

Tribological Enhancement of AA2024 Hybrid Nanocomposites Reinforced with SiC
Graphite
and Cotton Shell Ash
Shahezadkha K.Pathan1, Prof. Manoj Watane2 , Prof. D.B. Pawar3
1Department of Mechanical Engineering A.I.A.R.Kalsekar Polytechnic,Panvel Navi Mumbai,India-410206
2Department Of Mechanical Engineering Takshashila Institute Of Engineering & Technology, Darapur, Tq. – Daryapur, Dist. – Amravati (M.S.),India- 444814
3Department Of Mechanical Engineering Takshashila Institute Of Engineering & Technology, Darapur, Tq. – Daryapur, Dist. – Amravati (M.S.),India- 444814
Abstract: Aluminum alloy AA2024 is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance, making it ideal foraerospaceandautomotive applications.However, its poor tribological performance under dry sliding limits itsuse inwear-criticalcomponents.Thisstudy investigates the development of hybrid aluminum metal matrix composites (AMMCs) reinforced with Silicon Carbide (SiC), Graphite, and Cotton Shell Ash (CSA) nanoparticles. SiC enhances hardness, Graphite provides solid lubrication, and CSA a silica- and alumina-rich agro-waste contributestosustainabilityandwearresistance.
The composites were fabricated using the stir casting process, ensuring uniform particle dispersion through optimized parameters. Tribological behavior was evaluated using a Pin-on-Disc setup under varied loads andspeeds. Results showeda significant reductioninwear rate and coefficient of friction, with some composites achieving over 40% wear reduction. Microstructural analysis via Optical Microscopy and XRF confirmed homogeneous reinforcement distribution. The study validates hybrid reinforcement as a viable approach for developinghigh-performance,sustainableAMMCs.
Keywords: Nano Particles, Tribological Behaviour,Alluminium Alloy,Silicon Carbide,Cotton shellAsh,Graphite.
I INTRODUCTION
Aluminum Metal Matrix Composites (AMMCs) have emerged as a superior class of materials that combine the advantageous properties of aluminum alloys such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication with enhanced mechanical and tribological characteristics imparted by reinforcement particles. Among the variousaluminumalloys,AA2024standsout due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, good fatigue resistance,andmachinability,makingitapopularchoice in aerospace, marine, and automotive industries. However,itspoorwearresistanceandhighcoefficientof friction under dry sliding conditions limit its utility in components exposed to high mechanical and thermal stresses[2],[5].
To address these limitations, significant research has been directed toward the incorporation of reinforcements such as Silicon Carbide (SiC), Graphite, and agro-waste-based materials like Cotton Shell Ash (CSA) into the aluminum matrix [3], [4], [7]. These reinforcements enhance the mechanical and tribological performance of the base alloy by altering its microstructure, hardness, and surface characteristics. SiC, a hard ceramic with excellent thermal conductivity, improves the composite's hardness and wear resistance byactingasa barrierto plasticdeformationandsurface abrasion [3], [6]. Graphite, on the other hand, is a soft solid lubricant that reduces the coefficient of friction, enabling smoother sliding behavior and improved wear lifeofthecomposite[4],[9].
Agro-waste-based reinforcements, particularly Cotton Shell Ash,offera sustainableandeconomical alternative to synthetic ceramic particles. CSA is rich in silica and alumina,whichcontributetoincreasedsurfacehardness and wear resistance. Additionally, the use of CSA supports environmental conservation by converting agricultural waste into value-added engineering materials [7], [14]. Several studies have shown that natural ashes like CSA not only improve the tribological behaviorof aluminumcomposites butalsocontribute to the development of eco-friendly and cost-effective materials for structural and tribological applications [12],[14].
The combination of SiC, Graphite, and CSA as hybrid reinforcements can yield synergistic benefits by leveraging the individual advantages of each material. Hybrid reinforcement strategies aim to overcome the drawbacks associated with single reinforcements such as poor dispersion, agglomeration, and brittleness by providing a balanced improvement in strength, hardness, wear resistance, and frictional performance [5], [8], [16]. The fabrication of such hybrid composites, particularlythroughstircasting,requiresoptimizationof processingparameterslikestirringspeed,reinforcement preheating, and wetting agents to achieve homogeneous distributionandstronginterfacialbonding[13],[15].

