
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dr. Meenakashi L Rathod1, Chinmay J2, Likith Gowda K V3 , Lokesh D4 , KP Rohith5
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Dr Ambedkar institute of technology Bengaluru Karnataka ,India
Abstract - This report presents the design and implementationofanArduino-basedantennatrackingsystem aimed at optimizing signal reception by automatically orienting the antenna towards the signal source. The system utilizesDCmotorsforantennarotation,Bluetoothformanual user input to set specific angles, and LDRs for signal strength detection to enable automated antenna tracking. The integration of these components allows for efficient signal acquisition and enhances the usability of the antenna system
Key Words: (LDR , Arduino UNO)
1.INTRODUCTION
Antenna tracking systems are indispensable in various applications such as telecommunications, satellite communication, and radio astronomy. These systems are crucialformaintainingsuperiorsignalqualitybyensuring thatantennasremainpreciselyalignedwiththeirrespective signalsources.Thecontinuousadjustmentoftheantenna's directionality optimizes signal strength and reduces interference,whichisessentialforreliablecommunication and data integrity. In the telecommunications sector, antenna tracking systems are used to enhance the quality and reliability of wireless communication. These systems helpmaintainastrongconnectionbyadjustingtheantenna's position to follow the signal source, such as a moving satellite or a mobile transmitter. This capability is particularly important in mobile networks, where the position of the signal source can change frequently, necessitatingconstantrealignmentoftheantennatoensure uninterruptedservice.
In satellite communication, tracking systems are vital for maintainingastablelinkwithsatellitesorbitingtheEarth.As satellitesmoveacrossthesky,ground-basedantennasmust continuouslyadjusttheirorientationtoremainlockedonto the satellite signal. This ensures that data transmission betweenthesatelliteandthegroundstationremainsstrong and consistent, which is critical for applications such as television broadcasting, weather forecasting, and global positioningsystems(GPS).ThedevelopmentofanArduinobased antenna tracking system to achieve optimal signal reception by automatically adjusting the antenna's orientation. Arduino, a versatile and programmable microcontroller platform, offers a cost-effective and customizable solution for developing such systems. The proposedsystemwill utilize sensorsandmotorstodetect thedirectionoftheincomingsignalandadjusttheantenna's
positionaccordingly.Bycontinuouslymonitoringthesignal strength and making real-time adjustments, the Arduinobasedsystemaimstomaintaintheantenna'salignmentwith thesignalsource,ensuringmaximumreceptionquality.
Traditional fixed-position antennas often suffer from suboptimal signal reception due to factors such as signal obstructions, signal attenuation, and changes in signal strength over time. Manual antenna repositioning is impractical and inefficient, especially in applications requiringreal-timesignalacquisitionorinremotelocations. Therefore,thereisaneedforanautomatedantennatracking system capable of dynamically adjusting the antenna's positiontomaintainoptimalsignalreception.Thescopeof thisprojectincludesthedesign,implementation,andtesting ofanArduino-basedantennatrackingsystem.Thesystem will be capable of automatically adjusting the antenna's orientationbasedonreal-timesignalstrengthfeedbackfrom LDRs.Additionally,userswillhavetheoptiontomanually controltheantenna'spositionviaBluetoothinput
Existingantennatrackingsystemsoftenrelyoncomplexand expensive hardware, making them inaccessible to many users.Additionally,manual antenna repositioningistimeconsuming and impractical, especially in dynamic signal environments. While some commercial solutions offer automated antenna tracking, they are often prohibitively expensiveforsmall-scaleapplications
The proposed antenna tracking system employs Arduino microcontrollers to coordinate the various system components. To achieve precise antenna orientation, DC motors will be used for automated rotation. Bluetooth connectivity will allow users to manually input specific antenna angles for targeted signal acquisition. Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs) will serve as sensors for detecting signal strength, feeding this data back to the Arduinotoenableautomatedtrackingadjustments.
Thisintegratedapproachensuresacost-effectiveanduserfriendlysolutionforoptimizingsignalreception.Theuseof Arduino microcontrollers offers flexibility and ease of programming, making it accessible for a wide range of applications. The inclusion of Bluetooth connectivity

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
providesconvenientmanualcontrol,allowinguserstofinetune the antenna's position as needed. Meanwhile, the automated tracking system, driven by real-time feedback fromtheLDRs,ensurescontinuousoptimalalignmentwith the signal source. By combining these technologies, the system aims to enhance signal reception quality in fields suchastelecommunications,satellitecommunication, and radio astronomy. The result is a reliable, efficient, and affordable solution for maintaining strong and consistent signalconnections.
Themainobjectivesofthisprojectareasfollows:
I. Develop a system using Arduino microcontrollers to control and adjust the antenna'sorientationdynamically.
II. UseDCmotorstoprovidepreciseandreliable movementforadjustingtheantenna'sposition automatically.
III. Allowuserstomanuallyinputantennaangles via Bluetooth, using a mobile app or other Bluetooth-enableddevices.
IV. UseLightDependentResistors(LDRs)todetect signal strength and provide feedback to the Arduinoforreal-timeantennaadjustments.
