
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Alifa Mansoori 1 , Smita B. Patil 2
1ME, Structural Engineering, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Datta Meghe College of Engineering, Airoli, Navi Mumbai, India
2Associate professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Datta Meghe College of Engineering, Airoli, Navi Mumbai, India
Abstract - This study explores the structural behavior and analysis of waffle slabsbyvariousapproaches.Waffleslabs are well known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and material efficiency. This study investigated by analytical theories and numerical simulations using FEM. The research performs comparative analysis of deflection predictions using Kirchhoff's Plate Theory, Timoshenko's Plate Theory, and Finite Element Analysis(FEA)andconcludesthatFEAprovides better accuracy. Timoshenko's theory with shear deformation shows close results withFEAthanKirchhoff'stheory,especially for thinner slabs.
The study also optimized waffle slab design parameters rib spacing, depth, and slab thickness according to ACI 318-14 provisions. FEA in Abaqus analyzes failure modes under ultimate loads, verifying results against experimental results and also carried out analysis in ETABS to determines the impact of design variables on structural performance. Major conclusions are the need for FEA methods for accurate deflection prediction, the efficiencyofautomatedoptimization in minimizing material costs. The results the offer real-world advice for engineers and highlighting the incorporation of computational techniques to optimize structural efficiency in waffle slab design. The research fills gaps in conventional analytical solutions and presents a complete framework for waffle slab design and analysis
Key Words: Waffleslabs, Structuralbehaviour,Highstrengthto-weight ratio, Material efficiency, Analytical theories, Numerical simulations, Finite Element Method (FEM), Comparative analysis
Waffleslabshaveprovedtobeaneffectivestructuralsolution forbuildingswithlargecolumnwithlongerspan.[1].They arealsoknownfortheirimprovedload-carryingcapacityand minimizedmaterialuse.Theseslabshaveamonolithicform of a thin top slab and crossing ribs in two perpendicular directions[2].Theseareextensivelyusedincommercialas wellasindustrialbuildings.Waffleslabs'shapereducesdead weightwithoutcompromisinghighstructuralefficiencythat iswhytheyareanidealchoiceoverconventionalflatslabs [3]. Recent advances in structural analysis and design software, particularly finite element modelling (FEM) and designsoftwarehaveenabledengineerstoperformthorough
analyses of waffle slabs [4]. The application of nonlinear analysis and parametric studies has helped understand behaviouroftheseslabsandtheirfailuremodes[5].These programshavealsohelpedoptimizationmethodsforthem further.Despitetheseadvancementsthereisstillalimitation onaccuratelypredictingwaffleslabresponses.Also,thereisa knowledge gap in design variable optimization, and cost savingimprovement.
Waffle slabs also known as a grid slabs are reinforced concreteslabsystemmadebyanetworkofribsrunningin perpendiculardirections[6].Theseribscreateacreatinga grid-like pattern, resembling like a Waffle, hence they are calledasWaffleslabs.Atypicalribanddeckarrangementof theseslabsisasshowninfigurebelow
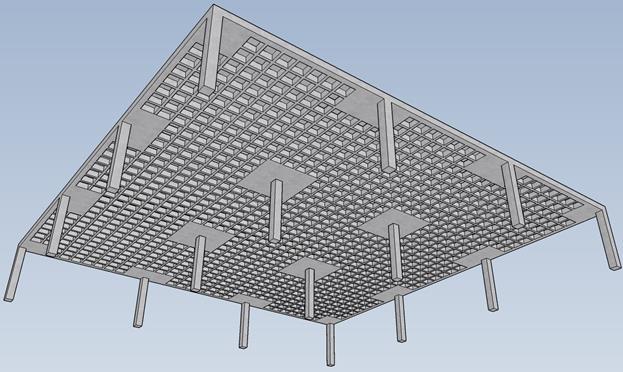
The article [6] "Two-Way Joist Concrete Slab Floor (WaffleSlab)SystemAnalysisandDesign"byStructurePoint isacompletemethodofdesigningwaffleslabsbasedonACI 318-14. It is centered on the Equivalent Frame Method (EFM) for two-way joist system analysis, explaining the structuralresponseunderdifferentloadingconditions.The articledescribesthestep-by-stepprocedureforcalculating flexuralstrength,shearstrength,andserviceabilitycriteria likedeflectionlimits.Bycombiningtheoreticalcomputations with software analysis, the research guarantees precision andadherencetodesignspecifications.Amajorcontribution

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
of this paper is its application in practice of ACI 318-14 provisions,andassuch,itisaworthyreferenceforengineers dealing with waffle slabs. The authors present design examples of manual calculation and compare it with software analysis. It shows the critical role of exact rib spacing, depth, and proper reinforcement placing. This process maximizes structural effectiveness. this paper includesanin-depthguidelinefordesignersandresearchers onhowtogetanunderstandingofandimplementACI31814criteriainwaffleslabdesign.
