
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 12 | Dec 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 12 | Dec 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dr. Vinay V. Kuppast1 , Meghana S. Biradar2 , Shivakumar S. Shidaraddi 3 , Sudeep Shettar4 , Shanmukhagouda M. Karakanagoudra5
1Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Basaveshwar Engineering College, Bagalkote, Karnataka, India 2,3,4,5 Students, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Basaveshwar Engineering College, Bagalkote, Karnataka, India
Abstract - Course selection plays a crucial role in determining a student’s academic growth and career trajectory.Traditionalmanualselectionprocessesoftenlack personalization, leading to confusion and misalignment of studentskillswithcourserequirements.Thispaperpresents an intelligent Engineering Education Support System that uses supervised machine learning, specifically a Random Forest Classifier, to recommend suitable courses to engineering students. The system analyzes student attributes such as GPA, mathematical proficiency, coding skill, interest areas, academic stream, and career goals to generate ranked course recommendations. A Python-based Tk inter GUI ensures user-friendly interaction, while an SQLite backend maintains structured records for administrative analysis. Experimental results demonstrate that the model provides accurate, transparent, and personalized recommendations. The system addresses critical challenges in engineering education by enhancing decision-making, reducing selection errors, and supporting digital academic planning.
Key Words: Machine Learning, Course Recommendation System,RandomForest,Python,Tk interGUI,Educational DataMining,SQLite
1.
Course selection in engineering education has become increasingly complex due to diversified electives, interdisciplinary learning pathways, and evolving skill requirements. Students often rely on informal advice or incomplete information, resulting in suboptimal course choices. With the rise of data-driven academic systems andAI-assistedlearningtools,thereisastrongneedforan intelligent, automated support mechanism that assists studentsinmakinginformedacademicdecisions.
This study proposes a Python-based recommendation system that uses machine learning techniques to analyze studentprofilesandrecommendappropriatecourses.The systemisequippedwithgraphicaluserinterface(GUI)and databasestoragetoensuretransparency,accessibility,and long-term usability. The model leverages historical training data to identify patterns and generate ranked course recommendations, providing students with
multiple suitable options and reducing uncertainty in the decision-makingprocess.
The growth of online learning platforms and MOOCs has created a strong need for intelligent course-selection support systems. Traditional advising often lacks personalization, clear prerequisite guidance, and structured pathways, leading to poor decision-making amonglearners.
Hour et al. [1] highlighted major challenges in MOOCs, including unclear prerequisites and information overload. Jenaetal.[2]showedthatstudentsstruggletomatchtheir skills and interests to suitable courses, and that collaborative filtering improves recommendations but suffersfromsparselyandcold-startissues.
Content- based models, though widely used, lack adaptability. Wang et al. [3] demonstrated that they often misssemanticrelationshipsbetweenconcepts.Toaddress this, Altars et al. [4] introduced Concept GCN, a graphbasedmodel thatintegrates semanticandbehavioral data forimprovedaccuracy.
Prerequisite- and sequence-aware models also enhance decision-making. Chanaa and El Faddily [5] proposed a prerequisite-matching framework, while Wong [6] developed a sequence-based planner using historical enrollment patterns. Khan [7] showed that session-based methodscapturetemporallearningbehaviorandimprove short-termrecommendations.
Overall, literature trends show a shift toward hybrid, semantic, and context-aware models that overcome limitations of traditional content-based and collaborative filteringmethods.Theseadvancedapproachesofferbetter accuracy, adaptability, and personalization essential for effective course recommendation in engineering education.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 12 | Dec 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Engineering students frequently struggle with selecting appropriateelectivesduetounclearprerequisites,limited guidance,andlackofstructureddecision-supportsystems. Existingregistrationportalsarelargelymanualandprone to errors such as exceeding credit limits or choosing noneligiblecourses.
Therefore, there is a need for a Python-based intelligent system that recommends suitable courses, validates prerequisites,andstoresacademicrecordsinacentralized database.
The overall methodology includes data collection, preprocessing,modeltraining,interfacedevelopment,and databaseintegration.
A. System Architecture
1) Data Collection
A structured dataset (student_course_dataset.csv) was developedcontainingfeaturessuchas:
GPA
MathScore
CodingSkill
InterestArea
Stream
CareerGoal
CourseChosen
2) Data Preprocessing
LabelEncodingforcategoricalfields
StandardScalingfornumericalfields
Splittinginputs(X)andtarget(y)
Saving trained model and preprocessing componentsusingjoblib
3) Machine Learning Model
A Random Forest Classifier (n_estimators=100, random_state=42)wasselecteddueto:
Robustnesswithmixeddatatypes
Highaccuracyonsmalldatasets
Abilitytogenerateprobabilityscores
4) GUI Development
APythonTkinter-basedinterfacewasdeveloped,allowing students to enter academic and personal details to obtain real-timerecommendations.
5) Database Integration
All user inputs and recommendations are stored in students.db,enablinglong-termdatamonitoring.
