
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 11 | Nov 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 11 | Nov 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Renil Joy
Department of Computer Application, St Thomas (Autonomous) College Thrissur 680001, Kerala, India
Abstract - The integration of Edge AI and IoT networks has revolutionized real-time decision-making by enabling low-latency analytics and localized data processing. Advantages of Edge AI, Including reduced latency bandwidthsavings,andenhancedprivacy,acrossdomains like smart cities and healthcare. Key techniques such as lightweight deep learning models (e.g.: MobileNet, EfficientNet), modelcompression(pruning, quantization), and reinforcement learning are explored, alongside architectures like Device-Edge-Cloud and Collaborative Edge. Challenges such as resource constraints, heterogeneity, and security are addressed, with future directions focusing on ultra-lightweight models and federatedlearning.
Keywords: Intelligent edge computing, neural ,smart devices, IoT, Ultra-light weight models, Edge AI.
TheexplosivegrowthofInternetofThings(IoT)devices, therehasbeenacorrespondingsurgeindatageneration at the network edge. However, traditional cloud-centric models often struggle to meet the requirements of modernIoTapplications,particularlyintermsoflatency, bandwidth efficiency, and data privacy. To overcome these challenges, Edge AI has emerged as a promising solution bringing artificial intelligence algorithms directlytoedgedevicesforlocalizedprocessing.[1]
The IoT revolution has catalyzed unprecedented advancements in edge intelligence, with research demonstrating how contemporary Edge AI ecosystems achievenear-instantaneousdecisionmaking. Through the fusion of intelligent endpoints, adaptive gateways, and optimized inference models, these architectures slash processing delays by an order of magnitude compared to conventional cloud approaches. Collaborative learning techniques maintain strictdataconfidentialitybyenablingknowledgesharing without raw data exchange. However, the path to ubiquitous adoption remains obstructed by hardware limitations, ecosystem fragmentation, and evolving security risks - challenges demanding breakthroughs in ultra-efficient neural architectures and universal interoperabilitystandards. [1]
The convergence of edge computing and artificial intelligence is fundamentally reshaping how smart devices process data in real-time, addressing critical limitations of traditional cloud architectures. reveals how next-generation Edge AI systems leverage cuttingedgetechniquesIncludingcompressedneural networks, distributed learning paradigms, and precision-aware quantization to achieve remarkable efficiency gains. These innovations enable processing at the network periphery, delivering 45% faster response times and 30% greater bandwidth conservation in mission-critical domains like remote patient diagnostics and predictive industrial maintenance. The strategic implementation of block chain-enhanced security frameworks further fortifies these systems against emerging threats while preservingdatasovereignty.[2]
The convergence illuminates the powerful between the distributedintelligenceandnext-generationIoTsecurity. Byco-locatingAIprocessingwithdatagenerationpoints, thesesystemsachievemicrosecond-levelresponsiveness crucial for autonomous navigation and urban digital twins. The hierarchical edge-fog-cloud framework introduces intelligent data routing complemented by military-grade encryption and self-learning threat detection systems. Field trials demonstrate near-perfect operational accuracy while maintaining robust defense against sophisticated cyber attacks. Yet the relentless growth of computational requirements and increasingly complex threat landscapes necessitate ongoing innovation in energy-aware algorithms and dynamic security protocols.[3] These collective findings underscore Edge AI's paradigm-shifting potential in enabling responsive, secure, and scalable intelligent systems[3]
