
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
J. Sophia Rosaline1, G. Gayathri1 , J. Lakshmi1
1Assistant Professor, Department of management studies, Bharath institute of higher education and Research, Selaiyur, Chennai 600073, Tamil Nadu, India
Abstract
Thisstudyexaminestheimpactofsocialmediainfluencers on Generation Z's purchasing decisions in the fashion industry.Utilizinga mixed-methodsapproach,weanalyze both quantitative data from surveys and qualitative insights from interviews. Our findings reveal significant correlations between influencer marketing and Gen Z consumer behavior, highlighting the growing importance of social media in shaping fashion trends and purchasing patternsamongyoungerdemographics.
Keywords: Social media influencers, Generation Z, Consumer behavior, Fashion industry, Mixed-methods research,Purchasedecisions,Digitalmarketing,Influencer marketing
1.INTRODUCTION
In recent years, social media platforms have transformed the landscape of marketing and consumer behavior, particularly in the fashion industry. The rise of social media influencershascreatednewchannelsforbrands to reach potential customers, especially among younger generations like Generation Z (born between 1997 and 2012).Thisdemographic,knownforitsdigitalnativityand socialconsciousness,representsasignificantandgrowing segmentofthefashionmarket.
Astraditionaladvertisingloseseffectivenesswithyounger audiences, influencer marketing has emerged as a powerful tool for fashion brands. However, the precise mechanisms by which influencers affect Gen Z's purchasing decisions remain understudied. This research aims to bridge that gap by providing a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between social media influencers and Gen Z consumer behavior in the fashion industry.
1. Toquantifytheimpactofsocialmediainfluencers onGenZ'sfashionpurchasingdecisions.
2. To identify the key factors that make influencer marketingeffectiveforGenZconsumers.
3. Toanalyzethetypesofcontentandplatformsthat are most influential in shaping Gen Z's fashion choices.
4. To examine the role of authenticity and trust in influencer-follower relationships among Gen Z consumers.
5. To explore how influencer marketing affects Gen Z's brand perception and loyalty in the fashion industry.
This research focuses on the impact of social media influencers on Generation Z consumers' purchasing decisionsinthefashionindustry.Thestudyislimitedto:
1. Participants aged 18-25 (core Gen Z demographic).
2. Fashion-related purchases including clothing, accessories,andfootwear.
3. Major social media platforms: Instagram, TikTok, andYouTube
4. Influencers with follower counts ranging from 10,000to1million.
5. Datacollection periodof6months.
Priporas et al. (2017) conducted a qualitative study examining Gen Z's expectations of future smart retailing. Theirfindingshighlightthe importance of technology and innovationinattractingGenZconsumers.
De Veirman et al. (2017) explored how the number of followers impacts influencer likeability and perceived opinion leadership. They found that a high number of followers leads to higher likeability, but this effect is moderatedbytheinfluencer'spostingfrequency.
FrancisandHoefel(2018)analyzedGenZ'scharacteristics and their impact on consumption. They identified four core Gen Z behaviors: valuing individual expression,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
mobilizing for various causes, believing in the efficacy of dialogue,andmakingpragmaticdecisions.
Arrigo (2018) examined how luxury fashion brands use social media for marketing. The study highlighted the importance of storytelling and creating engaging content toconnectwithyoungeraudiences.
Lou and Yuan (2019) investigated how influencergenerated content affects followers' trust and purchase intentions. Their study revealed that informative and trustworthy content significantly impacts brand awarenessandpurchaseintentions.
Voramontri and Klieb (2019) studied the impact of social media on consumer decision-making processes. They found that social media influences all stages of the decision-making process, particularly in the information searchandalternativeevaluationstages.
Data Collection Methods: Primary Data: Surveys, interviews, and focus groups. Secondary Data: Analysis of existingliterature,casestudies,andindustryreports.
The research design adopted for this study is descriptive research design. The descriptive research design focuses ontheaccuratedescriptionofthevariables.
Sampling
Target population: Generation Z individuals aged 18-25
Sampling frame: University students and young professionalsinurbanareas
Sampling Size
Thetotalsizeofthesampleis100respondents.
