
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Fousiya S A1 , T. Merlin Leo, M.E,2
1PG Scholar, BioMedical Engineering, Udaya school of engineering, Kanyakumari.
2Professor BioMedical department, Udaya school of engineering, Kanyakumari
Abstract Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a long-term neurological condition that causes dementia. Alzheimer's patientshavetroublerememberingrecentevents,reasoning, and even recognizing faces. Mood swings, loss of desire, difficultyspeaking,disorientation,includinggettinglost,and general behavioral problems are some of the symptoms that may appear as the illness worsens. Although some IT-based solutions are available to assist individuals with Alzheimer's, most of them provide highly specialized services for both patients andcaregivers. The goal of this project is to provide an assistive technology that will support Alzheimer's patients and their caregivers with activities including location tracking, medication reminders, and health monitoring. The evaluation study indicated that the recommended approach was effective and practical for patients and their caregivers. A number of usability tests and feedback sessions with patients and caregivers were used to assess the system. According to the findings, the tool considerably raises the standard of care, increases the independence of people with Alzheimer's, and lessens the stress experienced by caregivers. The system was deemed user-friendly and efficient by the participants in meeting dailyrequirements.
Keyword’s: Emergency Alert System,Arduino / ESP32, Remote Patient Monitoring, Real-Time Clock (RTC), EEG Monitoring, Smart Reminder System, Assistive Technology.
Since it allows for prompt intervention and lessens the substantial societal and financial burden of chronicdiseases,earlydiagnosisisanessentialcomponent of health promotion. Around the world, Alzheimer's disease(AD)iscommonlyacknowledgedasadegenerative chronic illness that mainly affects those 65 and older. As the population ages, this irreversible neurological disease is expected to grow at a pace of 60% between 2020 and 2030 and 204% by 2050. There are currently four different stages in the AD continuum: preclinical, mild,
moderate, and severe. The clinical beginning of AD dementiaischaracterizedbyprogressivesymptomslikeas behavioral abnormalities and memory loss, which eventually affect the patient's day-to-day functioning and demand for long-term care. Nevertheless, during a yearlong quiet phase, early symptoms are associated with structural and molecular alterations in the brain that can beidentifiedbychangedADbiomarkers.Thepathogenesis ofAlzheimer'sdiseaseisstillunknowndespiteagreatdeal of research. Notably, the main theories concerning this neurological condition suggest that aberrant changes in tau and amyloid beta (Aβ) proteins initiate the preclinical phase of AD, which results in the buildup of plaques and tangles in the entorhinal cortex and neocortex. These neurological advancements are comparable to the agingrelated alterations that occur naturally [1]. A neurological condition affecting the central nervous system, epilepsy is characterized by aberrant brain activity that can lead to convulsions or episodes of strange behavior, sensations, and occasionally unconsciousness. Epilepsy can affect everyone. Males and females of various racial and ethnic backgrounds and ages are affected by epilepsy. The symptomsofseizuresmightvarygreatly.Duringaseizure, some epileptics merely stare blankly for a few seconds, whileothersmovetheirlimbsorlegscontinuously.Youdo notnecessarilyhaveepilepsyifyouhaveonlyoneseizure. Inmostcases,adiagnosisofepilepsyrequiresatleasttwo unprovoked episodes. Most patients with epilepsy can control their seizures with medication or occasionally surgery. While some people's seizures eventually stop, others need lifetime treatment to manage them. As they get older, some kids with epilepsy may outgrow the disorder [2]. Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior.Astheconditionprogresses,individualsstruggle with routine activities such as remembering daily tasks, takingmedicationsontime,orcommunicatingtheirneeds effectively. This leads to increased dependency on caregiversandposessignificanthealthandsafetyrisksfor the patient In response to these challenges, this paper presentsthedesignandimplementationofaSmartHealth

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net
Monitoring and Reminder System aimed at supporting Alzheimer’s patients. The system integrates voice-based reminders, real-time health parameter monitoring, location tracking, and IoT-based notifications to ensure bothsafetyandindependence.Thesystemnotonlyassists the patient with daily activities but also helps caregivers monitor health conditions remotely and respond to emergencies promptly [3]. Guillaume Becq et.al Over 100 millionindividualsglobally,includingsick andthe elderly, are impacted by epileptic seizures and potentially fatal falls.Asofright now, there isno reasonablypriceddevice orsolutionforthedetectionofseizuresandfallsthatcould help millions of people live better lives. Continuous sensing with minimal user disturbance, precise real-time emergency categorization and warning notification, energy-efficient sensing and detection, and scalability and affordability of the developed solution are some of the main problems presented by this detection problem. In order to provide ambient assisted living for individuals with epilepsy and fall risk, this study introduces Seizario, thefirstmobileapplicationforcontinuous,energy-efficient seizure and fall detection [4]. Shyamal Patel.al By preventing needless hospital stays and guaranteeing that individuals in need of urgent treatment receive it sooner, remotehealthmonitoringhasthepotentialtosignificantly