
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1Janvi Jalit, 2Manasvi Deshmukh, 3Arya Raut, 4Gayatri Padole, 5Mansi Padole, 6Shri.R.M.Gharat
1,2,3,4,5Students, Electronics Engineering. 6HOD, Electronics Engineering, Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Polytechnic, Amravati, Maharashtra, India.
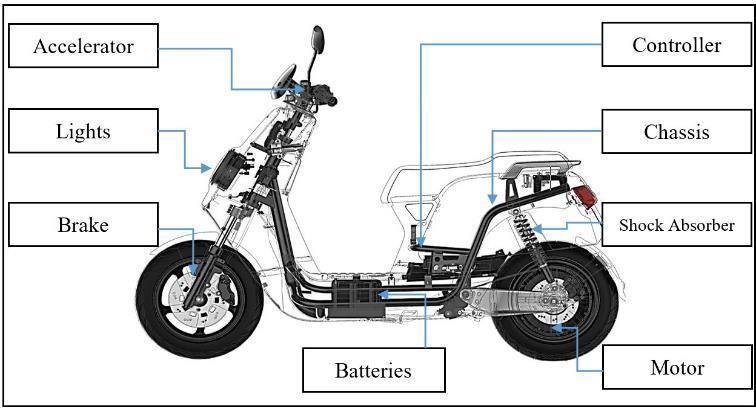
This paper presents a wireless regenerative braking system developed for electric two- wheelers. The main goal of the system is to recover the kinetic energy that is usually wasted as heat during braking and store it in the battery for later use. By doing this, the system helps increase the efficiency of the vehicle and supports longer battery life. A breaker circuit is included to automatically disconnect charging when the battery is full, which improves safety and prevents overcharging. The design also integrates “IOT” technology, where an LCD display and a mobile application “Blynk” show realtime data such as battery percentage, charging status, and vehicle speed. The accelerator is used to control the motor speed, while the brake activates regenerative charging to feed energy back to the battery. Studies have shown that regenerative braking can improve energy efficiency 15 to 20% in lightweight vehicles, while also reducing wear on mechanical brakes. With wireless monitoring and smart control, the proposed system offers a safer, more efficient, and sustainable solution for electric mobility.
Keywords: Regenerative braking system (RBS), Energy recovery, IOT, Battery management, Breaker circuit, Sustainable mobility.
Regenerative Braking System involves the removal of the kinetic energy of a moving object by converting it into anotherformofusefulenergy,suchaselectric,pneumatic, or stored kinetic energy. The use of regenerative braking can increase the overall efficiency of a motor vehicle by conserving some of its kinetic energy which can then be usedtobringthevehiclebackuptospeed[1].
Theregenerativebrakinghastheabilitytosavethewaste energy up to 8-25% [2]. Taking into account the needs of electric scooters to be able to reach their destination before the power stored in the battery is exhausted and the target of implementing electric scooters whose use is on small roads so that braking will often be carried out, thisregenerativebrakingsystemisconsideredsuitablefor application so that it can increase the mileage of electric scooters.[3]
Howeverfromthepointofviewofsavingenergy,mechanical brake increase out much energy while the EV’s kinetic energyisrenewedintothethermalone.Nowaday’selectric vehicles (EVs) have traditionally much attention for alternate to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.Thatcanbeseenduetohighlyincreasedawareness ofglobalwarmingandalsoriseincostofpetrolprices[2].
J. M. K. C. Donev et. al. (2018) explained different braking methods, with focus on regenerative braking as an energysaving approach. They describe how regenerative braking converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy instead of wasting it as heat.The paper highlights its importance for improving efficiency in electric vehicles comparedtoconventionalbraking[1].
Soniya K. Malode and R. H. Adware (2016) discussed the working and advantages of regenerative braking systems in electric vehicles. They explain how kinetic energy during braking isconvertedinto electrical energyandstoredinthe battery.Thisimprovesvehicleefficiencyandreducesoverall energyloss[2].
NabilaAsyifaCabrianiLestariet.alinvestigatearegenerative braking system for electric scooters using a permanent magnet DC motor to recover braking energy. The study shows that the recovered energy improves battery charging efficiency and extends scooter range. This confirms the practicality of regenerative braking in enhancing two-

