A Legacy
To Next Generation
+ To offer a safe, healthy, and biodiversity land to our next generation


LAND2413 Graduate studio | Project 3 Regenerate Kuo Cui | z5125613

+ To offer a safe, healthy, and biodiversity land to our next generation


LAND2413 Graduate studio | Project 3 Regenerate Kuo Cui | z5125613
As a largely coastal dwelling nation, most Australians are familiar with the coast and its daily and seasonal processes. This means that the dynamics of the shoreline are well known: high tides, storms, east coast lows, coastal erosion and accretion, flooding and inundation are all events observed by coastal residents.1
"The Sea Was 120 Metres Lower At The Time Of The Last Glacial Maximum"
-Professor Patrick Nunn,University of the Sunshine Coast.2
Coastal observations show that sea level rise has been occurring around Australia during the last century. Extreme sea level events occurred three times as often in the second half of the 1900s compared with the first half3

Coastal Line Nowadays
Australia's Coastal Line During The Coldest Part Of The Last Ice Age 20000 Years Ago
As one of the important components of Sydney, Sydney Harbour has also affected and plagued the city due to the problems caused by rising sea levels. At the same time, the NSW and Sydney governments have also begun to pay attention to and pay attention to the impact of the problem of sea level rise on the city. As A result of the NSW Government Sea Level Rise Policy, And also the Australian Government's first pass assessment of Climate Change Risks to Australia's consecutive year in 2009". Local Councils in the Sydney coastal region have begun to consider sea level rise in addition to existing flooding and inundation risks covered by the NSW Government Flood Policy.1
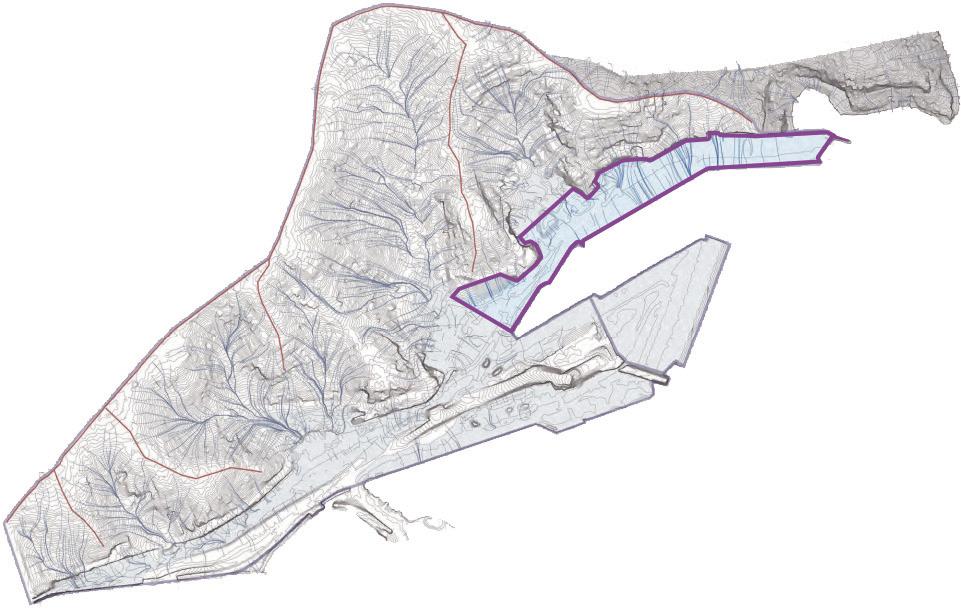
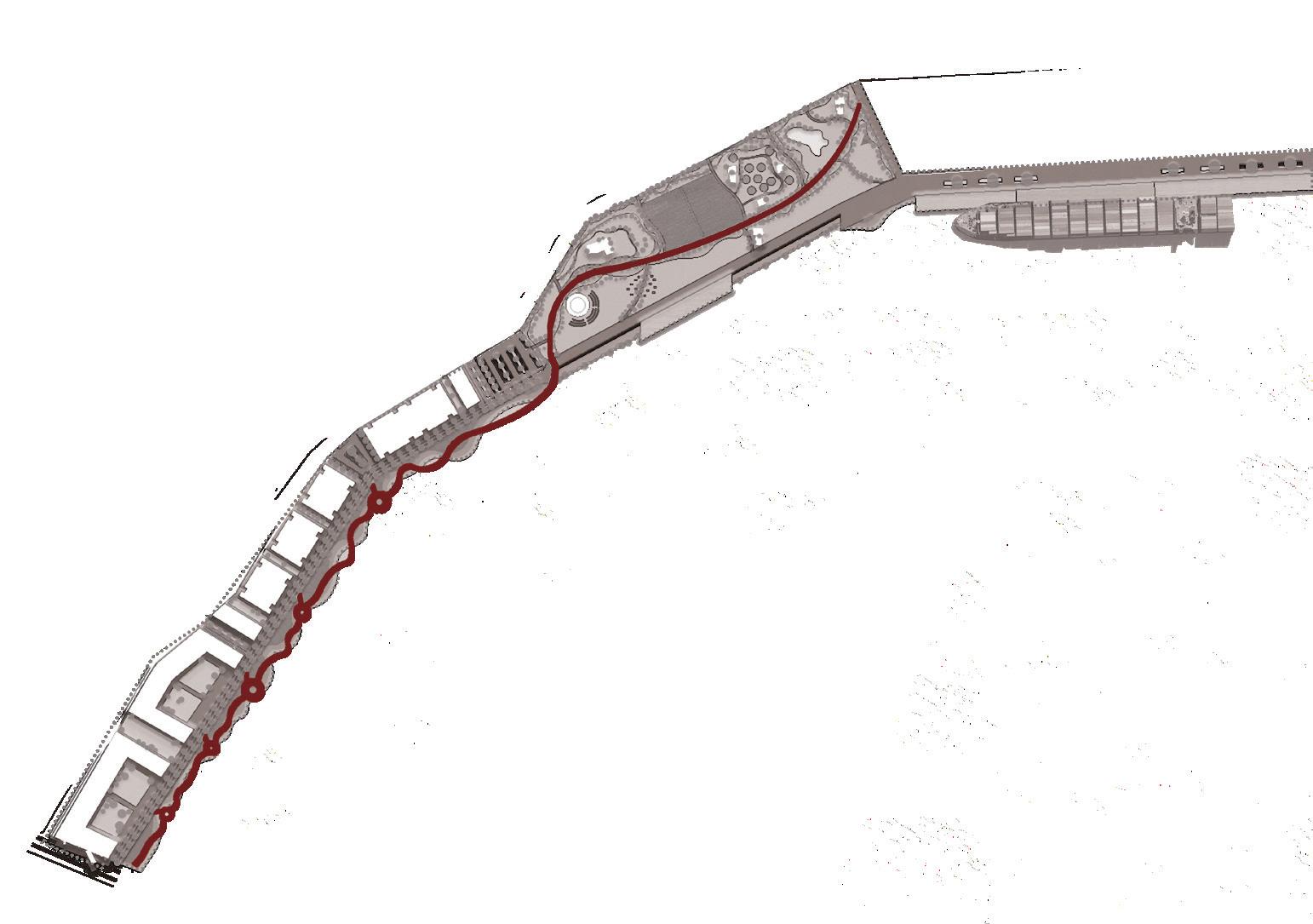
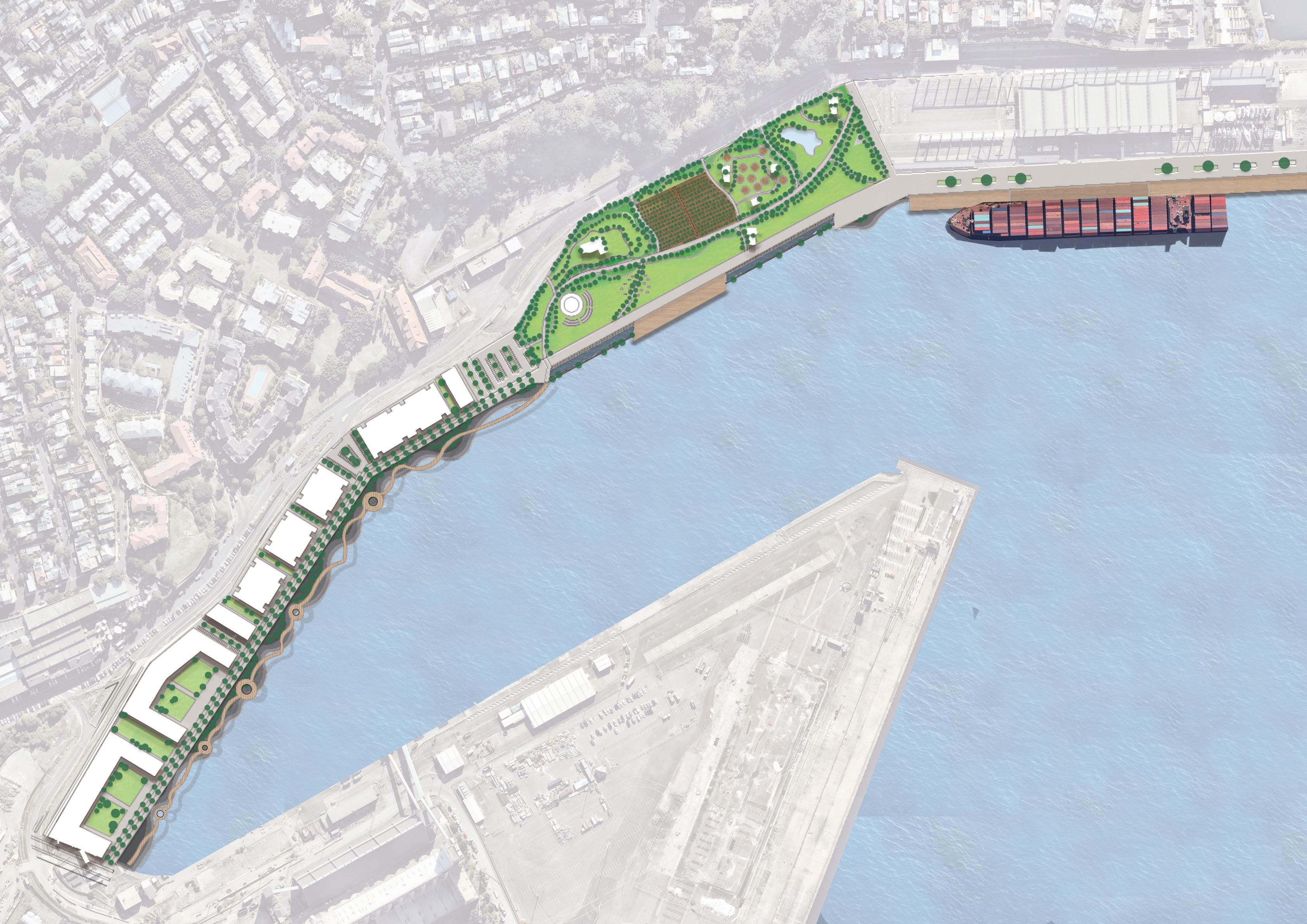
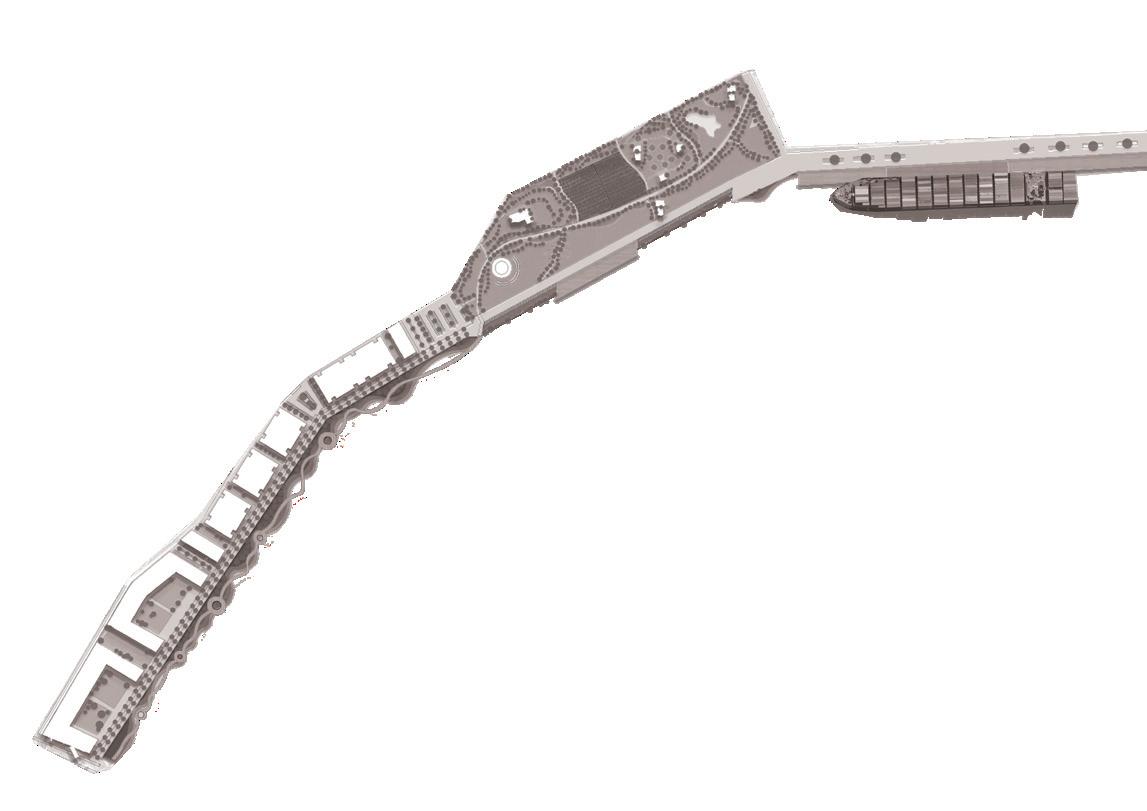
The Site is one of the most significant parts of Sydney's waterfront. Under the framework of sustainable development goals, this masterplan acknowledges the planning priorities outlined in the current The Bays precinct transformation plan, The Greater Sydney Commission’s guideline: Considering Flooding in Land Use Planning ‘Metropolis of Three Cities’ plan, as well as The NSW Government Architect’s Sydney Green Grid spatial framework. Each of these documents has guided the design decisions made in this masterplan.





