
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Shubham Gupta
Noblesoft Solutions, San Antonio, Texas, USA.
Abstract
Challengesintheaffordablehousingsectorincludeinsufficienttransparency,inefficientallocation,andsusceptibilitytofraud. This research presents an enhanced infrastructure framework, AI & Blockchain-based Secure and Transparent Affordable Housing Management and Distribution (AIBAHMAD), that addresses these challenges through the integration of blockchain technology with artificial intelligence. The proposed system will design a secure, traceable system using smart contracts, distributed ledger technology (DLT), artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, and crypto protocols. An auditable architecture of applications, housing authorities, property owners, and regulatory bodies is performed on an immutable blockchain system that leverages AI-driven decision support. It is embedded with multi-factor verification, privacy-preserving verification methods, and tamper-free record keeping, with AI for predictive analysis, fraud detection, and optimization. These have improved efficiency, security metrics, and user trust over conventional systems. Instead, AIBAHMAD removes intermediaries byautomating verification processesandusingAI forunadulterated decision-making,resultinginlower administrativecosts andincreasedtransparencyandfairnessinthedecision-makingprocess.Resultscontributetoaffordablehousingmanagement practiceandblockchain-AIintegrationliterature,offeringatechnicallyviablesolutiontolongstandingchallengesinthesector.
Keywords: Blockchain, Smart Contracts, Artificial Intelligence, Affordable Housing, Transparency, Machine Learning, DistributedLedgerTechnology,Multi-factorAuthentication
Asocialinfrastructureelementofaffordablehousingshouldaddressthemostfundamentalhuman needsandsocialequity[1]. The sector's sustained challenges include opaque allocation processes, inefficient application systems, high levels of fraud vulnerability, and fragmentation across multiple stakeholders. [2] Such issues have proven difficult to overcome using traditionalcentralizedmanagementapproaches,resultingintheneedfornewtechnologicalsolutions.
Blockchain technology has emerged as a promising solution in sectors that require transparency, security, and trust among multiplestakeholders[3].Blockchainwasinitiallythoughtthroughforcryptocurrencyapplications,butithasevolvedtomore subdomainsinsupplychain,governance,andhealthcare[4].Thisisbecausetechnologycanprovidetamper-proofrecordsand automateprocessesthroughsmartcontracts.
Some recent papers have studied applying blockchain [5], property registration [6], and rental market [7] in real estate. However,nosuchframeworksformanaging affordable housingusingartificial intelligencehave been proposed. Thissector's unique requirements including income verification, eligibility assessment, fair allocation, and compliance monitoring necessitatespecializedapproachesbeyondgeneralrealestateapplications.
This research fills this gap by forming the AIBAHMAD infrastructure framework (AI & Blockchain-based Secure and TransparentAffordableHousingManagementandDistribution).The infrastructureframeworkusesblockchainwithArtificial Intelligencetomakeasecure,clear,andefficientsystemofdecenthousingwithsmartcontracts,distributedledgertechnology, AIalgorithms,andcryptographicprotocols.
Themaincontributionsofnoteinthisresearchare:
1. Buildacompleteblockchain-AIarchitecturetailoredtomanagehousingonthecheap.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2. Creating specialized smart contracts enhanced with AI for eligibility verification, allocation optimization, and compliancemonitoring
3. Implementing privacy-preserving mechanisms that protect sensitive applicant information while enabling necessary verification
4. DevelopingAI-poweredfrauddetectionandanomalyidentificationsystems
5. Creatingpredictiveanalyticsmodelsforhousingdemandforecastingandresourceoptimization
6. Evaluating the infrastructure framework's performance, security, and user experience through prototype implementationandtesting
Therestofthispaperisorganizedasfollows:Section2reviewsrelatedworkinblockchainandAIapplicationsforhousing and social services. Section 3 provides the theoretical background. Section 4 details the proposed AIBAHMAD design. Section 5 presentsresultsandevaluation.Finally,Section6concludesthepaperanddiscussesfutureresearchdirections.
Blockchain technology has been increasingly explored in the real estate sector. Veuger [8] conducted one of the early comprehensiveanalysesof blockchain'spotential inreal estate,highlightingopportunitiesfor disintermediationandreduced transaction costs. Nijland and Veuger [9] examined how blockchain could transform property rights management through immutableownershiprecordsandsimplifiedtitletransfers.
