
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05| May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05| May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Santhosh B1 , Karishma Sree RI2 , Mukesh P3 , Subasri B4 , Vijay Kumar K5, Sonali S6
UG STUDENTS OF FACULTY OF ARCHITECTURE, DESIGN & PLANNING, KARPAGAM ACADEMY OF HIGHER EDUCATION, COIMBATORE-641021
Abstract - The construction industry has witnessed remarkable technological advancements in recent years, transforming traditional methodologies with cutting-edge equipment. Modern construction machinery has not only improved operational efficiency but has also contributed to cost reduction, enhanced safety measures, and reduced project timelines. The increasing complexity of infrastructure projects necessitates the integration of automated and intelligent machinery to meet growing demandseffectively.
This review focuses on emerging trends in construction equipment, highlighting innovations such as smart sensors, predictive maintenance systems, and AI-driven automation. Advanced construction techniques, including self-healing concrete and autonomous machinery, are revolutionizing site management and reducing human intervention in hazardous environments. Additionally, the rise of digital connectivity has enabledreal-time monitoring of machinery performance, ensuring proactive problem-solving and resourceoptimization.
Government regulations and sustainability initiatives have further accelerated the shift toward energy-efficient equipment, with an increasing focus on hybrid and electricpowered machinery. Many construction firms are adopting eco-friendly technologies to minimize carbon footprints while maintaining operational efficiency. Moreover, advancements in material science have led to the development of lightweight yet durable components, reducingtransportationandhandlingcosts.
The integration of robotics and AI has played a pivotal role in automating repetitive tasks, improving precision, and mitigating labor shortages. Additionally, the widespread adoption of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in construction planning has facilitated better decisionmaking, minimizing costly design errors and inefficiencies. As technology continues to evolve, the construction industry is expected to witness a paradigm shift in the way projects are executed, paving the way for smarter, safer, and more sustainabledevelopment.
This review consolidates various perspectives on the role of advanced construction equipment in shaping the future of the industry. By adopting cutting-edge technologies, firms can significantly enhance productivity, reduce costs, and achievelong-termsustainabilitygoals.
Key Words: construction equipment, life cycle cost, automationinconstruction.
The construction industry has always played a crucial role in economic development and infrastructure expansion. As global urbanization accelerates, the demand for efficient and high-quality construction has never been greater. Traditional construction methods, though effective in the past, are no longer sufficient to meet the scale and complexity of modern projects. The necessity of adopting advancedequipment,techniques,andmaterialshasbecome evident to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and ensure sustainability.
Modern construction equipment offers numerous advantages, including enhanced precision, faster project completion, and reduced dependency on labor-intensive processes. The use of cutting-edge machinery such as automated earth-moving equipment, high-performance cranes, and prefabrication technology allows for more streamlined construction operations. Furthermore, the integration of digital tools, including drones for site inspection and augmented reality (AR) for project visualization, has revolutionized the way construction projectsareplannedandexecuted.
Theadoptionofsmartconstructionequipment,suchasselfoperating machinery equipped with IoT sensors, has improveddata-drivendecision-makinginconstructionsites. Thesetechnologiesenablereal-timemonitoringofmachine performance, predictive maintenance, and automated adjustments based on environmental conditions. For example, smart excavators can analyze soil conditions and adjust their digging techniques tooptimize efficiency while reducingfuelconsumption.
Another emerging trend is the development of modular construction, where entire sections of a building are prefabricated in controlled factory environments before being transported and assembled on-site. This approach significantly reduces construction waste, enhances quality control, and accelerates project timelines. Countries like China and Sweden have already implemented modular construction extensively, leading to cost reductions and improvedsafetystandards.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05| May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The reliance on traditional construction methods often results in labor shortages, material wastage, and project delays. The integration of modern equipment reduces dependence on manual labor, increases execution speed, and ensures higher quality standards. However, the financial burden of high initial investments in machinery remains a crucial consideration, making cost-benefit analysis an essential factor in equipment selection. Additionally, advancements in automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence have further enhanced construction capabilities, allowing for more precise and efficient operations. Emerging technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and 3D printing have also demonstrated significant improvements in efficiency and costreduction.