This research by Olawale et al [7] the optimization of reinforced concrete waffle slab design by using genetic algorithms. It is done to obtain cost-effective and efficient designs. The authors check different design parameters. These parameters were rib spacing, slab thickness and reinforcement details etc. By the combination of this optimizationmethodswithconventionaldesignmethodsthe researchshowinghowgeneticalgorithmsmakewaffleslab designmoreefficientthantraditionalmethods.Theauthors alsofindtheproblemsoftraditionaldesignmethodologies andsuggestanewapproachwithreducedmaterialuse.This research is significant to understand the role of artificial intelligenceinstructuralengineering.Thismethodespecially useful in optimizing slab structures under ACI 318-14 standards.Thestudyisanadditiontotheexpandingbodyof research on automated design processes and is hence a valuable reading for practicing engineers and researchers interestedinnovelmethodsforwaffleslaboptimization.
This research by Salomão et al [8] study into slab system selectionutilizingamulti-criteriadecision-makingmethod. Theauthorsshowsthatevenifstructuralengineersusually make their decisions based on material consumption and design compatibility, other important elements like productivity,aesthetics,sustainability,andusercomfortare mostly neglected. There is also a research gap in their opinion. to close this gap the research uses the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). They also verified their results withusingtheDelphiMethodandmachinelearningapplied toadatabaseofmorethan2000alreadybuiltslabs.
TheresearchhasproventhatAHPworkswelltoincorporate subjective and objective elements, giving a systematic approachforcomparingalternativeslabsystems.TheDelphi Method has also been extensively applied to improve decision models making sure the credibility of chosen criteria.Includingofmachinelearninginthisworkimproves forecastingaccuracybytheidentificationofpatternsinvast datasets of construction activities The current research indicates that solid slabs are often most commonly used basedoneaseofconstructionandoverallusage,withwaffle slabsbeingattractiveintermsoflowerweightandhigher span effectiveness. as per these authors most studies typicallyfailtobebasedonaholisticmodelencompassing large-scaleconstructionandoperationfactors.Inintegrating AHP,expertexamination,andmachinelearningtechniques,
this paper progresses earlier investigations through the implementation of a holistic and applicable construction industrydecisionmodel.
ThisresearchbyPechorskayaandSophia[9]discussesthe structural analysisof high-risebuildingsusingETABSand RSA software. The aim of the paper is to compare their performance in design use. The authors say that despite many software applications being available for structural analysis it is still challenging for engineers to select appropriateapplication.Duetothesimplicityandgraphical interface of 3D analysis programs, structural engineers increasingly apply them. This research is comparing the performanceofathirty-storyreinforcedconcretebuilding undergravitationalandlateralloads,includingwindloads, usingbothETABSandRSA.
Theseresearchers are basedon existingstudiesthat have investigatedthecontributionofsoftware.Moststudiesare basedonincreasingmodelingefficiency,loadanalysis,and designaccuracy.ResearchhasindicatedthatETABSandRSA are commonly applied in high-rise building analysis, with enhanced simulation capabilities. Existing literature indicates limitation in the results produced by various software as a result of differences in their algorithms and modelingstrategies.Thisresearchmakesanadditiontothis areabycontrastingaxialforcesandmomentsderivedfrom both programs and thereby indicating that RSA tends to yieldgreaterforceandmomentvaluescomparedtoETABS. This presentation of the differences, the study offers structural engineers' useful information for choosing the best-suited software depending on the needs of their projects.