Several research prototypes have been developed for blockchain applications in property registration. Themistocleous et al. [10] built a landregistrysystem using Ethereumsmart contracts, moving awayfromcentralized record keeping.Zheng et al. [11] proposed a blockchain-based framework for property rights enrollment that reduces fraud and improves security. However,mostimplementationsfocusedonownershiprecordingratherthanaffordablehousingmanagementprocesses. Wouda and Opdenakker [12] researched blockchain solutions for rental agreements and payments with reduced administration and enhanced transparency. Karamitsos et al. [13] integrated blockchain with IoT to support property managementthroughautomaticconditionmonitoringandmaintenancetracking.
Althoughthesestudiesdemonstratedblockchain'sapplicabilityinrealestatesettings,theydidnotaddressaffordablehousing program-specificrequirementslikeeligibilityverification,fairallocationprocesses,andcompliancemonitoring.
AI applications in housing management have primarily focused on market analysis, property valuation, and maintenance optimization. Lee et al. [14] developed machine learning models to predict housing prices and demand patterns across differentsocioeconomicenvironments.Garcia-Teruel[15]exploredtheuseofAIforautomatedpropertyconditionassessment andmaintenancescheduling.
SeveralresearchershaveinvestigatedAIapplicationsinpublicadministration.ChenandZahedi[16]designedneuralnetwork modelsforoptimizingresourceallocationinpublicservices,showingsignificantefficiencyimprovements.Martinezetal.[17] developedadecisionsupportsystemusingmachinelearningforsocialbenefitdistributionthatreducedprocessingtimesand improvedtargetingaccuracy.
However,researchonintegratingAIspecificallyforaffordablehousingmanagementislimited.Despitetheproblemsuniqueto the sector, most existing work does not consider these problems, in particular, bias mitigation, fairness of allocation, and privacyinprocessingsensitivepersonaldata.
Thereisabrandnewresearcharea,knownasBlockchainandAI integrationthathasthepotentialtoharnessthistechnology. Salahetal.[18]proposed,inareviewofsynergiesbetweenthesetechnologies,thatblockchainmaysupplytrusted datatothe

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
AImodels,andtheAIcanhelptheblockchainbecomemoreefficientandsecure.ThisisaframeworkproposedbyWangetal. [19]toperformfederatedcollaborativeAImodeltraininginablockchain.
LimitedworkhasexaminedthecombinedpowerofblockchainandAIinpublicservicessofar.Zhangetal.[20]developedthe conceptual framework for integrating blockchain-AI in healthcare to enhance data security while supporting advanced analytics.Nevertheless,nocomprehensiveimplementationsinthehousingsectorhavebeenstudied.
ThelackofresearchariseswhentheintersectionofblockchainandAIwithaffordablehousingmanagementisconsidered.So far, none of these technologies address the unique ways in which they can be used to overcome face-to-face information transfer, agency inefficiency, and other challenges encountered by transparency, fairness, efficiency, and trust in the administrationofaffordablehousing.
3.1
Ablockchainisatechnologywherealedger,agrowinglistofrecords(blocks),islinkedandsecuredusingcryptography[21]. Thechunkofinformation,usuallymadeupofacryptographichashofthepreviousblock,atimestamp,andtransactiondata,is formed into an immutable chain of information. It’s secure and trustworthy without a central authority but doesn’t allow modificationofretrospectivedata.
Blockchain resides on a peer-to-peer network where nodes maintain the same copy of the ledger and are fail- or attackresistant. New transactions are validated through the consensus mechanism when they are initiated and added to the blockchain [22]. By doing this in a distributed validation, it eliminates trusted intermediaries and achieves transparent, tamper-resistantrecord-keeping.
There are public (permissionless) blockchains, private (permissioned) blockchains, and hybrid (permissioned with some accountability) blockchains [23]. Permissioned blockchain architectures are specifically relevant for applications related to affordable housing, as they enable controlled access for affordable housing lovers and ensure adequate regulatory oversight andprivacyprotections.
Artificial Intelligence covers several computational techniques that help systems perform tasks that usually require human Intelligence.AI is programming powered by machinelearning, referring to algorithmsthatlearn from experience and do not need manual programming [24]. Even deeper, neural networks with multiple layers can learn complex patterns from large datasets[25].
KeyAItechniquesrelevanttoaffordablehousingmanagementinclude:
Supervisedlearningforclassificationandpredictiontasks
Naturallanguageprocessingfordocumentanalysisandinformationextraction
Computervisionforidentityverificationandpropertyassessment
Anomalydetectionforfraudidentification
Recommendationsystemsforapplicant-propertymatching
Reinforcementlearningforoptimizingresourceallocation
These technologies can address various challenges in affordable housing management, including applicant screening, fraud detection,fairallocation,andpredictivemaintenance.