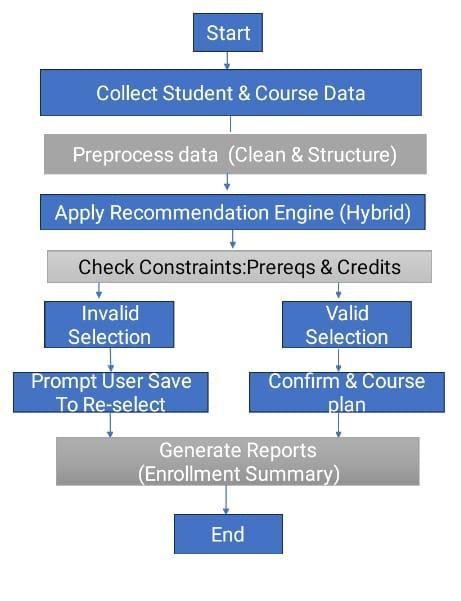
B. Project Flow Diagram
Figure1showsthecompleteworkingflowoftheproposed system.
1. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
A. GUI Output
The user interface allows students to enter academic records and generate top recommendations. TheactualGUIusedintheprojectisshownbelow.
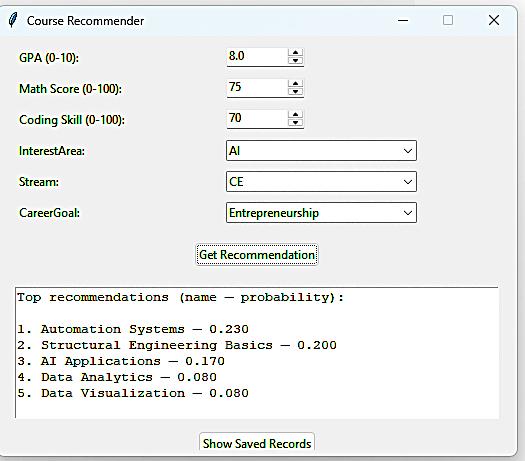
Figure2. PythonTkinterGUIforCourseRecommendation System

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 12 | Dec 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
SampleInput
GPA:8.0
MathScore:75
CodingSkill:70
InterestArea:AI
Stream:CE
CareerGoal:Entrepreneurship
SampleOutput
1. AutomationSystems 0.230
2. StructuralEngineeringBasics 0.200
3. AIApplications 0.170
4. DataAnalytics 0.080
5. DataVisualization 0.080
Interpretation:
The system successfully generated a ranked recommendation list aligned with the student’s interest andskillset.
B. Model Performance Insights
The Random Forest model produced stable predictionsdespitedatasetsizeconstraints.
Probability-based ranking enhances decisionmakingflexibility.
Model persistence significantly reduces execution timeinrepeateduse.
C. Database Storage Results
Asampleentryfromstudents.db:
GP A Ma th Codi ng Inter est Strea m Career Goal Recomme nded Dat e 8.5
This ensures long-term academic analytics for faculty and administrators.
D. Project Output Analysis
The GUI is responsive and easy to use for nontechnicalstudents.
Predictionsalignaccuratelywithinputattributes.
SQLite storage enables data mining, trend analysis,andinstitutionaldecisionsupport.
The system provides quick feedback and eliminatesambiguityincourseselection.
The Engineering Education Support System presented in this paper demonstrates the effectiveness of supervised learning in academic decision-making. By integrating machinelearning,GUIdevelopment,anddatabasestorage, the system offers a robust platform for personalized courserecommendations.ThestudyconfirmsthatPython-
based models can significantly improve accuracy, transparency, and efficiency in course selection. This approach reduces manual counseling efforts, minimizes selection errors, and supports data-driven academic planning. Overall, the system is a scalable and practical solution for engineering institutions aiming to modernize theircourseselectionprocesses.
Futureenhancementsmayinclude:
Expanding the dataset with multi-institutional recordsforhigheraccuracy
A web or mobile-based application with login authentication
Hybrid recommendation systems combining behavioralandpredictiveanalytics
Integration with real-time academic performance tracking
Automated prerequisite verification using institutionalERPsystems
Theseimprovementscantransformthesystemintoafully intelligent academic assistant for large-scale educational environments.
[1] Y. Hou, P. Zhou, T. Wang, L. Yu, Y. Hu, and D. Wu, “Context-Aware Online Learning for Course Recommendation of MOOC Big Data,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:1610.03147,2016.
[2] K. K. Jena, S. K. Bhoi, T. K. Malik, K. S. Sahoo, N. Z. Jhanjhi, S. Bhatia, and F. Amsaad, “E-Learning Course Recommender System Using Collaborative Filtering Models,”Electronics,vol.12,no.1,p.157,2023.
[3]S.Wang,J.Gong,W.Feng,H.Peng,J.Tang,andP.S.Yu, “Attentional Heterogeneous Graph Convolutional Deep Knowledge Recommender (ACKRec) for MOOCs,” in Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference onKnowledgeDiscoveryandDataMining(KDD),2020.
[4] R. Alatrash, M. A. Chatti, W. Alaoui, and A. Yates, “ConceptGCN: Knowledge Concept Recommendation in MOOCs Based on Knowledge Graph Convolutional Networks and SBERT,” Computers & Education: Artificial Intelligence,vol.6,p.100193,2024.
[5] A. Chanaa and N. El Faddouli, “Prerequisites-Based Course Recommendation: Recommending Learning Objects Using Concept Prerequisites and Metadata Matching,” Smart Learning Environments, vol. 11, no. 1, 2024.
[6] C. Wong, “Sequence-Based Course Recommender for Personalized Curriculum Planning,” in Artificial

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 12 | Dec 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Intelligence in Education (AIED), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10948, Springer, 2018, pp. 531–534.
[7] M. A. Z. Khan, “Session-Based Methods for Course Recommendation,” Journal of Educational Data Mining, vol.16,no.1,pp.164–196,2024.
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page116