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
wheelerEVperformance.[3].
Edgar Andre Manzano et. al. studied regenerative braking system for the Sakura M500 motorcycle, showing that braking energy can be effectively recovered to improve batteryperformanceandefficiency.[4].
Prof. Harsha Sarode et. al. demonstrate a battery monitoring system for electric bikes to track charging status,batteryhealth,andenhancesafetyinEVusage.[5].
Akshay N. Chakole et. al. illustrates energy generation using a dynamo, explaining that mechanical motion can induce current in a conductor via electromagnetic induction.Thisprincipleissimilartoregenerativebraking, where vehicle motion is partially converted into reusable electricalenergy,makingthesystemenergy-efficient.[6].
ChunhuiLiuet.al.investigateenergyrecoverystrategiesin EVs, showing optimized regenerative braking improves battery life and efficiency. The paper analyzes braking torque distribution and control algorithms for effective energyregeneration.[7].
Kadri Mohd Ismail et. al. discussed regenerative braking system without conventional brakes, recovering energy while reducing mechanical wear. The study highlights theoreticalaspectsoftorquegenerationandenergyflowin fullyelectricbrakingsystems.[8].
BigaliyevaZhanarSerykhanovnaet.al.introduceamethod forregenerativebrakinginscootersusingsupercapacitors, enhancing energy capture and battery life. The paper also discusses the theory behind rapid charge/discharge cycles inenergystoragedevices.[9].
Alistair Teasdale et.al discussed an energy-regenerative braking model using super capacitors and DC motors to improve energy efficiency in electric vehicles. The research shows that combining super capacitors with batteries enhances performance and lifespan. Regenerative braking recovers energy during braking [10].
Nurul Muthmainnah Mohd Noor et.al demonstrate regenerativebrakingsystemforelectricmotorcyclesusing MOSFET switches to recover energy during braking. The systemistestedunderUS60andNEDCurbandrivecycles to evaluate performance. Results show an increase in battery state of charge by up to 12.55% at 80% initial charge. This approach improves energy efficiency and supports the development of IOT- enabled electric twowheelers[11].
Bigaliyeva Zhanar et.al investigated regenerative braking system for electric scooters using a super capacitor in parallel with the battery. The system efficiently recovers
braking energy and allows faster acceleration after stops. It reduces battery load and minimizes mechanical wear. Experimental results show around 15% energy recovery, supporting IOT-enabled energy-efficient two-wheeled vehicles[12].
The proposed paper contains critical data from vehicle sensors and the data which can later be processed for intelligent system development and to display the current speed, distance covered, battery percentage and range prediction information for the rider. There are various existing system on smart E-bike monitoring where mobile phone is used as a dashboard to display the relevant informationfortheriderandwebpageapplication.C,C+and Python functionality which will receive data from sensor in user friendly format. The LCD is used to display the ride metrics and an IOT application for displaying the data on webpagei.e.Blynk.
WithIOT,datacanbetransmittedatrealtimeandthispaves way for an entirely new era in the transportation sector leadingtointelligentconnectedtransportationsystems.
For this design, ESP 32 WI-FI Module and the interfacing components such as voltage sensor, speed sensor, Wi-Fi moduleandLCDdisplayarerequired.Voltagesensorisused tosensethevoltageofbatterypack.Speedsensorisusedfor displayingthecurrentspeedonLCDdisplay.[5]
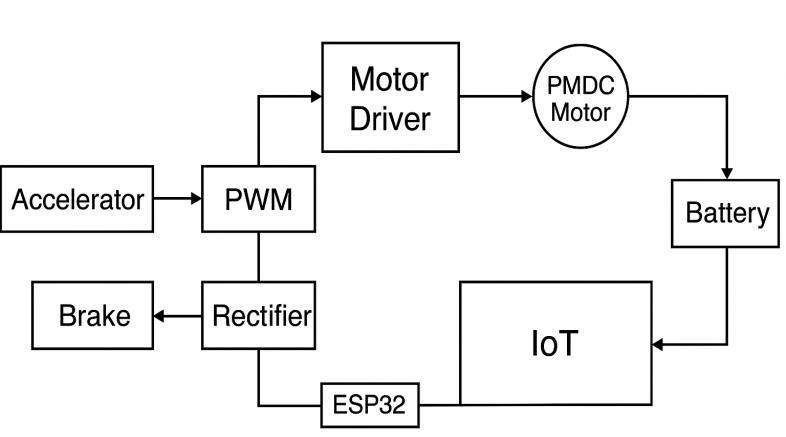
As shown in fig b. The block diagram shows the working of the regenerative braking system with IOT integration. The accelerator provides input to the PWM, which controls the motor driver and PMDC motor during vehicle motion. When the brake is applied, the motor acts as a generator and the rectifier converts the generated energy into DC to charge the battery. The ESP32 with IOT monitors parameters such as battery voltage, charge level, and vehicle speed, displaying them on the LCD and Blynk app. This system improves efficiency, prevents energy loss, and ensures safe charging withthebreakercircuit.

Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net
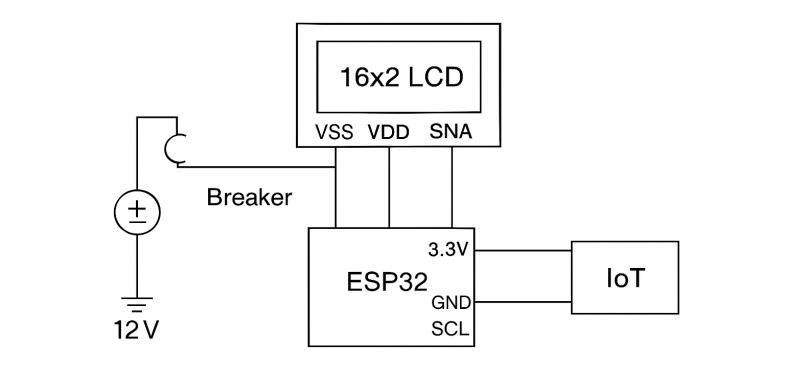
As shown in fig. c. The block diagram which represents the monitoringandprotectionsystemoftheproject.TheESP32 collectsdatafromsensorsandsendsittotheLCDaswellas theIOTplatformforreal-timedisplay.Thebreakercircuitis controlledtostopchargingoncethebatteryisfullycharged, ensuring safety. Thus, the system provides live monitoring, protection,andefficientenergymanagement.
Here’s how it works:
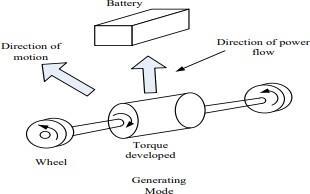
Regenerative braking is a brake method to use mechanical energy from the motor and convert kinetic energy to electrical energy and give back to the battery. In the regenerative braking mode, the motor slows downhill the car. When we apply force to pedal of brake, then car gets slow down and motor works in reverse direction. When running in invalidate direction motor acts as the generator andthuschargethebatteryasshowninfigured
1. ESP32

Fig.e.Esp32WifiModule
ESP32 is used because it has inbuilt Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making our project wireless and IOT-enabled.It monitors voltage, current, and battery charging status in real time. It processes sensor data faster than a normal Arduino and controlsthebreakercircuit.
2. PMDC Motor
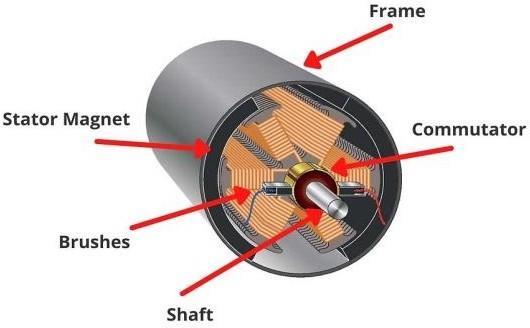
f.PMDCMotor
A PMDC (Permanent Magnet DC) motor is used as a generator in system. When the wheel rotates during braking, the PMDC motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Thisgeneratedenergyissentthrough the rectifierandbreakertochargethebattery.Itissimple,lowcost,efficient,andsuitableforsmallEVapplications.
3. LCD Display

Fig.g.LCD16×2

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
LCD is used to display important parameters like voltage, current, and battery charging status. It gives real-time feedback of regenerative braking performance. This helps the rider and project demonstrator to monitor system output easily. Thus, LCD acts as the user interface between hardwareanduser.

Fig.h.RelayforInterfacing
Relayisusedasanelectronicswitchinthe breakercircuit. Itconnectsordisconnectsthebatterychargingpathduring regenerative braking. Arduino/ESP32 controls the relay coil to automate ON/OFF operation. It provides isolation, safety,andsimplecontrolforthesystem.
5. Tyre

