinder seamless financial access and create unnecessaryburdensforbothindividualsandinstitutions. Beyondcustomerinconvenience,financialinstitutionsface significant administrative challenges in managing KYC data.Maintainingmultiplerecordsforthesameindividual leads to inconsistencies, complicating identity verification and compliance processes. Discrepancies across different databasescanresultindelays,increasedoperationalcosts, and regulatory non-compliance, ultimately weakening trust in the financial system. Furthermore, the security risks associated with centralized KYC storage are substantial. Storing sensitive customer data in multiple locations heightens the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. A single security breach can expose confidential information across various financial platforms,leadingtoidentitytheft,fraud,andreputational damage to institutions. To address these challenges, a blockchain-based decentralized KYC system is proposed. Bysecurelystoringverifiedcustomerdataonadistributed ledger,thissystemeliminates redundantdatasubmission.
Customers would only need to undergo KYC verification once,afterwhichtheirauthenticatedinformationcouldbe accessed by authorized financial institutions with user consent, significantly improving efficiency and reducing administrative workload. Smart contracts will play a crucial role in automating KYC verification, ensuring realtime updates, and enforcing compliance rules. These automated processes enhance data integrity, minimize human errors, and accelerate verification procedures, leading to a smoother customer experience and streamlined regulatory adherence. Additionally, blockchain technology enhances security and transparency by granting customers greater control over their personal data. Users can selectively grant access to institutions, ensuring privacy while maintaining compliancewithregulatorystandards.
This decentralized approach strengthens trust in the financial system and mitigates risks associated with centralizeddatastorage.ByleveragingblockchainforKYC verification, financial institutions can transform the existing system into a more efficient, secure, and usercentric model. The proposed solution not only enhances security and compliance but also simplifies identity verification,ultimately fostering a more seamless and trustworthyfinancialecosystem.
–RequirementAnalysis:
• Identify the necessary personal details required for variousKYCprocess(e.g.,Aadhar,PAN,voterID).
