





J.J. (Sjaak) de Wit1,4, H. Bataille1, E. Boerhout2, L. Stooker2, M. Zuanaze3
1 Royal GD, Deventer, the Netherlands;
2 Vaxxinova Nederland B.V., Nijmegen, the Netherlands;
3 Vaxxinova Brazil, Sao Paolo, Brazil;
4 Department of Farm Animal Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht University, the Netherlands
IBV is notable for its growing number of variants, known as serotypes or genotypes, which arise due to its high mutation rate and the occurrence of recombinations. As a result, chickens in most regions of the world face challenges from multiple IBV variants, requiring broader protection than a single vaccine strain can offer (Cook et al., 1999; De Wit et al., 2013). This provides a continuous challenge to existing vaccination programmes.
It is of great value if a vaccine combination can protect birds against infections of both the homologous strains covered by the vaccine combination and other heterologous strains that may be prevalent. In this report the results of five vaccination-challenge trials (A-E) are reported using Vaxxon® CHB, a live attenuated vaccine that includes an IBV Massachusetts strain (H120, GI-1), an IBV Q1 like strain (BNF 28/86, GI-16) and a Newcastle disease virus (NDV) Clone strain.
Materials and methods
The efficacy of the vaccine was tested in SPF layers and in commercial layers (maternally derived antibody positive) against infection with IBV M41, D388(QX), Variant 2 (hereafter Var2), Q1 or 793B challenge virus (Table 1) by assessing the ciliary activity of the tracheal epithelium post challenge. All groups were housed in HEPA-filtered isolators. The vaccine was applied at day of hatch by eye-drop, all challenges were performed at 3 weeks of age. The challenge viruses were given in a dose of 104.0 EID50 per 0.1 mL for the IBV M41, D388(QX) and Var2 challenge viruses, in a dose of 104.5 EID50 per 0.1 mL for the Q1 challenge virus and in a dose of 105.0 EID50 per 0.1 mL for the 793B challenge virus.
At five days post challenge, the ciliary activity of tracheal explants was examined to determine the level of protection. The tracheal rings were placed into 24 well plates containing HMEM with 1% antibiotic-antimycotic solution, one ring per well, and examined using a light microscope within two hours after collection. The activity (beating) of the cilia in each tracheal ring was scored (Table 2).
Ciliostasis protection score (CPS)
Level of protection after vaccination with Vaxxon® CHB vaccine
IBV challenge strains

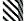
Results
The level of protection in the SPF layers against IBV M41, D388(QX) and Var2 challenge was 89%, 69% and 96%, respectively. The level of protection induced by Vaxxon® CHB in commercial layers against IBV M41, D388(QX), Q1 and 793B challenge was 91%, 73%, 84% and 94%, respectively (Figure 1).
Conclusion
This study shows that vaccination with Vaxxon® CHB provides a high level of protection against several homologous and heterologous challenge viruses, which are representatives for the IBV strains circulating worldwide.
References
Cook, J. K. A., Orbell, S. J., Woods, M. A., & Huggins, M. B. (1999). Breadth of protection of the respiratory tract provided by different live-attenuated infectious bronchitis vaccines against challenge with infectious bronchitis viruses of heterologous serotypes. Avian Pathology, 28, 477-485.
De Wit, J. J., Boelm, G. J., van Gerwe, T. J. W. M., & Swart, W. A. J. M. (2013). The required sample size in vaccination-challenge experiments with infectious bronchitis virus, a meta-analysis. Avian Pathology, 42(1), 9-16.