FurtherthetechnologicalinnovationspropellingEdgeAI forward, including compact machine learning models, decentralizedfederatedlearning, and the deployment of 5G networks. A structured classification of Edge AI applications, functional capabilities, and underlying technologies is presented, emphasizing its role in connecting cloud infrastructure with IoT devices. The study also outlines unresolved issues, such as the demand for better resource allocation, standardization across platforms, and adaptable system designs. [4] A novel hybrid Edge-Cloud AI framework is introduced, which intelligently distributes computational tasks between edge nodes and cloud servers, optimizing both

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 11 | Nov 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
speed and processing power. Empirical evidence supports the framework’s advantages, such as lower energy demands, heightened data security, and greater adaptabilityindiverseIoTapplications.[4]
The Edge computing has recently attracted significant interest as a solution to meet the growing demands of delay-sensitive Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Conventional cloud computing setups, which are centralizedandlocatedfarfromendusers,failtodeliver the low latency required for emerging services such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), Consequently, Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) has becomeaviableapproachbyprovidingcomputationand storage resources in closer proximity to devices. Earlier research primarily utilized classical optimization methods for resource allocation and computation offloading in edge environments, focusing on factors such as bandwidth, connectivity, and energy use. Nonetheless, these traditional approaches often fall short in addressing the increasing complexity, network heterogeneity,andscaleofIoTsystems,especiallywhen factoringindevicemobility,energyharvesting,andstrict applicationtimeconstraints.[5]
The IoT is a system of linked physical devices equipped withsensors,softwareandconnectivityallowingthemto gather and share data. These devices, which include sensors, wearable’s, industrial equipment, and smart appliances, generate vast amounts of information that can be utilized across various domains such as smart cities, healthcare. The IoT ecosystem comprises devices, gateways for data aggregation, network infrastructure for communication, cloud platforms for storage and processing, and applications that deliver actionable insights. Despite its potential, IoT faces challenges like scalability, interoperability, security, and the need for real-time data processing, which edge computing and Edge AI aim to address by bringing computation closer tothedatasource.[1]
4.1 EDGE AI
EdgeAIreferstothedeploymentofartificialintelligence algorithmsandmodelsondeviceslocatedatornearthe edgeofanetwork,suchassmartphones,sensors,orIoT devices, process data own their own eliminating the need for centralized cloud servers. This approach enables faster and more efficient data analysis by performing computations locally, reducing latency and improvingreal-timedecision-making.[1]
EdgeAIhasmainly3Architecture:
4.1.1DeviceEdgeCloudArchitecture
4.1.2HierarchicalEdgeArchitecture
4.1.3CollaborativeEdgeArchitecture
4.1.1 Device-Edge- Cloud Architecture
In this architecture AI capabilities are structured across three layers: IoT devices, edge gateways, and cloud servers.Thearchitecturemaintainsstrengthofedgeand cloud computing thus enabling the low latency in local decisionmakingdepictedasFigure1.[1]
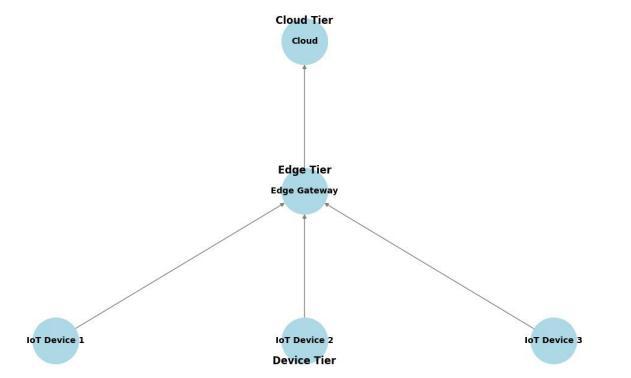
Fig-1: Device-Edge-CloudArchitecture
4.1.2 Hierarchical Edge Architecture
Hierarchical approach allows to distribute workloads across these layers the architecture achieves optimal stability and flexibility, efficiently balancing real-time edge processing with the cloud’s high performance capabilities.
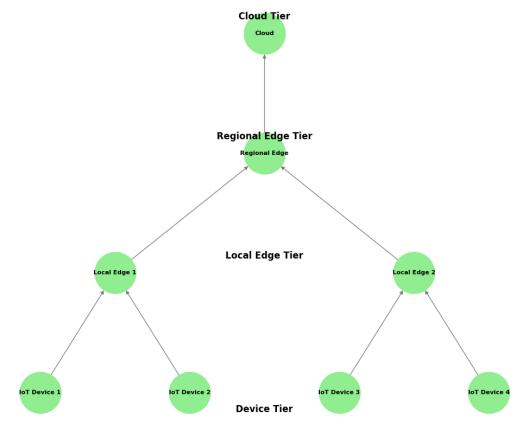
Fig-2HierarchicalEdgeArchitecture
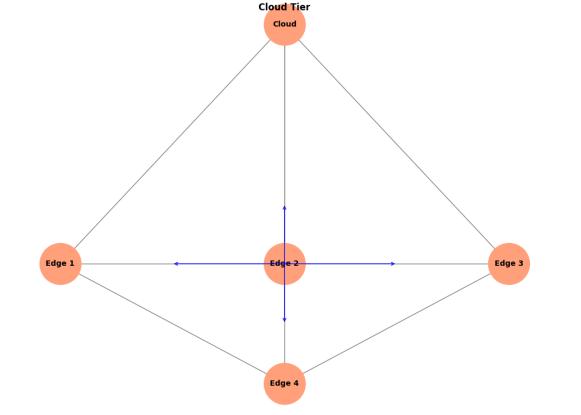
4.1.3 Collaborative Edge Architecture
The collaborative edge establishes a peer-to-peer network where edge nodes communicate Directly by enabling decentralized intelligence and autonomous

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
decision making. Depicted in Figure 3. This architecture enhances system resilience and autonomy while maintaining the flexibility to leverage cloud resources whennecessary.