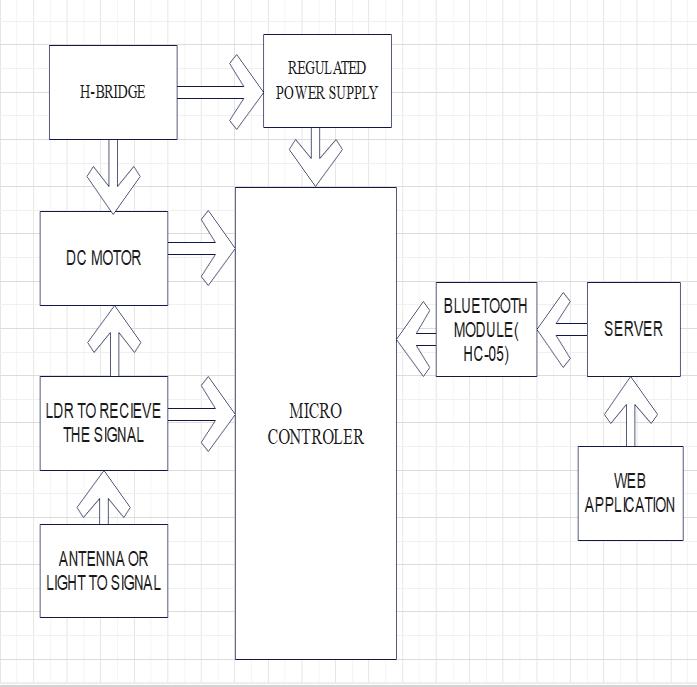
Fig 3.1
The antenna tracking system aims to enhance signal reception by automatically aligning the antenna with the signalsource.Itcomprisesadirectionalantennamountedon a rotating platform, operated by DC motors. An Arduino
microcontrolleractsasthecentralprocessor,coordinating antennarotationbasedoninputsignalsandsensorfeedback. Additionally, Bluetooth connectivity enables manual adjustment,allowinguserstofine-tuneantennapositionfor optimizedreception.Signaldetectionreliesonstrategically placed light-dependent resistors (LDRs) to gauge signal strength. LDRs react to varying light levels, facilitating accuratesignalmeasurement.ArduinointerpretsLDRdata todeterminesignaldirectionandstrength,guidingantenna adjustments.
Using LDR feedback, the Arduino activates DC motors to align the antenna continuously. A closed-loop control algorithmmonitorssignalstrength,adjustingazimuthand elevation angles accordingly. This iterative process maximizes signal reception, maintaining optimal connectivity with the signal source. Beyond automated tracking, the system offers manual control via Bluetooth communication. Users can connect smartphones or computers to the Arduino, manually adjusting antenna angles. This feature complements automated tracking, particularlyusefulinscenarioswherepreciseadjustments areneeded,likesignalobstructionsorsourceswitching.
The fusion of automated tracking and manual control via Bluetooth provides a comprehensive solution for robust signal reception. Continuous monitoring and adjustment ensurereliableconnectivity,evenindynamicenvironments. Combining precision control with user-friendly interfaces enhances communication system reliability, making it valuableforvariousprofessionalandamateurapplications.
ThesuccessfulimplementationofaDCmotor-basedantenna rotationsystem,coupledwithBluetooth-enableduserinput for manual antenna positioning and Light-Dependent Resistor (LDR)-based signal strength detection for automatedantennatracking,yieldedpromisingoutcomesin achievingoptimalsignalreception.Byseamlesslyintegrating these components, the system showcased improved flexibility,precision,andoperationalefficiencyinoptimizing antenna orientation for enhancedsignal reception. fig 4.1 shows the prototype of hardware setup. The DC motordriven antenna rotation system played a pivotal role in ensuring accurate and seamless rotation of the antenna assembly. Through Arduino-based control, users could manipulatetheazimuthalrotationoftheantenna,allowing fineadjustmentstospecificanglesbasedonBluetoothinput. fig 4.2 depicts the signal strength of different LDRs This manualcontrolmechanismempowereduserstotailorthe antenna orientation to their preferences or specific signal requirements.
