
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Mr. Kishan S1 , Mr. Bharath S B2 , Mr. Abhishek3 , Dr. Balaji S4, Dr. Nayana G.Bhat5
1,2,3Students, Computer Science and Engineering, Jyothy Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India
4Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, Jyothy Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India
5Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, Jyothy Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India
Abstract - AgroSense is an intelligent irrigation monitoring device designed to help farmers make faster, more informed irrigation decisions. The system collects real-time data such as temperature, humidity, electric conductivity, and soil moisture using a field-deployed network of sensors. The data are transferred to a server, where a decision tree-based machine learning algorithm determines whether or not irrigation is required. Users can then access the insights using a mobile and web application, which allows them to view historical data in charts, monitor current conditions, and get timely irrigation warnings. AgroSense, developed utilizing cutting-edge technology and with a focus on simplicity and sustainability, is intended to reduce water waste and enable more informed farming via smart automation.
Key Words: Smart Irrigation, IoT Sensors, Machine Learning, Flutter, Real-time Data, Web and Mobile Application, Precision Agriculture, Decision trees, Flask , PostgreSQL, LH-SLTHPHECR sensor, USR-W610
1.INTRODUCTION
In most countries, especially developing ones like India where the vast majority of people depend on agriculture for their livelihood, it continues to be the foundation of botheconomicstabilityandfoodsecurity. Technologyhas advancedinotherfields,butagriculturehaslaggedbehind inadoptingnewsolutions,primarilyduetoignoranceand resource constraints. Water management stands out as one of the most pressing issues facing farmers these day. It is more important than ever to control water use in agriculturebecauseoftherisingstrainthatclimatechange is placing on freshwater resources and the unpredictable weather patterns it produces. Traditional irrigation techniques, including hand watering or schedule-based systems,frequentlyleadto eitherexcessiveorinsufficient irrigation,whichnegativelyimpactscropproductivityand health. Conventional approaches typically overlook timesensitiveaspectsincludingtemperature,humidity,andsoil moisture,whichresultsinwaterwasteand,insomecases, crop damage. These inefficiencies may have significant socioeconomic repercussions in regions with limited water supplies. This calls for a more intelligent, datadriven approach to irrigation one that reduces waste
without compromising output and enables farmers to makebetterdecisions.
Mismanagement of agricultural water is still a major problem, with common consequences such as crop loss, lowyields,andlong-termenvironmentaldamage.Farmers continue to use conventional irrigation techniques, which mayresultinexcessiveorinsufficientusageofwatersince they do not take into consideration the actual soil or weather conditions. This not only wastes valuable resourcesbutalsohasanimpactonfarmproductivityand profitability. According to research, smart irrigation systems based on the Internet of Thingscan reduce water consumption by up to 40% while maintaining or even increasing crop yields. AgroSense, our solution, uses a sensor-driven, real-time decision-support system to solve these issues. AgroSense uses machine learning to provide preciseirrigationrecommendationsbytakingtemperature, soil moisture, and other environmental factors into account. In addition to improving water efficiency and enabling sustainable agriculture, this technology gives farmerspracticalinsights.