This research by Anjali Mishra and Anurag Bajpai [10] examine the investigation of waffle slabs from various computational and theoretical approaches. This study is basedonassessmentofstructuralperformance.Atwo-way joistslabstructuremadeupofintersectingribsatregular gridpoints, madetocreate column-freespaces. Thestudy aims to compare analysis methods such as Rankine Grashoff'smethod(asanapproximate),Timoshenko'splate theory(asanexact),andthestiffnessapproachwithETABS 2018software.Froma comparison of reinforcedconcrete slabsofdifferingsizes 12×18m,18×24m,and24×30m the work studies significant flexural parameters, namely bendingmoments(Mx&My),shearforces(Qx&Qy),and mid-spandeflections.Theseresearchersexpandonprevious research that identifies the benefits of waffle slabs in minimizedmaterialcost.Theyalsoshowedhowwaffleslab enhancedstructuralefficiency,andbetterloadtransfer.Past studies have proven that waffle slabs provide superior structural behavior in large-span structures through minimized deflection at the same strength. The present investigation further enhances the understanding of the behaviorofwaffleslabsinthelightofIS4562000.

International
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
While waffle have many applications because of their efficiency in structural application, especially under longspan buildings. So, they have been analyzed for years but somegapsinknowledgeexistwithincurrentliterature.Few studies concentrate either on simplified analyses or numerical analysiswithouttakinga completecomparative approachtowardsboth.Conventionalanalyticalmodelslike Kirchhoff'sandTimoshenko'splatetheoriesareusuallyused separatelyandnotoftencomparedtohighlyaccuratefinite element simulations. This reduces the knowledge of their respectiveaccuracyandapplicability.
Inaddition,eventhoughfiniteelementanalysisisnowwidely used in structural engineering, few research studies have comprehensively compared its outcome with analytical predictions using design codes like ACI 318-14. The significanceofgeometricparameters ribspacing,ribdepth, andslabthickness indesigningwaffleslabbehaviourisalso not yet fully explored. Also, even with the existence of software such as ETABS and Abaqus, there isn't much recordedworkflowwithoptimization
The analysis of these slabs involves understanding parameterssuchasdeflectionbendingmomentsshearforces and stress distribution. There are multiple methods to analyzewaffleslabsviz:Grashoffmethod,Timoshenko’sPlate Theory, Yield Line Theory and Finite Element Analysis (FEA).According to [10] the Rankine-Grashoff method is a simplifiedmethodforanalyzingslabs.Ittreatsthewaffleslab asaseriesofconnectedbeams.Thisassumptionsimplifies thecalculationofmomentanddeflection.Tounderstandthe behaviour of these slabs, lets assume a1 and b1 are the spacingalongXandYdirectionsrespectively.
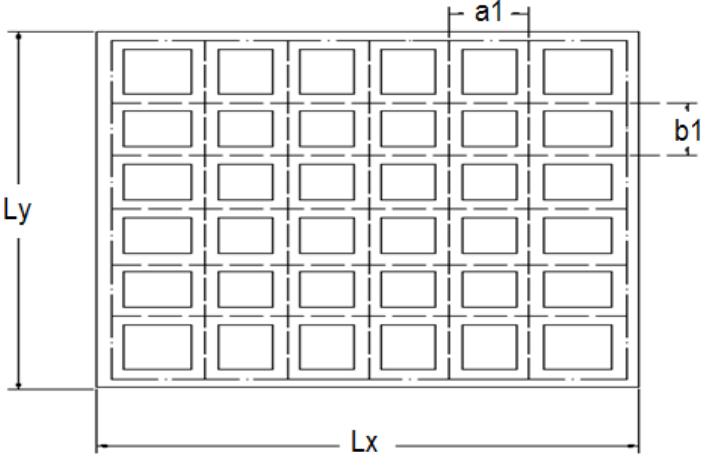
Fig -2:Topviewofwaffleslabsfrombottomdirection showinglongitudinalandtransverseribs[23].
Kirchhoff’splatetheory[15]
AccordingtoRankine-Grashofftheorydeflectionsofribsat junctionsaremadeequalandisgivenby
(1)
Where,,q1andq2aretheloadssharedinXandYdirections, respectively.Thesevaluesoftheloadsaregivenby,
(2)and
Thebendingmomentsforthecentralribsaregivenby,
(4)and
(5)
Theseareequivalentformulaefordesignoftwowayslabs because Rankine-Grashoff method is an approximate analyticaltechniqueusedfortheanalysisoftwo-wayslabs. Because of this it has several limitations when applied to waffleslabs,whichhaveagrid-likeribbedstructurerather thanauniformplate.