lower the overall cost of healthcare. These days, smart miniaturization, non-invasive biomedical monitoring, and wearable sensing, processing, and communication are all made possible by recent advancements in micro- and nanotechnologies, information processing, and wireless communication.The"smarthealthwearable"researchand industrial community faces a number of common critical issues,suchasbiomedicalsensors,scenariosofuse(linked to the business scenarios), data security and confidentiality, risk analysis, user interface, medical knowledge/decision support, dissemination, user acceptance and awareness, business models, and exploitation, even though they are developing specific systems and applications to address specific user needs. Real future obstacles, such clinical validation and effect assessment of the recently developed smart wearable applications, lie ahead, despite technology that appears to be proof of concept. The current state of research and development of smart wearable health applications, namely under EU research initiatives, is reviewed in this study along with the unresolved problems and future difficulties that need to be overcome. [5],[6]., System architectureisillustratedinFig.1.Toguaranteesafetyand independence, the system incorporates voice-activated reminders, location tracking, real-time health parameter monitoring, and Internet of Things-based notifications. In addition to helping the patient with everyday tasks, the
p-ISSN:2395-0072
system enables caregivers to remotely monitor health status and quickly address emergencies. Utilizing deep learning advances, we present a transformer-convolution framework for predicting at-risk subjects based on dFNC, incorporating spatial-temporal self-attention to capture temporal dynamics and brain network dependencies, in ordertoidentifyat-risksubjectsandcomprehendchanges of dFNC in various stages. model performs noticeably better than other well-known machine learning techniques. We examined the course of AD by examining people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and confirmed AD. [7],[8]. Kewei Chen.et.al proposed. Three brain synchrony assessment methods phase synchrony, magnitudessquaredcoherence,andcrosscorrelation are used on a dataset of people with mild Alzheimer's disease (MiAD) and healthy individuals in order to identify this disturbance. The application of principle component analysis (PCA) prior to neuronal synchronization measurement methodologies is discussed in this study, and the Mann-Whitney U test is used to compare the methodology with others. The findings demonstrate that, in comparison to using conventional procedures, improvementsareachievedwhenPCAisappliedbeforeto synchrony measurement techniques. Using existence probabilities derived by segmenting brain pictures into four region types gray matter (GM), white matter (WM), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and background this method objectively assesses changes in the structure of the brain betweentwotimepoints.A4x4matrixwith16coefficients representing probability changes (CPCs) was produced by assumingalinearrelationshipbetweentheprobabilitiesat two places. Using CPCs as features, we classified ten AD patients and ten HS patients. With the exception of the CPCs that matched the backdrop, we examined three different feature types: all nine CPCs, diagonal CPCs that showedstructuralpreservation,andsixnon-diagonalCPCs that showed structural alterations like atrophy. When characteristicsandimagesatthe firstandlasttimepoints were compared using non-diagonal CPCs, the maximum accuracy was 95%, even though nine CPCs performed the best in terms of average accuracy (77%). [9]. Xiaojuan Guo.et.al proposed. Several technologies have been developed to assist elderly and Alzheimer’s patients. Wearable devices for health monitoring, mobile applications for reminders, and GPS trackers for location tracking are common. However, many of these systems work in isolation and are either too complex for patients or lack real-time responsiveness. Cerebrospinal fluid samples were subjected to surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using commercially available gold nanoparticle substrates in order to identify early-stage Alzheimer's disease. This technique is quick and

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net
affordable. With a 100% classification accuracy for Alzheimer's patients and an 85% classification accuracy forthehealthycontrolgroup,biomarkersthatwereinline with earlier research were found using machine learning. The receiver operational characteristic (ROC) curve analysisisfrequentlyusedtocharacterizeperformancesin terms of sensitivity and specificity in differentiating two conditions/groups given a single index. The single-indexbased ROC underutilizes all available information by ignoring the availability of numerous data sources (also known as multi-indices), such as multimodal neuroimaging data sets, cognitive tests, clinical ratings, and genetic data in AD investigations. Many algorithmic/analyticmethodsthatcombineseveralindices have been utilized for a long time to incorporate multiple sources at once. In order to create multivariate ROC (multiV-ROC) and describe the statistically significant sensitivity and specificity linked to the use of multiple indices, we suggest an alternative method for combining multiple indices using logical operations like "AND," "OR," and "at least (n)" (where (n) is an integer). We demonstratedthepossiblyhighersensitivity/specificityof the multiV-ROC compared to the single-index ROC and linear discriminant analysis (an analytical method of combining several indices) using two data sets from AD research,bothwithandwithoutthe"leave-one-out"crossvalidation.[10].
