
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net



International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net

Vishakha
Kshirsagar1 , Mansi Gawade2 , Mayuri Hande3 , Prof. Shital Kalokhe-Mandlik4
123Undergraduate Student, Department Of Computer Science And Engineering, Jaihind College of Engineering , Kuran, Pune
4Professor, Department Of Computer Science And Engineering, Jaihind College of Engineering,Kuran ,Pune ***
Abstract – In recent years, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) a distinct category of blockchain-based virtual assets have rapidly gained immense popularity among investors. Often regarded as both a digital art revolution and a passing trend, NFTs have commanded multimillion-dollar prices at high-profile auctions. This growing fascination stems from the unique characteristics of NFTs, which hold the potential to transform blockchain-based development and asset exchange. Central to understanding NFTs is the principle of non-fungibility: unlike fungible assets that can be exchanged one-for-one, NFTs are inherently unique and irreplaceable. This departure from the interchangeability of traditional currencies paves the way for innovative forms of digital ownership and creative expression. Creating an NFT generally involves uploading a digital item to an online auction platform, where it is minted as a distinct token on the blockchain. Artists can tokenize their digital creations as exclusive NFTs and may generate multiple tokens based on the same work. While NFT buyers do not typically receive the original digital file, they obtain a blockchain-verified proof of ownership for a digital asset. Furthermore, the NFT model extends beyond visual art to include audio and other digital media, significantly expanding the range of opportunities within this emerging ecosystem.
Key Words: Blockchain Technology; Tokenization; Digital Art; NFT Creation Process;
INTRODUCTION-
The advent of blockchain technology has led to groundbreaking innovations in the way digital assets are created, owned, and exchanged. Among the most transformative developments is the emergence of NonFungible Tokens (NFTs), unique digital assets that represent ownership of content such as art, music, collectibles, and virtual real estate. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, whichare fungibleandinterchangeable, NFTs are distinct and indivisible, making them ideal for certifying the uniqueness and provenance of digital goods.the NFT ecosystem. NFT marketplaces have emerged as critical platforms in this new digital ecosystem, serving as intermediaries where creators, collectors, and investors can mint, buy, sell, and trade NFTs. These marketplaces not only facilitate transactions butalsoplaya pivotalroleinestablishingtrust,enforcing smart contracts, and maintaining ownership records on theblockchain. Asaresult,NFTmarketplaceshaveopened
up new economic opportunities for digital artists and innovators, empowering them to monetize their creations in ways previously unimaginable.NFT marketplaces built on blockchain platforms provide a decentralized environment whereuserscanmint,buy, sell,andtradethesedigitalassets securelyandtransparently.
Smart contracts ensure that transactions are automated and tamper-proof,eliminating the need for intermediaries and enabling creators to receive royalties on secondary sales. Despitechallengessuchashighgasfees,scalabilityissues,and environmental concerns, the popularity of NFTs continues to grow, attracting artists, collectors, gamers, and investors worldwide. This project aims to design and implement a blockchain-based NFT marketplace that leverages the core benefits of decentralization, immutability, and trustless transactions to create a secure and efficient platform for digitalassetexchange.
Despite the rapid growth and widespread adoption of NFT marketplaces, several critical challenges continue to hinder their scalability, security, accessibility, and long-term sustainability.ManyNFTplatformssufferfromissuessuchas high transaction fees, limited interoperability across blockchains, and environmental concerns due to energyintensive consensus mechanisms. Furthermore, the lack of standardized regulations and ownership rights creates ambiguity and legal uncertainties for both creators and buyers. Additionally, while the hype around NFTs has attractedsignificantinvestmentandinterest,ithasalsogiven rise to fraudulent activities, copyright violations, and speculative behavior, which undermine the credibility and trustworthinessofNFTecosystems.
This paper addresses the need for a comprehensive analysis of these challenges and explores how NFT marketplaces can evolve to support a more secure, userfriendly,andequitabledigitalasseteconomy.
This summary highlights the key research and developments in the field of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) from the documents you uploaded.Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have emerged as unique digital assets that leverage blockchain technology to authenticate ownership and provenance. The