This study seeks to develop and deploy a smart irrigation system that utilizes the potential of IoT and machine learning to optimize water management in agriculture. The primary objective is to create a system that is capable of providing precise and timely irrigation suggestions based on real-time soil data received from IoT-based sensors. One of the most significant goals is assessing the efficiency of a decision tree algorithm in interpreting this sensor data and making irrigation decisions. Another significant goal is the creation of an easy-to-usemobileapplicationthatenablesfarmerstosee important soil parameters and obtain irrigation recommendations in an intuitive and user-friendly manner. In general, this research adds to the emerging body of precision agriculture by offering a real-world and effectivesolutiontomaximizewateruseandenhancecrop yieldsthroughsmartautomation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
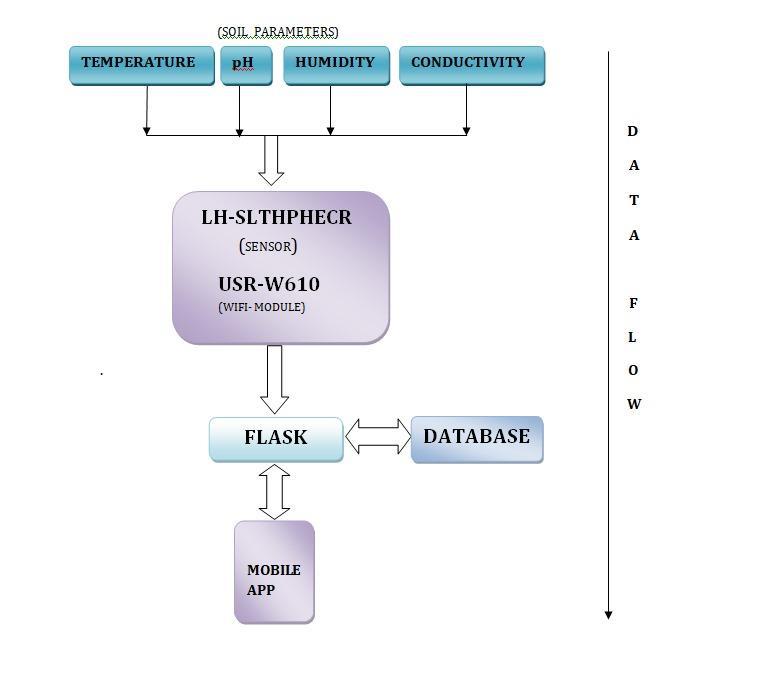
The goal of this project is to develop a smart irrigation system that uses machine learning and real-time soil monitoring to optimize agricultural water management. UsinganLH-SLTHPHECR sensor,thesystemkeepsaneye on four crucial soil parameters: temperature, pH, humidity, and electrical conductivity. A Flask-based backend receives the data wirelessly via a USR-W610 WiFi module, processes it, and stores it in a PostgreSQL database.Thesensorvaluesareprocessedusingadecision tree algorithm to determine whether irrigation is necessary. A Flutter-based smartphone application that displays historical patterns, real-time sensor values, and intelligent irrigation recommendations is how users interactwiththesystem.Thescopeofthiseffortislimited to system creation and initial testing; automated control functionsandextensivefielddeploymentmaybeaddedin thefuture.
Precision agriculture is a cutting-edge farming method that uses location-specific, real-time data that is immediatelygatheredfromthefieldtoinformagricultural decisions. This approach allows for the customized administration of inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides based on the unique needs of each location rather than employing standard procedures throughout a farm. This focused strategy minimizes environmental damage, cuts waste, and increases crop yield and quality. Bykeepinganeyeonenvironmentalvariables,crophealth, andsoilconditions,technologieslikeGPS,GIS,anddifferent field sensors are essential. The fundamental tenet of precision agriculture is to apply the appropriate input at the appropriate time, location, and quantity. Some advanced modelsalsohighlighta fifth element executing thesetasksinthemosteffectiveandresponsibleway.
2.1 The Role of Internet of Things (IoT) Devices in Modern Agriculture, Focusing on Sensor Technologies for Soil Monitoring
InternetofThings(IoT)hasrevolutionizedfarminginthe currenterabyunitingacollectionofintelligentdevicesand systems.Inthiscase,IoTconnectsdifferentelementssuch as sensors, agricultural machinery, and controllers so that tasks are automated and there is real-time feedback on essential factors such as soil health, weather, and crop status. This connection allows farmers to make welleducated,data-drivendecisions,leadingtoimprovedyields and greener farming practices. Among the core applications of IoT in agriculture is the use of sensor technologies to monitor soil properties continuously. In thisproject,theLH-SLTHPHECRsensorhasbeenutilized a multifunctional multi-parameterdevicethatcanmonitor soil temperature, pH, humidity (moisture), and electrical
conductivity. The sensor sends data using the USR-W610 Wi-Fi module, which provides uninterruptible transmission of data to linked systems. In contrast to traditional manual sampling, IoT sensors offer continuous streams of data, which are essential in applying machine learning modelsusedto optimizeagriculture andimprove decision-making.