Policy framework
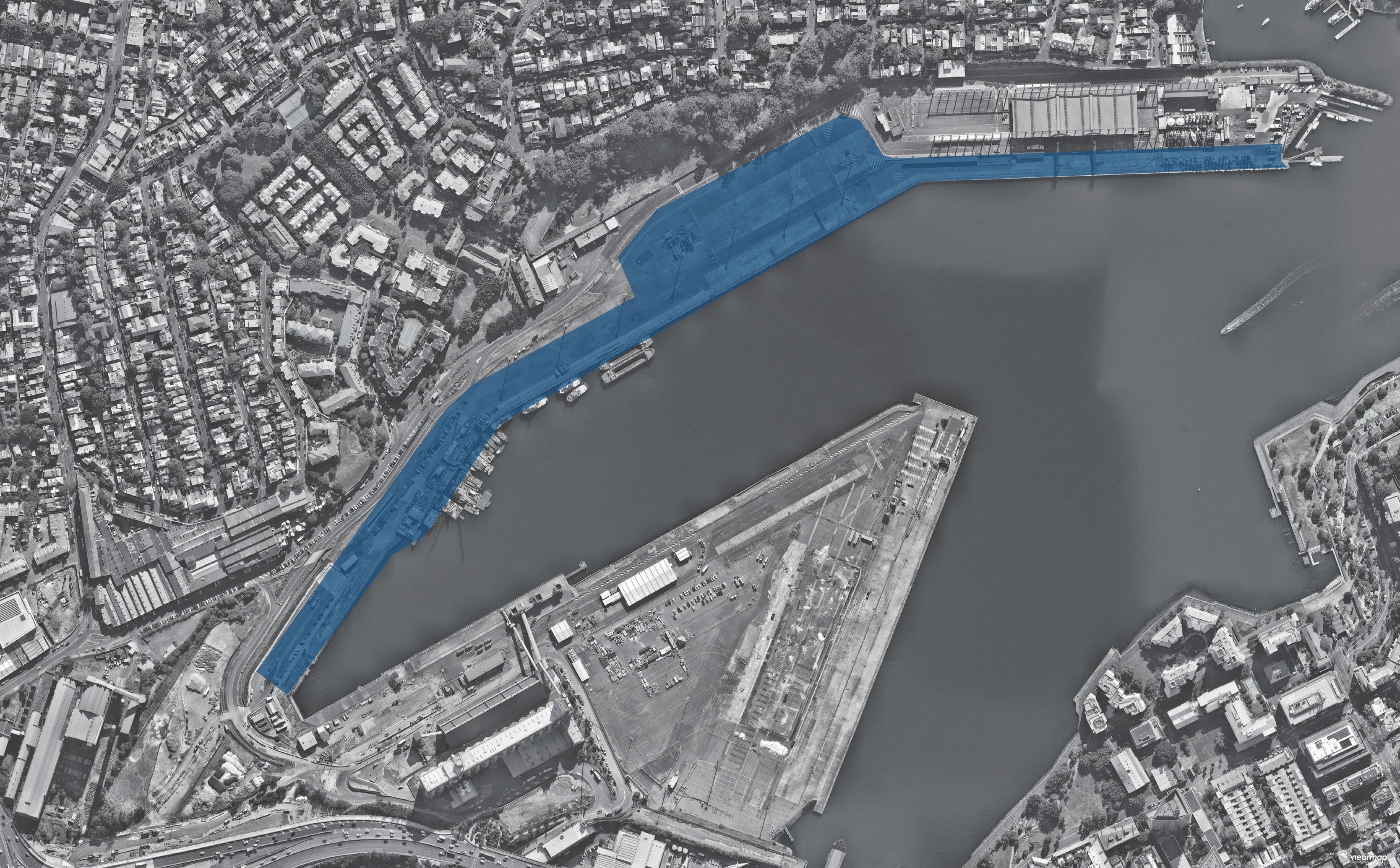
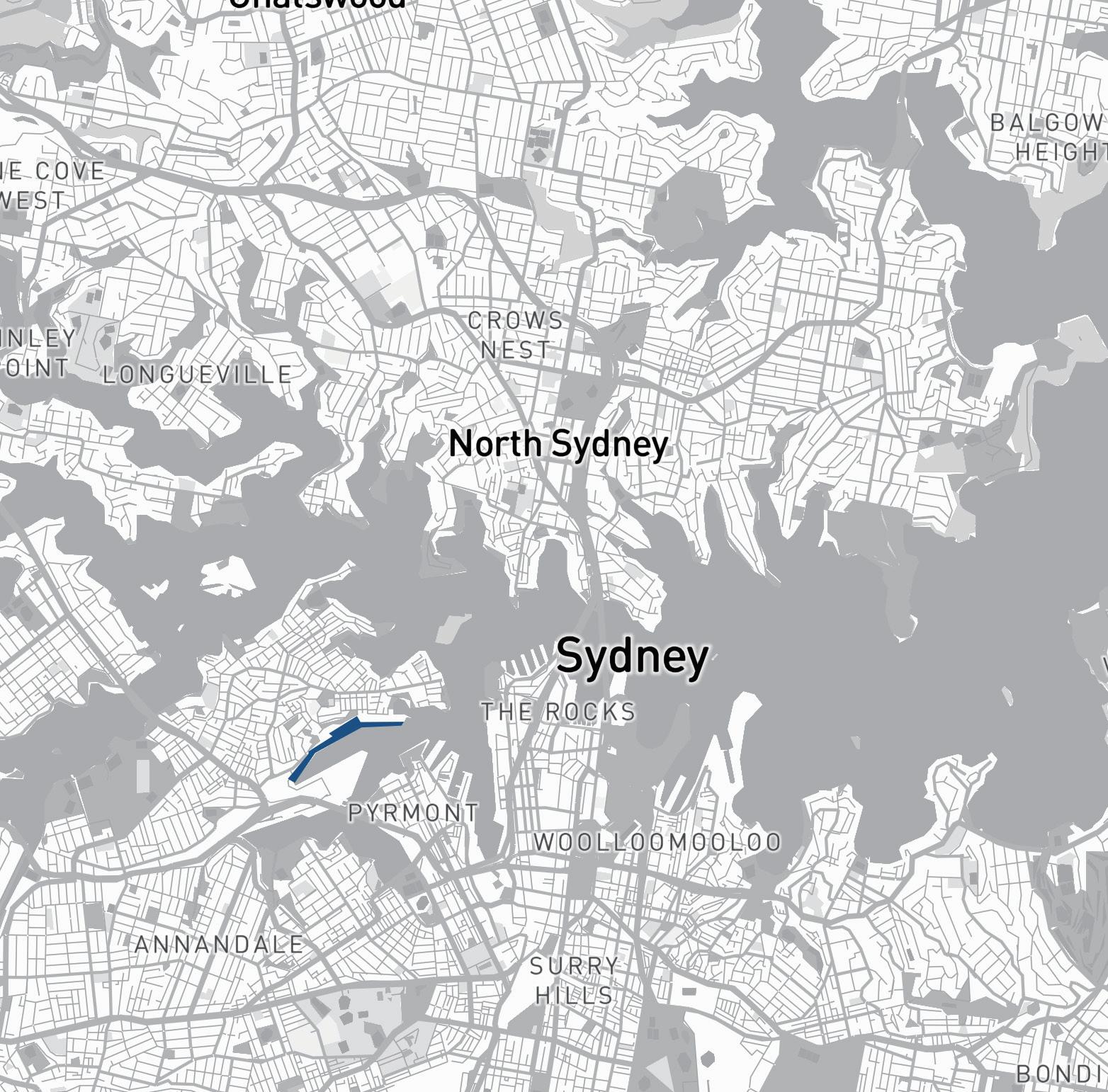
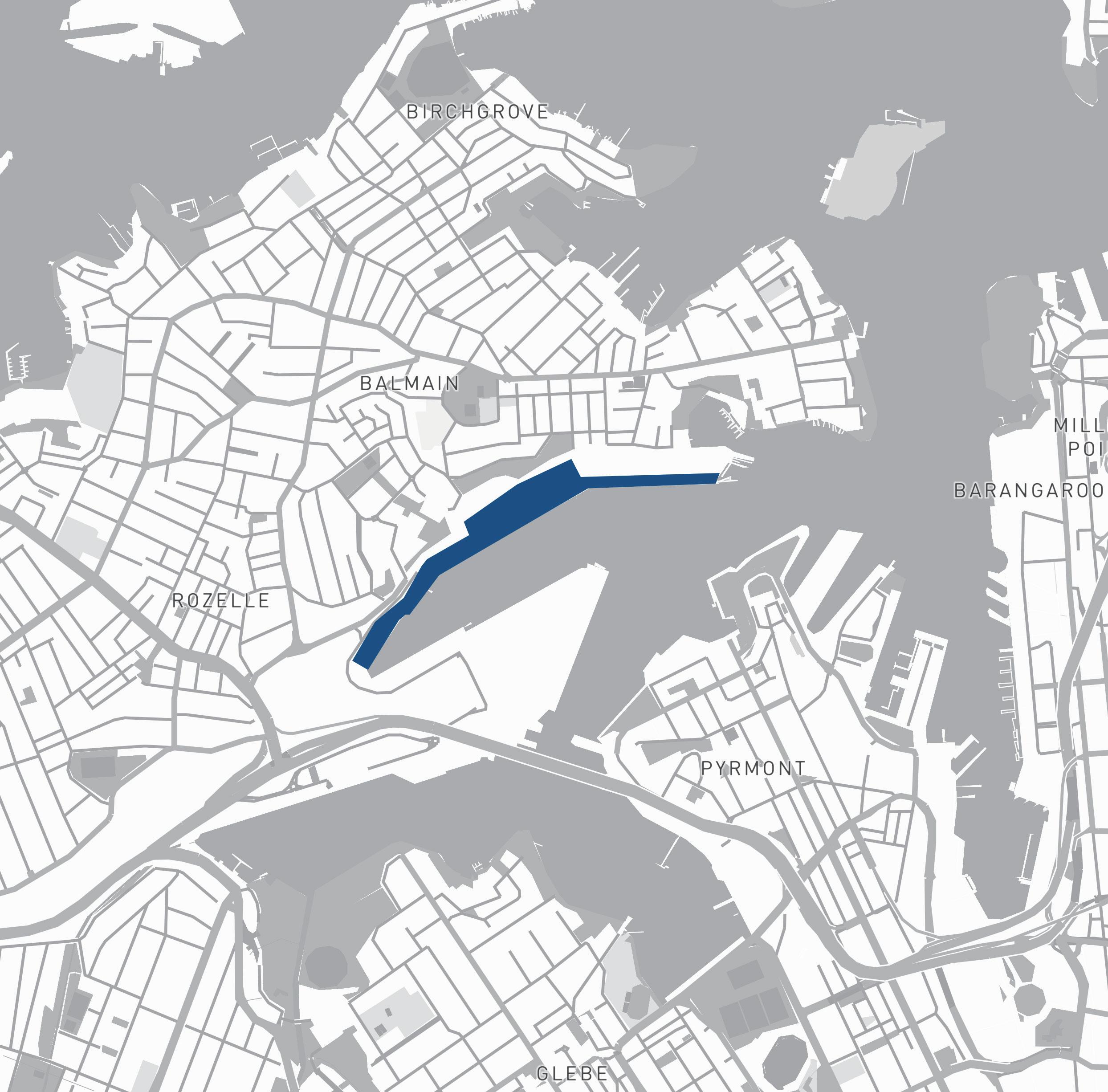