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net
literature shows rapid advancements in NFT applications acrossdomainssuchasart,gaming,virtualrealestate,and collectibles.NFTs are distinct from traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum due to their non-fungibility and uniqueness [1]. NFTs are primarily built on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Flow, ensuring the uniqueness and provenance of digital assets. The role of blockchain technology in NFTs is central to their functionality, providing security, immutability, and decentralization. Ethereum’s ERC-721 and ERC-1155 standards are commonly used for creating NFTs.NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are unique digital assets that represent ownershiporproofofauthenticityofaspecificitem,often linkedtodigitalfilessuchasart,music,orvideos.
Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which are interchangeable with each other (fungible), NFTs are distinctive, meaning each token has unique data that cannot be replicated or replaced. This uniqueness is enabled by blockchain technology, which ensures that every NFT has a secure, verifiable history of ownership. [2]. Blockchain is the foundational technology behind NFTs. It is a distributed ledger system that records transactions in a decentralized and transparent manner. Ethereum, the leading blockchain for NFTs, uses smart contracts to create and transfer NFTs. NFT marketplaces playa crucial roleinthedigital asseteconomy byoffering a platform for creators to monetize their digital works. These platforms democratize access to global buyers, enabling direct sales without needing intermediaries like galleries or auction houses[3]. Furthermore, NFT marketplaces allow for programmable royalties, meaning creatorscanreceiveapercentageofsaleseverytimetheir work is resold in the secondary market.[4]. The marketplaces also create a digital economy around NFTs. Artists, musicians, game developers, and other creators can generate income from their work, while buyers can invest in unique assets that may appreciate in value. Additionally, NFT marketplaces have facilitated the creation of new forms of digital ownership and the establishmentofvirtualgoodsmarkets. Studiedthefactors thatinfluencetheadoptionofNFTmarketplacesandfound thatfactorssuchasusefulness,easeofuse,andtrusthavea hugeimpactontheadoptionofNFTs.NFTmarketplacesare not only economic platforms but also cultural catalysts, enabling new forms of creative expression and asset ownership.Theyarereshapingthenotionofownershipin the digital age. [5]. The Study related to a descriptive overviewofNFTanditstechnologiesspecificallyblockchain and Ethereum. The emergence of NFT marketplaces has significantly impacted cultural and economic domains. From an artistic standpoint, NFTs have created new avenues for digital artists, offering them unprecedented visibility and monetization opportunities. Artists can now directly engage with their audience, bypassing traditional gatekeepers like galleries and auction houses. Non-

fungible tokens (NFT) utilized blockchain technology for the firsttime in early2021ina waythatwasreadilyapparent to the general public. NFTs have also created new forms of digital ownership. Collectors can own, buy, sell, and trade unique digital assets, fundamentally altering how ownership is perceived in the digital world. In the broader economic context, NFTs are contributing to the growth of the digital economy by enablingthecreation ofvirtual goodsand digital realestatemarkets. NFTmarketplaceshavebecomepowerful catalysts for the digital economy, transforming how creators monetize their work, how collectors engage with digital art, andhowwethinkaboutownershipinthedigitalage.
While the journey has been marked by challenges, the rapid growthofthissectorpoints toan excitingfuturewhere NFTs canintegratewithvarioussectors,fromartandentertainment to gaming and real estate.The energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly Ethereum, is a significant issue. Ethereum’s current proof-of-work consensus mechanism consumes a large amount of energy, contributing to environmental concerns[6].Popular NFT marketplaces like OpenSea, Rarible, Foundation, SuperRare, and Magic Eden offer creators a platform to tokenize their work, list them for sale, and engage directly with collectors. Marketplaces differ in terms of curation, decentralization, supported blockchains, royalty structures, and user communities.Dowling (2023) analyzed the growth of NFT platforms, noting their economic potentialfordemocratizingartandownership.[7].
NFT marketplaces are reshaping how value is created and exchanged in digital environments. Creators gain autonomy and new revenue models, while collectors engage in digital asset trading with speculative potential.NFT marketplaces have emerged as vital infrastructures in the digital economy, enabling new models of ownership, creativity,andmonetization.
The working process of NFTs begins with minting, whereacreatoruploadsadigitalfileanddefinesmetadata including the name, description, and image URL often stored in a JSON format. This metadata, along with a link to the actual digital content (usually stored on decentralized storage like IPFS), is embedded into a smart contract on a blockchain, typically following standards such as ERC-721 or ERC-1155.Onceminted,theNFTisassignedauniquetokenID and becomes a permanent record on the blockchain. This record includes details such as the current owner, creation date, and transaction history, all of which are publicly verifiable.NFTscanthenbelistedondigitalmarketplaceslike OpenSea,Rarible,orMagicEden,whereuserscanbuy,sell,or trade them using cryptocurrency. When an NFT is sold, ownership is automatically transferred through the smart contract, and the transaction is recorded on the blockchain. This system ensures transparency, security, and proof of authenticity.NFTsalsoofferaddedutility suchasgranting access to exclusiveNon-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) work by