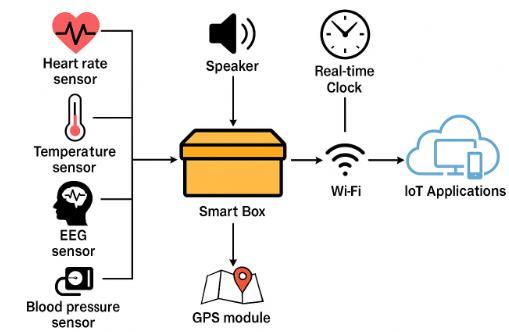
2.METHODOLOGIES
The development of the proposed smart monitoring and reminder system for Alzheimer’s patients involved a structured and modular approach combining embedded hardware, biomedical sensors, and IoT technologies. The initial phase began with identifying the practical needs of Alzheimer’s patients, such as the requirement for regular reminders, real-time health monitoring, emergency alerts, and GPS-based location
p-ISSN:2395-0072
tracking. Based on this requirement analysis, a system architecture was designed that divides the solution into distinctfunctionalmodules,namely:thevoicealertsystem, health monitoring unit, emergency notification mechanism, GPS tracking module, and IoT integration platform.
The hardware integration phase involved selecting suitable sensors and modules. A heart rate sensor, temperature sensor, blood pressure monitor, and EEG sensor were chosen for continuous physiological monitoring. Thesewereinterfaced witha microcontroller, such as Arduino Uno or ESP32, which acts as the brain of thesystem.AGPSmodulewasaddedforlocationtracking, while a Real-Time Clock (RTC) module ensured accurate timing for reminders. The voice alert system uses a speaker and an SD card module to play pre-recorded messages that guide the patient through their daily routine, such as taking medications or eating meals. All components are powered by a regulated power supply with a backup battery to ensure uninterrupted operation. The software was developed using the Arduino IDE, with embedded C/C++ code to handle sensor data collection, real-time clock synchronization, reminder scheduling, and IoT communication. The system reads sensor inputs, checks them against predefined safe thresholds, and triggersalertsif abnormalitiesaredetected.Insuchcases, the Wi-Fi module (ESP8266 or ESP32 built-in) sends a real-timealerttocaregiversviaanIoTplatformlikeBlynk or Firebase. At the same time, the GPS module provides real-time location updates, which are also transmitted to the cloud. These features allow caregivers to monitor the patient’s health and whereabouts remotely through a mobileapplicationorwebinterface.