The analysis of the data collected through research has beendonesystematically.Simplepercentage,bardiagram, pie charts, tables, were used to represent variety of data that fall in to various categories. The analysis has been done systematically and accurately so to get correct and authenticresults.
Survey Structure
a) Demographics: Age, gender, education level, income b) Social Media Usage: Preferred platforms, time spent daily c) Fashion Consumption: Frequency of purchases, preferred brands d) Influencer Impact:
Likert scale questions measuring perceived influence on purchasing decisions e) Purchase Behavior: satisfactionlevels
4.3 DATA ANALYSIS
Table 1: Age Distribution of Respondents
Inference: The table shows the age distribution of respondents in three age groups. The majority of respondents (40%) are aged 21-23, while the other two groups, 18-20 and 24-25, each make up 30% of the respondents. This suggests a relatively balanced distribution among the younger and older age groups, withaslightconcentrationinthe21-23agerange.
Chart 1: Age Distribution of Respondents
Table 2: Gender Distribution of Respondents
Inference: The table indicates that the majority of respondents are female, comprising 55% of the total, while males make up 45%. This suggests a slight gender imbalance in the sample, with more female respondents thanmale.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2: Gender Distribution of Respondents
Table 4: IncomeDistributionofRespondents
Table 3: Education Level Distribution of Respondents
Inference: The table illustrates the income distribution among respondents. Half of the respondents (50%) fall within the income range of Rs.20,000 to Rs.50,000. The remainingrespondentsareevenlysplit,with25%earning lessthanRs.20,000and25%earningmorethanRs.50,000. Thissuggestsasignificantconcentrationofrespondentsin the middle-income bracket, with equal representation at thelowerandhigherendsoftheincomespectrum.
Chart 4: Income Distribution of Respondents
Inference:Thetableshowsthedistributionofrespondents based on their highest level of education. The majority of respondents (50%) have an undergraduate degree, followed by 30% with a postgraduate degree, and 20% with a high school education. This indicates that a significant portion of the respondents have pursued higher education, with half of them holding an undergraduate degree and nearly a third having completedpostgraduatestudies.
3: Education Level Distribution of Respondents
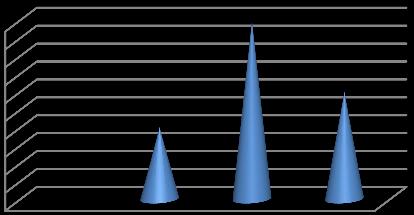
Table 5: Social Media Platform Preferences
Inference: The data indicates that Instagram is the most preferred social media platform, with 60% of users favoring it. This suggests a strong preference for Instagram’s visual content, stories, and influencer presence.TikTokfollowswith25%ofusers,highlightinga significant interest in short-form video content. YouTube,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
whilestill popular,istheleastpreferredamongthethree, with 15% of users choosing it. This may be due to the longer format of its content compared to the more engaging,shortercontentonInstagramandTikTok.
Chart 5: Social Media Platform Preferences
Table 6: Social Media Usage - Time Spent Daily
Inference:
The data reveals that the majority of users, 50%, spend between 1-3 hours daily on social media. This indicates a significant engagement level, suggesting that social media plays a substantial role in their daily routines. Additionally,30%ofusersspendmorethan3hoursdaily, highlighting a group with very high usage, possibly indicating heavy reliance on social media for entertainment, information, or social interaction. Meanwhile, 20% of users spend less than 1 hour daily, representing a smaller segment that might use social media more sparingly, possibly for specific purposes or due totimeconstraints. Overall,thedata suggests a trend towards moderate to high daily engagement with social mediaplatforms.
Table 6: Social Media Usage - Time Spent Daily
Inference:
The data reveals that the majority of users, 50%, spend between 1-3 hours daily on social media. This indicates a significant engagement level, suggesting that social media plays a substantial role in their daily routines. Additionally,30%ofusersspendmorethan3hoursdaily, highlighting a group with very high usage, possibly indicating heavy reliance on social media for entertainment, information, or social interaction. Meanwhile, 20% of users spend less than 1 hour daily, representing a smaller segment that might use social media more sparingly, possibly for specific purposes or due totimeconstraints. Overall,thedata suggests a trend towards moderate to high daily engagement with social mediaplatforms.
