
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Kavitha H C1 , H.P. Mohan Kumar2
1Department of MCA, P.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, India
2Department of CS&E, P.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, India
Abstract - The shift in lifestyle among today’s youth, particularly college students, has led to a noticeable increase in health issues. Lack of physical activity, irregular routines, and frequent consumption of fast food contribute to unbalanced body weight and poor overall health. One of the key indicators of health is Body Mass Index (BMI), which is used to classify individuals into categories such as underweight,normalweight,overweight,andobesebasedon their height and weight. Being underweight may result in malnutrition, lack of essential vitamins, poor immunity, and developmental delays. On the other hand, excess weight is often linked to serious conditions like Type-2 diabetes. To detect and prevent these issues early, machine learning (ML) can be used to create predictive health models. This project presents a smart application called E-Nurse, which functions like a digital nurse in colleges. It uses machine learning algorithms such as Naive Bayes, Decision Tree, and Random Forest to analyze student health data. These algorithms are evaluated to find the most accurate model for predicting health risks. The system considers multiple factors including age, gender, food habits, academic pressure, family background, BMI, height, and weight to assess both physical and mental health issues. Based on the results, it suggests personalized and evidence-based diet recommendations to promote better student health. Developed using Microsoft tools like Visual Studio and SQL Server, this system aims to support students and educational institutions by providing timely health insights and tailored dietary guidance.
Key Words: Data science, Naive Bayes, SVM, Random Forest, GUI, Student, Mental Issues, Machine learning, fertilizer.
Educationalinstitutionsstrivetoensuremaximumacademic successforallstudents.However,academicperformanceis often affected by several factors including gender, communicationability,memorycapacity,healthconditions, family background, and participation in extracurricular activities.Understandingtheseinfluencesearlycanhelpin addressing issues before they impact a student’s performance. Often, students struggle with learning, especiallyintheearlystagesofacourse.Thisprojectaimsto
explorehoweffectivelystudentscopewiththeiracademic journeyandidentifythechallengestheyface.Insightsgained from this analysis enable educators to recognize each student’s learning style and determine the most effective teachingstrategies.
To accomplish this, machine learning algorithms such as NaiveBayes,RandomForest,andDecisionTreeareapplied to educational datasets. These models evaluate various attributes including age, gender, eating habits, family environment,mentalstress,academicscores,height,weight, and BMI to detect possible health-related issues. The predictiveaccuracyofeachmodeliscomparedtodetermine themosteffectiveapproach.
The project includes the development of a user-friendly software application that utilizes these trained models to identifypotentialhealthrisksamongstudents.Bydiagnosing issues early, the system supports educators and health professionals in taking proactive steps to assist students. Thisresultsinimprovedacademicoutcomesthroughtimely intervention and personalized support. This intelligent system is an innovative step toward integrating health analysis into academic monitoring, ensuring a holistic approachtostudentsuccess[6].
[1]Inafoundationalstudy,theWorldHealthOrganization (2019)developedevidence-basednutritionguidelinesrooted inclinicaltrialsandscientificresearch.Theseguidelineshelp individuals make healthier food choices and assist professionalsincreatingnutritionplans.Althoughthestudy emphasizeddietaryassessmenttechniques,itdidnotexplore AI-drivenpersonalization.
[2] Smithand Doe(2020)investigatedthe use ofArtificial Intelligence(AI)forgeneratingpersonalizeddietplansbased onindividualhealthprofilesanddietarypreferences.They employed deep learning and natural language processing (NLP)toprocessnutritionaldatasetsandproduceoptimized mealsuggestions,improvingdietaryadherenceandhealth outcomes.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[3]Johnetal.(2021)focusedonmachinelearningtechniques for health risk prediction. By using algorithms such as Random Forest and SVM, they predicted risks like obesity anddiabetesbasedonhealthindicatorsincludingBMI,blood glucose, and activity levels. However, their models were limitedinreal-timeadaptabilityanddatasetdiversity.
[4]Leeetal.(2022)analyzedstudenthealthrisksusingdata miningtechniquesandclassificationalgorithms.Thestudy emphasizedearlydetectionofhealthconcernssuchasstress, poordiet,andhypertensioninstudents.Althoughitoffered practical insights, it lacked integration with automated recommendationsystemsforintervention.