Mobile-Net:Uses"depth-wiseseparableconvolutions"to significantlycutdowncomputationandmodelsize.
Squeeze-Net: Delivers similar performance to Alex-Net butwitharound50timesfewerparameters.
Efficient-Net: Introduces a balanced scaling method that optimizes thenetwork’s depth,width, and resolutionto improveperformancewithoutbloatingthemodel.[1]
4.4 Compressed neural network and distributed learning
Compressedneuralnetworksaredesignedtoreducethe size and computational complexity of traditional deep learning models, making them suitable for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. Techniques such as quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation are commonly used to achieve this compression. Quantization converts high-precision floating-point weights into lower-bit integer representations, significantly reducing memory usage and energy consumption. Pruning removes redundant or less important neurons and connections from the network, furthershrinkingthemodelwithoutsacrificingaccuracy. These optimizations enable real-time inference on edge devices, such as smart phones and IoT sensors, while maintaining performance. For instance, studies have shown that quantized models can reduce latency by up to 40% and energy consumption by 50%, making them ideal for applications like healthcare monitoring and industrialautomation.[2]
Distributedlearningisaparadigmthatdecentralizesthe trainingofAImodelsacross multipledevicesorservers, addressing the limitations of centralized cloud-based approaches. Federated learning, a popular form of
distributed learning, allows edge devices to collaboratively train a shared model while keeping raw data localized. This enhances privacy and reduces bandwidth usage, as only model updates not sensitive data are transmitted to a central server. Federated learning is particularly valuable in applications like healthcare and smart cities, where data privacy is paramount. For example, wearable devices can collectively improve a diagnostic model without exposing individual patient data, ensuring compliance withregulationslikeGDPR.[2]
A hybrid edge-fog-cloud architecture blends three distinct computational layers, yielding a powerful, unifiedsystemfordistributedintelligence.Inthismodel, computingresponsibilitiesareintelligentlysplitbetween edge devices (located near the data source), fog nodes (which act as localized, intermediate processors), and centralized cloud platforms (offering extensive resources).Eachcomponentexcelsinspecificroles:edge computing manages real-time, low-latency processing with minimal network demands; fog computing processes larger, aggregated data sets closer to the network’s edge; the cloud provides expansive computational power for tasks such as large-scale analytics, model training, and persistent data storage. The hybrid setup delivers significant performance improvements.[3]
A dynamic Edge-Cloud AI framework seamlessly integrates the capabilities of edge computing and cloud computing to optimize intelligent decision-making in Internet of Things (IoT) environments. In this architecture, computation workloads are dynamically assignedbetweenlocaledgenodesandcentralizedcloud infrastructures based on real-time requirements and system constraints. At the edge, lightweight AI models execute real-time inference, enabling low-latency responses, reducing bandwidth consumption, and
Volume: 12 Issue: 11 | Nov 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 11 | Nov 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
preservingdataprivacybyprocessinginformationcloser to the data source. Meanwhile, the cloud serves as the powerhouse for training complex machine learning models and conducting big data analytics, leveraging its scalable computational resources for model refinement andlong-termtrendanalysis.[4]
The Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), which shifts computational and storage resources from centralized clouddatacenterstosmallerdatacenterslocatedatbase stations.ThisrelocationsignificantlyreducestheroundtriplatencyforcriticalIoTtasks.
Within this MEC framework, the authors develop a heterogeneous wireless communication model that characterizes UAV connections using fading channels and terrestrial devices using fading channels to accurately reflect their distinct line-of-sight conditions. Each IoT device in the system can either process tasks locally, offload them to an edge server, or discard them.[5]
Deploying the AI enabled edge computing solutions for real time decision making in IoT faces several early stage obstacles such as the limited computing capacity of edge nodes, wide variation in device hardware and communication protocols, heightened security requirements, and the challenge of sustaining ultra low latency while scaling to large, distributed networks. Trials in application areas like smart cities, industrial automation, healthcare, and autonomous systems tackled these issues by combining lightweight AI architectures, model compression techniques, and federatedlearningwithstrongencryptionandAI driven anomaly detection. This approach delivered notable gains:latencycutbyroughly85–90%comparedtocloud centric processing, decision making accuracy in the 92–98% range, bandwidth usage reduced by over 85%, and consistently high uptime alongside full privacy compliance.