Timoshenko’sPlatetheory[11]
Timoshenko'sPlateTheoryisanadvancedstructuralanalysis methodusedtostudythebehaviorofplates.Itextendsthe classicalKirchhoffPlateTheory.Itdoesitbyincorporating the effects of shear deformation and rotary inertia. This makes it more accurate for analyzing complex structural systemslikewaffleslabs.
Where, D–FlexuralRigidityofthePlategivenby

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net
∇4w–BiharmonicOperator(Fourth-OrderDerivative)given by,
are slightly lower compared to those predicted by Timoshenko'stheory.
Thisformulationrepresentsthebendingdeformationinthe plate.Alsoβ–ShearDeformationCoefficientisgivenby,
(9)
Kirchhoff’stheoryassumesplanesectionsremainnormalto the mid-surface, but Timoshenko’s theory considers transverse shear deformations. Due to this there is a development of bending and shear. The rotations due to bendingandsheararegivenby,
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) differs higly from both Kirchhoff’sPlateTheoryandTimoshenko’sPlateTheoryinits approachtoanalyzingwaffleslabs.FiniteElementAnalysis (FEA) is quite different from Kirchhoff's Plate Theory and Timoshenko'sPlateTheoryinhowitgoesaboutanalyzing waffleslabs.WhereasKirchhoff'sandTimoshenko'stheories are based on analytical solutions with pre-established assumptions. FEA gives a numerical solution by breaking down the slab into smaller finite elements and solving for theirinteractions[16]
FEAtendstoyielddataclosertoexperimentalfindingsasit does not make limiting assumptions about the slab's performance [17]. FEA can model different boundary conditions,unevenloadsandcomplexstructuralgeometries withease.However,FEAaccuracydependsonthemesh,the typeofelements,andtheresourcesavailable,andtheseneed tobewellassessedwhileperformingsuchanalyses[18].
whereQx andQyareshearforcesperunitlength.Alsothe bendingmomentsperunitwidthinthexandydirectionsare givenby:
(12)
(13)
Mx ,My= Bending moments per unit width in the x and y directions(N·m/m).
TounderstandthedifferencebetweenKirchhoff'stheoryand Timoshenko'stheory,wesimulatedwaffleslabwassimulated withequalloadingconditions.Thedeflectionwascalculated incrementallyforvaryingslabthicknessesfrom100mmto 300 mm. Kirchhoff Plate Theory with transverse shear deformationassumedtobenegligible,wascontrastedwith Timoshenko'sPlateTheorywhichconsiderstransverseshear effects. Calculations were done based on established governing equations for both theories. From the graph, Kirchhoff'stheoryisseentopredictvaluesofdeflectionthat
The firststep in FEA is to divide the waffle slab into finite elements(typicallyshell,solid,orbeamelements).Thenodes oftheseelementsrepresentthedegreesoffreedom(DOFs)of thestructure.Eachnodehasdisplacementcomponentsu,v,w and, in some cases, rotational DOFs θx,θ y. The element deflectionthencanbecalculatedusing,
(15)
Where,w(x,y)=deflectionatagivenpoint,Ni(x,y)=shape functions,wi=nodaldisplacement.
ThegeneralequilibriumequationforplatebendinginFEAis derived from the weak form of the governing differential equation.Usingtheprincipleofvirtualwork,theequilibrium equationcanbewrittenas[19].
(16)
=Globalstiffnessmatrixofthewaffleslab,{d}=displacement vector(unknownstobesolved),{F}=appliedforcevector.
For a thin plate, the stiffness matrix is derived from the bendingstrainenergy:
Where, [B] = strain-displacement matrix,[D] = material stiffnessmatrix,dA=differentialelementarea.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net
For a plate bending element, the stiffness matrix includes bendingterms:
Where, E =Young’s modulus, ℎ= slab thickness = Poisson’s ratio.Oncetheglobalstiffnessmatrixisassembled,boundary conditionsandloadsareapplied.Thesystemofequationsis solved to obtain the displacements at each node. Bending momentsintheslabareobtainedfrom.