[5]Wangetal.(2023)exploredtheapplicationofpredictive analytics in healthcare, emphasizing the use of machine learningandartificialintelligencetoanticipatemedicalrisks and improve clinical outcomes. Their approach involved analyzing historical health records, wearable sensor data, and clinical reports to identify risk factors and optimize treatmentstrategies.UsingmodelslikeLogisticRegression, RandomForest,andNeuralNetworks,thestudysuccessfully predicted disease likelihood and supported early intervention planning. However, the research highlighted challengesinintegratingthesesystemsforreal-timehospital resourcemanagementandpatient-specificcare.
The proposed system is a browser-based real-time web application tailored for the education sector, where both lecturersandstudentscaninteractwiththeplatform.The system's primary objective is to identify potential health risksamongstudentsusingmachinelearningtechniquesand offer personalized diet recommendations aimed at improvingstudentwell-being.
Thisapplicationanalyzesmultiplebehavioralandlifestyle parameters such as study hours, attendance regularity, financialproblems,family-relatedissues,peerpressure,and social relationships (e.g., friend-related issues). These features are crucial in understanding a student’s physical andmentalhealthcondition,whichinturninfluencestheir academicperformance[7].
To predict health risks accurately, the system employs efficientsupervisedlearningalgorithmslikeNaïveBayes,KNearest Neighbor (KNN), and Random Forest. The performanceofeachalgorithmisevaluatedusingcommon metricssuchasaccuracy,precision,recall,andF1-score.The results are compared to determine the best-performing modelforpredictingstudenthealthrisks.
In addition to health risk prediction, the system also recommendsevidence-baseddietarysuggestionstailoredto the individual needs of students based on their predicted
risk category. This enables early intervention and encourageshealthierlifestylehabitsamongstudents.
The entire platform is developed using full-stack web technologies. The backend is built using C# within the MicrosoftVisualStudioenvironmentandconnectedtoSQL Serverfordatamanagement.Thefrontendiscreatedusing HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and jQuery to ensure a responsive and user-friendly experience. The system architecture supportsscalability,real-timeupdates,andinteractivevisual analysisforadministrativeusers[9]
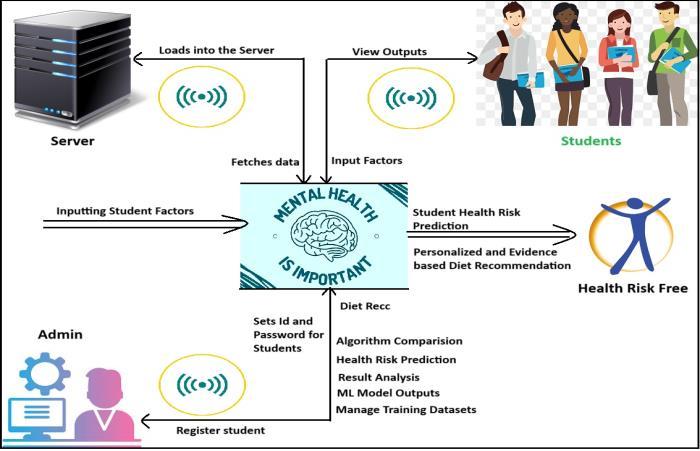
The workflow begins with the admin, who registers students,assignslogincredentials,andmanagesthetraining datasets for machine learning models. Once registered, students submit health-related data such as diet, lifestyle habits,andpersonalhealthmetrics.
This information is stored on the server and used for analysis. The system then applies machine learning algorithms to predict possible health risks and generate personalized, evidence-based diet recommendations for eachstudent.
The outcomes including risk levels and dietary suggestions arepresentedtostudentstosupportinformed health decisions. The system also includes continuous learning features such as algorithm comparison, performanceevaluation,andmodelrefinementtoimprove accuracyovertime.