Studies on equipment management practices reveal that mechanizationisessentialduetotheincreasingcomplexity of projects, shortage of skilled labor, and strict project timelines.Properequipmentselectioncriteria,maintenance schedules, and procurement strategies are critical in optimizingperformanceandminimizingcosts.Thefindings suggest that a well-structured management approach significantlyimpactsprojectsuccessbyreducingdowntime andimprovingoperationalefficiency.
The transition to advanced construction equipment is not just a trend but a necessity for meeting modern infrastructure challenges. Governments and private firms are increasingly investing in research and development to create sustainable and energy-efficient construction technologies. Some countries have already introduced tax incentives and subsidies for companies that invest in ecofriendly machinery. This shift toward sustainability is further supported by hybrid and electric-powered construction equipment, whichnot only reduces emissions butalsodecreaseslong-termoperationalcosts.
This review consolidates these perspectives, emphasizing thattheevolutionofconstructionequipmentplaysapivotal role in shaping the industry's future. By incorporating advanced technologies and effective management strategies, construction firms can enhance productivity whileensuringcost-effectivenessandsustainability.
The literature highlights both the technical evolution of construction equipment and the management strategies formaximizingtheiruse:
Nilesh Ayane & Mangesh Gudadhe (2015): Emphasized the role of standard equipment in improving operational output. They introduced the concept of Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)toassessmachineperformance.
D. B. Phadatare & S. B. Charhate (2016): Studied how structured equipment maintenance schedulesimpactprojectproductivity.Theyfound that equipment efficiency was closely tied to maintenanceandrepairfrequency.
Bantamlak Abebe (2013): Conducted field surveys revealing that poor planning in equipmentmaintenanceleadstohighrepaircosts anddowntime.
Tavakoli, Taye & Erktin (1989): Surveyed large constructionfirmsandstressedtheimportanceof equipment standardization, financial planning, andoperatortraining.
Aviad Shapira & Marat Goldenberg (2005): Proposed using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)forselectingconstructionequipmentbased onmultiplesoftandhardfactors.
Shlomo Selinger (1983): Created mathematical models for determining the economic life of construction equipment and scheduling replacementsbasedoncost-benefitanalysis.
David J. Edwards & Gary D. Holt (2009): Recommended the integration of predictive maintenance technologies, including AI, to improveequipmentlifeandreducefailures.
Inadditiontotheabove,studieshavealsoemphasizedthe importance of aligning equipment investments with longtermprojectgoalsandregionalconstructionneeds
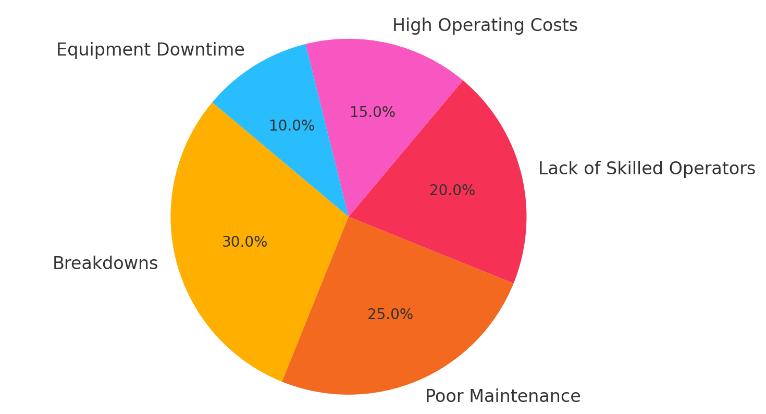
Chart-1:majorchallengesfaced

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05| May 2025 www.irjet.net
Author(s) Research Focus Key Concepts
Anirban Deshmukh (2017)
Needformodern construction techniquesinIndia
Tavakoli, Taye & Erktin (1989) Construction equipmentpolicyin largecompanies
Prabhu Kumar T. K. (2002)
Growthof mechanizationin construction
Reddi S. A. (1995) Progressive mechanizationin construction
Aviad Shapira & Marat Goldenberg (2005, 2007)
Ittiphol Bhurisith & Ali Touran (2002)
V. Kyong Ju Kim & Kyoungmin Kim (2011)
Shlomo Selinger (1983)
Cliff J. Schexnayder & Scott A. David (2002)
Michael C. Vorster & Glenn A. Sears (1986)
John Whittaker (1986)
Thanapun Prasertrungruang & B.H.W. Hadikusumo (2007)
David J Edwards & Gary D. Holt (2009)
Nilesh Ayane & Mangesh Gudadhe (2015)
Equipmentselection forconstruction projects
Productivitytrendsin earthmoving equipment
Trafficflowimpactof construction equipment
Economicservicelife ofconstruction equipment
Evolution of construction equipment
Equipmentretirement andreplacement models