To ensure usability and reliability, an IoT dashboard was configured to display live health readings, alert messages, and a map showing the patient’s location. The entire system was rigorously tested under simulated conditions. The testing phase focused on validating the accuracy of the sensors, the responsiveness of the alert system, and the stability of the IoT connectivity. Voice alertswereevaluatedforclarityandtiming,whilelocation data wascross-checkedwithstandardGPStools.Thefinal system proved effective in delivering timely alerts, accurate monitoring, and reliable communication, making itavaluableassistivetoolforAlzheimer’spatientcare.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net
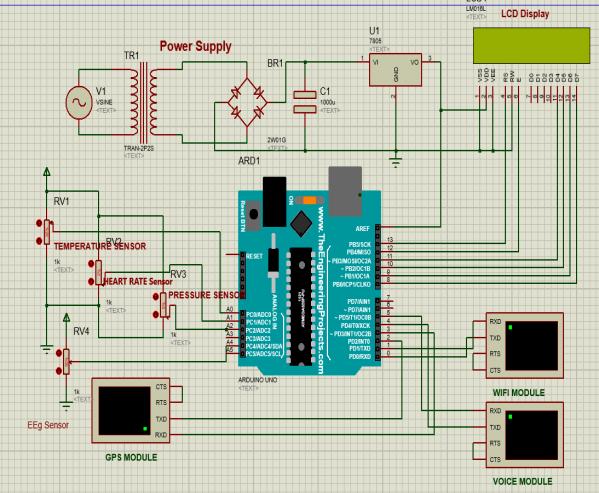
Infig2thecircuitdiagramconsists ofseveral key components interconnected to monitor and process the patient'svitalsignseffectively.Atthecoreofthesystemis an Arduino microcontroller, which serves as the central processing unit. The suggested system may monitor the patient's development in real time and record every task the patient completes, enabling the patient to become independent. With the use of an app, the patient will benefit from having a caregiver at all times. providing an audioalerttoanAlzheimer'ssuffererabouttheireveryday responsibilities By measuring temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, and other sensors, fresh data may be gathered and analyzed more quickly and precisely. The sensor is a device that sends data or signals to the controller after detecting, measuring, and recording them. The components include a speech module, temperature and heart rate sensors, and a GPS module for patient position tracking. From a smart app, all metrics may be monitored.
This module is responsible for providing timebased voice alerts to help the patient follow their daily routine. It uses a Real-Time Clock (RTC) module (such as DS3231) to maintain accurate timekeeping. Predefined schedules are programmed into the microcontroller to trigger voice messages stored in an SD card module or internal memory. The voice output is delivered through a minispeakerorbuzzer.Thisvoiceguidanceeliminatesthe need for manual checking or visual cues, which Alzheimer’s patients often forget or misinterpret. The module is flexible and can be customized to include multiple reminders such as medication times, hydration alerts,exerciseroutines,orsleepschedules.
p-ISSN:2395-0072
This critical module monitors the patient's vital signs in real time using various biomedical sensors. The systemincludesaheartratesensor,atemperaturesensor, abloodpressuresensor,andanEEGsensorformonitoring brain activity. These sensors are interfaced with a microcontroller which processes the data continuously. If any of the readings deviate from normal ranges, the system identifies the situation as a potential health risk andactivatestheemergencyalertmechanism.
This module is activated when the health monitoring system detects irregularities such as high blood pressure, abnormal heart rate, or elevated body temperature. The microcontroller immediatelytriggers an alert message that is transmitted via the Wi-Fi module (ESP8266orESP32)toanIoTcloudplatform.Notifications are sent in real-time to caregivers through a mobile app, email,orSMS,dependingontheconfiguration.Thisfeature is crucial for initiating immediate medical attention in critical situations. The module ensures that even if the patientisunabletocommunicate,caregiversareinformed ofpotentialemergencies.
Thismoduleensuresthereal-timetrackingofthepatient's geographical location using a GPS module (NEO-6M or similar). The system fetches latitude and longitude coordinates and sends them periodically to the cloud. The locationisthenvisualizedona mapwithinthecaregiver’s application or dashboard. This is particularly useful in managing the risk of wandering behavior, which is common among Alzheimer’s patients and can lead to dangerous situations. Geo-fencing can also be implemented to send alerts if the patient moves beyond a definedsafezone.
All sensor data, alerts, and GPS information are consolidated and transmitted to an IoT platform such as Blynk, Firebase, or ThingSpeak. The IoT dashboard provides caregivers with a user-friendly interface to Monitor real-time health parameters, Track the patient’s location, View alert logs, Receive emergency notifications. The platform is accessible via smartphones or web browsers, making it convenient for remote monitoring. The integration of all data into a centralized cloud system ensures seamless access and historical data tracking,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net
At the core of the system lies the microcontroller (ArduinoUno,NodeMCU,or ESP32).Itactsasthebrainof the system, processing input from sensors, controlling outputs (like the speaker), and managing data flow to the IoT module. The program logic is written in embedded C/C++usingtheArduinoIDE.Thecontrollerensuresrealtime responsiveness and coordination among all other modules. Additionally, power management, exception handling,anddatavalidationarehandledinthismodule.