Ultimately, the goal is to support students in maintaining better health through AI-powered, real-time insights and proactiveguidance[10]
Inbothpastandpresentgenerations,significantchangesin the lifestyle of young individuals such as decreased

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
physicalactivityandincreasedconsumptionoffastfood haveledtoaconcerningriseinhealth-relatedissuesamong collegestudents.Poordietaryhabitsareamajorcontributor toimbalancedbodyweightandrelatedhealthcomplications. A lack of health awareness, inadequate nutrition, and insufficientphysicalactivityarekeyfactorsthatnegatively affectstudentwell-being.
These issues often manifest as stress, anxiety, depression, andchronicconditionsliketype2diabetes,whichpresent serious challenges within the educational environment. Addressingstudenthealthrisksatanearlystageiscrucialto preventing long-term health problems and improving academicoutcomes.Therefore,earlyidentificationofthese risks and the provision of personalized, evidence-based dietary recommendations are essential steps toward enhancingtheoverallhealthandperformanceofstudentsin thecurrentacademiclandscape[12].
The methodology followed in this project adopts a structured and systematic approach that includes data collection, preprocessing, health risk prediction using the Naïve Bayes algorithm, and generation of personalized dietary recommendations. The aim of the system is to identifypotential healthrisksamongcollegestudentsand provide evidence-based nutritional suggestions through a browser-basedapplication.
Thefirststageofthemethodologyisdatacollection,whichis conductedthroughhealth-relatedsurveysorquestionnaires distributedamongstudents.Thecollecteddatasetincludes key attributes such as financial challenges, family-related stress, academic pressure, study duration, attendance regularity,dietaryhabits,andsocial/emotionalfactorssuch asfriendship-relatedissues. Theseparametersarechosen for their significant influence on a student's physical and mentalwell-being.
Following data collection, the dataset undergoes preprocessingtoensureitissuitableformachinelearning analysis.Thisincludeshandlingmissingorincompletedata, encoding categorical variables into numerical form, and normalizing data to maintain consistency. These preprocessingstepshelpimprovethequalityofinputdata andenhancetheperformanceofthepredictivemodel.The pre-processeddataisthensplitintotrainingandtestingsets. ThecorepredictionalgorithmusedinthissystemisNaïve Bayes,asimpleyetpowerfulprobabilisticclassifierbasedon Bayes' Theorem with an assumption of feature independence.Itisespeciallyeffectivefortextclassification and prediction problems where the input features are categoricalordiscrete,asinthiscase.
TheNaiveBayesmodelistrainedusingthetrainingdataset toclassifystudentsintopredefinedhealthrisk categories: low risk, moderate risk, and high risk. After training, the modelistestedusingthereservedtestdatatoevaluateits performance.Standardevaluationmetricssuchasaccuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score are used to measure the model’seffectiveness.
Oncethehealthrisklevelispredicted,thesystemmovesto therecommendationstage,whereitgeneratespersonalized dietarysuggestions.Theserecommendationsaretailoredto thehealthriskcategoryofeachstudentandaredesignedto supportphysicalandmentalwell-being.
The complete system is developed using full-stack technologies.ThebackendisimplementedinC#usingthe VisualStudioenvironment,whilethedatabaseismanaged using SQL Server. The frontend is built using HTML, CSS, JavaScript,andjQuery,providinganintuitiveandresponsive userinterface.
Thismethodologysupportsproactivehealthmonitoringin educational institutions by enabling earlyidentification of healthrisksanddeliveringtimelydiet-basedinterventions. It ultimately aims to promote healthier lifestyles and improveacademicoutcomesforstudents[8]
Thepredictionofstudenthealthriskintheproposedsystem is carried out using the Naïve Bayes algorithm, a probabilistic classification technique based on Bayes' Theorem.Thealgorithmworkseffectivelywhendealingwith categoricalinputfeaturessuchasattendance,studyhours, familyissues,anddietaryhabits.Belowisthestep-by-step procedureusedforclassifyingstudenthealthrisks:
Step 1: Dataset Scanning and Retrieval
In the initial stage, the required dataset is retrieved from storage sources such as local databases, cloud storage, or externalfiles(e.g.,Excelsheets).Thesystemscansandloads therelevantstudenthealthdata,whichisthenpreparedfor furtherprocessing.