2.2 Application of Machine Learning Algorithms, Specifically Decision Trees, in Agricultural Decision-Making, Particularly for Irrigation Management
Machine learning has emerged as a robust tool in precisionfarming,providingadvancedtechniquestomodel intricate agricultural data and make forecasts that can optimize resource management and improve decisionmaking.Ofthemanymachinelearningalgorithms,decision trees are notable for their interpretability and robust classification performance, and hence are especially suitable for use in applications such as irrigation management. A decision tree is a tree structure in which everyinternalnodeisasoilparameter,everybranchisthe result of that parameter,and everyleaf node isa decision. For irrigation management, leaf nodes would generally be whether or not to irrigate. The algorithm operates by continuously dividing the data according to input feature values to produce balanced subsets that relate to a given outcome.Decisiontreeshaveanumberofbenefitsforfarm use, such as their capacity to process bothcategorical and numerical data without the need for extensive data preparation
Variousresearchstudieshaveexploredtheconvergence of IoT and machine learning to improve irrigation efficiency and foster agricultural sustainability. Mohammad Hussain Seyar et al. [1] designed a precision irrigation system that integrates neural networks, fuzzy logic, and IoT sensors, facilitating real-time monitoring of soilmoistureandsmartwaterdeliveryingreenhouseand open-field implementations. Their application showed substantial reductions in water loss and increased crop yield. Also, Ban Alomar and Azmi Alazzam [2] used a Mamdani-type fuzzy logic controller in their IoT-based irrigation model, controlling water flow based on predefined fuzzy rules associated with soil temperature and moisture. Efficiency of the system was confirmed through MATLABsimulations.
J.N.KaggwaandA.Telukdarie[3]introducedanML-aided IoT irrigation system optimized for crops including beans and potatoes. Their method reduced overwatering by turning on irrigation only when soil moisture fell below a

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
certain level, lowering the cost of operations and increasingtheaccuracyofirrigation.SwapnaliB.Pawaret al. [4] came up with a low-cost implementation using IoT and Raspberry Pi and automated irrigation depending on crop-based moisture requirements in order to save labor and water. In a more general context, Ravesa Akhter and Shabir Ahmad Sof [5] discussed the use of IoT, data analytics, and ML in precision agriculture, proposing a predictive model for detecting apple disease while describing the challenges of integrating technology into conventionalfarmingpractices.
Additional developmentsareRevanth Kondavetietal.[6], who integrated rainfall forecasting and motor optimization with Romyan's method in a smart irrigation schemeforruralwaterandenergyefficiency.R.N.Kirtana et al. [7] suggested a Zigbee-based, solar-powered irrigation system that makes use of ETcrop modeling and machine learning to forecast crop water requirements, thus improving sustainability. Khaled Obaideen et al. [8] presented a meta-analysis presenting the effect of IoTbased smart irrigation on UN Sustainable Development Goals, focusing on enhanced water resource management andenvironmentalgains.J.Karpagametal.[9]proposeda sensor-driven automated irrigation system using microcontrollers, enabling real-time crop monitoring and autonomous water management to eliminate labor and ensure sustainable agriculture. Finally, Kiran Kumar Gopathoti et al. [10] utilized a logistic regression-based modelwithIoTsensorsandpastirrigationdatatodevelop a smart scheduling system that facilitates effective water usageandenhancedagriculturalproductivity.
4.1
The idea is made up of a number of clever parts that work together to create an intelligent irrigation system thatdisplaysdatainrealtime. Themaincomponentofthe arrangement is the LH-SLTHPHECR sensor, which keeps an eye on important soil characteristics like conductivity, temperature, pH, and humidity. A Flask-based backend server receives the readings wirelessly via the USR-W610 Wi-Fi module. A consistent record of soil conditions is created over time by the Flask server, which handles all processingandstoresthedatainaPostgreSQLdatabase.
The Flask backend uses an integrated decision tree machinelearningalgorithm toassessthisdataanddecide whetherirrigationisnecessary. Thesystem'sfrontend,a Flutter mobile application, then conveys the information to users.The application's straightforward, user-friendly interface with graphs and summaries shows real-time sensor readings, trends, and recommendations for intelligentirrigation.
Together,theseelementscreateaclosed-loopsystemthat includes data gathering, analysis, and application. As a result,producersorendusersmaymonitorsoilhealthand make data-driven, more educated decisions about when and how to irrigate to boost crop health and conserve resourcesinabeautifulandefficientprocess.