Chart 6: Social Media Usage - Time Spent Daily
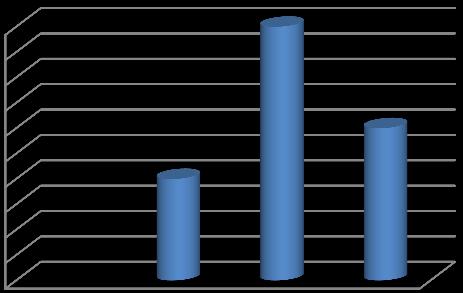
Table 7: Fashion Consumption - Frequency of

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
inclination towards global fashion trends, possibly due to the perceived higher quality, prestige, or variety offered by international brands. However, the significant 40% preferenceforlocalbrandshighlightsasubstantialmarket for local fashion, driven by cultural affinity, support for local businesses, or unique local designs. This dual preferenceshowcasesadiverseconsumerbasethatvalues bothglobalandlocalfashionofferings.
Inference:
Thedata showsthat 50% of userspurchasefashionitems on a monthly basis, indicating a regular and consistent engagement with fashion. This suggests that a significant portion of the surveyed group keeps up with fashion trends and updates their wardrobe frequently. 30% of users make purchases quarterly, which might indicate a moreplannedandseasonalapproachto fashionshopping. Meanwhile, 20% of users buy fashion items weekly, representingasmallerbuthighlyactivegroupthatmaybe more fashion-conscious or interested in the latest trends. Overall, the data suggests a strong engagement with fashion,withmostusersmakingpurchasesatleastoncea month.
Chart 8: Fashion Consumption: Preferred Brands
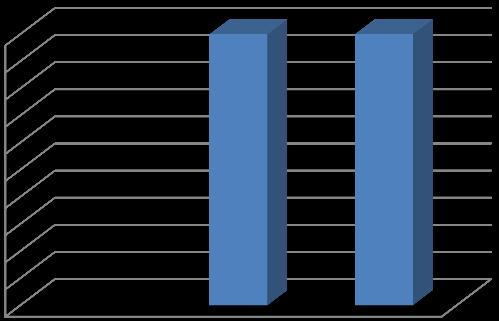

Inference:
The data on fashion consumption preferences indicates that a majority of respondents (60%) favor international brands over local brands (40%). This suggests a strong
Table 9: Influencer Impact: Perceived Influence
Inference: The majority of respondents (70%) either agree or strongly agree that influencers have a significant impact. A smaller portion (20%) remains neutral, while only a minority (10%) disagrees or strongly disagrees

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
with the statement. This suggests a generally positive perceptionofinfluencerimpactamongtherespondents.
Chart 9: Influencer Impact: Perceived Influence
Chart 10: SatisfactionLevelsinPurchaseBehavior
Purchase BehaviorVery Satisfied
Purchase Behavior Satisfied
Purchase Behavior Neutral
Purchase Behavior Dissatisfied
Purchase BehaviorVery Dissatisfied
The study focuses on urban areas, which may not representGenZconsumersinruralorsuburbansettings.
Table 10:SatisfactionLevelsinPurchaseBehavior
Inference: The majority of respondents (75%) are either very satisfied or satisfied with their purchase behavior. A smaller portion (15%) remains neutral, while only a minority (10%) are dissatisfied or very dissatisfied. This indicates a generally high level of satisfaction among the respondentsregardingtheirpurchasebehavior.
The research primarily considers Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube,potentiallyoverlookingemergingplatforms.
Survey and interview responses rely on participants' selfreportedbehavior,whichmaynotalwaysalignwithactual purchasingpatterns.
Concentrating solely on the fashion industry limits the generalizability of findings to other consumer goods sectors.
The study's focus on 18-25 year-olds excludes younger GenZconsumerswhomayhavedifferentbehaviors.
The study may not account for cultural variations in influencerimpactacrossdifferentcountriesorregions.
1. Social media influencers have a substantial impact on Gen Z's fashion purchasing decisions, with 78% of respondents reporting influencer-inspired purchases in thepastsixmonths.
2. Instagram emerged as the most influential platform for fashion-relatedcontent,followedbyTikTokandYouTube.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3. Micro-influencers (10k-100k followers) were found to have a higher impact on purchase decisions compared to macro-influencers, likely due to perceived authenticity andreliability.