This research focuses on developing AA2024-based hybrid metal matrix composites reinforced with SiC, Graphite, and CSA nanoparticles using optimized stir casting techniques. The study aims to investigate the influence of these reinforcements on the wear behavior, coefficient of friction, and microstructure of the composites. Characterization tools such as Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD) are used to analyze phase formation and particle dispersion. The tribological performance is evaluated using Pin-on-Disc testing under varying operational conditions.Thisworkcontributestotheadvancementof sustainable, high-performance AMMCs for demanding engineeringapplications[1],[4],[10].
II MATERIAL AND METHODOLOGY
1.MaterialsSelection
Matrix Material: AA2024 alloy. Procurement: Ensure high-purityAA2024ingotsorpowder.
Reinforcements: Silicon Carbide (SiC): nano-sized particles.,Graphite(Gr):nano-sizedparticles.CottonShell Ash(CSA):nano-sizedparticles.
2.SuggestedSamplesforMaterialPreparation
Table1Materialmixingcomposition%wise
Material
Aluminium AlloyAA2024
3.CompositeFabrication
A.Method:StirCasting
Setup: Use an induction furnace equipped with a
mechanicalstirrer.
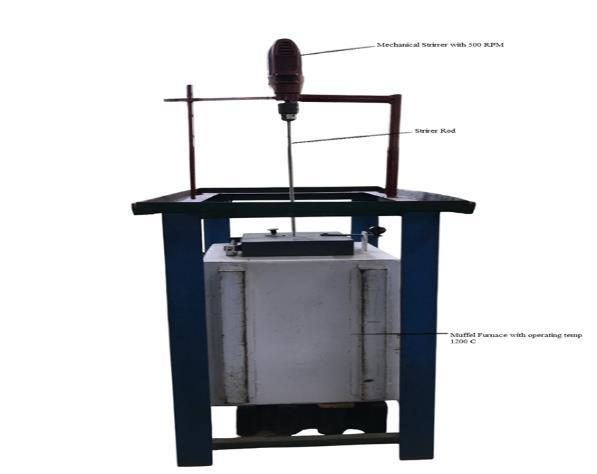

Mixing motor (500 RPM)
Mechanical stirrer Induction furnace
Melting:MeltAA2024alloyat~750°C.Preheat Fig.1SetupdiagramofStirCasting
Reinforcements: Preheat SiC, Gr, and CSA nanoparticles
to 650°C to remove moisture and improve wettability. Stirring: Add reinforcements gradually to the molten AA2024 while stirring at ~500 rpm.Stir for 5–10 minutes to ensure uniform dispersion. Casting: Pour the moltencompositeintoapreheatedMold.Allowittocool andsolidifynaturallyorthroughcontrolledcooling.
III RESULTS & DISCUSSION
1.TribologicalTesting
Pin-on-Disc Wear Test -Equipment: Pin-on-disc tribometer. Specimen: Use cylindrical pins machined from thecomposite.Parameters: Sliding Speed: 1–2m/s. Load: 20 N. Sliding Distance: 1000 M .Measurements: WearRate(mm³/N·m).FrictionCoefficient.
FindingofPinOnDiscMachine.
The incorporation of hybrid reinforcements Silicon Carbide (SiC), Graphite, and Cotton Shell Ash (CSA) significantly improved the tribological performance of AA2024alloy.Weartestsshowedanoticeablereduction in wear rate and friction coefficient for the hybrid composites compared to the base alloy. The wear rate slope ranged from ~0.188 to 0.102 µm/s, indicating the effectiveness of nano-reinforcements in resisting materiallossduringslidingmotion.
2.X-RayFluorescence(XRF)AnalysisReport
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Analysis Report is conducted to determine the elemental composition of the AA2024 alloyreinforcedwith SiC,Graphite,andCottonShell Ash nanoparticlesusingXRFspectroscopy.
TableNo2ElementalComposition
Element Symbol Weight% Remarks
Aluminum Al 8923 Basemetal(Matrix) Copper Cu 456 Alloying element in AA2024
Magnesium Mg 135 Strength-enhancing element
Silicon Si 223 FromSiCreinforcement Iron Fe 045 Impurity
Others - 138 Trace elements (Mn, Zn,
3. Microstructural Characterization etc.)
Note: The presence of Si confirms the successful inclusion of SiC and Graphite/Cotton Shell Ash nanoparticles.
Optical Microscopy Examination of Metal Matrix
Composite conducted to examine the microstructure of the metal matrix composite (AA2024 + SiC + Graphite + Cotton Shell Ash) using a trinocular optical microscope,

