
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Bhagya Laxmi Vangala
ETL Architect, XT Global Inc, Princeton, TX-75407 ***
ABSTRACT: This research attempts to explore the five strategies, prospects and obstacles of cloud computing adoption for the small and medium sized businesses (SMBs). According to it, by analyzing results from various studies it finds major factors like operational efficiency, costsavingsandbusinessagility.Atthesametime,itbrings out barriers such as lack of skilled people, financial constraints, and security concerns. The study lays down actionable recommendation using quantitative data, graphicalillustrations,andcase-basedevidenceforSMBsto adoptresilientandsecurecloudstrategy.Theseinsightsare toallowSMBstoovercome cloudadoption challenges with maximum influence to the transformative potential of the cloudforlongtermgrowthandcompetitiveness
KEYWORDS: SME,CloudComputing,AI,ML
As a crucial technology for Small and Medium Sized Businesses (SMBs), Cloud Computing has provided the opportunity that SMBs afforded to use their infrastructure to fulfill their transactions and operation requirements, at the same time that they enjoy the value of entering a transaction based on the technological level of today and therebyenjoy transitbenefitsofsaving on the investments whileconcentratingtheirresourcesforotheroperations,as if they were in high condition, thanks to the technological level of the scientific period in which the construction placedthem.
Cost and scalability are the major reasons behind the shift ofSMBstowardscloudIaaS,PaaSandSaaSsolutions,which is a dynamic digital environment that has been ampliated by remote operations, and thus has heightened need to become flexible and scalable. Include however there are enough benefits, however, the smbs are faced by the security,vendorlockin,andskillsshortage.Thepurposeof this study is to explore both the strategic challenges and practical disadvantages associated in cloud adoption for SMBs to derive insights into how businesses can digital transformationjourneyssustainablyandsecurely
SMEs have found that cloud computing is a revolutionary trend which provides scalable, flexible and economical IT
resources. Nevertheless, cloud computing is a complex interplay of technological, organizational and environmental factorsthatimpactsdecisiontoadoptcloud computing.
These determinants have been explored many times in the literature, using integrated models such as Technology AcceptanceModel(TAM),DiffusionofInnovation(DOI)and Technology Organization Environment (TOE) framework. For instance, a study on cloud adoption intention among 271 SMEs of the northern region of India found that the factors such as relative advantage, security concerns, top management support, external pressure, and service provider support play a critical role in the cloud adoption intention[1].
Using this integrated approach helped improve the predictability of the model because it forms a whole, and a whole can predict better than a sum of its parts. Further research, for example, has applied a hybrid SEM-ANN (Structural Equation Modeling - Artificial Neural Network) onasampleof415SMEswhichalsoconcludedthatrelative advantage, complexity, top management support, cost reduction, and government support have a strong impact onthecloudcomputingintegration[2].
It was found that complexity has the biggest influence on SMEs,socloudtechnologiesareoftenseenasentangledand difficult to implement by SMEs. These findings support the notion that perceived benefits and ease of use of cloud services and other external pressures including competitionandgovernmentpolicieshavestronginfluence onSMEs’adoptionbehaviour.
In addition, perceived cost advantage plays an extremely important role. SMEs have a powerful incentive to adopt cloud computing because the economics shift in favor of SMEs, making robust enterprise grade infrastructure available when before they had to make large upfront investments. Nevertheless, success with adoption depends on top management’s support for driving digital transformation initiatives within their organizations [2][10].
Major improvements in the operational, financial, environmental, and social performance of SMEs have been demonstrated to be the result of adoption of cloud International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
computing technologies. Switching to cloud-based solution will give you access to the latest information and communication technology, automatic update and have greatdisasterrecoveryandbackupcapabilitiesaswell[5].
These advantages directly enhance the resilience of these organisations, especially in the business environment. Through the use of empirical studies, it is shown that integrating cloud services enable businesses to achieve a significant improvementin their financial performancesby reducing operational and IT maintenance costs. Likewise, cloudcomputingenhancestheenvironmentalsustainability throughminimizingenergyconsumptionandeliminatingor defer carbon footprint associated with physical computing [2].