•Understandthecurrentprocessesfordocumentissuance and the challenges customers face, such as redundancy andlengthyverificationtimes.
–BlockchainDesign:
• Create a blockchain framework designed to securely store and manage customer data, guaranteeing that the information remains immutable and protected from tampering.
• Establish access control measures to ensure that only authorizedbankofficialscanaccessandvalidatethisdata.
–UserRegistrationandVerification:
• Develop a process for citizens to register for their first KYCbyfillingoutacomprehensiveform.
• Implement a secure method for verifying the details provided bycitizens, utilizingbank databasesandmanual checksifnecessary.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
–DataStorage:
•Useadecentralizedledgertechnology(DLT)tostorethe verifieddetailsontheblockchain.
• Assign a unique password to customers, allowing them toaccesstheirdataforfutureapplications.
–SubsequentKYCApplications:
•Createastreamlinedprocessforcustomersapplyingfor additional KYCs in other banks to retrieve their existing datafromtheblockchainusingtheprovidedpassword.
• Ensure that the application process is simple and userfriendly.
–Interoperabilitywithexistingbanksystems:
• Design the system to be compatible with existing databases and processes to facilitate smooth transitions anddatasharing.
•Trainbankofficialsonusingthenewsystemforefficient documentissuance.
–TestingandValidation:
•Conductthoroughtesting oftheentiresystem,including user interfaces, blockchain functionalities, and data retrievalprocesses.
• Validate the system against security, efficiency, and usabilitybenchmarks.
–DeploymentandUserTraining:
• Deploy the system in a phased manner, starting with pilotprogramsinselectregions.
• Provide training sessions for customers and bank officials to ensure effective use of the new system.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
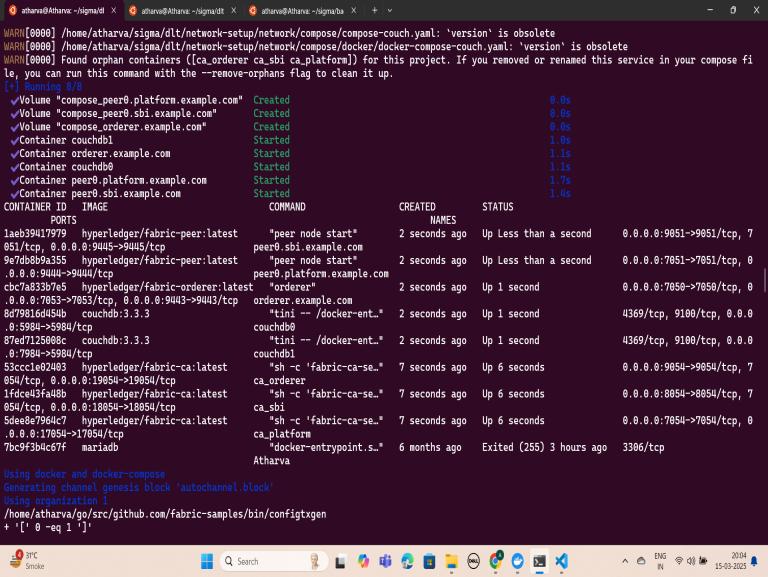
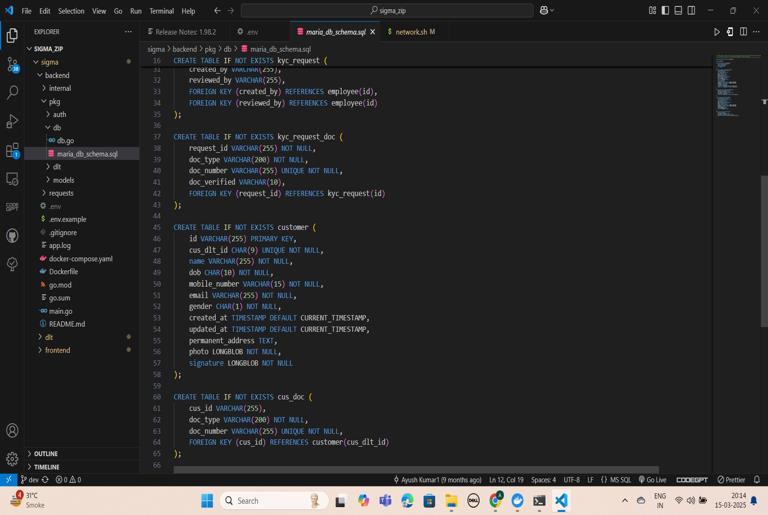
Fig -4: Backend & Database
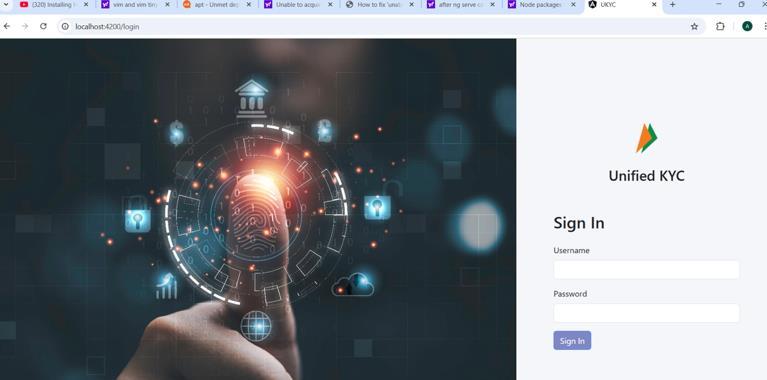
Fig -5: Frontend
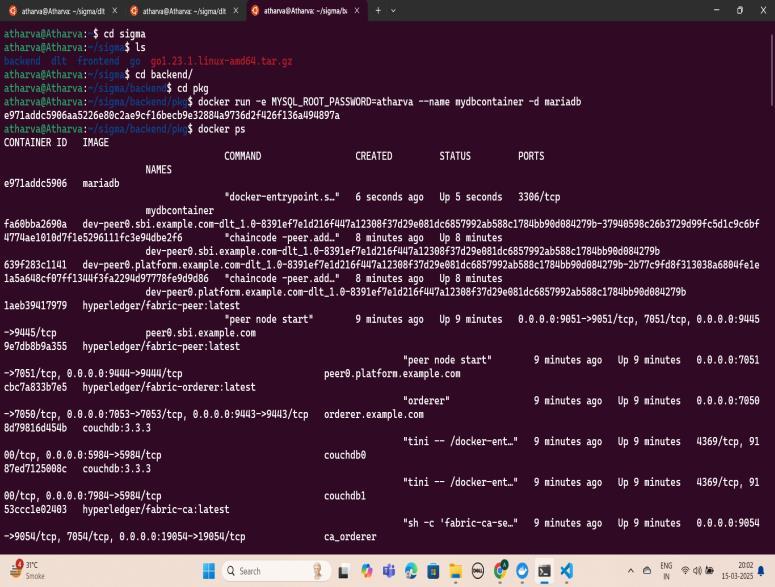
Inthefirstandsecondimages(Fig-2&Fig-3),youcansee the implementation of the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)usingHyperledgerFabric.Thisformsthecoreofthe decentralized KYC system, ensuring secure, immutable, and tamper-proof storage of customer verification data. The blockchain network enables financial institutions to retrieve pre-verified KYC information without redundancy, enhancing efficiency and security. Smart