A smart contract is a contract in which the terms cannot be changed securely from a particular point onward; it is merely executed by the computer, and it follows the code of instructions that the terms it is written to embrace [26]. Contractual

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
clausesareenforcedautomaticallywhenpredeterminedconditionsaremet,withoutintermediaries,andwithminimaldispute potential. Smart contracts run on a distributed network, so they inherit the blockchain's security, immutability, and transparencyproperties.
Modernsmartcontractplatformssupportcomplexlogicimplementation,including:
Conditionallogicandbusinessrules
Multi-signaturerequirements
Time-lockedtransactions
Oracleintegrationforexternaldata
Cryptographicverification
In affordable housing, smart contracts can encode eligibility criteria, automate application processing, manage waiting lists, and ensure fair allocation based on predetermined rules. This compliance monitoring can also be automated through continuousverificationthroughoutatenancy.
Affordablehousing systems containsensitivepersonal andfinancial information,so robustprivacypreservation isnecessary. VariousprivacytechniquesweredevelopedforblockchainandAIsystems.
Zero-KnowledgeProofs(ZKPs):Allowonepartytoproveastatementistruewithoutrevealingadditionalinformation [27]
SecureMulti-PartyComputation(MPC):Enablesmultiplepartiestojointlycomputefunctionsovertheirinputswhile keepingthoseinputsprivate[28]
FederatedLearning:AllowstrainingAImodelsacrossmultipledecentralizeddevicesholdinglocaldatasamples[29]
DifferentialPrivacy:Addscalibratednoisetodataorqueriestoprotectindividualprivacywhilepreservingstatistical validity[30]
HomomorphicEncryption:Permitscomputationonencrypteddatawithoutdecryption[31]
By combining these techniques, comprehensive privacy architectures can be built to secure user data while facilitating necessaryverificationprocessesinaffordablehousingmanagement.
4. AIBAHMAD Infrastructure Framework Design
4.1
The AIBAHMAD architecture has five layers, each connected with the others so that the overall architecture can be used to achieveefficient,affordablehousingmanagement.
1. User Interface Layer: Web and Mobile application interfaces (User Interface Layer) that act as interfaces for all stakeholders(applicants,housingauthorities,propertyowners,auditors)
2. AI and Business Logic Layer:Contains:
o AIcomponentsfordecisionsupport,frauddetection,andoptimization
o Smart contracts provide business logic for eligibility verification, processing of applications, and compliancemonitoring
3. Consensus Layer: Use Proof of Authority (PoA) consensus mechanism whereby authorized entities are responsible forvalidatingthetransactions.
4. Data Layer:Hybridstorageapproachwith:
o On-chainstorageofverificationresults,decisions,andaudittrails
o Off-chainencryptedstorageofsensitivepersonaldata
o AImodelstorageandmanagement

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
5. Network Layer:Securecommunicationinfrastructurebetweenpeerparticipants
Figure1showsthisenhancedlayeredarchitecturewithAIintegration.
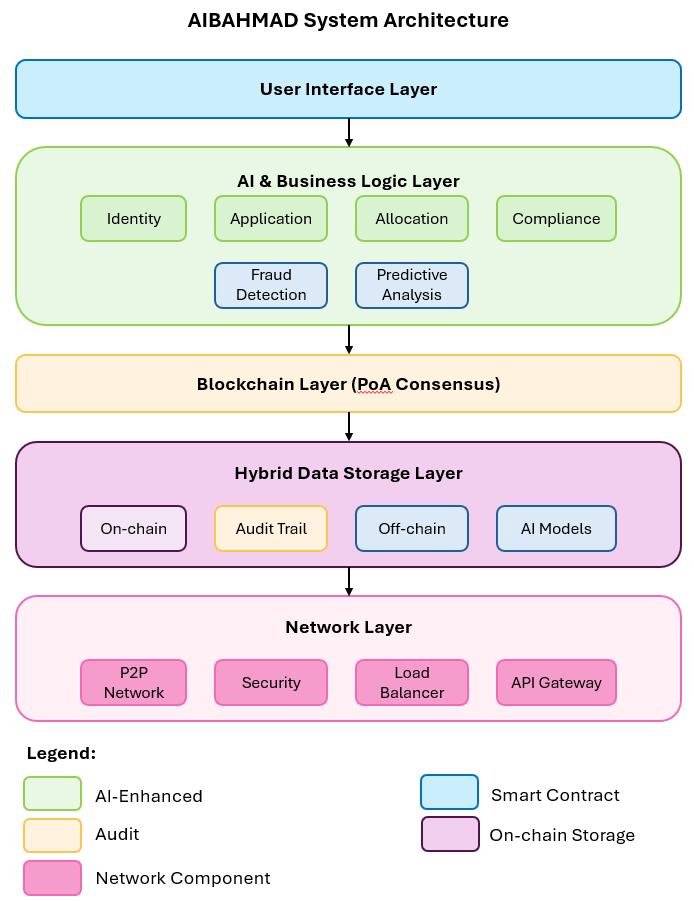
Figure1:SystemArchitectureofAIBAHMADInfrastructureFramework,comprisedoffivelayers,ofwhichAIcomponentshave beenintegrated
4.2 AI Components Integration
SeveralAIaspectsareincludedintheAIBAHMAD infrastructureframeworktoincreasetheefficiency,fairness,andsecurityof affordablehousingmanagement.