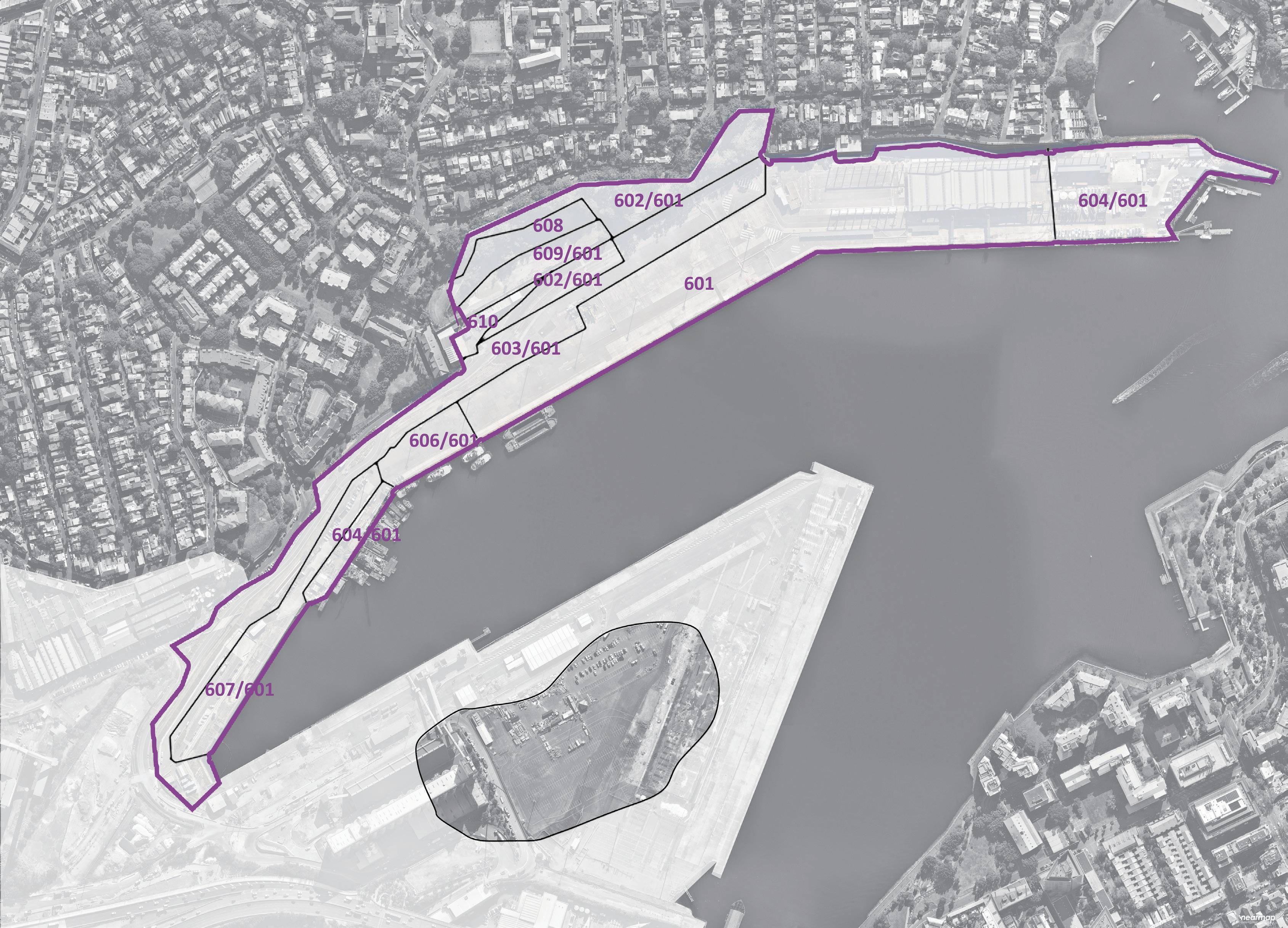
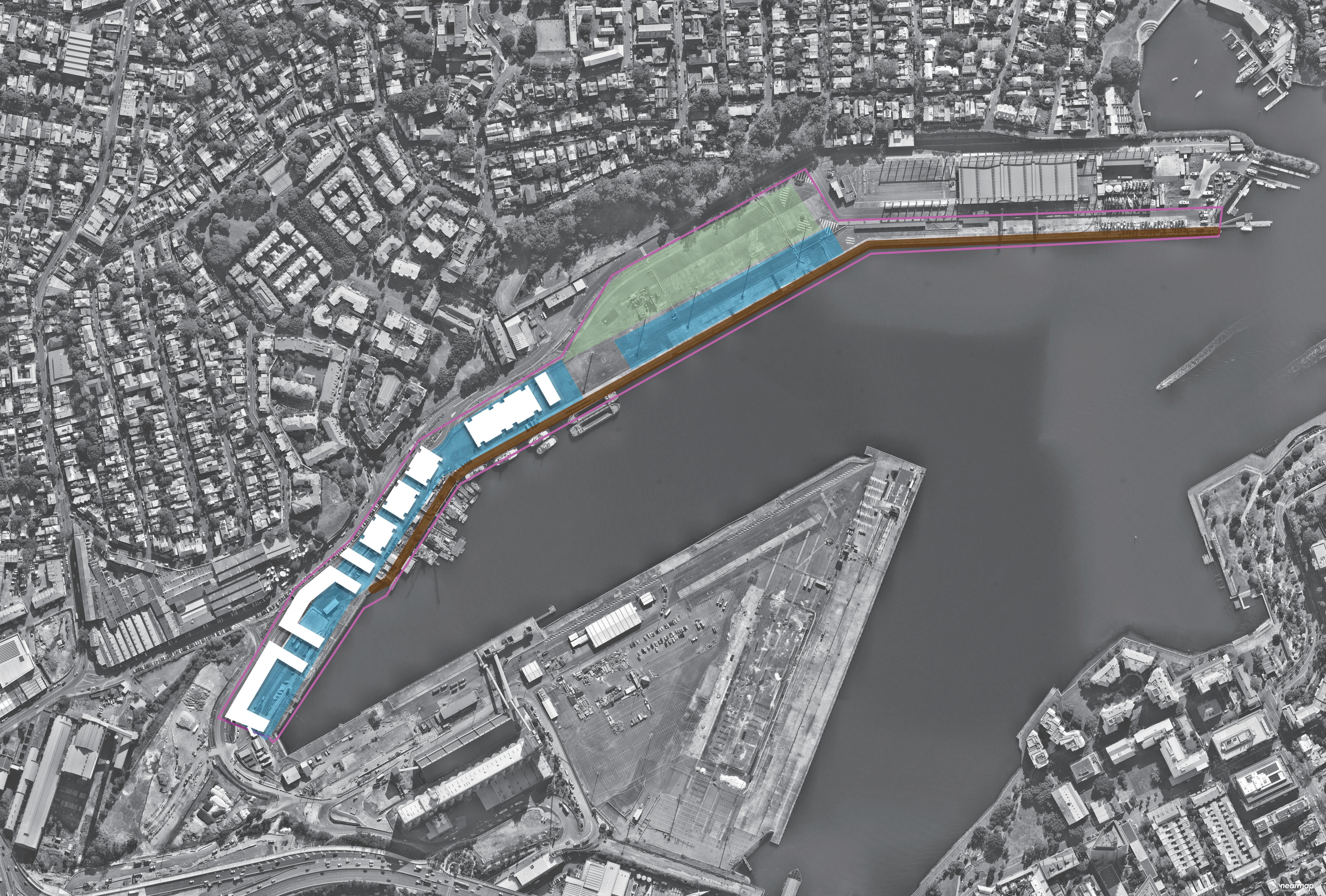
Area of Site: 67325 sqm Location
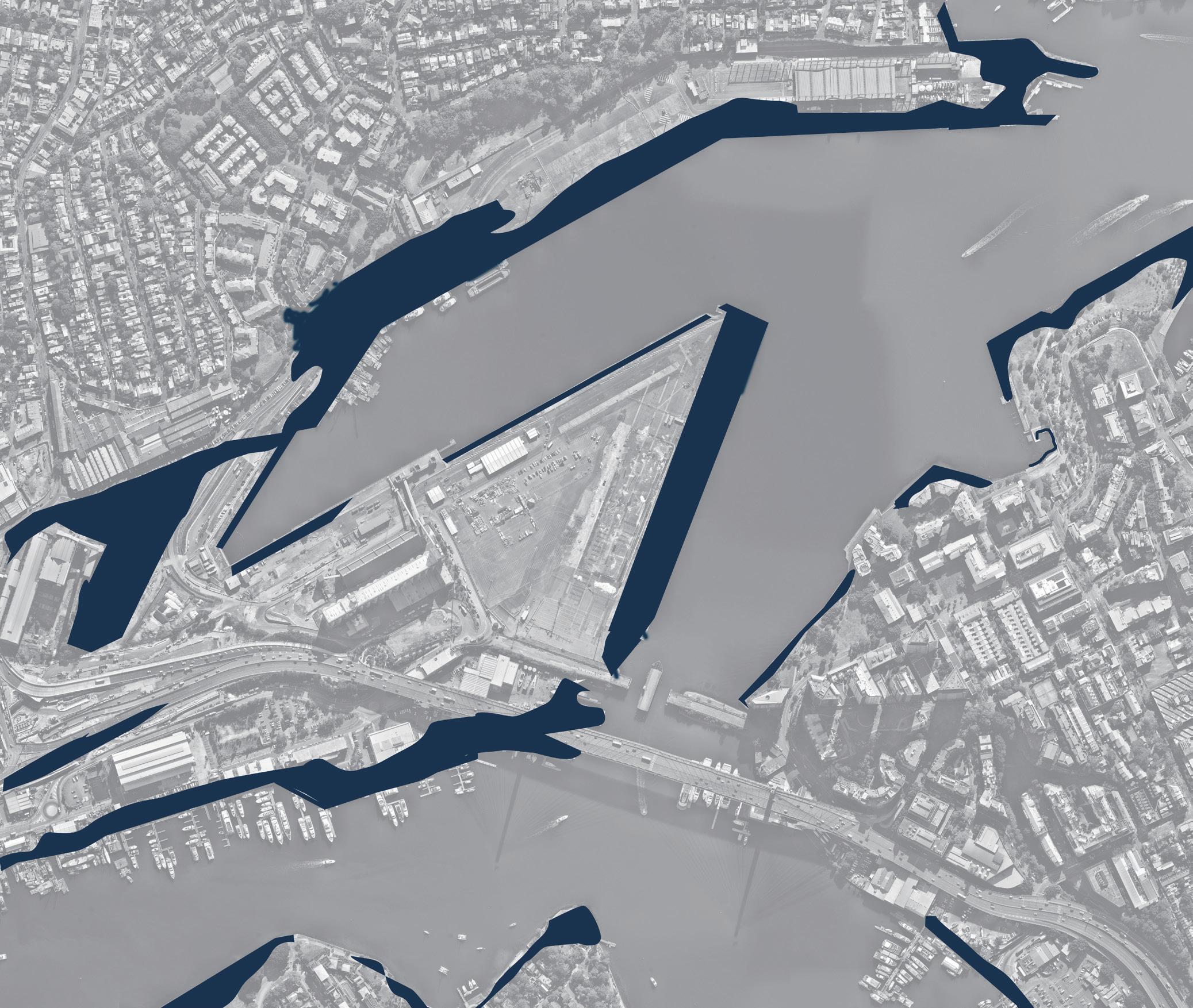
The north shoreline of The bays precinct is adjacent to White Bay and Balmain and is one of the most future promising waterfronts of The bays precinct. At the same time, because the potential risks of sea level rise were not considered at the beginning of the site construction, the site has a serious potential flood threat caused by sea level rise.