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net

utilizing blockchain technology to represent ownership of unique digital assets. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and interchangeable, NFTs are indivisible and distinct. Each NFT is created (or "minted") using specific token standards like ERC-721 or ERC-1155 on blockchains such as Ethereum or Polygon. These tokens contain metadata and a unique identifier that distinguishes one NFT from another.The process begins when a user mints an NFT, uploading digital content (such as artwork, video, or music)andlinkingittothetoken.
The digital file itself may be stored off-chain on decentralized file storage systems like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System), while the token metadata and ownership information are recorded on the blockchain.When an NFT is sold or transferred, the blockchain updates its ownership status through a smart contract, which ensures the transaction is secure, verifiable,andirreversible.Thesesmartcontractscanalso include royalty logic, ensuring that the original creator receives a percentage of profits every time the NFT is resold. All transactions are recorded transparently on the blockchain, making them traceable and tamper-proof.NFT marketplaces serve as platforms for these transactions, providing users with the ability to browse, buy, sell, or auction NFTs. Wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet are used to interact with these platforms, enabling users to securely manage their tokens and participate in the decentralized economy.In essence, NFTs combine the benefitsofdigitalownership,verifiablescarcity,andsmart automation, enabling a wide range of applications in art, gaming,music,virtualrealestate,andbeyond.
Atitscore,anNFT(Non-FungibleToken)marketplaceisa decentralizedplatformwhereuserscanmint,buy,sell,and tradeNFTssecurelythroughblockchaintechnology.These marketplacesnotonlyrevolutionizedigital ownership but also unlock value for creators, collectors, investors, and developers alike.NFT marketplaces provide proof of ownership and authenticity for digital assets such as art, music, videos, and collectibles. Blockchain ensures these records are tamper-proof, permanently storing metadata like ownership history and creator identity.Artists and content creators can monetize their work directly by mintingNFTswithoutintermediaries.Smartcontractsalso enableautomated royalties, socreators earna percentage from every resale, supporting long-term income. Moreover, addressing current challenges, including standardization, security, and regulatory compliance, will be crucial for their sustained growth. The rise of NonFungible Tokens (NFTs) has created many NFT marketplaceswhereartistsandcollectorscantradedigital items. However, these marketplaces face important problems. They don't organize items, making it hard for users to find what they want. The scope of NFT