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page960
1. Machine Learning-based Eligibility Assessment Engine: Cross-verifies applicant documentation, evaluates informationfrommultiplesources,andautonomouslyflagsforreviewbasedonpotentialinconsistencies.
2. Anomaly Detection and Pattern Recognition: Applicable to fraudulent applications or activity submissions using anomalydetectionandpatternrecognition.
3. This is elaborated in the algorithm of the Fair Allocation Algorithm: It quantifies learning to optimally allocate housingusingmultiplecriteriawhilefosteringfairnessandavoidingbias.
4. Time Series Analysis & Predictive Modeling: It forecasts the demand for housing needs in various regions and demography.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
5. IoT data and predictive analytics for maintaining a Prediction System: This helps predict when problems may ariseandhelpspreventthembeforetheybecomecritical.
6. Unstructured Document Processing: This reduces manual documentation review by using a Natural Language ProcessingEnginethatprocessesandextractsinformationfromunstructureddocuments.
TheseAIcomponentsinteractwiththeblockchaininfrastructurethroughsecureoraclesthatmaintaintheintegrityofthedata exchangebetweenon-chainandoff-chainsystems.
AIBAHMAD is characterized by a secure registration and identity management system that authenticates all the participants and keeps sensitive information out of reach. It consists of several levels of verification based on stakeholder type for the registration:
Applicants: Verify identity through government ID, proof of address, and biometric verification where legally permissible
Housing Authorities:Verifyorganizationalcredentials,authorizedrepresentatives,andadministrativejurisdiction
Property Owners:Verifypropertyownership,compliancewithhousingstandards,andlegalstatus
Auditors:Verifyregulatoryauthorityandaccesspermissions
Registrationthenprovidesallstakeholderswithcryptographiccredentialsthatallowthemtoaccessthesystemsecurelyand sign transactions. The system provides role-based access control to protect participants from accessing only the information andfunctionsthattheyneed.
Using enhanced multi-factor authentication with biometric integration, AIBAHMAD ensures that only authorized users can access the system and perform transactions. The housing allocation decisions and personal data involved are particularly sensitive,whichmakesthisprocedureespeciallyimportant.
Securityrequirementsarechangedaccordingtothesensitivityofarequestedoperationusingthisauthenticationmechanism. For instance, determining application status might need to be completed with two-factor authentication, while altering allocationdecisionswouldnecessitatethefullmulti-factorprocedurewithbiometrics.
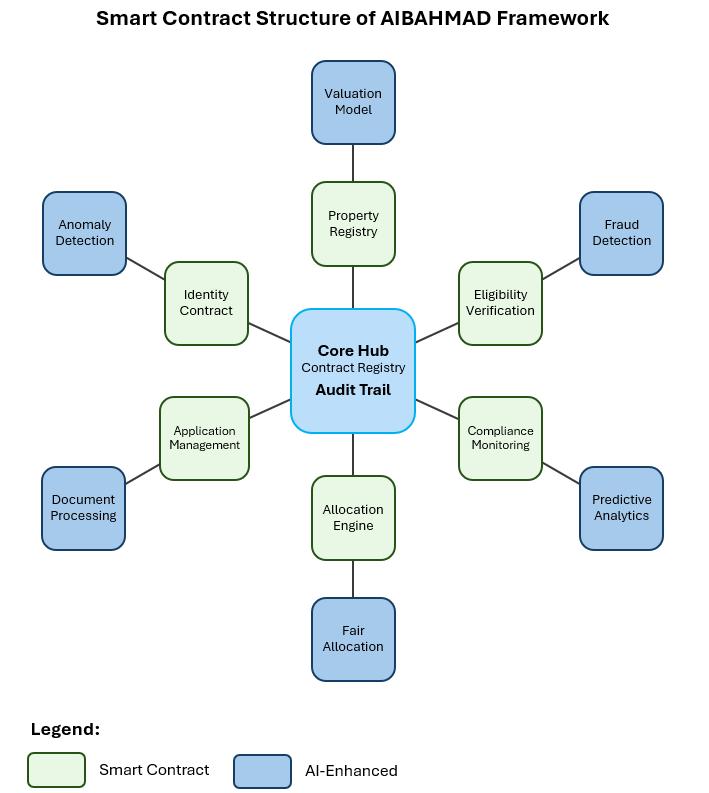
AIBAHMADisimplementedasasetofinterconnected(smart)contractsthataddAItoitscorefunctionality.