Revenue-based equipmentpricing model
Equipment managementin highwayconstruction
Futuretrendsin equipment management
Roleofstandard equipmentin construction
Equipmentselection, ISM(Interpretive StructuralModeling)
Equipmentfinancing, replacementanalysis, maintenance management
Equipmentselection, management,and maintenance
Planning,scheduling, operationalresearch techniques
AnalyticHierarchy Process(AHP)for selection
Long-term performancestudy over15years
Simulation-based evaluation
Mathematicalmodels forequipment longevity
Impact of industrialization on machinery
Downtimecosts, financialrecovery
Operatingcosts, depreciation,taxes
Digitaltracking systems,investment planning
Machinelearningin predictive maintenance
Equipment differentiationin heavyvs lightprojects
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Challenges Faced Key Takeaways
Lackofstructured selectionmethods, dependencyon traditionalequipment
Highcostsof replacement,lackof standardization
Laborshortages, increasedprojectsizes
Poorplanningleadsto projectdelays
Lackofsystematic evaluationmethods
Costincreasevs. productivity improvementimbalance
Trafficcongestion, decreasedefficiency
Equipmentlifecyclecosts
High costs of innovation
Unreliableequipment leadingtodelays
Equipmentpricing inconsistencies
Lackofstandardization
Properselection improvesproductivity andsafety
Financialplanning improvesequipment longevity
Mechanizationis necessaryforlargescaleprojects
Properscheduling reducesinefficiencies
Multi-attribute decision-making improvesselection
Regularupgrades preventobsolescence costs
Optimizedtraffic controlenhancessite performance
Propermaintenance maximizeslifespan
Technological advancements reduce labor dependency
Replacementdecisions mustfactorin downtimecosts
Economicforecasting optimizesequipment investments
Digitaltracking reducesinefficiencies
Limiteddata-driven solutions
Poorequipment optimization
AIimprovesefficiency
Properselection improvesmachine performance

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05| May 2025 www.irjet.net
D. B. Phadatare & S. B. Charhate (2016)
Bantamlak Abebe (2013)
Equipmentpolicies andcontractor profitability
Equipment managementpractices survey
Agbo (1983) Costimpactof equipment breakdowns
John & Herman (2009)
Schenayder et al. (2002)
D. B. Phadatare (2016)
M. Manikandan, M. Adhiyaman & K. C. Pazhani (2018)
Rehan Baji & Mayank Gupta (2021)
Rintu Thomas (2023)
Roleofoperator trainingin
Equipment failure and maintenance strategies
Equipmentefficiency inlarge-scaleprojects
Equipmentutilization inIndianconstruction
Advancedconstruction techniquesinIndia
Equipment classificationand economicimpact
Structured maintenance schedules
Real-timemonitoring ofequipmentusage
Equipmentdowntime losses
Impactofunskilled laboronproject efficiency
Preventive vs. reactive maintenance
Optimizingmachine availability
RIIanalysisofkey efficiencyfactors
Reducinglabor dependencywith mechanization
Selection, maintenance,lifecycle costs
Highdowntime, unplannedfailures
Unplannedrepairs increasecosts
Highrepaircostsleadto delays
Accidentsdueto untrainedlabor
High maintenance costs
Lackofstructured management
Breakdownissues, outdatedequipment
Highinitialinvestment
Highcostofacquisition
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Preventive maintenanceenhances efficiency
Maintenanceplanning optimizes performance
Preventive maintenance minimizes breakdowns
Trainingprograms reducerisks
Scheduled servicing increases productivity
Improvedscheduling enhancesproductivity
Upgradingmachinery improvessiteoutput
Modernequipment acceleratesproject timelines
Economicplanning ensureslong-term costsavings
4.CONCLUSION:
Advanced construction equipment has emerged as a backbone of the modern construction industry in India, enabling faster, safer, and more precise project execution. However, owning advanced machinery alone is not sufficient. Its success depends on thoughtful equipment selection, skilled operators, and structured maintenance strategies.