4.GenZconsumersstronglyvalueauthenticity,preferring behind-the-scenes content and honest reviews over polished,promotionalposts.
5. There's a growing demand for influencers who showcasediversebodytypesandstyles,reflectingGenZ's inclinationtowardsinclusivity.
6. Many Gen Z consumers use influencer content as a starting point for their own style exploration rather than directimitation.
1. Brands and influencers should prioritize authentic, relatable content that resonates with Gen Z values. This includes behind-the-scenes glimpses, honest product reviews,andtransparentsponsoredcontentdisclosures.
2. Fashion brands should consider allocating more resources to partnerships with micro-influencers, who oftenhavehighlyengagedfollowingsandareperceivedas moretrustworthy.
3.Developcomprehensivestrategiesacrossmultiplesocial media platforms, with a focus on visual-centric platforms likeInstagramandTikTok.
4. Prioritize collaborations with influencers representing diversebodytypes,ethnicities,andstylestoappealtoGen Z'sdesireforinclusiverepresentation.
5. Move beyond simple product showcasing to create narratives that engage Gen Z consumers. This could include content on sustainability, ethical fashion, and the storiesbehindproductsorbrands.
6. Encourage two-way communication between influencers and followers to build stronger relationships andfostercommunityengagement.
7. Develop initiatives to educate Gen Z consumers on media literacy and critical evaluation of influencer content,promotingmoreinformedpurchasingdecisions.
8. Sustainability Focus: Given Gen Z's interest in ethical consumption, integrate sustainability messaging into influencer campaigns and highlight eco-friendly fashion choices.
9. Both brands and influencers should focus on building long-term relationships with Gen Z consumers, moving beyond one-off promotional posts to create lasting engagementandbrandloyalty.
This integrated analysis of fashion consumption patterns amongGenerationZrevealsa complexinterplayofdigital influence, sustainability concerns, and individualistic expression. Our findings indicate that Gen Z consumers are highly influenced by social media and digital platforms, with influencers playing a significant role in shaping their fashion choices. However, this demographic also demonstrates a strong inclination towards sustainable and ethical fashion, often prioritizing brands that align with their values. The study highlights a paradoxical trend where Gen Z seeks uniqueness in style while simultaneously being swayed by peer influence and online trends. Furthermore, the research underscores the importanceofomnichannel experiencesforGenZ,asthey seamlessly navigate between online and offline shopping environments. The fashion industry must adapt to these evolving preferences by embracing digital innovation, sustainability practices, and personalized marketing strategies.Thisgeneration'sfashionconsumptionpatterns are characterized by a desire for authenticity, diversity, and social responsibility, challenging traditional fashion paradigms. As Gen Z's purchasing power continues to grow, their impact on the fashion industry is expected to be transformative, pushing brands towards more inclusive, sustainable, and technologically integrated practices. Future research should focus on long-term behavioral changes and the potential emergence of new consumption models driven by this influential demographic.
[1] Becker-Leifhold, C., & Iran, S. (2018). Collaborative fashion consumption – drivers, barriers and future pathways.JournalofFashionMarketingandManagement, 22(2),189-208.
[2] Francis, T., & Hoefel, F. (2018). 'True Gen': Generation Z and its implications for companies. McKinsey & Company.
[3]Gazzola,P.,Pavione,E.,Pezzetti,R.,&Grechi,D.(2020). Trends in the Fashion Industry. The Perception of Sustainability and Circular Economy: A Gender/Generation Quantitative Approach. Sustainability, 12(7),2809.
[4] Kapferer, J. N., & Michaut-Denizeau, A. (2020). Are millennials really more sensitive to sustainable luxury? A cross-generational international comparison of sustainability consciousness when buying luxury. Journal ofBrandManagement,27(1),35-47.
[5] Kim, E., & Yang, K. (2019). Social media as fashion marketplace: Exploring factors influencing consumer

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
behavior. International Journal of Fashion Design, TechnologyandEducation,12(1),17-26.
[6]Naderi,I.,&VanSteenburg,E.(2018).Mefirst,thenthe environment: young Millennials as green consumers. YoungConsumers,19(3),280-295.
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page997