1. Identity Contract: Authenticates user identity, manages credentials, provides access controls, and uses AI anomaly detectiontodetectpossiblesuspicioususeraccesspatterns.
2. AI Property Valuation Module: A Property Registry Contract records available housing units, their characteristics, andtheirownershipthroughreleasedpropertyvaluationmodels.
3. NLP Contract: ProcessesdocumentsusingNLPandhandleshousingapplicationsandwaitinglistmanagement
4. Automating Eligibility Verification contract: Machine learning-basedcross-verificationof theapplicant’seligibility basedonprogramcriteria
5. AI-Driven Matching Algorithm: ImplementationoftheAllocationEngineContract,whichinvolvedmatchingeligible applicantstosuitablehousingunitsinafairmanner
6. Compliance Monitoring Contract: Tracks ongoing compliance with program requirements, with anomaly detection forpotentialviolations
7. Audit Trail Contract: Recordsallsystemtransactionsfortransparencyandaccountability

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Figure2showstheSmartContractStructureoftheAIBAHMADInfrastructureFrameworkAIintegration.
4.6 AI-Enhanced Allocation Algorithm
AIBAHMAD is a matching algorithm that matches eligible applicants to suitable housing units using various methods. The ‘algorithms enhanced by AI create allocation logic that merges rules and machinelearning, leveraging the outcomes to avoid biasandmanipulation.
KeyfeaturesoftheAI-enhancedallocationalgorithminclude:
Multi-objectiveoptimizationconsideringapplicantneeds,locationpreferences,andresourceefficiency
Fairnessconstraintsthatpreventdiscriminationbasedonprotectedattributes
ExplainableAItechniquesthatprovidejustificationsforallocationdecisions
Continuouslearningfromallocationoutcomestoimprovefuturedecisions
Regularbiasauditstoensureequityinhousingdistribution

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The algorithm is encoded in smart contracts and executes automatically when specified conditions are met, providing transparencyandauditabilityforallallocationdecisions.
The enhanced AI-based privacy-preserving verification mechanism is a key innovation provided in AIBAHMAD. It verifies an applicant'seligibilitywithoutexposingsensitivepersonalinformationontheblockchain.
1. Requireddocumentationissubmittedtothesecureapplicationinterfacebyapplicants.
2. DocumentsarethenprocessedusingAI,andtherelevantinformationisextractedandanalyzed.
3. Federatedlearningmodelsverifytheinfoacrossmanysourceswithoutcentralizingthedata.
4. Eligibilityisdemonstratedwithzeroproofofknowledge,thusrevealingnospecificdetails.
5. Thus,differentialprivacytechniquesensurethatouraggregationsdonotre-identifytheoriginaldata.
6. Theblockchainstoresverificationresultsaswellascryptographicproofs.
7. Verifiedresultsareautomaticallyusedforapplicationstatusupdates.
It combines AI's analytical capabilities with blockchain's transparency and audibility while maintaining strong privacy protection.
AIBAHMAD provides enhanced compliance monitoring through AI-driven analytics. The system automatically tracks compliancerequirements,predictspotentialissues,andgeneratesverificationrequests:
Continuousmonitoringofoccupancypatternstodetectunauthorizedsubleasing
Anomalydetectioninutilityusageandfinancialtransactionstoidentifypotentialprogramviolations
Automatedschedulingofphysicalinspectionsbasedonriskassessmentmodels
SmartrenewalprocesseswithAI-basedeligibilityreassessment
Earlyinterventionsystemforpotentialnon-compliancesituations
The compliance monitoring system balances program integrity with resident privacy through careful data minimization and purposelimitationprinciples.