There is low water quality within the Bays harbour areas, particularly the shallow zone of White Bay, due to the stormwater runoff flow through contamination and finally into the Bays. Waterfront is the filter between The Bays Precinct and White Bay; the next step is fostering the marine ecology at the waterfront to contribute to natural remediation.

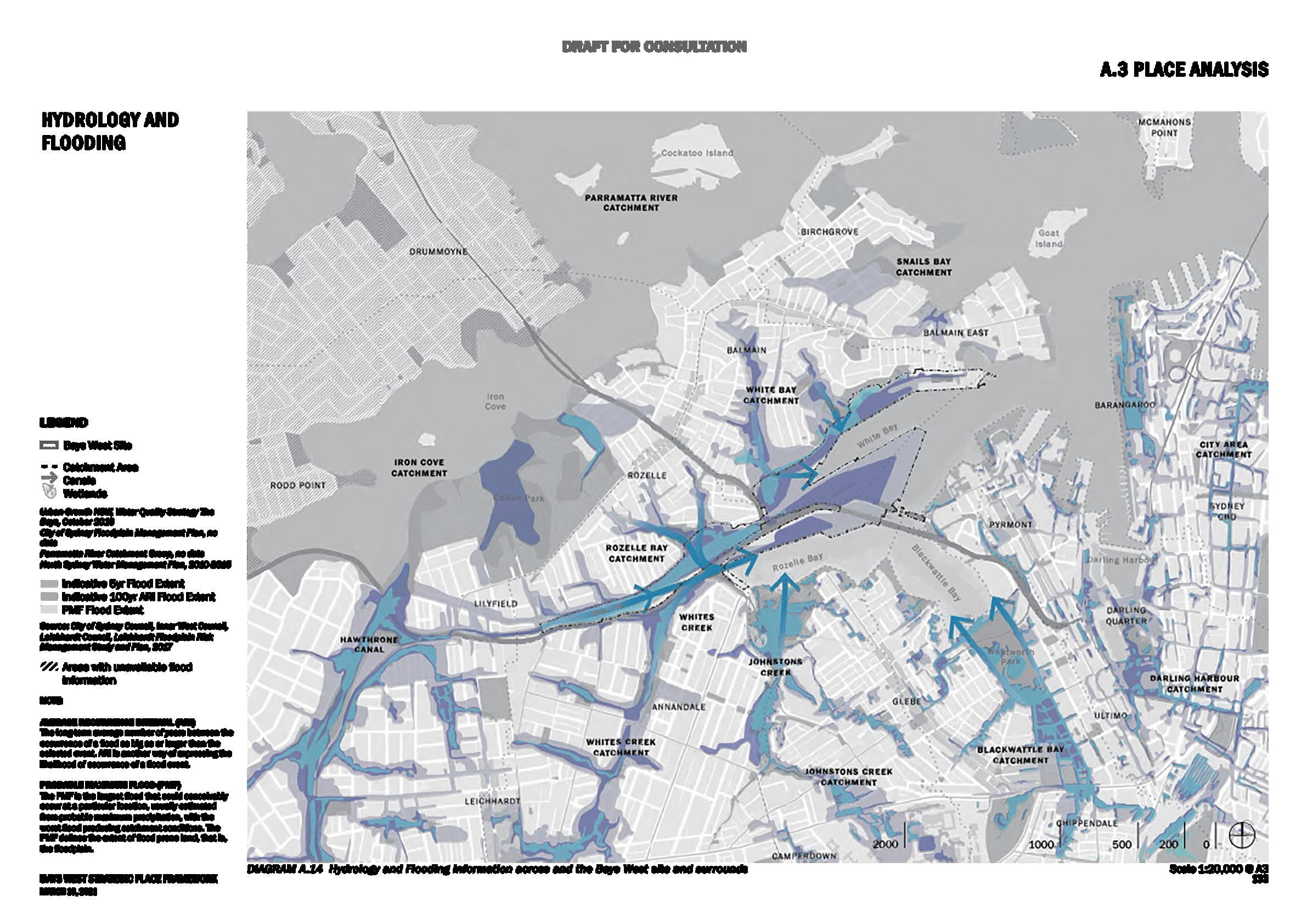
Most serious flood risk area
Catchment Area
Canals
Indicative 5yr Flood Extent
Indicative 100yr ARI Flood Extent
PMF Flood Extent
Notes:
AVERAGE RECURRENCE INTERVAL (ARI)
The long-term average number of years between the occurrence of a flood as big as or larger than the selected event. ARI is another way of expressing the likelihood of occurrence of a flood event.
PROBABLE MAXIMUM FLOOD (PMF)
The PMF is the largest flood that could conceivably occur at a particular location, usually estimated from probable maximum precipitation, with the worst flood producing catchment conditions. The PMF defines the extent of flood prone land, that is, the floodplain
Groundwater flows through the bays precinct and underground contaminants into the White bays to become the toxic tide.
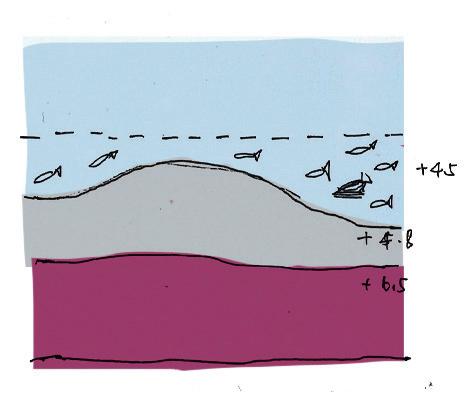
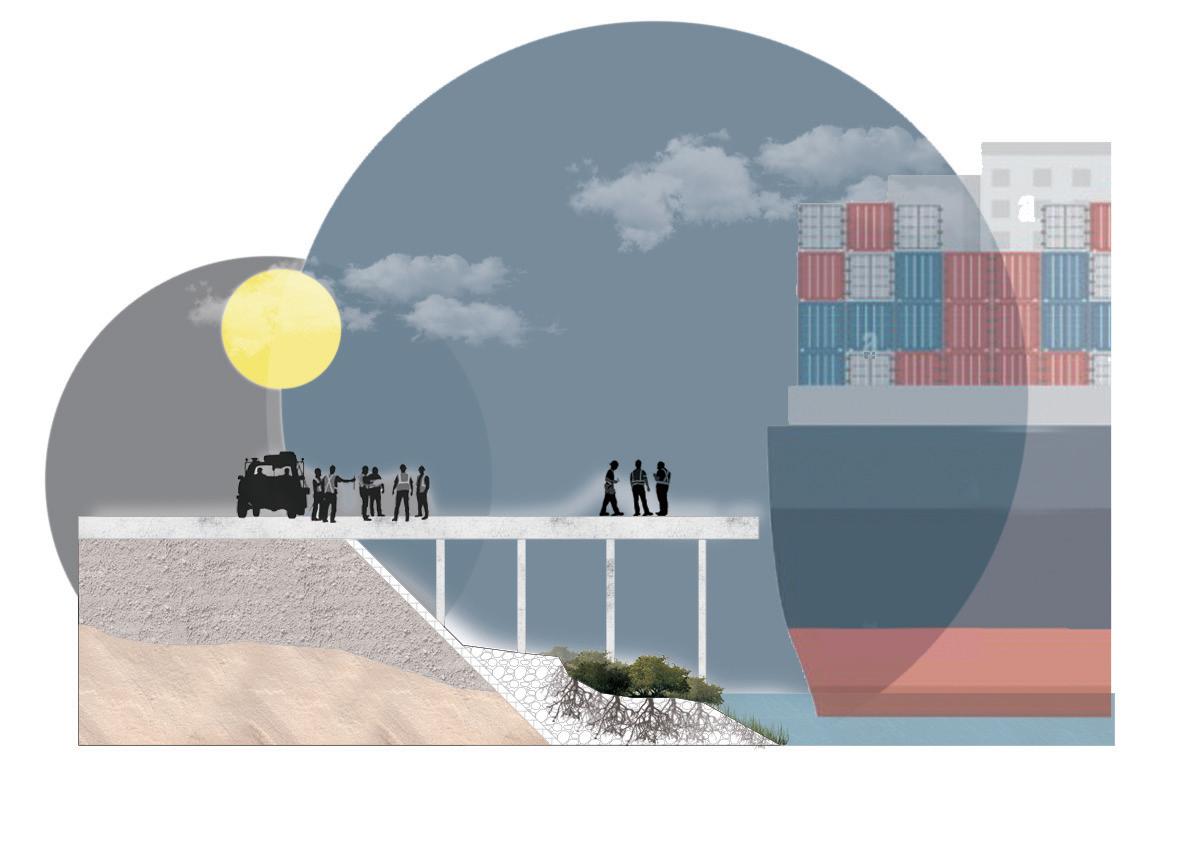
2.0 STORM SURGE - Part of Site will be inundated temporary or permanent
A storm surge is a rise in sea level that occurs during tropical cyclones, intense storms also known as typhoons or hurricanes. The storms produce strong winds that push the water into shore, which can lead to flooding.1
3.0 EROSION - Vertial Concrete&wooden water edge
Coastal erosion is the loss of beach sand or sediment volume and can be a single event of long term over several decades.