p-ISSN:2395-0072
marketplaces in the blockchain ecosystem is vast and rapidly expanding, offering transformative opportunities across multiple sectors. In gaming, NFTs are used for owning and trading in-game items, skins, characters, and land (e.g., in metaverse platformslikeDecentralandorThe Sandbox).NFT marketplaces enable a player-owned economy and crossgame asset usage.Emerging NFT marketplaces are becoming blockchain-agnostic, supporting multiple networks (e.g., Ethereum, Polygon, Solana, BNB Chain). This allows users to tradeNFTsacrossecosystems,enhancingliquidityandreach.
NFT marketplaces are evolving to support financial utilities likecollateralization(usingNFTsasloancollateral),fractional ownership, and staking, bridging NFTs with DeFi (Decentralized Finance) platforms.Beyond art and gaming, NFT marketplaces are being used in supply chain, real estate tokenization, digital identity, and academic certifications, offeringreal-worldassetrepresentationandtraceability.
With Web3 adoption, the scope includes integration withAI-generatedcontent, DAOs(DecentralizedAutonomous Organizations) for governance, AR/VR experiences, and NFTbased access to communities, events, and services.The scope of NFT marketplaces is not limited to digital art. It spans across entertainment, finance, education, healthcare, real estate, and beyond, redefining how assets are owned, transferred, and monetized on the blockchain. The system allows users to mint new NFTs by uploading digital content and associating it with metadata stored on decentralized storage like IPFS. Smart contracts deployed on blockchains like Ethereum or Polygon automate the marketplace functions,includinglistingNFTsforsale,executingpurchases, handling royalties for creators, and transferring ownership. Wallet integration enables seamless user authentication and transaction signing, while optional analytics and dashboard featuressupporttrackingperformanceanduserengagement.
Integration of artificial intelligence and augmented reality (AR)canenhanceuserexperiencebyenablingsmartersearch, personalized recommendations, and immersive viewing of digital assets. Additionally, NFTs are poised to disrupt not only the art and gaming sectors but also real estate, fashion, academic certifications, and identity verification systems, offering secure and tamper-proof digital records. As legal frameworks and standardization improve globally, NFT marketplaces will likely gain broader acceptance and institutional backing.Cross-chaininteroperabilitywill further enable NFTs to move freely between different blockchain ecosystems,increasingliquidityandadoption.Moreover,with the emergence of the metaverse, NFT marketplaces are expected to play a central role in virtual economies by powering the buying, selling, and ownership of digital land, avatars,and items. Overall, the future of NFT marketplacesis promising, with immense opportunities for innovation, decentralization, and global economic impact.The future scope of NFT marketplaces using blockchain is vast and continuously evolving, with the potential to redefine digital ownership across various industries. As blockchain

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net
technology matures, scalability solutions such as Layer-2 protocols (e.g., Polygon, Arbitrum) and next-generation blockchains (e.g., Solana, Flow) are expected to significantly reduce transaction costs and latency, making NFT trading more accessible to a wider audience.Beyond art and gaming, NFT marketplaces are being used in supply chain, real estate tokenization, digital identity, and academic certifications, offering real-world asset representationandtraceability.
ThecorecomponentsofNFTareasfollows:
A smart contract is a self-executing program stored on a blockchain that defines the rules for creating (minting), transferring, and interacting with NFTsMost NFTsuseERC-721(forsingleuniqueassets)or ERC-1155 (for batch or semi-fungible tokens) standards on Ethereum or similar standards on other blockchains (e.g., SPLonSolana).Asmartcontractisaself-executingpieceof codedeployedonablockchainthatautomaticallyenforces andexecutespredefinedrulesandagreementswithoutthe need for intermediaries. In the context of NFTs (NonFungible Tokens), smart contracts play a central role by definingthelogicbehindthecreation,ownership,transfer, andinteractionoftokens.
The owner wallet address is a unique cryptographic address on the blockchain that holds ownership of a specific NFT.Whena user mintsorpurchasesanNFT, the smart contract assigns the NFT to their wallet address, which becomes the recorded proof of ownership. This walletaddressiscrucialintheNFTecosystem,asitallows users to manage, transfer, or sell their digital assets securely without needing intermediaries. Wallets like MetaMask.
A blockchain network is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple nodes in a secure, transparent, and immutable manner.InthecontextofNFTs(Non-FungibleTokens),the blockchain serves as the foundational infrastructure that ensures the authenticity, ownership, and traceability of each token. When an NFT is minted or transferred, the blockchain records this activity as a transaction, which is permanently stored and publicly verifiable. Ethereum, for example, is widely used due to its strong developer support and established standardslikeERC-721andERC1155.
The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the needforcentralauthorities,providinguserswith trustless