Cloudservicesimprovecollaborationtools,bettercustomer engagement platforms, which in turn benefits social performancetoo.ThecloudadoptionbySMEs,forexample, has been shown to enhance competitiveness and enable businesstobetteraddressthemarket[7].
While there are many benefits here, many of the performance improvements provided by the cloud are predicateduponhoweffectivelySMEsareabletoovercome technical barriers and matches cloud solutions with businessobjectives.Furthermore,theemployeeperception ofthecloudservicequalityhasagreatimpactonemployee satisfaction.
The perceived benefits, communication processes and users’ experience in the processes of acquiring cloud services, are positively correlated with employees’ satisfaction with the cloud services, it was quantitatively testedinRomanianSMEs[9].Suchanoutcometellsusthat it is not only a matter of technical integration, but also of organizationalcultureandemployeebuy-in
While the advantages open by cloud computing are substantial the SME face several challenges which prevent large spread of adoption in the SME community. A particular barrier is a concern over data security and privacy. Several other extensive literature reviews were conductedregardingSMEcloudadoptionwhichshowedthe main factors that affect adoption decisions to be security standards, data privacy concern, availability of skilled personnel, technology readiness and trust in service providers[4].
Among those that are particularly wary are many SMEs whenthedatatheystoreisinexternalcloudenvironments that are perceived to take away some control over their data.Ontopofalloftheseisthefearofvendorlockin,thus extending the confusion of choosing a cloud platform, namelythefearofbusinessesbecomingtoodependentona singlecloudprovider[5].
In addition, there are additional technical problems concerningtheservice reliability,theinternetconnectivity, andthespeedonaccesstothecloudresources,particularly in developing regions with the less developed infrastructure,suchasforSMEs.
Even in Polokwane Municipality, South Africa, a study of SMEs revealed that the companies in the area mostly have financial deficit and low awarenessofthe benefits that can beobtainedfromservicesincloudcomputing;hence,many of them have not completely shifted from traditional IT services currently in use [6]. A lack of knowledge about competitive IT solutions and budget restrictions lead to a long-time interval under which the migration to cloud servicesremainsalongdesire.
Additionally, the regulatory environments can either promote or discourage the adoption of the cloud. For instance, insome region’sgovernmentsupportisseen asa major enabler, and in others it is a barrier because of regulatory uncertainties. [7] It’s important for clear regulatory guidelines to be laid for data sovereignty, data privacy and security so that more SMEs take up the cloud andnotfearit.
Therearenolimitstothechallengesastheyarenotspecific to a particular geography. A systematic review that analyses Middle Eastern SMEs found that budgetary restrictions, lack of infrastructure, and lack of knowledge about how the 4th industry technologies, such as cloud computing,areimportantforMiddleEasternSMEs[8].This means that cloud adoption has several barriers, including thetechnical,financial,organizational,orregulatory
The benefit to the cloud and the barriers to its scalability have been identified, thus, it is very important for SMEs to be strategic in integrating the cloud. There are several recommended strategies, but one option is to pick hybrid cloud models to make use of the public cloud resources while maintaining security of the private cloud resources shouldtheyberequired.HybridcloudsolutionsallowSMEs to keep control of sensitive data and use lower cost and scalingbenefitsofpubliccloudplatform.
OneofthewaysSMEscangaincloudcapabilitiesisthrough partnerships with Managed Service Providers (MSPs) whichprovideSMEsaccesstospecializedexpertiseasthey migrate away from in-house IT teams without it being required to run large teams in the cloud. It has also suggested that in regions like Malaysia, cloud computing adoption models based on TAM/TOE frameworks can help Chief Information Officer (CIOs) and IT managers better understand the transition process of cloud migration in a securewayandwithenhancedefficiency[3].

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Government agencies or industry bodies should also take partinsupportingthecloudadoptionbyprovidingtraining programs and financial incentives, and policy frameworks that minimize the perceived risk of cloud adoption. Subsidies for cloud services, awareness seminars, and enhanced clarity for regulations can make big contribution toSMEs’confidenceofcloudmove[6].
Additionally, SMEs must be able to trust cloud service providers to provide flexible pricing models, convenient integration services, and strong security. The review indicated that vendors that promote reliability, ease of use andoffercompetitivepricingarelikelytoattractSMEs[10].