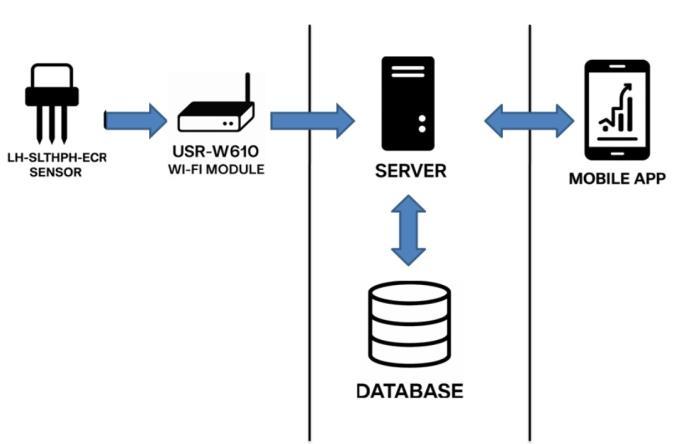
The flow of data in this system begins with the LHSLTHPHECR sensor, which continuously monitors major soil parameters such as temperature, pH, humidity, and conductivity. This raw data gets transmitted wirelessly to the backend via the USR-W610 Wi-Fi module, typically employingaprotocollikeRS485toTCP/IP.Afterreceiving the data from the Flask backend, it gets processed and validated and then saved in a PostgreSQL database. A decision tree algorithm, implemented in the backend, subsequently processes this data to produce irrigation suggestions. Concurrently, a Flutter mobile application on the user's device interacts with the backend by making API requests to fetch both real-time sensor readings and the most recent suggestion. The Flask server returns by extracting the data requested from the database and the outputofthemachinelearningmodelandrelayingitback to the app. The app shows this information in a straightforward, visual way displaying live soil information, past patterns in graphs, and personalized irrigation recommendations. The smooth, bidirectional flow of data keeps the user continuously informed with precise, intelligent insights to make improved irrigation decisions.

International
2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thesmartirrigationsystem'sbackendwasimplemented using the Flask framework due to its versatility and lightweightnature. Flaskisamicroframeworkthatworks well for developing targeted web apps and RESTful APIs that efficiently connect to databases and IoT devices. Because of its simplicity, we were able to quickly set up APIendpointstocontrolreal-timedataexchangebetween the Flutter mobile app, PostgreSQL database, and USRW610Wi-Fimodule.
Additionally, Flask has session management and user authentication built in, enabling safe access and focused user interactions. As the main server, it handles user sessions, reacts to incoming sensor data, and starts the appropriatereactions.
Libraries like psycopg2 were used to manage the PostgreSQLintegration,allowingforsmoothdataretrieval and storage. In order for the system to offer real-time irrigation recommendations based on real-time sensor information,theDecisionTreemachinelearningalgorithm wasalsointegratedintoFlask.
Allthingsconsidered,Flaskprovidedastrongandefficient backend that enabled the hardware, database, mobile application, and machine learning model to guarantee smoothsystemintegration.
Because the Flutter framework is cross-platform, a singlecodebasewasusedfordevelopmentonboththeiOS and Android platforms, allowing for a broad user base.
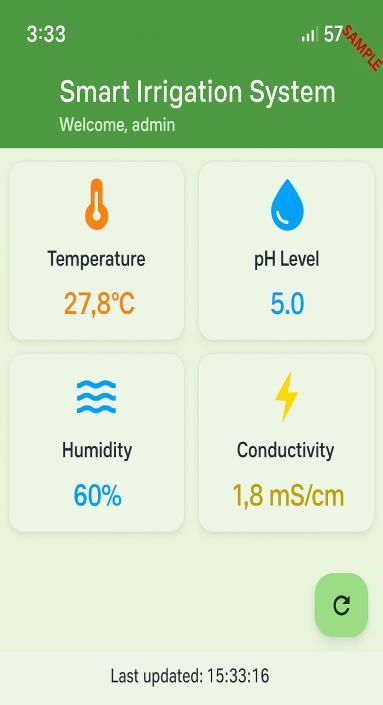
This allowed for the development of the mobile application. Thedirectinterfaceforuserstoengagewith thesmartirrigationsystemisthesmartphoneapplication. The smartphone application displays real-time sensor measurementsthroughaneasy-to-useuserinterface. The application'sgraphicaldepictionofthehistoricaltrendsof eachsoilparameterisamongitsmostcrucialfeatures.The application uses charting libraries to graph time series plots by retrieving data from the PostgreSQL database using the Flask backend. This allows users to observe the evolution of soil conditions over time.HTTP requests are used to communicate between the Flask backend and the Flutterapplication.Inordertoobtaincurrentsensordata, historical data for charting, and irrigation recommendations, the application sends calls to certain API endpoints on the backend. The requested data is returnedformattedbythebackend.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
IntheFlaskbackendoftheintelligentirrigationsystem, a Decision Tree machine learning algorithm was used to make smart and data-based irrigation recommendations. The model operates on a straightforward binary response eithersuggestingirrigationornot basedona range of soil parameters. These parameters were scrutinized using a dataset constructed from past agronomic records that associate certain combinations of conditions with optimal irrigation action on particular crops.