interactionswhereownershipissecuredbycryptographyand consensusalgorithms.
TOKENIZATION:
Tokenization is the process of converting a real-world or digital asset into a digital token that can be stored, transferred, and managed on a blockchain. In the context of NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), tokenization refers specifically to the creation of a unique, indivisible token that represents ownershiporproofofauthenticityofaparticularasset such as artwork, music, video clips, virtual land, collectibles, or even documents.When an asset is tokenized, the creator or owner uses a smart contract to generate a new NFT on a blockchain. This NFT contains metadata such as the asset's name, description, image URL,andattributes. Unlikefungible tokens (like Bitcoin or Ethereum), each NFT has a unique token ID and is non-interchangeable, making it ideal for representingsingularandrareitems.
The NFT (Non-Fungible Token) marketplace is designed to facilitate the creation, trading, and ownership of digital assets securely and efficiently. At its core, the architecturecomprisesseveralkeycomponents.Firstly,there is the frontend interface, accessible to users through web or mobile applications, providing an intuitive platform for browsing,buying,andsellingNFTs.Thisfrontendinterfaceis complemented bya backend server responsible for managing userauthentication,handlingtransactions,andinterfacing with the blockchain network. The blockchain network itself forms the backbone of the marketplace, serving as a decentralized ledger to record the ownership and transaction history of NFTs.Smartcontracts,deployedontheblockchain,encodethe business logic governing the creation, transfer, and verification of NFTs, ensuring transparency and immutability of transactions. Additionally, decentralized storage solutions, suchasIPFS(InterPlanetaryFileSystem),areintegratedinto thearchitecturetostorethedigitalfilesassociatedwithNFTs securelyandefficiently.
Additionally,anoptional databaselayer(e.g.,MongoDBor Firebase) may be used for storing non-sensitive data such as userpreferencesandcachedmetadata.Walletintegrationand payment handling are enabled via Web3 technologies, allowing users to securely sign and approve blockchain transactions. This architecture ensures a seamless, decentralized experience for users while maintaining the security,transparency,andscalabilitynecessaryforamodern NFT marketplace.The user interface is built using web technologies such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Vue.js. It allows users to interact with the platform includingbrowsingNFTs,uploadingdigitalassets, connecting crypto wallets (e.g., MetaMask), and performing transactions.At the frontend layer, a responsive web application is developed using technologies like React.js, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This layer provides the user

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net
interface through which users can interact with the platform such as connecting their crypto wallets (like MetaMask),mintingNFTs.
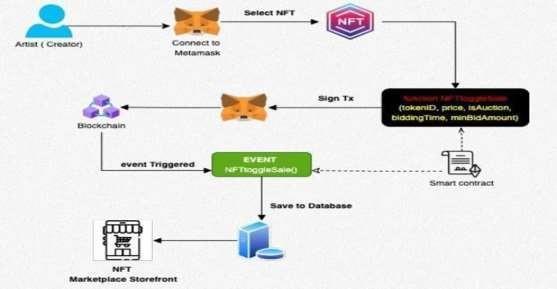
Fig:proposedsystemarchitecture
Toenhancescalabilityandperformance,thesystem mayincorporatecachingmechanisms,loadbalancers,and distributed computing frameworks. Moreover, robust securitymeasures,includingencryption,authentication,and authorizationprotocols,areimplementedatvariouslayers tosafeguarduserdataandassetsfromunauthorizedaccess andcyberthreats.Overall,theproposedsystemarchitecture aimstoprovideaseamlessandtrustworthyenvironmentfor creatorsandcollectorstoengageintheburgeoningmarket ofdigitalartandcollectiblesthroughNFTs.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION-