contracts (chaincode) automate the verification process and enforce data access permissions, ensuring regulatory compliance.
The third image (Fig-4) showcases the backend of the project, developed using Node.js and Hyperledger Fabric SDK. The backend is responsible for handling KYC requests, executing smart contracts, and managing interactions between the frontend and blockchain network. A REST API is implemented to facilitate secure communication between financial institutions and the ledger, ensuring seamless retrieval and validation of customer data. The fourth image (Fig-5) presents the frontend interface built withAngular.js, designedfor both customers and financial institutions. Customers can submit their KYC details, manage access permissions, and trackverificationstatus.Financialinstitutionscanrequest and verify KYC data based on user consent. The UI is intuitive, ensuring a seamless experience for all users involvedintheKYCprocess.
The Decentralized KYC Verification System is designed to eliminate redundant identity verification processes in financial institutions using blockchain technology. Traditional KYC systems require customers to repeatedly submit personal information for different financial services, leading to inefficiencies, high operational costs, and security risks. This project leverages Hyperledger Fabric to securely store verified KYC data on a permissionedblockchain,allowingfinancialinstitutionsto access pre-verified customer information with user consent.
By implementing smart contracts (chaincode), the system automates KYC verification, enforces access control policies, and ensures data integrity. This approach enhances efficiency, security, and privacy, reducing manualverificationeffortsandimprovinguserexperience.
The traditional method of issuing government documents in India is riddled with inefficiencies, security vulnerabilities,andbureaucraticdelays.Citizensareoften required to submit the same personal information multiple times, leading to redundancy, data inconsistencies, and an increased risk of breaches. Additionally, the centralized nature of current systems makes them prone to cyberattacks and unauthorized modifications,furthercompromisingtrustandsecurity.
By leveraging blockchain technology, specifically Hyperledger Fabric, a decentralized document issuance system can effectively address these challenges. Through secure, immutable, and transparent data storage, this system ensures that once a citizen’s information is verified, it remains protected from tampering or unauthorized access. Smart contracts