Step 2: Probability Calculation of Attribute Values
Foreachattributeinthedataset,thealgorithmcomputesthe conditionalprobabilityofthatattributegiveneachpossible class(i.e.,healthriskcategory).Thesevaluesarecalculated usingaprobabilisticformulathataccountsfortrainingdata frequencyandpriorestimates.
Step 3: Applying the Naïve Bayes Formula
The conditional probability for each attribute value is computedusingthefollowingformula: P(attribute_value(ai)∣class(vj))=n+mnc+mp
Where:

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
nnn = total number of training examples where class=vjv_jvj
ncn_cnc=numberofexampleswhereclass=vjv_jvj andattribute=aia_iai
ppp=priorestimatefortheprobabilityP(ai∣vj)P(a_i \midv_j)P(ai∣vj)
mmm = equivalent sample size (a parameter that determinestheweightgiventopriorestimates)
Step 4: Probability Aggregation for Each Class
After calculating the conditional probabilities for each attribute, these values are multiplied along with the prior probability(p)ofeachclass.Thisgivesafinalscoreforeach classbasedonthegiveninput.
This step enables the system to assess how likely a new input belongs to each of the predefined health risk categories.
Step
Finally,thealgorithmcomparesthecalculatedprobabilities forallclassesandassignstheinputdatatotheclasswiththe highestprobability.Thisresultisthenusedtodeterminethe student’s health risk level (e.g., Low Risk, Moderate Risk, High Risk). Based on the classification result, the system providespersonalizeddietrecommendations[11]
Sample Example
Parameters[m=3]
1. Gender
2. FinancialIssues
3. FamilyIssues
Outcomes–Stress,Depression[p=1/2=0.5]
Training Data-set
Anil Male Yes Yes
Ajay Male No No
Aruni Female Yes No
Kumari Female Yes
Naveen Male No No
NewStudentdata–Akash
Parameters (Gender - Male, Financial Issues - Yes, Family Issues-No) Outcome=?
NaiveBayesworksbasedonprobabilitycalculation,ituses formula:
P=[n_c+(m*p)]/(n+m)
Stress – 0.58 * 0.58 * 0.41 * 0.5 (p) = 0.068
Depression–0.41*0.41*0.58*0.5(p)=0.048
SinceStress>Depression
Sothisnewstudentisclassifiedto Stress
Stress Depression
Male
P=[n_c+(m*p)]/(n+m)
n=3,n_c=2,m=3,p=05 p=[2+(3*0.5)]/(3+3) p=058
Yes
P=[n_c+(m*p)]/(n+m)
n=3,n_c=2,m=3,p=0.5 p=[2+(3*05)]/(3+3) p=058
No
P=[n_c+(m*p)]/(n+m)
n=3,n_c=1,m=3,p=05 p=[1+(3*05)]/(3+3) p=0.41
Male
P=[n_c+(m*p)]/(n+m)
n=3,n_c=1,m=3,p=05 p=[1+(3*0.5)]/(3+3) p=041
Yes
P=[n_c+(m*p)]/(n+m) n=3,n_c=1,m=3,p=05 p=[1+(3*0.5)]/(3+3) p=041
No
P=[n_c+(m*p)]/(n+m)
n=3,n_c=2,m=3,p=05 p=[2+(3*05)]/(3+3) p=0.58
5.1 RF Algorithm Results
Discussion
Here we build a real time application useful for the educationaldepartment.ThisprojectbuildusingMicrosoft technologies.EducationalTrainingdatasetstrainedusingRF algorithm and we got very good results. RF algorithm is programmed in such a way that, it works for dynamic datasets. RF algorithm logic is written and it’s our own library.Wearegettingaround88%ofaccurateresultsandit takesaround1000millisecondsforprediction.