The north shoreline of the White Bay
84 cm
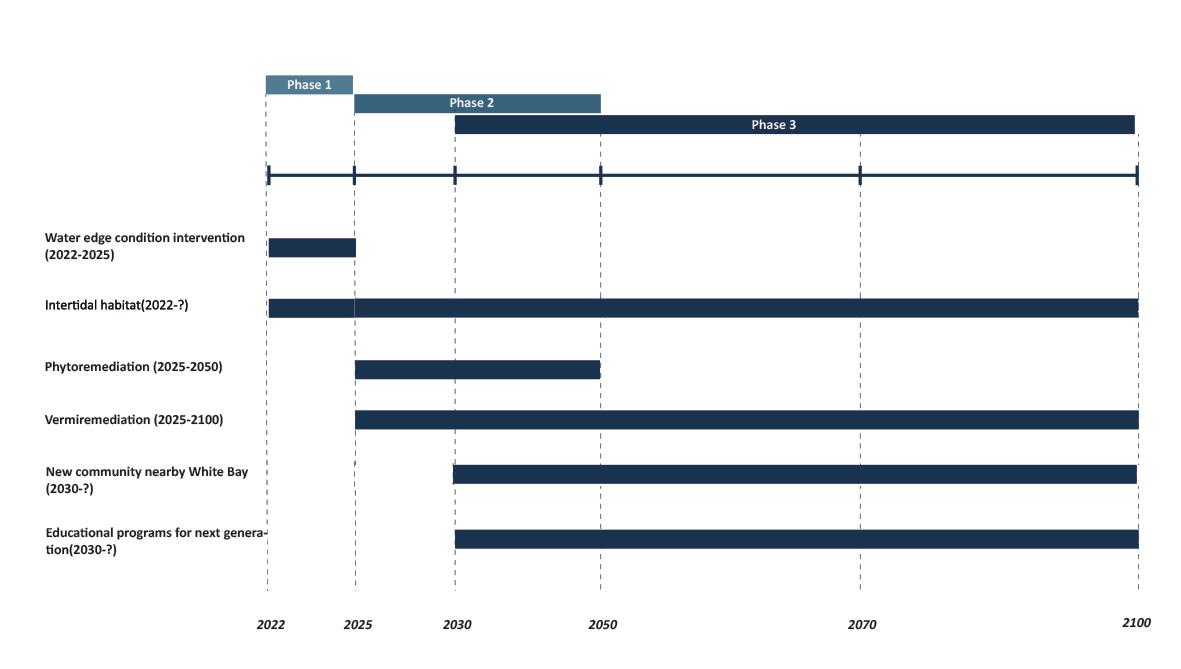
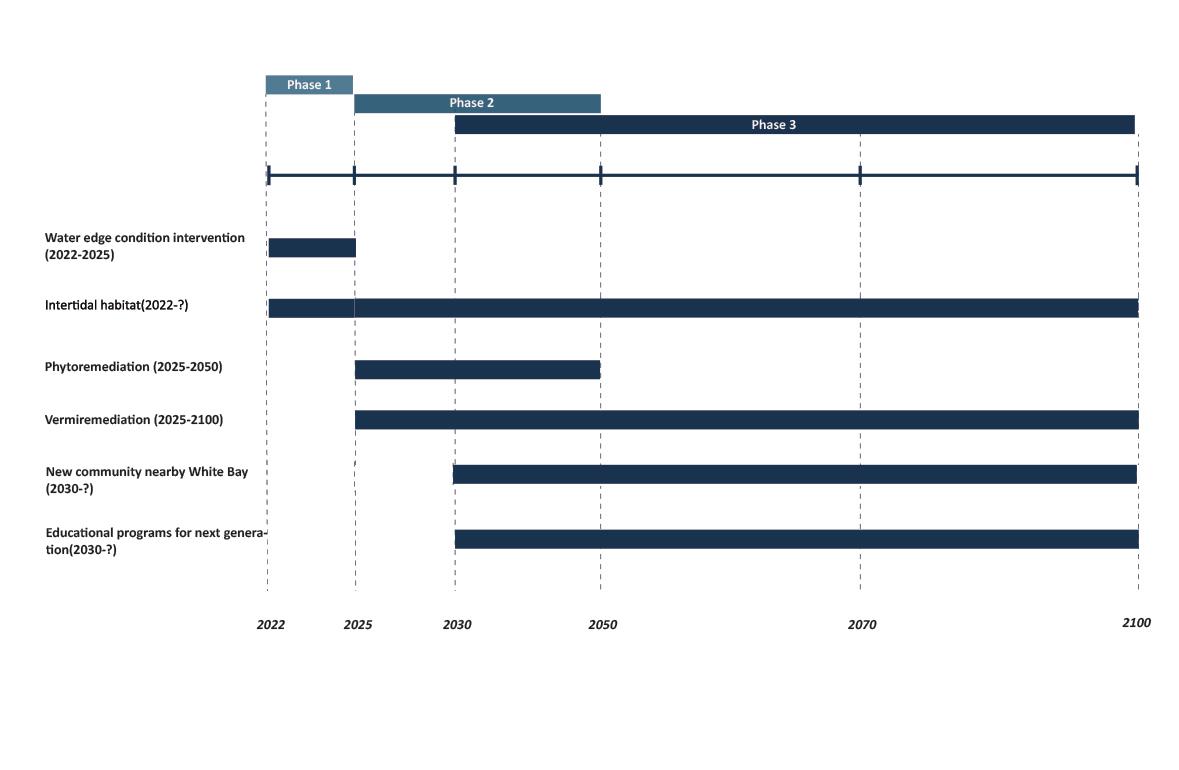
Sea level rise(2022-2100)
Flood frequency due to sea level rise (2022-2100)
Waterfront erosion level(2022-2100)
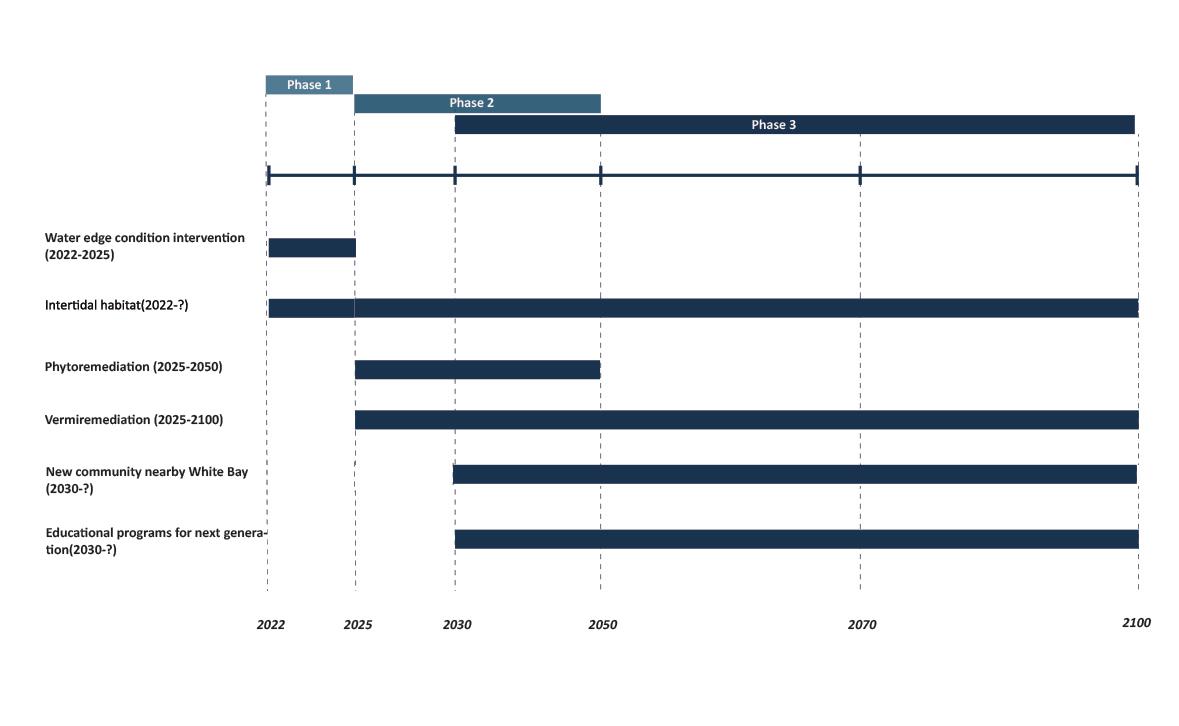
Next generation(2022-2050)
Consider the flood resilience strategy that suits the site characteristics. Protect buildings, infrastructure and residents from flooding.
Re-establish the intertidal zone and restore the ecology of the intertidal zone. Increase the buffer area between the
and the
and increase the biodiversity of the site.
Introducing biological intervention to solve the challenges and crises caused by the rising sea level of White bay and give educational meaning to the process of interventions.
- Edge Design & Habitats Introduction