The developed NFT marketplace successfully integrates core blockchain features such as minting, listing, buying, selling, andtransferringNFTsusingsmartcontractsontheEthereum blockchain (or relevant testnet like Rinkeby/Polygon). The followingkeyfunctionalitieswereobserved:
NFT Minting: Users can mint unique NFTs by uploading metadata(image,description,title)andstoringitonIPFSora similardecentralizedstoragesystem.
Smart Contract Deployment: The ERC-721 (or ERC-1155) smartcontractdeployedsuccessfullyusingtoolslikeRemixor Truffle. All NFT ownership and transfer history were tracked immutablyon-chain.
Marketplace Listings: NFTs could be listed for sale and buyers could purchase listed NFTs via MetaMask or similar cryptowallets.
Transaction Transparency: Every buy/sell action created a verifiable transaction hash on the blockchain explorer (e.g., Etherscan),ensuringtransparencyandtraceability.
Blockchain's immutability ensured secure, trustless ownership of NFTs. Smart contracts minimized the need for intermediaries,ensuring peer-to-peer transactions.However, the reliance on front-end interfaces (e.g., React UI) and storage services (like IPFS) introduced some centralized touchpoints.The integration with MetaMask offered seamless wallet connections, but first-time users may face a steep learning curve. Improving UX with guided prompts and gas estimationcanhelpwideradoption.On-chainstorageofmedia files is impractical due to gas costs. IPFS provided a decentralized alternative, but retrieval speed and persistence (withoutpinningservices)werepotentialconcerns.
NFT marketplaces powered by blockchain are transforming digital ownership. The ability to sell art, music, and collectibles directly opens new monetization avenues for creators. However, market volatility, scams, and lack of regulations remain challenges.By using blockchain and IPFS, the system avoids central points of failure, ensuring secure andtransparenttransactions. Allactionslikeminting,buying, and selling were traceable via transaction hashes on the blockchain explorer (e.g., Etherscan)NFTs were uniquely identifiable and linked to specific wallet addresses, establishing clear digital ownership.Gas fees and network congestionarelimitationsonEthereum.
In the future, the NFT marketplace can be significantly enhanced by incorporating multi-chain support to allow interoperability across various blockchain networks such as Ethereum,Polygon,andSolana,therebyreducinggasfeesand improving accessibility. Layer-2 scaling solutions can be implemented to ensure faster and more cost-effective transactions. Additionally, integrating AI-driven

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net
recommendation systems can personalize the user experiencebysuggestingNFTsbasedonuserinterestsand market trends. The platform could benefit from improved search functionality and filtering options, making NFT discovery more intuitive. Introducing decentralized identity (DID) systems will help verify creator authenticity, boosting trust and transparency. Furthermore, features such as advanced auction mechanisms, enhanced royalty management, and support for fractional ownership can provide better monetization for creators. Mobile application development with augmented reality (AR) integration can make NFT interactions more immersive. Social features like commenting, sharing, and community forums can foster userengagement,whiledecentralizedgovernancethrough DAOs can ensure democratic decision-making. Lastly, adoptingenvironmentallyfriendlyblockchaintechnologies or carbon offset mechanisms can promote sustainability andappealtoeco-conscioususers.
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to all those who supported and guided me throughout the development of this project titled “NFT Marketplace using Blockchain.” Iamdeeplythankfultomyprojectguide,Prof S.Y Mandlik, for their valuable insights, continuous encouragement, and technical guidance, which played a crucial role in shaping this work. I also extend my thanks tothe[DepartmentName],[College/UniversityName],for providing the necessary resources and a supportive environmentforthesuccessfulcompletionofthisproject.I am grateful to my friends and family for their constant motivation and moral support. Finally, I would like to acknowledge the open-source community and online platforms whose tutorials and documentation helped me gain deeper knowledge of blockchain technology and NFT systems.I am also grateful to the online developer communities and open-source contributors whose tutorials, forums, and documentation helped me explore and apply blockchain and NFT technologies effectively. Their indirect support greatly enhanced my learning and implementationexperience.
AnNFTmarketplacebuiltonblockchaintechnologyoffers numerous advantages, starting with decentralization, which eliminates the need for intermediaries and ensures transparent peer-to-peer transactions. Immutability of blockchain records guarantees the authenticity and ownership of NFTs, preventing duplication and fraud. Through smart contracts, the marketplace can automate processes like royalty payments, ensuring that creators receive a share every time their digital asset is resold. Security is significantly enhanced due to cryptographic techniques, protecting user data and digital assets. The platform also allows for global accessibility, enabling