Thegraphshowsacomparativeanalysisofdeflectionvalues inawaffleslab.Itisobtainedusingthreedifferentmethods: Kirchhoff’s Plate Theory, Timoshenko's Plate Theory, and Finite Element Analysis (FEA). As slab thickness increases thedifferencebetweenKirchhoffandTimoshenko'smodels reduces.Thisisindicatingthatsheardeformationsbecome less significant. This confirms work done by [20]. The deflectionvaluesareslightlydifferentfrombothanalytical theories.Thishappensduetotheconsiderationofadditional factorssuchasmaterialnon-linearity,boundaryconditions, and load distribution [21]. For thicker slabs, all three methodsshowrelativelysimilarresults,astheinfluenceof sheardeformationreducesasthicknessincreases[22].
The analysis of the waffle slab was carried out using ETABS version 20.0.0. The structure was modeled consideringaCartesiangridsystemwithgridlinesspacedat 10metersintheX-directionand8metersintheY-direction. The slab was divided into multiple panels based on point coordinatesdefinedpreciselytomatchthebaylayouttypical for a waffle slab system. The resultant slab system can be seeninthefigurebelow.
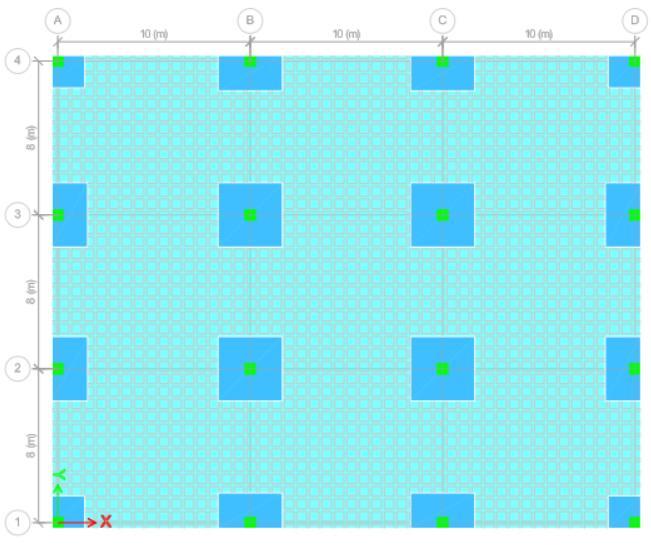
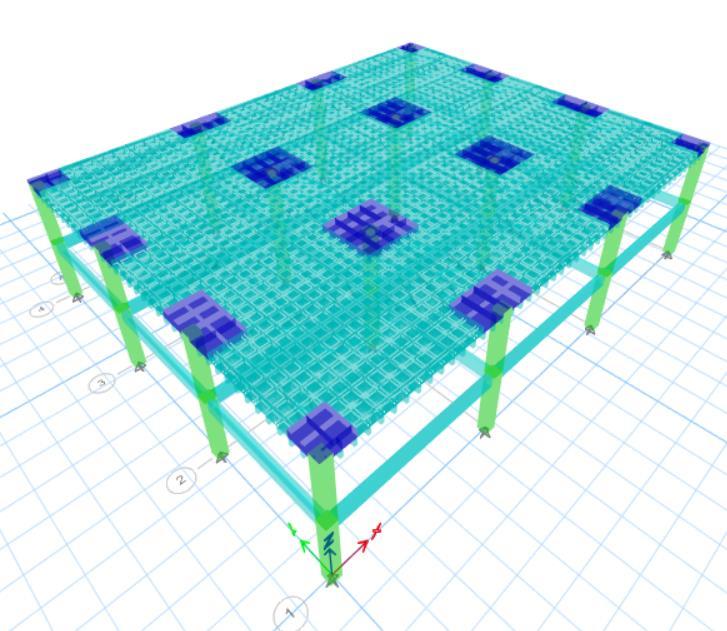

Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net
Table-1: Summaryofsectionsusedforanalysis
The material properties used included M25 grade concretefortheslab,beams,andcolumns,alongwithFe500 grade reinforcement. The slab was modeled as a shell elementwiththematerialpropertysettoM25concrete,and appropriatethicknesswasassignedtorepresentthewaffle slab’s behavior accurately. Dead loads and live loads were assigned through area load patterns defined in the model. Loadcombinationsweregeneratedasperstandarddesign practicestoensurethestructurewascheckedforallpossible criticalloadconditions.