Intraining,thedatasetwassplitintotrainingandtestsets so that the model can be trained without overfitting. The Decision Tree was trained to identify patterns and relationships between the inputs of soil data and the resultantirrigationdecision.Thetreestructureconsistsof decision nodes that check particular soil characteristics, such as moisture or temperature, with the results branchingtoarecommendationattheleavesofthetree.
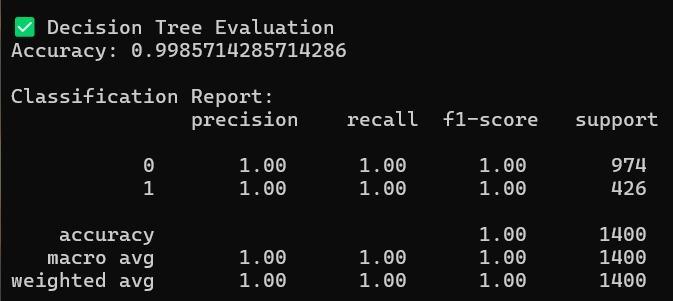
The thresholds and decision rules were not pre-specified; rather, they were learned from the data in training. This improvesthesystemtobeflexibleandadaptabletomany different soil conditions. For evaluating the effectiveness of the model, common evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score were employed. The above metrics validated the reliability of the model and its appropriateness over other machine learning methodstothisapplication.

PostgreSQL was named as the database result for the smart irrigation system because of its high scalability, trustability, and superior time- series data operation capabilities. As a important object- relational database operation system, PostgreSQL is well- suited for storing structured detector data particularly when powered by extensions similar as TimescaleDB, designed to give effective runningoftemporaldata.
Twokeytables live in the databasedesignone reserved for storing the credentials of druggies securely, and another reserved for logging detector measures of soil temperature, humidity( moisture), pH, and conductivity, each with a timestamp. The timestamp is either an indicator or a primary key so that queries can be queried snappily and efficiently over a certain time range, a demand that's imperative for examining trends and producingdatavisualizations.
TheFlaskbackendinteractswithPostgreSQLtoaddnew detector records transferred by the USR- W610 Wi- Fi module. This operation is performed with the help of database libraries similar as SQLAlchemy and psycopg2, which make SQL commands for performing data operations similar as insertions and queries more manageable.
When druggies pierce the mobile app to view literal detectordata,thebackendfetchesaffiliateddata fromthe databaseasperthechosen time window.Formaintaining performance as data increases, timestamp indexing was done to allow effective and fast data reclamation so that the system remains responsive indeed with large data sets.
BoththeLH-SLTHPHECRsensorandtheUSR-W610WiFi module are used in this intelligent irrigation system to collectdataaswellastransmitdatawirelessly.Thesensor measures vital soil parameters and transmits the same through a serial interface on the Modbus RTU protocol. The sensor is connected to the USR-W610 module, which isconfiguredtoreceivethisserialdatathroughaspecified port.
To send the data, the USR-W610 will be used as a Wi-Fi client and connect to a local wireless network with an internet connection. The module then processes the sensor readings, encoding the data into network packets, usuallyintheMQTTprotocol,andsendsthepacketstothe Flask backend server via the server's IP address and port number.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
This configuration ensures that real-time soil information is accurately communicated from the field to the backend system,allowingresponsiveandsmartirrigationcontrol.
Data on soil parameter trends gathered by the LHSLTHPHECRsensorandsavedinthePostgreSQLdatabase were presented in an intuitive manner by the Flutterbased mobile application. In order to understand how temperature, pH, moisture (humidity), and conductivity varied over time, users could simply see line graphs that displayed historical values of these parameters. Farmers were able to make better judgments about crop management and irrigation by learning more about soil behavior and how it responds to agricultural and environmentalfactorsthankstothesegraphicalinsights.