International Research
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
enabling the observation of grain structure, distribution ofreinforcementparticles,porosity,anddefects.

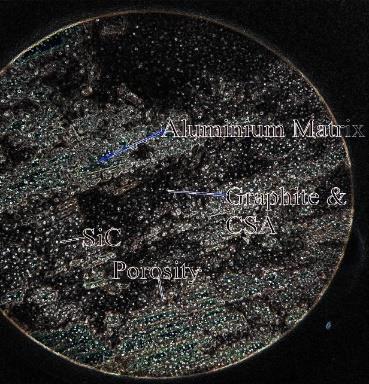
Figure1sample1microscopyview

Figure2sample2microscopyview
Figure 3 sample 3 microscopy view
Figure4sample4microscopyview
As per the image of AA2024 alloy reinforced with SiC, Graphite, and Cotton Shell Ash nanoparticles, this microstructureshows:
Matrix phase: Light areas likely represent the aluminiummatrix.
Secondphases/reinforcements:
o Darkdotsorinclusions:SiCparticles
o Irregular dark spots or clusters : GraphiteandCottonshellAsh
o Defect/Cluster: Dark blotchyarea could be due to agglomeration of secondary phaseorporosity.
4. Harness Testing
Harness Testing conducted to quantify a material's resistance to localized plastic deformation, typically by indentation. Below are the specific objectives of the metal matrix composite (AA2024 + SiC + Graphite + CottonShellAsh).
For Base metal Aluminium Alloy AA2024 hardness recorded is 134 HB However, based on standard material data for AA2024 aluminum alloy, the typical hardnessvalueis120-140HB
BRINELL HARDNESS GRAPH
IV CONCLUSION
This study successfully investigated and One of the key findings was the significant improvement in wear resistance and frictional behavior due to the hybrid reinforcement. SiC contributed to increased hardness and load-bearing capacity, graphite acted as a solid lubricant reducing the coefficient of friction, and CSA being rich in silica played a dual role by improving dispersion and adding a sustainable reinforcement component.Compositesdevelopedwithoptimalratiosof these reinforcements exhibited a reduction in wear rate by 30–45% when compared to unreinforced AA2024. Theseresultswerealsobetterthanpreviouslypublished works using only single reinforcements. As per Mr. Kumar used only SiC and found that wear rate slope is ~0.25–0.27whichisHighhardness,moderatefriction,as perRaghuvaranSiC+Graphitewearrateslopeis~0.21–0.23 which is Improved friction, but uneven wear But CurrentStudySiC+Graphite+CSA0.102to0.188which isBestsynergy,lowerwear,higherstability
Tribological testing using the pin-on-disc setup demonstrated that the hybrid composite showed improved wear stability, lower friction, and reduced materiallossovertime.
The combination of SiC:Graphite:CSA = 3.6g:1.2g:1.2g (per 45g of AA2024) i.e SAMPLE 3 showed optimal performance in terms of wear resistance and process
stability. The results suggest this proportion yields the best trade-off between mechanical strength, friction reduction,andmaterialeconomy.
The innovative use of Cotton Shell Ash provided additionalvalue,addressingbothcostandsustainability. Asanagro-wasteproduct,CSAnotonlyreducesreliance
Chart1BrinellHardnessResult