Themasssourcefordynamicanalysiswasdefined byconsideringbothself-weightandappliedloads,without lumping mass at nodes, ensuring a realistic distributionof seismicforces.Modalanalysiswasconductedtodetermine natural frequencies, modal mass participation ratios, and mode shapes. After defining the model, structural analysis was performed to obtain results for base reactions, story drifts, story forces, and point displacements. The slab behavior under different load cases was evaluated by studyingthedeflectionpatterns,bendingmoments,andshear
forces.Allrelevantoutputswereextractedandinterpretedto assesstheperformanceofthewaffleslabsystemunderthe appliedloads.Theanalysisresultswerethenusedtovalidate theadequacyofthedesignandtocheckserviceabilitycriteria suchasdeflectionlimits.
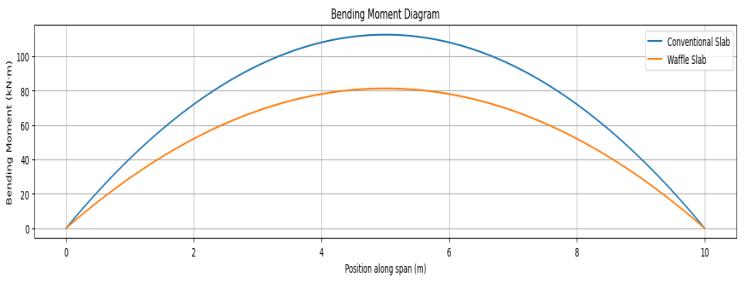
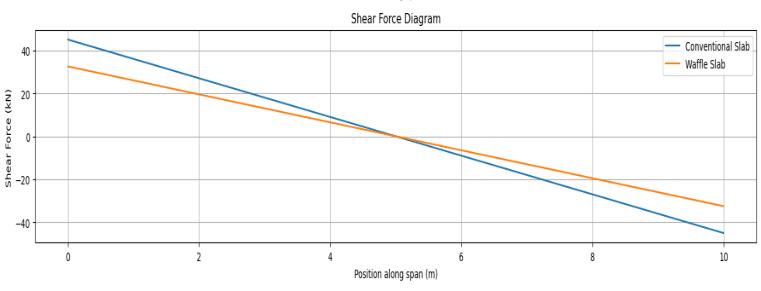
8

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thisstudycompletelyinvestigatedthestructuralbehaviorof waffle slabs by using analytical methods and numerical methods with ETABS analysis too. A comparison by using Kirchhoff's Plate Theory, Timoshenko's Plate Theory, and FiniteElementAnalysis(FEA)showedthatFEAisthebestfor makingdeflectionpredictionsbutETABSisbestforpractical design and analysis. Among analytical techniques, Timoshenko's theory, considering shear deformation, exhibited better conformity with FEA outcomes than Kirchhoff'stheory,especiallywhendealingwiththinslabs. Thestudyalsoemphasizedimportantdesignparameterslike rib spacing, rib depth, and slab thickness according to ACI 318-14 recommendations, resulting in better utilization of materials.ETABSanalysissimulationsconfirmedthefailure mechanisms and structural behavior under various loads. Overall,theresultshighlightissueswiththeclassicalmethods of analysis. in understanding behavior of waffle slabs and recommendtheuseofsophisticatedcomputationaltoolsin the design process. The paper offers useful practical guidelines for engineers who seek to attain material efficiencyandstructuralsecurityinwaffleslabsystems
[1] Designofsolidribbedandwaffleslabsforresidential buildings: A review. Indian Journal of Engineering, 2023, 20, e14ije1014 doi: https://doi.org/10.54905/disssi/v20i53/e14ije1014
[2] Curth,Alexander&Hartwell,Ashley&Brodesser,Tim & Mueller, Caitlin. (2022). Parametric waffle slabs: Optimal geometry materialized with additive construction.
[3] Portland Cement Association, Flat Slabs and Waffle Slabs:AnalysisandDesign:ReinforcedConcreteDesign Programs for Desk Calculators. Portland Cement Association,1972.