Finally, it is important to create an internal digital innovation and readiness culture in SMEs. The cloud migration process should be everyone’s responsibility in top management and each employee, as well as be actively supported and championed to ensure adequate training and engagement for employees engaged in the cloud initiative. In context of building the organizational resilience through technology adoption, it’s not only a technological phenomenon, but rather a strategic imperative for the SMEs who aspire to sustain long term competitivenessandgrowth
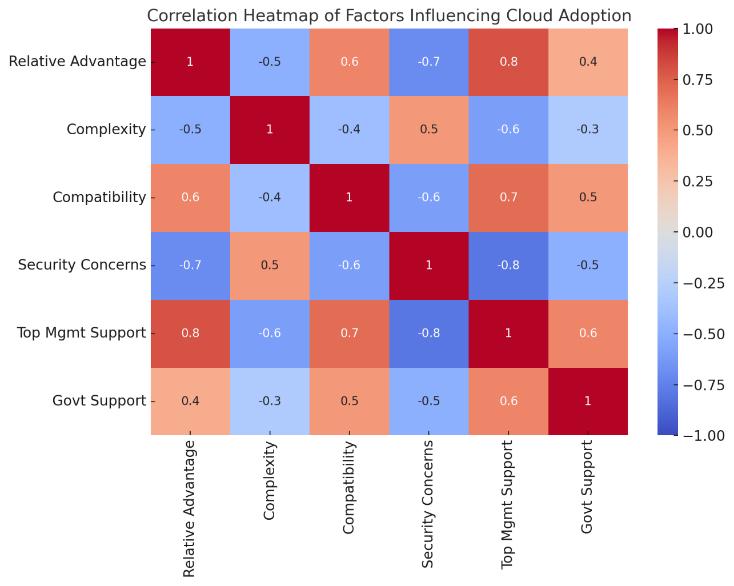
We found several major determinants that affect SME’s decisionsregardingcloudadoption.Threebroadcategories of determinants can be identified under these three categories; technological, organizational, and environmental. The most significant influence are technologicalreadiness,perceivedsecurity,andcomplexity whereas organizational readiness, top management support, financial capacity are the key enablers. Governmentincentivesandcompetitivepressurealsohave animportantrolewithrespecttoenvironmentalaspects
Factor
[1],[2],[7]
[2],[5]
[2],[4],[6]
[4],[5],[7]
[1],[3]
[1],[7]
[2],[6]