The implemented system was tested in a controlled environment to evaluate its performance, accuracy, and practical applicability in assisting Alzheimer’s patients. The main functionalities tested includethevoice-based remindersystem,real-timehealth monitoring, emergency alert triggering, and GPS location tracking, along with IoT-based remote monitoring capabilities.
The voice alert system successfully played prerecorded messages at predefined times, reminding the user to take medicines, drink water, and perform daily activities. The Real-Time Clock (RTC) ensured precise timekeeping, and the speaker produced clear, audible instructions. This functionality helps mitigate the forgetfulness commonly associated with Alzheimer’s, improving the patient's ability to follow daily routines independently. The health monitoring module showed effective real-time tracking of vital signs. The heart rate sensor (MAX30100) and temperature sensor (LM35) demonstrated consistent readings within acceptable error margins compared to standard clinical devices. The EEG sensor responded to changes in mental activity, and the blood pressure sensor recorded values comparable to digital BP monitors. When values crossed preset thresholds for instance, a heart rate above 100 bpm or body temperature above 38°C the system promptly triggered an emergency alert. The Wi-Fi module (ESP8266) transmitted these alerts through the IoT platform, and notifications were received by the caregiver’s smartphone within a few seconds. This rapid responsetimeiscrucialinreducinghealthrisksassociated withdelayedmedicalattention.
TheGPSmodule(NEO-6M)accuratelytrackedthe location of the patient. During testing, the latitude and
p-ISSN:2395-0072
longitude values were updated in real time and correctly plotted on the IoT dashboard map. This feature is particularly useful in preventing wandering or getting lost common issues for Alzheimer’s patients. The geolocation updates were precise within 5–10 meters, ensuring reliable tracking. The IoT integration using the Blynk platform provided a clean and interactive user interface. Caregivers could view real-time sensor values, receive emergency alerts, and monitor the patient’s location from any internet-connected device. Historical logs were also available for reviewing previous alerts and health readings. This cloud-based monitoring eliminates the need for constant physical supervision, offering peace ofmindtocaregiversandimprovedautonomytopatients. Overall,theresultsdemonstratethattheproposedsystem effectively combines embedded hardware, biomedical sensing, and IoT technology to offer a reliable and userfriendlysolutionforAlzheimer’spatientcare.Themodular design also makes the system scalable for future enhancements, such as fall detection, voice command recognition,ormachinelearning-basedhealthpredictions.
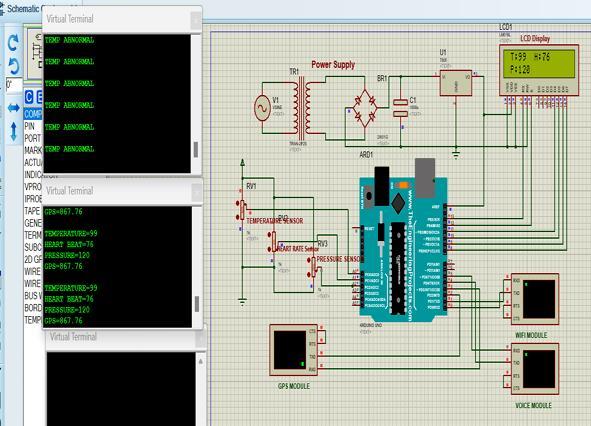
As shown in Fig.3 when Temperature is abnormal The results of the IoT system for Alzheimer patients can vary depending upon the specific implementation and the accuracy of the sensor used. In this section, the performance of the system is evaluated and compared with existing methods. Additionally, insights into the advantages and limitations of the proposed approach are discussed,andpotentialimprovementsarehighlighted.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
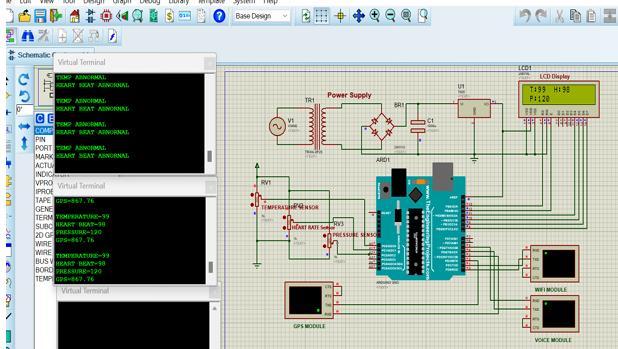
InFig.4,Inthesimulatedcircuit,theArduinoUnowasused as the central controller. A temperature sensor (LM35) was connected to the analog input pin to continuously monitor the patient's body temperature. To simulate the heart rate sensor, a pulse generator was used to produce digital signals, representing heartbeat inputs. A 16x2 LCD module was interfaced with the Arduino to display realtime temperature readings and alert messages. A buzzer wasconnected tooneofthe digital output pinsto actasa voice alert substitute, activated whenever a health parameterexceededthesafethreshold.Forexample,when the body temperature surpassed 38°C, the Arduino triggered the buzzer and displayed a warning message on theLCDscreen.