AIBAHMADimplementscomprehensivesecuritymeasuresattheintersectionofblockchainandAItechnologies:
Blockchain Security:Immutableledger,consensusmechanisms,cryptographicverification
AI Security:Adversarialtesting,modelrobustness,securefederatedlearning
Data Security:Encryption,accesscontrols,securemulti-partycomputation
Network Security:Securecommunicationchannels,intrusiondetection,DDoSprotection
SecurityanalysisdemonstratesthatAIBAHMADeffectivelyprotectsagainstcommonattackvectors:
1. Sybil Attacks:Preventedthroughrigorousidentityverificationandthepermissionedblockchainstructure
2. Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Mitigated through formal verification, code audit, and standardized security patterns
3. Oracle Manipulation:Addressedusingmultipleindependentdatasourcesandcryptographicverification
4. Privacy Leakage:Preventedthroughzero-knowledgeproofsandoff-chainstorageofsensitiveinformation
5. AI Model Attacks:Mitigatedthroughadversarialtraininganddifferentialprivacytechniques

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
AIBAHMADemploysagovernancemodelthatstructurestheinterestsandneedsofmultipleplayersintheaffordablehousing ecosystem.
1. Technical Governance Committee:Maintainssystemmaintenance,upgrades,andtechnicalstandards.
2. Policy Governance Committee: Setsallocationcriteria,compliancerequirements,andprogramrules
3. AI Ethics Committee: EnsuresresponsibleAIdevelopmentanddeployment,withregularbiasaudits
4. Advisors Council: Thisincludespeoplefromcommunitiesofapplicantstooffertheuser'sperspectives.
5. Regulatory Oversight: Itregulateshousinglawsandprivacyacts.
It includes a transparent decision-making process, voting mechanisms on major changes, dispute resolution schemes, and a feedbackmechanismforallstakeholders.
5.1
Basedonaprototypeimplementation,weassessedtheAIBAHMAD infrastructureframeworkonpractical,affordablehousing managementscenarios.Thetechnologiesusedinclude:
Blockchain Platform:HyperledgerFabric(version2.2)
Smart Contract Language:JavaScript(Node.js)forchaincodedevelopment
AI Framework:TensorFlowwithFederatedLearningextensions
Off-chain Storage:IPFSwithAES-256encryption
User Interface:React-basedwebapplicationwithresponsivedesign
Authentication:Multi-factorauthenticationwithFIDO2integration
Privacy Layer:Zero-knowledgeproofsimplementedwithZoKrates
The prototype was deployed in a simulated test environment mimicking a mid-sized housing authority managing 1000 housing units and 5,000 applicants. It was an implementation of all the core components of the AIBAHMAD infrastructure framework.
SeveralmetricswerecomparedinperformanceevaluationbetweentheAIBAHMAD infrastructureframeworkandtraditional housingmanagementsystemsasshowninthetable1below.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
This shows major improvements in all measured metrics, with especially impressive reductions in processing time and administrativecost,aswellasimprovementsindisputereductionandtransparency.
AIBAHMAD was evaluated using formal verification, penetration testing, and security audits. Security properties regarding authenticationandaccesscontrolprotocolswereformallyverifiedusingtheScythertool.
Security professionals performed penetration testing to attack the system through different vectors. No critical security vulnerabilitieswerefound,butseveralminorvulnerabilitieswereidentifiedandsolved.
The security assessment proved that AIBAHMAD offers high-level security of system integrity and user privacy against both externalattacksandinsiderthreats.
AIBAHMADwasuser-testedusingkeystakeholdergroups,includingapplicants,housingauthoritystaff,propertyowners,and auditors.Theevaluationincludedtaskcompletionactivities,satisfactionsurveys,andqualitativeinterviews.
Asaresult,usersatisfactionscoreswereimprovedcomparedtotraditionalsystems.
Applicants:4.7/5(vs.2.8/5fortraditionalsystems)
HousingAuthorityStaff:4.3/5(vs.3.1/5)
PropertyOwners:4.5/5(vs.3.3/5)
Auditors:4.9/5(vs.2.5/5)
Keyusabilityimprovementsidentifiedbyusersincluded:
Transparentapplicationstatustracking
ReduceddocumentationrequirementsthroughAI-poweredinformationextraction
ClearerexplanationofallocationdecisionsthroughexplainableAI
Simplifiedcompliancereporting
Intuitiveinterfacesfordifferentuserroles
ExperimentswithkeyAIcomponentsoftheAIBAHMADinfrastructureframeworkarealsoevaluated.
1. Fraud Detection System: A achieved 97.8% accuracy in classifying fraudulent vs. non-fraudulent applications, with a falsepositiverateof1.2%.