Furthermore, the incorporation of Bluetooth connectivity facilitated seamless communication between the user interface and the Arduino controller. Users could conveniently input desired azimuthal angles via

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
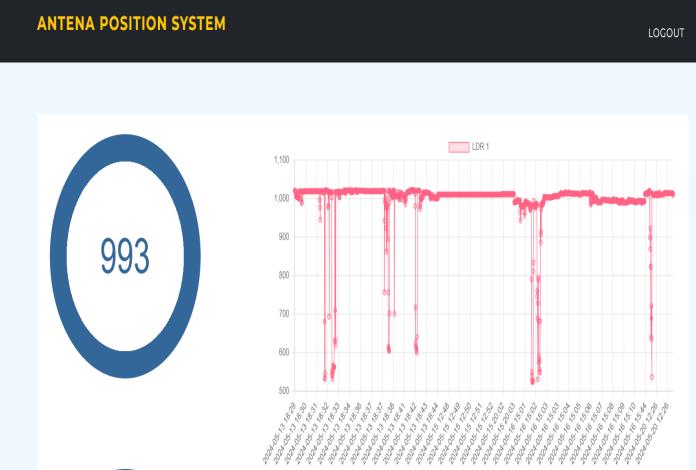
smartphonesorotherBluetooth-enableddevices,ensuring an intuitive and user-friendly experience during system operation. In parallel, the system featured automated antenna tracking capabilities using LDR sensors. These strategicallypositionedsensorsdetectedvariationsinsignal strength corresponding to changes in antenna orientation relative to the signal source. By continuously monitoring signal strength and adjusting the antenna’s azimuthal positionaccordingly, fig 4.3 showsvisualizerepresentation ofdataexchange,thesystemautonomouslyoptimizedsignal reception,consistentlyachievingmaximumsignalstrength.
The harmonious integration of manual and automated controlmechanismsprovidedredundancyandadaptability, allowing the system to thrive in diverse operational scenariosandenvironmental conditions.Userscouldfinetune antenna positioning manually or rely on automated tracking for hands-free operation and continuous signal receptionoptimization.
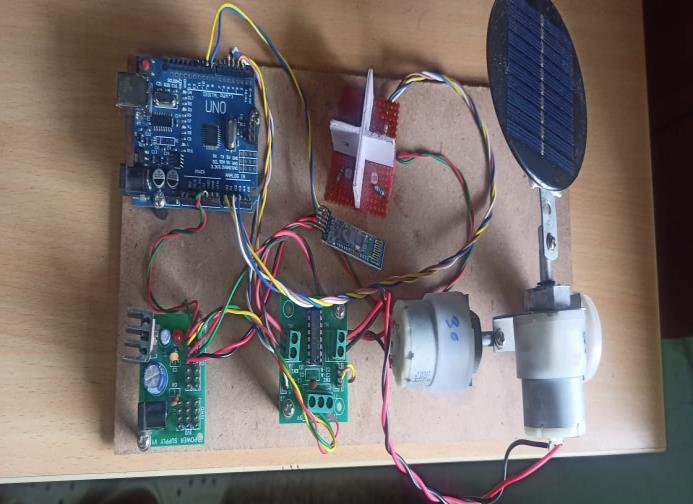

ThesuccessfulimplementationofanArduino-basedsystem designed to maximize signal reception through antenna rotation represents a significant leap forward in telecommunicationstechnology.Byseamlesslyintegrating DCmotor-drivenantennarotation,Bluetooth-enableduser inputformanualadjustments,andLight-DependentResistor (LDR)-based signal strength detection for automated tracking,thissystemoffersaversatileandefficientsolution foroptimizingsignalreception.
The automated antenna tracking ensures continuous alignment with the strongest signal source, thereby enhancing communication reliability and overall performance. Furthermore, the inclusion of user-friendly Bluetoothcontrolallowsforconvenientmanualadjustments, providing flexibility and ease of use for operators. In summary, the Arduino-based system holds immense potential for enhancing signal reception across various applications,fromamateurradiocommunicationtoremote sensingandbeyond.
1A.V.Raut,D.D.Salunke,andS.S.Patil,"ArduinoBasedSun Tracking Solar Panel System: Design, Development, and Analysis," in Proceedings of the 2019 10th International ConferenceonComputing,CommunicationandNetworking Technologies(ICCCNT),2019,pp.1-6.ConferenceonInternet ofThings:SmartInnovationandUsages(IoT-SIU),2019,pp. 1-5.
2. M. S. Kumar, S. K. Singh, and S. Kumar, "Arduino Based Antenna Positioning System for SatelliteCommunication," International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology(IJEAT),vol.9,no.3,pp.341-345,2019.
3. S. Mishra, S. K. Rout, and A. S. Mandal, "Design and Development of Arduino-based Antenna Positioning

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
System,"InternationalJournalofEmergingTechnologyand AdvancedEngineering(IJETAE),vol.4,no.3,pp.7-11,2014.
4. S. K. Maheshwari, P. N. Chaturvedi, and N. K. Verma, "Development of Bluetooth Controlled Robotic Arm Using Arduino," International Journal of Computer Applications, vol.97,no.9,pp.23-27,2014.
5..J.S.Bisen,P.R.Deshmukh,andA.K.Khare,"Designand ImplementationofArduino-basedAntennaPositionControl SystemforWirelessCommunication,"inProceedingsofthe 20194thInternational
6. R. Gupta, A. K. Tyagi, and R. Kumar, "Bluetooth Based Wireless Device Control Using Arduino," International JournalofEngineeringandTechnicalResearch(IJETR),vol. 3,no.5,pp.35-37,2015.
© 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008
|