In conclusion, an aid was created specifically for those with Alzheimer's. This research made two contributionstothepriorworks:first,itintegratedseveral features into a single system, and second, it created a mobile application that makes good use of those features fromasingleplatform.Asaresult,thesuggestedapproach offers patients integrated, 24-hour care both indoors and out.ThedevicewillbeextremelybeneficialtoAlzheimer's patients and their caretakers because it will provide continuous monitoring,help with medication,monitor the patient's heart status, and assist in finding the patient's thingsasneeded.
[1]C.MarlingandP.Whitehouse,“Case-basedreasoningin the care of alzheimer’s disease patients,” in Lecture Notes inComputerScience(includingsubseriesLectureNotesin ArtificialIntelligenceandLectureNotesinBioinformatics), 2001,pp.702–715,doi:10.1007/3-540-44593-5_50.
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page145
[2] D. Zamolodchikov, T. Renné, and S. Strickland, “The Alzheimer’sdiseasepeptideβ-amyloidpromotesthrombin generation through activation of coagulation factor XII,” Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 995–1007,May2016,doi:10.1111/jth.13209.
[3] S. Wang and M. Colonna, “The microglial immunoreceptor tyrosine‐based motif‐Syk signaling pathway is a promising target of immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease,” Clinical and Translational Medicine, vol.13,no.2,Feb.2023,doi:10.1002/ctm2.1200.
[4] F. Gaubert and H. Chainay, “Decision-making competenceinpatientswithAlzheimer’sdisease: areview of the literature,” Neuropsychology Review, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 267–287, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1007/s11065-020-094722.
[5] M. A. Rather et al., “Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease: mechanisms and therapeutic implications by natural products,” Mediators of Inflammation, vol. 2021, pp.1–21,Aug.2021,doi:10.1155/2021/9982954.
[6] R. Rodrigues, R. B. Petersen, and G. Perry, “Parallels between major depressive disorder and Alzheimer’s disease:roleof oxidativestressandgeneticvulnerability,” Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 925–949,Oct. 2014,doi:10.1007/s10571-014-0074-5.
[7] L. Troncone et al., “Aβ amyloid pathology affects the hearts of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: mind the heart,” Journal of the American College of Cardiology, vol. 68, no. 22, pp. 2395–2407, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.08.073.
[8]S.O.Bachurin,E.V.Bovina,andA.A.Ustyugov,“Drugs inclinicaltrialsforAlzheimer’sdisease:themajortrends,” MedicinalResearchReviews,vol.37,no.5,pp.1186–1225, Sep.2017,doi:10.1002/med.21434.
[9] G. Bar-David, “Three phase development of caring capacity in primary caregivers for relatives with Alzheimer’s disease,” Journal of Aging Studies, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 177–197, Jun. 1999, doi: 10.1016/S08904065(99)80050-4.
[10] I. Baldeiras et al., “Addition of the Aβ42/40 ratio to the cerebrospinal fluid biomarker profile increases the predictive value for underlying Alzheimer’s disease dementia in mild cognitive impairment,” Alzheimer’s ResearchandTherapy,vol.10,no.1,p.33,Dec.2018,doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0362-2.