2. Allocation Algorithm: Achieved 96% match between allocations, optimal placements, and fairness metrics with no significantbiasbydemographicgroups.
3. EligibilityAssessmentEngine:Achieved 99.3% accuracyin eligibilitydetermination witha 92%reduction in manual reviewrequirements
4. The housing need prediction system: demand forecasting model (predicted housing needs with 94% accuracy for a three-monthhorizonand89%foraone-yearhorizon)
The AI components met the fairness and privacy requirements while still performing well. The processes of retraining and validationaresubjecttobeingrunregularlytomaintaineffectivenessinthefaceofpatternevolution
The AIBAHMAD infrastructure framework was subjected to a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis of conventional housing managementsystemsforfiveyears.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Implementationcostsincluded:
Blockchaininfrastructuredevelopment
AImodeldevelopmentandtraining
Smartcontractdevelopmentandauditing
Userinterfacedevelopment
Integrationwithexistingsystems
Trainingandtransitionsupport
AIBAHMAD infrastructure framework has demonstrated a positive ROI in less than 2.3 years, even with its initial implementationcosthigherthanthatinaclassicalupgradesystem.Dependingonhousingauthoritysize,thesystemprojected cumulativecostsavingsof45to65percentbyyear5versustraditionalsystems. Additionally, the analysis revealed significant nonfinancial benefits like increased transparency, reduced fraud, enhanced publictrust,andimprovementofthepublichousingdistribution.
6.1
AIBAHMADinfrastructureframeworkisageneralframeworkintegratingblockchainwithartificialintelligenceforsecureand transparent, cost-effective, and affordable housing management, which was presented in this research. The framework approachesthesetechnologiesinanewwayandmeetslongstandingsectoralchallenges.
Keycontributionsinclude:
1. Aspecializedblockchainarchitecturesuitablefortheaffordablehousingmanagementrequirements
2. AIcanachieveprivacy-preservingverificationmechanismsthatwillenableeligibilitycheckswithouttheknowledgeof applicantinformation.
3. Fairbuttransparent,bias-mitigatingalgorithmsforhousingallocation.
4. Reducesadministrativeburdenandincreasesprogramintegrityviaautomatedcompliancemonitoringsystems.
5. Comprehensiveaudittrailcapabilitiesforaccountabilityandtransparentgovernance
TheevaluationresultsshowthattheAIBAHMADinfrastructureframeworkhasindeedachievedverysignificantimprovements comparedtoexistinghousingmanagementsystemsintermsofadministrationtimeandcost,transparency,security,anduser experience.
Though AI and blockchain are two separate worlds, their integration brings about synergistic effects. Blockchain serves as a secureandtransparentsystemofhousingmanagement,andAIhelpstomakedecisions,automatecomplicatedprocesses,and ensure fair allocation. It combines technological and governance solutions to address the problems of technological and governanceissuesthathavehinderedtheefficiencyandreliabilityofaffordablehousingprograms.
Although the infrastructure framework put forth in the AIBAHMAD opens a strong avenue for applying blockchain to AI use cases in affordable housing management, several future research and development directions are available in the hopes of creatinganewandeffectivesystem.
1. Comprehensive household support: Expanding the infrastructure framework to provide support within the other socialserviceprograms.
2. Advanced Privacy Techniques: Implementing fully homomorphic encryption and multiparty computation for enhanceddataprotection
3. Interoperability Standards: Developing standards for interoperability between different housing authority implementationsacrossregions
4. Resource Governance:Structuringaccessanduseofresources,includingland,water,andfood

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
5. Augmented Reality Integration: IncorporatingARtechnologiesforvirtualpropertytoursandinspections
6. Expanded AI Applications: Developing additional AI capabilities for community development planning and neighborhoodintegration
7. Climate Resilience Planning: Incorporating environmental data and predictive models for sustainable housing development
8. Mobile-First Implementation: Creatinguserinterfacesthatoptimizeforareaswithpredominantmobilecomputing access.
AIBAHMAD’sestablishedfoundationwillserveasthebasisforfuturedirections,aimingtoachievethemaximumrealizationof blockchain and AI technology in the development of more equitable, efficient, and transparent, affordable housing systems worldwide.
References
[1]Schwartz,A.F.(2021).HousingPolicyintheUnitedStates.Routledge.
[2]Kimura,D.(2020)."ChallengesinAffordableHousingManagement."JournalofHousingEconomics,67,101-115.
[3]Nakamoto,S.(2008)."Bitcoin:APeer-to-PeerElectronicCashSystem."CryptographyMailingList.