This review demonstrates that poor management practices such as unplanned maintenance, lack of operatortraining,andimproperequipmentdeployment are significant contributors to cost overruns and project delays.Ontheotherhand,adoptinglifecyclecostanalysis, preventive maintenance, and digital tools can drastically enhanceperformanceandeconomicreturns.
In conclusion, construction firms must view equipment management not as an expense but as a strategic investment. By integrating technology with effective management, the construction sector can achieve greater
productivity, sustainability, and competitiveness in the longrun.
[1]. Anil Kumar, Ravi Sharma, "Innovative Construction Techniques: A Review", International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology, Vol. 5, Issue 3, 2023, pp. 45-56.
[2]. Priya R., Manoj P., "Advanced Equipments and Techniques in the Construction Industry", International JournalofCivilEngineeringandTechnology,Vol.12,Issue 5,2022,pp.102-115.
[3]. Sandeep T., Ramesh K., "Study on Smart Construction Materials and Techniques", Periodica Polytechnica Architecture,48(3),2021,pp.87-99.
[4]. Vishal N., Ritu P., "A Study and Analysis of Construction Equipment", IOP Conference Series: Earth andEnvironmentalScience,2020.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
[5]. Harish G., Amit R., "Heavy Construction Equipment: PlanningandMethods",OxfordandIBHPublishingCo.Pvt. Ltd.,SecondEdition,2019.
[6]. Sunil J., Meena K., "Construction Equipment and its Management",KhannaPublishers,2018.
[7]. Pooja D., Arun V., "Impact of Modern Construction Technology on Workforce Productivity", International Journal of Engineering Research, Vol. 7, Issue 2, 2017, pp. 56-70.
[8]. Karthik S., Neha M., "A Review on Implementation of Modern Construction Techniques in Indian Construction Sector", International Journal of Applied Research, Vol. 3, Issue8,2016,pp.379-386.
[9]. Nilesh C., Pranay K., "Planning and Selection of Heavy Construction Equipment in Civil Engineering", International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications, Vol. 4, Issue 12(Part 1), December 2014, pp. 29-31.
[10]. Rajesh P., Ananya T., "Smart Construction: Trends and Future Perspectives", International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, Vol. 6, Issue 9, 2023, pp.120-134.
[11]. Deepak M., Sneha R., "Innovations in Sustainable ConstructionMaterials",JournalofGreenEngineering,Vol. 9,Issue4,2022,pp.200-215.
[12]. Rohit K., Meenal J., "Automation and AI in Modern Construction",ProcediaEngineering,2021,pp.300-315.
[13]. Aditya S., Manish R., "Construction Productivity and Equipment Efficiency", ASCE Journal of Construction EngineeringandManagement,Vol.146,Issue5,2020.
[14]. Kumar P., Shalini D., "A Comparative Analysis of Traditional and Modern Construction Techniques", International Journal of Civil and Structural Engineering, 2019,pp.90-105.
[15]. Vikram B., Kavita L., "Impact of Construction Equipment on Project Performance", Journal of InfrastructureSystems,Vol.25,Issue3,2018.
[16]. Preethi G., Karan V., "Advanced Robotics in the Construction Sector", Robotics and Automation Journal, 2017,pp.150-167.
[17]. Tarun J., Megha S., "Prefabrication in Modern Construction", International Journal of Structural Engineering,Vol.12,Issue6,2016,pp.410-425.
[18].AjayP.,VandanaK.,"HeavyMachineryandSiteSafety Considerations",SafetyScienceJournal,2015,pp.55-70.
Volume: 12 Issue: 05| May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008
[19]. Rakesh Y., Ishita M., "A Study on High-Rise Construction Challenges", International Journal of HighRiseBuildings,2014,pp.120-135.