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page845

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
RESULTS
Table 5.1: Experiment result
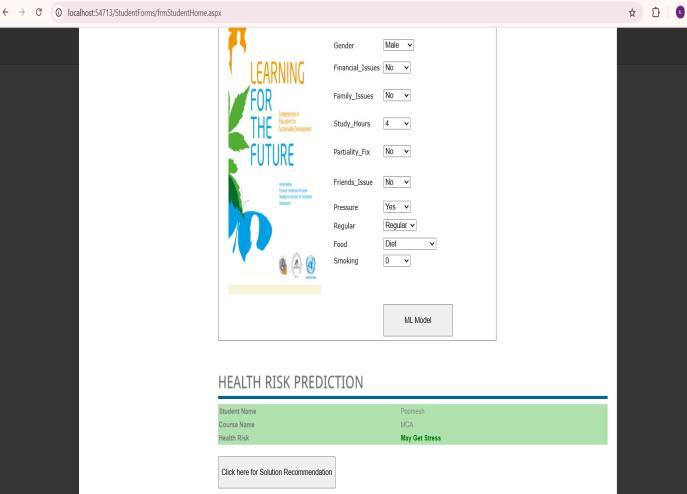
Poorhealthawareness,unhealthydietaryhabits,andlackof physicalactivityamongcollegestudentsoftencontributeto varioushealthproblemssuchasstress,depression,anxiety, andtype2diabetes.Identifyingandaddressingtheseissues presents a significant challenge within the educational environment.Earlydetectionofstudenthealthrisksandthe provision of personalized, evidence-based dietary recommendations are crucial for improving student wellbeing.Theproposedsystemaimstoautomatetheprediction ofstudenthealthrisksusingmachinelearningalgorithms. WeimplementedtwoMLmodels,bothofwhichproduced highlyaccurateresults.Thissystemissuitableforreal-time application in colleges, offering a practical solution to supportstudenthealththroughdata-driveninsights[9]

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Additional machine learning algorithms can be implemented to improve prediction accuracy and allow comparative analysis to identify the most effectivemodel.
More health-related factors and behavioral parameters can be integrated to enhance the predictionscopeandreliability.
Thesystemcanbetrainedonlargerandmorediverse datasets to improve model generalization and performanceinreal-worldapplications.
[1] World Health Organization (2019). Healthy diet: Factsheet.
[2] Smith,R.,&Jones,L.(2022).AI-PoweredDiet RecommendationsBasedonHealthMetrics. IEEEAccess,10,12345–12356.
[3] Jackson, T., & Lee, W. (2021). Health Risk Prediction in Students Using AI Models. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 134, 104450.
[4] Kim,H., &Park, Y.(2023). TheRoleofAI in Student Health Risk Analysis. Journal ofHealthcareEngineering,2023,1–15.
[5] Garcia, E., & Martinez, R. (2023). AI-Driven Health Risk Prediction in College Students. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,70(3),567–578.
[6] Garcia, E., & Martinez, R. (2023). AI-Driven Health Risk Prediction in College Students. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,70(3),567–578.
[7] Liu,B.,&Zhang,C.(2021).PredictingStudent Health Risk Using Machine Learning Techniques. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 150, 104432.Research on the College Students’ Psychological Health ManagementbasedonDataMiningandCloud Platform,FangLi,2016.
[8] PREDICTIVEANALYSISOFSTUDENTSTRESS LEVEL USING NAÏVE BAYESIAN CLASSIFICATION ALGORITHM. Monisha S, Meera R,Vijay Swaminath.R, Dr.Arun Raj L, 2020.
[9] Smith,R.,&Jones,L.(2022).AI-PoweredDiet RecommendationsBasedonHealthMetrics. IEEE Access,10,12345–12356.
[10] Jackson, T., & Lee, W. (2021). Health Risk Prediction in Students Using AI Models. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 134, 104450.
[11] ClassificationAlgorithmsbasedMentalHealth Prediction using Data Mining Authors: Vidit Laijawala, Aadesh Aachaliya, HardikJatta,VijayaPinjarkar(2020)
[12] Fang Li, "Research on the College Students’ Psychological Health Management based on Data Mining and Cloud Platform," 2016.


Kavitha H C, received her Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Applications from University of Mysore, India and she Currently pursuing MCA in P.E.S. College of Engineering,Mandya
Dr H.P Mohan Kumar, Obtained MCA, MSc(Tech) and PhD from University of Mysore, India in 1998,2009and2015respectively. He is Working as a Professor in Dept. of CS&E, P.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, India, His Area of Interest are Computer Vision, video analysis andDataMining.