artists and collectors from anywhere in the world to participate. Furthermore, blockchain ensures transparency in transaction history, permanence of data, and low operational costs over time. These advantages make NFT marketplaces notonlymoresecureandefficientbutalsomoretrustworthy andcreator-friendlycomparedtotraditionaldigitalplatforms.
Decentralization- Eliminates the need for intermediaries, enablingpeer-to-peertransactions.
Security: Blockchain's cryptographic design ensures highlevelprotectionofdigitalassetsanduserdata.
Immutability: All transactions and ownership records are permanentandtamper-proof.
Authenticity & Ownership: Guarantees the originality and verifiableownershipofdigital
High Energy Consumption: Many blockchain networks (like Ethereum)consumesignificantenergy,raisingenvironmental concerns.
High Gas Fees: Transactions, especially on Ethereum, can involveexpensivegasfees,makingsmalltradeslessviable.
Market Volatility:NFTpricescanfluctuatewildly,leadingto investmentrisksandmarketunpredictability.
Lack of Awareness: Many users are unfamiliar with blockchain and NFTs, creating a barrier to mainstream adoption.
Transaction Throughput (TPS)
Measures how many transactions are processed per second ontheplatform.HigherTPSindicatesbetterscalability.Foran NFT marketplace, higher TPS indicates better scalability, enabling it to handle a larger number of users and transactions simultaneously without delays. This metric is crucial for maintaining a smooth user experience, especially during high traffic periods. A higher TPS ensures faster confirmation of transactions, which is essential for maintaining a dynamic marketplace where NFTs are bought andsoldfrequently.
Time taken for a transaction (e.g., minting, buying, or selling an NFT) to be confirmed and visible on the blockchain.Low latency is vital for a seamless experience, as users expect quicktransactions.Highlatencycanleadtodelays,frustrating usersandpotentiallycausingmarketinefficiencies.InanNFT marketplace,fasterlatencyiscritical toensurethatuserscan interactwiththeplatforminreal-time,reducingwaittimesfor transactionprocessingandconfirmation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net
Percentage of time the marketplace is accessible and operational. Critical for user trust and reliability.A marketplace with high uptime ensures that users can access and use the platform without interruptions, fostering trust and reliability. Downtime or service disruptions can cause loss of user engagement, transactions,andrevenue.Ensuringconsistentavailability is crucial for maintaining user confidence and ensuring that the marketplace remains a dependable space for buying,selling,andmintingNFTs.
Timeittakestoexecutesmartcontractlogic,whichaffects overallperformanceanduserexperience.Itmeasureshow long it takes for smart contracts to execute and finalize tasks like minting NFTs, transferring ownership, or distributing royalties. Faster execution times improve the user experience, as it leads to quicker transaction finalization and reduced wait times for users. Optimizing smart contract execution time can help ensure that users have a smooth and efficient interaction with the marketplace, increasing overall satisfaction and platform performance.
The development of an NFT marketplace using blockchain technology represents a significant step forward in the digital economy by enabling secure, transparent, and decentralized trading of digital assets. Throughtheintegrationofsmartcontractsandimmutable ledgers, this platform ensures authenticity, ownership verification,andautomatedroyaltydistribution,providing substantial benefits for both creators and buyers. While there are challenges such as high gas fees, scalability issues,andusereducation,thelong-termpotentialofNFTs in areas like art, gaming, real estate, and identity is immense. This project has demonstrated how blockchain can revolutionize digital ownership and commerce by creating a trustless, global marketplace that empowers creators and fosters innovation. With continued improvements in scalability, user experience, and ecofriendlysolutions,NFTmarketplacesarepoisedtobecome acorepartofthefuturedigitallandscape.
[1]V. Buterin, “Ethereum White Paper,” [Online]. Available: https://ethereum.org/en/whitepaper/. [Accessed:May13,2025].
[2]“Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs),” Investopedia, [Online]. Available: https://www.investopedia.com/non-fungibletokens-nft-5115211.[Accessed:May13,2025].

[3]“OpenSea Developer Documentation,” OpenSea, [Online]. Available: https://docs.opensea.io/. [Accessed: May 13, 2025].
[4] “Solidity Documentation,” Solidity Language, [Online]. Available: https://docs.soliditylang.org/. [Accessed: May 13, 2025].
[5] “What is Blockchain?,” IBM Blockchain Guide, [Online]. Available: https://www.ibm.com/topics/what-is-blockchain. [Accessed:May13,2025]
[6]D. KhatriandA. Jain,“A Review on Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and Their Use Cases,” International Journal of Computer Applications,vol.183,no.17,pp.1–6,July2021.
[7] “Smart Contracts,” Ethereum.org, [Online]. Available: https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/smart contracts/. [Accessed:May13,2025].
[8] M. Mougayar, The Business Blockchain: Promise, Practice, and the Application of the Next Internet Technology, Wiley, 2016.
[9]S.Shen,C.Monteleone,andA.Saxena,“NFTs:ASurveyof Technical and Legal Challenges,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.07447,2021.