With precision,recall,andanF1-scoreof 0.99(99%), the decision tree model used in the irrigation suggestion system was incredibly precise. These results demonstrate how well the model can process soil data and offer trustworthy suggestions regarding when irrigation is necessary.
Overall, by facilitating the convergence of IoT and machine learning to better manage water resources, this research contributes to the dynamic future of smart farming. This approach offers a comprehensive view of soilhealth,unlikemethods thatsolelytrack soilmoisture. By putting real-time data and practical suggestions at the farmer's fingertips, the intuitive mobile app improves the system'susefulness.
In order to support more intelligent agricultural methods,thisstudywasabletopresentAgroSense,arealtimesmartirrigationmonitoringsystemthatusesIoTand machine learning. The system incorporates a PostgreSQL database for storing time-series and structured data, a Flask backend for handling data and executing machine learning algorithms, a USR-W610 Wi-Fi module for optimal wireless communication, the LH-SLTHPHECR sensor for detailed soil data collection, and a Flutter
mobile application that presents the data in an intuitive, user-friendlyformat.
These technologies work together to provide a complete andusefulprecisionfarmingsolution. Basedonactualsoil conditions, the decision tree model proved to be a very successfultoolforaccuratelyrecommendingirrigation.
Thesystem'smainvalueisinfacilitatingsustainablewater use by providing farmers with dependable, data-based information. Future improvements could include the addition of more environmental factors (like crop or weather), autonomous irrigation system control, research into sophisticated machine learning algorithms, and additional testing in various agricultural environments to confirm performance and adaptability in a range of circumstances.
[1] M. H. Seyar, P. D. Kahandage, and T. Ahamed, "An IoT-BasedPrecisionIrrigationSystemtoOptimize Plant Water Requirements for Indoor and Outdoor Farming Systems," in IoT and AI in Agriculture,Singapore:SpringerNature,2023.
[2] B. Alomar, Azmi Alazzam, "A Smart Irrigation System Using IoT and Fuzzy Logic Controller," in Proc. 5th HCT Information Technology Trends (ITT2018),Dubai,UAE,Nov,2018.
[3] J.N.KaggwaandA.Telukdarie,"Applicationof an IoT and Machine Learning Smart Irrigation System to Minimize Water Usage Within the Agriculture Sector," in Proc. 2023 IEEE Int. Conf. on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Singapore, Singapore, Dec. 2023.
[4] S.B.Pawar,P.Rajput,andA.Shaikh,"Smart IrrigationSystemUsingIoTandRaspberryPi," Int.Res.J.Eng.Technol.(IRJET),vol.5,no.8,pp. 1163–1166,Aug.2018.
[5] R. Akhter and S. A. Sofi, "Precision agriculture using IoT data analytics and machine learning," Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 5602–5618,Sep.2022.
[6] R. Kondaveti, A. Reddy, and S. Palabtla, "Smart Irrigation System Using Machine Learning and IoT," in Proc. 2019 Int. Conf. on Vision Towards Emerging Trends in Communication and Networking (ViTECoN), VIT University, Vellore, India,Mar.2019.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[7] R.N.Kirtana,S.Kavitha,B.Bharathi,B.Keerthana, and K. Kripa, "Smart irrigation system using Zigbee technology and machine learning techniques," in Proc. 2018 Int. Conf. on Smart Technologies for Smart Nation (SmartTechCon), Bengaluru,India,Aug.2018.
[8] K.Obaideen,B.A.A.Yousef,M.N.AlMallahi,Y.C. Tan,M.Mahmoud,H.Jaber,andM.Ramadan,"An overviewofsmartirrigationsystemsusingIoT," EnergyNexus,vol.7,Sep.2022.
[9] J. Karpagam, P. Bavithra, I. Infranta Merlin, and J. Kousalya, "Smart irrigation system using IoT," in Proc. 2020 6th Int. Conf. on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore,India,Mar.2020.
[10] K. K. Gopathoti, A. Gopatoti, N. Swathi, and S. S. Pendyala, "Enhancing crop water management: A logistic regression approach integrated with IoT for smart irrigation," Int. J. Sci. Methods Comput. Sci.Eng.,vol.1,no.1,pp.1–8,May2024.