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
automate the issuance process,eliminatingbureaucratic inefficiencies, reducing manual intervention, and significantly expediting approvals. Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain removes single points offailure,improvingsystemresilienceandreliability.
The implementation of this blockchain-based approach has the potential to transform how citizens interact with government services, making document issuance faster, safer, and more user-friendly. By minimizing redundancy, enhancing transparency, and strengthening security, this solution not only streamlines administrative processes but also establishes a more trustworthy and efficient digital governance framework.AsIndiamoves towards broader digital transformation initiatives, adopting blockchain for document issuance represents a forward-thinking step that could set a new standard for publicsectoroperationsworldwide.
The road to full implementation will require collaborations between government agencies, policymakers, and technology experts, ensuring regulatory compliance and seamless integration with existing systems. However, with the right infrastructure and support, blockchain technology could redefine the futureofpublicdocumentmanagement offeringa faster, more secure, and citizen-centric approach to governance.
As India continues its journey toward digital transformation, the adoption of blockchain for government document issuance represents a pivotal shift toward modernized, efficient, and secure public services.Byensuringthatverifiedcitizendataisstoredon a tamper-proof distributed ledger, this system minimizes the risk of fraud, unauthorized modifications, and data breaches. Additionally, with role-based access control, only authorized entities can access relevant citizen records, maintaining privacy and regulatory compliance The adoption of blockchain technology in government document issuance systems holds transformative potential for the public sector. By addressing core issues such as redundancy, inefficiency, and security vulnerabilities, blockchain offers a solution that not only enhances administrative processes but also fosters trust between citizens and government institutions. Through a decentralized, immutable ledger, citizen data is securely stored and easily accessible, ensuringthatonceinformationisverified,itcanbereused without the need for repetitive submission. This significantly reduces the bureaucratic burden on both citizensandgovernmentagencies.
The integration of Hyperledger Fabric ensures that sensitive citizen data is protected through permissioned access and private channels, allowing only authorized entities to access and share the data. Smart contracts further streamline document issuance by
automating the process, reducing human error, and ensuring faster approvals. These mechanisms are particularlybeneficialinacountrylikeIndia,wheredigital governance needs to be scaled to meet the demands of a large and diverse population. Additionally, this decentralized approach paves the way for a more transparent and accountable system. Citizens can track the progress of their document applications, ensuring greater transparency in processing times and providing a clearaudittrail.Thisreducesthechancesofcorruptionor mishandling of applications, as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that is visible to all participants.
[1] Maliha Zahan Chowdhury, "A Blockchain-Based Decentralized Document Au- thentication System for Multiple Organizations," in *2022 IEEE International WomeninEngineering(WIE)ConferenceonElectrical and Computer Engineering (WIECON-ECE)*, 2022. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3717114 82ABlockchain − BasedDecentralizedDocumentAuthenticationSystemfo rMultipleOrganizations
[2] Syed Azhar Hussain F., Zeeshan-ul-hassan Usmani S., "Blockchain-based Decentralized KYC (Know-Your-Customer)," in *ICSNC 2019: The Fourteenth International Conference on Systems and Networks Communications*, 2019. https://personales.upv.es/thinkmind/dl/conferences /icsnc/icsnc2019/icsnc201943028005.pdf
[3] Bodicherla Digvijay Sri Sai F., Ramisetty Nikhil S., Shivangini Prasad T., "A Decen- tralised KYC-Based Approach for Microfinance Using Blockchain Technology,"*CyberSecurityandApplications*,vol.1, Dec.2023,p.100009.
[4] Pradnya Patil F., M. Sangeetha S., "Blockchain-based DecentralizedKYCVerificationFrameworkforBanks," *ProcediaComputerScience*,vol.215,2022,pp.529536.
[5] Archangel : Trusted Archives of Digital Public Documents, Authors: John Collomosse, Tu Bui, Alan Brown,etal. Publication:arXivpreprint,2018.
[6] DocCert : Nostrification, Document Verification and Authenticity Blockchain Solution, Authors: Monther Aldwairi, Mohamad Badra, Rouba Borghol. Publication:arXivpreprint,2023.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072





AtharvaKumtakar

B.Tech.in Computer Engineering,VJTI, Mumbai.
NishantKhandagale

B.Tech.inComputer Engineering,VJTI, Mumbai. AmrishKarpe

B.Tech.in Computer Engineering,VJTI, Mumbai. NarhariJoglekar

B.Tech.in Computer Engineering,VJTI, Mumbai.
Prof PramilaChawan

Pramila M. Chawan serves as an associate professor in the computer engineering department at VJTI, which is affiliated with Mumbai university. With 31 years of teaching experience, she has supervised over 100 M.Tech projects and over 150 B.Tech projects. Dr. Chawan has authored 181 paper in peerreviewed international journals