[4]Casino,F.,Dasaklis,T.K.,&Patsakis,C.(2019)."Asystematicliteraturereviewofblockchain-basedapplications."Telematics andInformatics,36,55-81.
[5]Veuger,J.(2018)."Trustinaviablerealestateeconomywithdisruptionandblockchain."Facilities,36(1/2),103-120.
[6] Themistocleous, M., et al. (2020). "Blockchain in Real Estate: Disrupting the Industry with a New Paradigm." Journal of InformationTechnologyCaseandApplicationResearch,22(4),202-225.
[7]Wouda,H.P.,&Opdenakker,R.(2019)."Blockchaintechnologyincommercialrealestatetransactions."JournalofProperty Investment&Finance,37(6),570-579.
[8]Veuger,J.(2018)."Trustinaviablerealestateeconomywithdisruptionandblockchain."Facilities,36(1/2),103-120.
[9]Nijland,M.,&Veuger,J.(2019)."Influenceofblockchainintherealestatesector."InternationalJournalofAppliedScience, 2(2),22-41.
[10] Themistocleous, M., et al. (2020). "Blockchain in Real Estate: Disrupting the Industry with a New Paradigm." Journal of InformationTechnologyCaseandApplicationResearch,22(4),202-225.
[11] Zheng, Q., et al. (2018). "An Innovative IPFS-Based Storage Model for Blockchain." IEEE/WIC/ACM International ConferenceonWebIntelligence,704-708.
[12]Wouda,H.P.,&Opdenakker,R.(2019)."Blockchaintechnologyincommercialrealestatetransactions."JournalofProperty Investment&Finance,37(6),570-579.
[13]Karamitsos,I.,etal.(2018)."DesignoftheBlockchainSmartContract:AUseCaseforRealEstate."JournalofInformation Security,9(3),177-190.
[14]Lee,D.,etal.(2020)."Machinelearningandhousingpriceprediction."HousingStudies,35(5),873-890.
[15]Garcia-Teruel,R.M.(2020)."Legalchallengesandopportunitiesofartificialintelligenceintherealestatesector."Journal ofProperty,PlanningandEnvironmentalLaw,12(2),157-172.
[16] Chen, J., & Zahedi, F. M. (2022). "AI-driven resource allocation in public services." Government Information Quarterly, 39(2),101653.
[17]Martinez,C.,etal.(2021)."Machinelearningforsocialbenefittargeting."PublicAdministrationReview,81(3),432-451.
[18]Salah,K.,etal.(2019)."BlockchainforAI:Reviewandopenresearchchallenges."IEEEAccess,7,10127-10149.
[19] Wang, S., etal.(2021). "When blockchainmeets artificial intelligence: A survey." IEEEInternet of Things Journal,8(13), 10634-10653.
[20] Zhang, P., et al. (2020). "Blockchain and artificial intelligence for healthcare." Studies in Health Technology and Informatics,275,61-70.
[21]Yaga,D.,etal.(2019)."Blockchaintechnologyoverview."NationalInstituteofStandardsandTechnology.
[22]Mingxiao, D., etal.(2017)."Areview on consensus algorithm of blockchain." IEEEInternational Conference on Systems, Man,andCybernetics,2567-2572.
[23]Wust,K.,&Gervais,A.(2018)."Doyouneedablockchain?"CryptoValleyConferenceonBlockchainTechnology,45-54.
[24]Russell,S.,&Norvig,P.(2020).ArtificialIntelligence:AModernApproach.Pearson.
[25]Goodfellow,I.,etal.(2016).DeepLearning.MITPress.
[26]Szabo,N.(1997)."Formalizingandsecuringrelationshipsonpublicnetworks."First Monday,2(9).

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
[27]Goldwasser,S.,etal.(1989)."Theknowledgecomplexityofinteractiveproofsystems."SIAMJournalonComputing,18(1), 186-208.
[28] Evans, D., et al. (2018). "A pragmatic introduction to secure multi-party computation." Foundations and Trends in PrivacyandSecurity,2(2-3),70-246.
[29] McMahan, H. B., et al. (2017). "Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data." Proceedingsofthe20thInternationalConferenceonArtificialIntelligenceandStatistics,1273-1282.
[30]Dwork,C.,&Roth,A.(2014)."Thealgorithmicfoundationsofdifferentialprivacy."FoundationsandTrendsinTheoretical ComputerScience,9(3-4),211-407.
[31]Acar,A.,etal.(2018)."Asurveyonhomomorphicencryptionschemes."ACMComputingSurveys,51(4),1-35.
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008