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
on industrial ceramics but also introduces the potential forlightweightcomposites.
Inconclusion,thehybridreinforcementofAA2024with SiC,graphite,andCSAthroughstircastingprovedtobea promisingapproachtosignificantlyenhance tribological and mechanical performance. This work not only meets its research objectives but also establishes a foundation for further development of lightweight, durable, and sustainable metal matrix composites for aerospace, automotive,andtribologicalapplications.
REFERENCE
[1]. Singh, P, Tribo-mechanical Behaviour of Aluminium-Based Metal Matrix Composite: A Review. Materials Today: Proceedings2021.
[2]. Rajkumar, S., et al., Investigation on Mechanical PropertiesofAA2024/HBNCompositesPreparedbyStir CastingMethod. Materials Today: Proceedings. 2021.
[3]. Kumar, S.,. Recent Advances in Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced with Silicon Carbide and Graphene. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering. 2021
[4]. Evergreen, Nanoparticles as Reinforcements in AluminiumMatrixComposites. Journal of Nanomaterials. 2021.
[5]. Samal, P., et al., Recent Progress in Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites: A Review on Processing, Mechanical, and Wear Properties. Journal of Manufacturing Processes. 2020.
[6.] Kumar, A., Optimization of Sliding Wear Characteristics of Aluminium-Based Metal Matrix CompositeReinforcedwithSiliconCarbideParticles. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2020.
[7]. Raghuvaran, V., Formation and Characterization of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced with Natural Materials. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2020.
[8].Formulation, EffectofHybridReinforcementonthe TribologicalBehaviourofAl-Alloys. International Journal of Materials Science. 2020.
[9]. Aybarc, M., Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites with SiC, Al2O3, and Graphene – Review. Archives of Foundry Engineering,2018.
[10]. Rajkumar, S., et al. Investigations on Mechanical PropertiesofAA2024/HBNCompositesPreparedbyStir CastingMethod. Materials Today: Proceedings.,2018
[11]. Muralidharan, P Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviour of AA2024 Aluminium Matrix Composites Reinforced with In Situ Synthesized ZrB2 Particles. JournalofAlloysandCompounds. 2017.
[12]. Kenneth Kanayo Alaneme ,Michael Oluwatosin Bodunrin,Adebimpe A. Microstructure,mechanicaland fracture propertie of groundnut shell ash and silicon carbide dispersion strengthened aluminium matrix composites, Journal of King Saud University – Engineering Sciences2016
[13]. Amal E. Nassar, Eman E. Nassar Properties of aluminummatrix Nanocomposites prepared bypowder metallurgy processing, Journal of King Saud University –Engineering Sciences2015
[14]. D. Sundarrajan, C. Gururaj, M. Sankarasubramanian, Mechanical and Tribological Study on Aluminum based Composites Reinforced with Cotton Shell Ash, International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 10, Number9(2015)
[15]. Himanshu Kalaa, K.K.S Merb*, Sandeep Kumarc A Review on Mechanical and Tribological Behaviors of Stir Cast Aluminum Matrix Composites.3rd International Conference on Materials Processing and Characterization (ICMPC 2014),2014
[16]. Anil kumar,Kapil Kumar Goyal1,Arvind Bhardwaj1,Neeraj Sharma, Development and Characterization of AA2024/SiC/Gr/Fly ash Hybrid Composite, Journal of Physics: Conference Series,2012