Fig.i.Tyre
The tyre is a critical component that provides contact between the scooter and the road surface. It ensures stability and traction during acceleration, braking, and cornering. In a regenerative braking system, the tyre’s grip affectshow effectivelykineticenergy can beconvertedinto electricalenergy.
Thereviewedliteraturehighlightsthatregenerativebraking is a vital technology for improving the efficiency of electric vehicles. Studies [1], [2], [4] consistently show that recovering kinetic energy during braking reduces energy loss,enhancesbatterylife,andcontributestolongerdriving
anges.Arecurringthemeacrossresearchistheimportance of integrating regenerative braking with conventional braking systems, since regenerative braking alone may not meet safety demands in emergency situations or when the battery is fully charged. This balance ensures both safety andefficiency.
Another major finding is the growing use of IOT for realtime monitoring and control. Works such as [5], [11] emphasize that platforms like Blynk allow users to track vehicle speed, battery status, charging levels, and energy recovery in real time. This improves rider experience and also enables predictive maintenance, making the systems more practical for daily use. The literature also indicates a trend toward wireless monitoring, aligning with the vision ofsmarterandmoreconnectedelectricvehicles.
In addition, studies [6], [7], [8] highlight the importance of effective energy conversion methods, such as dynamos and MOSFET-basedswitching,tomaximizeenergyrecoveryand improvesystemreliability.
The inclusion of breaker circuits, as discussed in some works, plays a crucial role in protecting the battery by stoppingchargingonceitreachesfullcapacity.
Finally, many papers point out challenges that remain for real-world implementation. Factors such as uneven road conditions, frequent braking in urban traffic, heat generation, and long-term durability of components are still areas requiring attention. Overall, the literature suggests that regenerative braking systems, when combined with IOT-based monitoring and smart control strategies, have the potential to make electric twowheelers more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly, but further work is needed to optimize cost, safety,andperformance.
ThedevelopmentofanIOT-enabledwirelessregenerative braking system for electric scooters represents a significant step toward energy-efficient and sustainable urban transportation. By converting the kinetic energy generated during braking into electrical energy, the system reduces energy loss and extends the vehicle’s battery life, enabling longer trips without recharging. IntegrationofIOTtechnologyallowsreal-timemonitoring of speed, distance traveled, battery status, and energy recovered, which not only provides useful ride metrics to the rider but also supports predictive maintenance and enhances overall safety. Additionally, the system aligns with environmental objectives by reducing reliance on conventional energy sources and minimizing pollution, supporting the shift toward greener transportation solutions. Overall, this paper highlights the potential of

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
combining regenerative braking with IOT-based monitoring to make two-wheeled electric vehicles smarter, safer, and more efficient. Future work can focus on optimizing energy recovery under different road conditions, improving IOT communication reliability, and further enhancing the scooter’s range and performance. Thisapproachsetsafoundationforintelligent,connected, andeco-friendlymobilityinurbanareas.
1. J.M.K.C. Donev et al., “Energy Education – Braking,” Energy Education,2018.
2. S.K.Malodeand R.H. Adware, “RegenerativeBraking SysteminElectricVehicles,” IRJET,2016.
3. N.A.C.Lestarietal.,“RegenerativeBrakingonElectric Scooters with DC Magnet Permanent Motors,” EAI India,[Yearnotspecified].
4. E. A. Manzano and W. M. Narciso, “Regenerative Braking System for an Electric Motorcycle Model SakuraM500,” Proceedings of LACCEI,July2024.
5. H. Sarode, S. Kale, A. Pawar, and A. Aghawane, “Battery Monitoring System for Electric Bike,” IJARCCE,May2021.
6. A.N.Chakole,V.A.Dhotre,andP.V.Raut,“Generationof ElectricalEnergybyDynamo,” IRJET,Jan.2019.
7. C.LiuandK.Zhang,“ResearchonRegenerativeBraking EnergyRecoveryStrategyofElectricVehicle,” Journal of Physics: Conference Series,2021.
8. K. M. Ismail, K. Abuzar, K. Amaan, S. Fahad, and S. Ahmed, “Regenerative Braking System without ConventionalBrakes,” IRE Journals,[Yearnotspecified].
9. Z. S. Bigaliyeva et al., “Development of a Method for Regenerative Braking of an Electric Scooter,” IJPEDS, Sept.2023.
10. A. Teasdale et al., “A Study on an Energy-Regenerative Braking Model Using Super capacitors and DC Motors,” MDPI Energies,July2024.
11. N. M. M. Noor et al., “Regenerative Braking System (RBS) MOSFET Switching-Based Drive Cycle for an ElectricMotorcycle,” IIUM Engineering Journal,2025.
12. Z. S. Bigaliyeva et al., “Development of a Method for Regenerative Braking of an Electric Scooter,” IJPEDS, 2023.