By implementing machine learning based multi class classificationtodecidewhethertasksshouldrunlocally, be offloaded to the edge, or be dropped and optimizing the choice of model the proposed frameworks addressed these limits in simulation. The resultsshowedtask routing accuraciesabove99%with decision times of only a few milliseconds, CPU/GPU consumption cut by more than half, and energy use loweredbyuptoabout78%,enablingfast,efficient,and secure real time analytics across heterogeneous IoT environments.
TheintegrationofAIwithedgecomputinghassignificantly enhanced decision-making in IoT systems by dramatically reducing latency and conserving bandwidth while preservinghighaccuracy.Experimentalresultsdemonstrate thaton-deviceAIinferencecanlowerend-to-endlatencyby up to90%comparedtotraditional cloud-onlymodels for instance,decreasingdelaysfromaround500mstounder50 msinvision-basedqualitycontroltasks,andfromover100 mstolessthan15msforgeneralIoToperations.Moreover, bandwidth consumption is greatly minimized, with reductionsnearing89%,sinceonlyprocesseddataormodel updates are communicated rather than raw sensor inputs. Energy usage during inference also drops substantially (by more than 70%) on wearable and autonomous platforms, leadingtolongerbatterylives.Despiterunningonresourcelimiteddevices,edgeAImodels maintainaccuracywithina smallmargin(2–3%)fromtheircloud-trainedcounterparts by employing optimized architectures and compression techniquessuchaspruningandquantization.
Future research must focus on developing ultra-efficient AI algorithms and hardware specifically designed for lowpower microcontrollers, including emerging accelerator technologieslikeASICsandneuro-morphicchips.Enhancing security and privacy through adaptive, on-device defense mechanisms such as lightweight anomaly detection combined with federated threat intelligence sharing and block-chainbasedauthentication willbecrucialtoprotect distributed IoT environments. Addressing scalability challenges requires hierarchical and collaborative learning protocols, including federated, split, and meta-learning strategies,enablingthousandsofheterogeneousedgenodes to coordinate AI workloads amid dynamic network conditions.
[1] Chinta, S. (2024). Edge AI for Real-Time Decision Making in IoT Networks. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering,12(9),11293–11309
[2] Bargavi, S.K.M., Muhammed, H., Harish, P.S., & Dhanush,D.(2025).EdgeComputingandAIforReal-time AnalyticsinSmartDevices.AsianJournalofBasicScience &Research,7(2),1–9.
[3] Gbaja, C. (2024). Next-Generation Edge Computing: Leveraging AI-Driven IoT for Autonomous, Real-Time Decision Making and Cybersecurity. Journal of Artificial IntelligenceGeneralScience(JAIGS),5(1),August.
[4] Murthy, V.S.N., Kumari, R., Goyal, M., Dubey, P., Meenakshi,ManikandanS.,&Ramesh,P.(2025).Edge-AI in IoT: Leveraging Cloud Computing and Big Data for Intelligent Decision-Making. Journal of Information SystemsEngineeringandManagement,10(20s).

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 11 | Nov 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[5] Atan, B., Basaran, M., Calik, N., Tedik Basaran, S., Akkuzus,G.,&Durak-Ata,L.(2023).AI-EmpoweredFast Task Execution Decision for Delay-Sensitive IoT Applications in Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Access, 11,1324–1334.
[6] A. Cynthia, R. Deepakkumar, R. Naveen, and M. Thennarasu, "Edge AI for Real Time Decision Making in IoT Devices," International Research Journal of Education and Technology, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 2047-2053, Mar.2025.
[7] J. Xie, X. Zhou, and L. Cheng, "Edge Computing for Real-Time Decision Making in Autonomous Driving: Review of Challenges, Solutions, and Future Trends," InternationalJournalofAdvancedComputerScienceand Applications,vol.15,no.7,pp.598-607,2024
[8] M. S. K. Darla, "Edge AI: Revolutionizing IoT Data Processing," Journal of Computer Science and TechnologyStudies,vol.7,no.7,pp.258-264,Jul.2025.
[9]T.Al-MomaniandM.Al-Hussein,"Real-TimeDecision Making with Edge AI Technologies: Advanced Techniques for Optimizing Performance, Scalability, and Low-Latency Processing in Distributed Computing Environments," Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Management, vol. 71, pp. 71-91, Feb.2024.
[10]K.K.P.Brahmaji,"EdgeComputingandAnalyticsfor IoT Devices: Enhancing Real-Time Decision Making in Smart Environments," International Journal for MultidisciplinaryResearch(IJFMR),vol.6,no.5,pp.1-9, Sep.-Oct.2024.