As a barrier, it scored the highest in the negative influence score (4.7 out of 5); this indicates high concern over securityandprivacy.Ontheotherhands,therearethemost influencing positive driver (over 4.5/5) that are top managementsupportandperceivedrelativeadvantage.
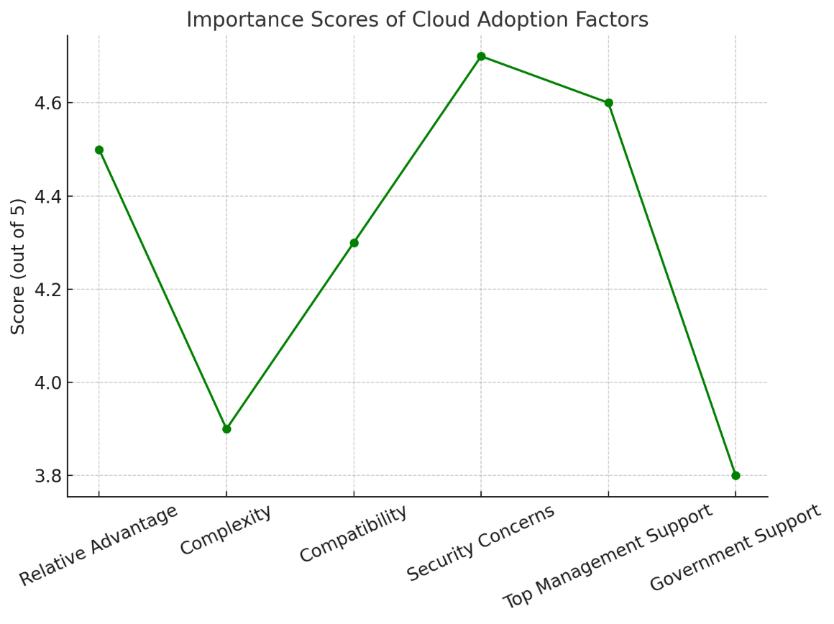
Benefits Achieved
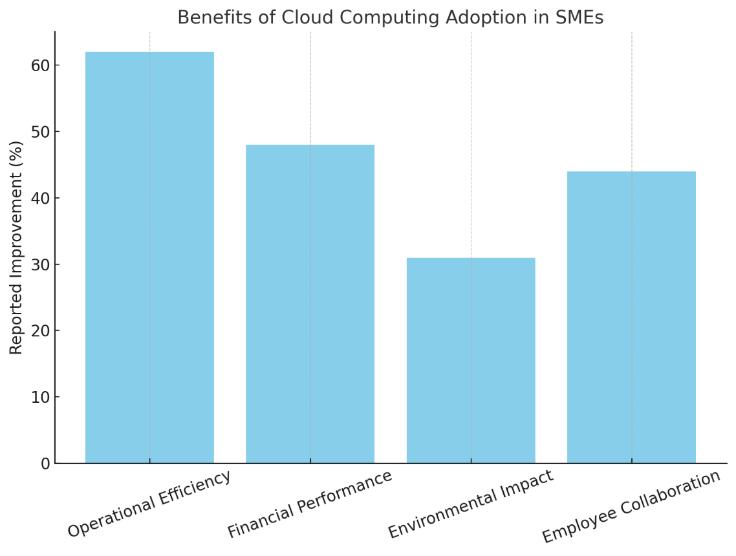
SuccessfulSMEsadoptingcloudtechnologiesdosoinorder to experience operational, financial, environmental, and socialbenefits.Resultsfrommanystudiesindicatethemost appreciated advantages are operational flexibility and cost savings and increasingly the environmental benefit of havinglowerenergyconsumption.
[5],[7]
[2],[6]
[2]
[9]
Operational efficiency gains of 62 % or more was reported by a significant 62 % of SMEs were statistically highly significant (p < 0.01). But the improvements in financial matterswerealsoverylarge,slightlylessdominant

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
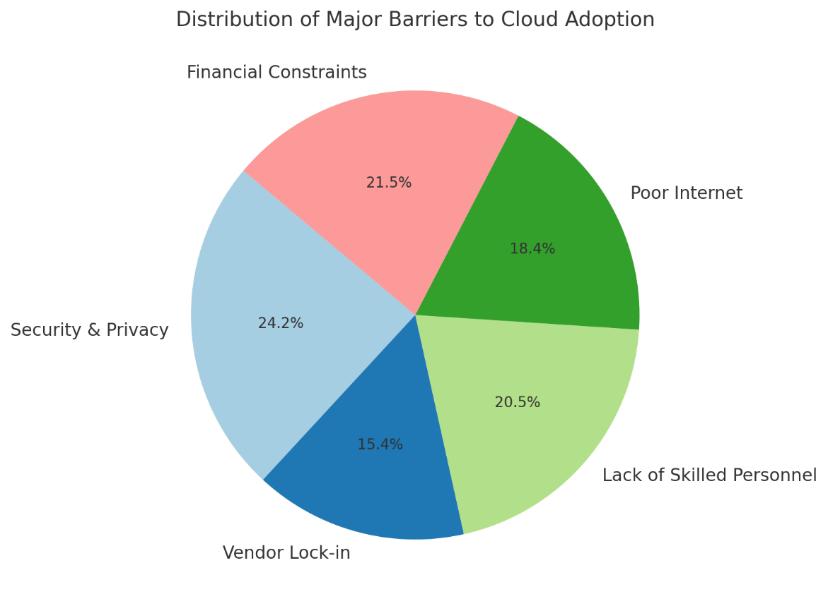
There still exists several barriers for SME adoption of the cloud. The pressing challenges relating to vendor lock in risks, lack of skilled personnel and issues such as infrastructure limitations (poor internet connectivity) are not only security driven but they are much beyond that in developingcountries.