[4] Plos,Mario& Johansson,Morgan &Zandi, Kamyab& Shu, Jiangpeng. (2024). Recommendations for structural assessment of RC slabs using the finite elementmethod.10.1201/9781003483755-453.
[5] Al-Dala’ien,RayehNasr,AgusrilSyamsir,MohdSupian Abu Bakar, Fathoni Usman, and Mohammed Jalal Abdullah.2023."FailureModesBehaviorofDifferent Strengthening Types of RC Slabs Subjected to LowVelocity Impact Loading: A Review" Journal of Composites Science 7, no. 6: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7060246.
[6] Singh,S.(1994).FlatSlabandWaffleSlabSystems.In: CostEstimationofStructuresinCommercialBuildings. Macmillan Building and Surveying Series. Palgrave,
London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-130306_4
[7] Olawale,Simon&Akintunde,Olutosin&Afolabi,Mutiu & Tijani, Murtadha. (2020). Design Optimization of Reinforced Concrete Waffle Slab Using Genetic Algorithm. 4. 46-62. 10.22115/SCCE.2020.224460.1195.
[8] Nithyambigai G., Rameshwaran P.M., Stella Mary F., Behaviourofwaffleslab,MaterialsToday:Proceedings, Volume46,Part9,2021,Pages3765-3768,ISSN22147853,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.016.
[9] J. Prasad, S. Chander, and A. K. Ahuja, "Optimum dimensionsofwaffleslabformediumsizefloors,"Asian JournalofCivilEngineering(BuildingandHousing),vol. 6,no.3,pp.183-197,2005.
[10] Ali Alraie, Manoranjan Barik, Effect of continuity on reductionfactorsofbendingmomentsandshearforces ingridslabs,JournalofBuildingEngineering,Volume 13, 2017, Pages 291-297, ISSN 2352-7102, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2017.08.010.
[11] S.P.TimoshenkoandS.Woinowsky-Krieger,Theoryof PlatesandShells,2nded.NewYork,NY,USA:McGrawHill,1959.
[12] S.P.TimoshenkoandD.H.Young,TheoryofStructures, 2nded.NewYork,NY,USA:McGraw-Hill,1965.
[13] W.J.M.Rankine,AManualofAppliedMechanics,6th ed.London,UK:CharlesGriffin&Company,1872.
[14] M.YoosafK.T.,R.S.,andJ.Ramanujan,"Finiteelement analysis and parametric study of grid floor slab," AmericanJournalofEngineeringResearch(AJER),vol. 3,pp.20-27,2014.
[15] J. N. Reddy, Shear Deformable Beams and Plates: RelationshipswithClassicalSolutions,1sted.Oxford, UK:Elsevier,2000.
[16] Y.M.Desai,T.I.Eldho,andA.H.Shah,FiniteElement Method withApplicationsin Engineering.NewDelhi, India:PearsonEducationIndia,2011.
[17] O.O.R.Famiyesin,K.M.A.Hossain,Y.H.Chia,P.A.Slade, Numericalandanalyticalpredictionsofthelimitloadof rectangular two way slabs, Computers & Structures, Volume 79, Issue 1, 2001, Pages 43-52, ISSN 00457949, https://doi.org/10.1016/S00457949(00)00113-9.
[18] Liu,Yucheng.(2013).EffectsofMeshDensityonFinite Element Analysis. SAE Technical Papers. 2. 10.4271/2013-01-1375.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[19] C. S. Jog, Introduction to the Finite Element Method. Bangalore,India:IndianInstituteofScience2012.
[20] Ramsay,Angus&Maunder,E.A.W..(2016).AnErrorin Timoshenko's 'Theory of Plates and Shells'. The StructuralEngineer.94.36-39.10.56330/UYQU3957.
[21] Kk, Riyas & Dewangan, Uk. (2016). Effect of Material NonlinearityonDeflectionofBeamsandFrames.Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 9. 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i28/92375.
[22] Birkle,Gerd&Dilger,Walter.(2008).Influenceofslab thickness on punching shear strength. ACI Structural Journal.105.180-188.
[23] S.C.Woodson,TestsandEvaluationofUpgradedFlatPlateandWaffle-SlabFloorSystems.PN,1983.