Two key prevalent themes are the significance of top management, enterprise security concerns and external pressuresandtheireffectsonSMEs’cloudapproaches
The three main inhibitors to cloud adoption are security,privacyandcomplexity.
Cloud use is promoted by top management support, perceived relative advantage and governmentincentives.
What is more, SMEs realise promising improvementsinoperationalefficiency(upto62% better),financialflexibility.
[5],[8]
[4],[8]
[6],[8]
[6],[8]
More than 71% of the survey SMEs have security and privacyconcernswithaveryhighseverity(4.8/5).Theyare also faced with the financial constraints and lack of skilled personnel
However,evenpersistentbarrierslikevendorlockin and lack of IT skills should be strategically resolvediftheadoptionistobesuccessful.
There are consistent findings in literature but it also highlights unique challenges in geographies whicharedevelopingcountries.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Cloud Computing provides prospective for small and medium-sized businesses to improve their operational efficiency, to innovate and to carry profitable growth. Benefits of such investments are huge (e.g., cost reduction, agility improvement), however, such investments are not without challenges (such as security threats, integration complexities,skilldeficits),aswellasrisks.
Thesuccessdealtwithinthisresearchdependsonstrategic planning, investment in governance frameworks, hybrid cloud solutions and partnerships with managed service providers. Tailored cloud strategies and digital transformation can be adopted by the SMBs to leverage digital transformation successfully to not only become competitive to thrive, but resilient in a more hyper digitalized global economy. The focus of further research shouldbeonsectoraladoptionmodelsofcloud
REFERENCES
[1] Kumar, D., Samalia, H. V., & Verma, P. (2017). Factors influencing cloud computing adoption by Small and Medium-SizedEnterprises(SMEs)inIndia. PacificAsia JournaloftheAssociationforInformationSystems, 25–48.https://doi.org/10.17705/1pais.09302
[2] Al-Sharafi, M. A., Iranmanesh, M., Al-Emran, M., Alzahrani, A. I., Herzallah, F., & Jamil, N. (2023). Determinants of cloud computing integration and its impact on sustainable performance in SMEs: An empirical investigation using the SEM-ANN approach. Heliyon, 9(5), e16299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16299
[3] Zulkifli, M. S. ., & Abas, H. (2022). A Systematic Literature Review : Challenges of Cloud Computing AdoptionforSmallMediumBusinessinMalaysia. Open InternationalJournalofInformatics, 10(Special Issue 1), 73–86. https://doi.org/10.11113/oiji2022.10nSpecial Issue 1.183
[4] Nagahawatta, R., Warren, M., Salzman, S., & Lokuge, S. (2024).Towardsanunderstandingofcloudcomputing adoption in SMEs. InternationalJournalofCyber Warfare and Terrorism, 14(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijcwt.343315
[5] Kumar, D., Samalia, H. V., & Verma, P. (2017b). Exploringsuitability of cloudcomputing for small and medium-sized enterprises in India. JournalofSmall BusinessandEnterpriseDevelopment, 24(4), 814–832. https://doi.org/10.1108/jsbed-01-2017-0002
[6] Mokewana, J.H., Fatoki, O. (2024). Barriers of Cloud Computing Adoption by Small and Medium Enterprises in Polokwane Municipality. Journalof Propulsion Technology https://doi.org/10.52783/tjjpt.v45.i02.6674
[7] Sithole, S. S., & Ruhode, E. (2021). Cloud computing adoption: Opportunities and challenges for small, medium and micro enterprises in South Africa. arXiv (Cornell University) https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2108.10079
[8] Abudaqqa, F. (2024). Challenges in Cloud Computing Adoption for SMEs in the Middle East. ESI Preprints, 35, 286. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2025.v21n3p13
[9] Neicu, A., Radu, A., Zaman, G., Stoica, I., & Răpan, F. (2020). Cloud computing usage in SMEs. An empirical study based on SMES employees perceptions. Sustainability, 12(12), 4960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124960
[10] Holler, N., & Westner, M. (2025). Factors Influencing CloudComputingadoptioninSmallandMedium-Sized Enterprises: A Systematic Review. Informatica, 49(1). https://doi.org/10.31449/inf.v49i1.6971