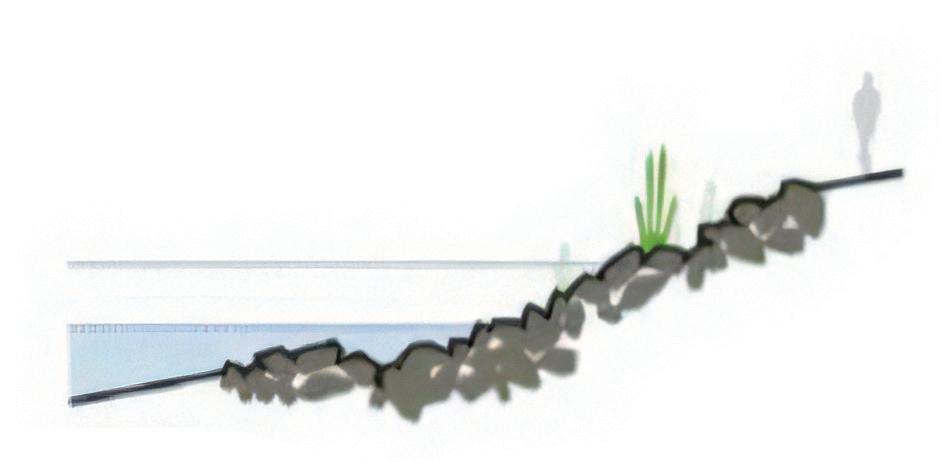
Use both cut and fill method and intertidal habitat restoration to reduce the risk of flooding and erosion on the water edge, build biodiversity resilient waterfront and protect the future communities and infrastructure when flood events happen caused by sea level rise.

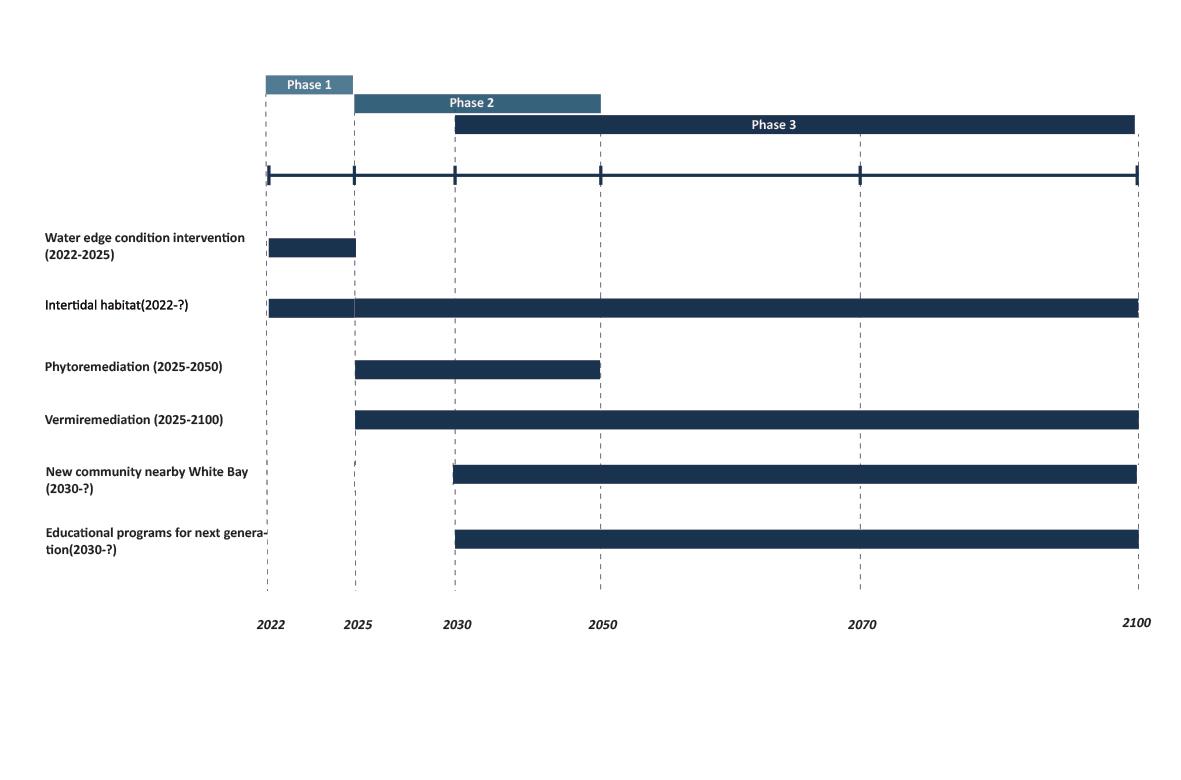
Phase
- Bioremediation

Use the phytoremediation and vermiremediation method to reduce the toxic level of waterfront soil and indirectly reduce the marine pollution and toxic tide of the white bay.
Phase
- The Legacy To Next Generation

Give an educational function to the process of intervention of the site’s sea level rise. Educational programs effectively foster the interconnectivity of the entire area and pass the knowledge of interventions and the site’s memories to the next generation.



Use both cut and fill method and intertidal habitat restoration to reduce the risk of flooding and erosion on the water edge, build biodiversity resilient waterfront and protect the future communities and infrastructure when flood events happen caused by sea level rise.

Hard edge design


habitat Grey Mangrove habitat Soft and adaptable edge design
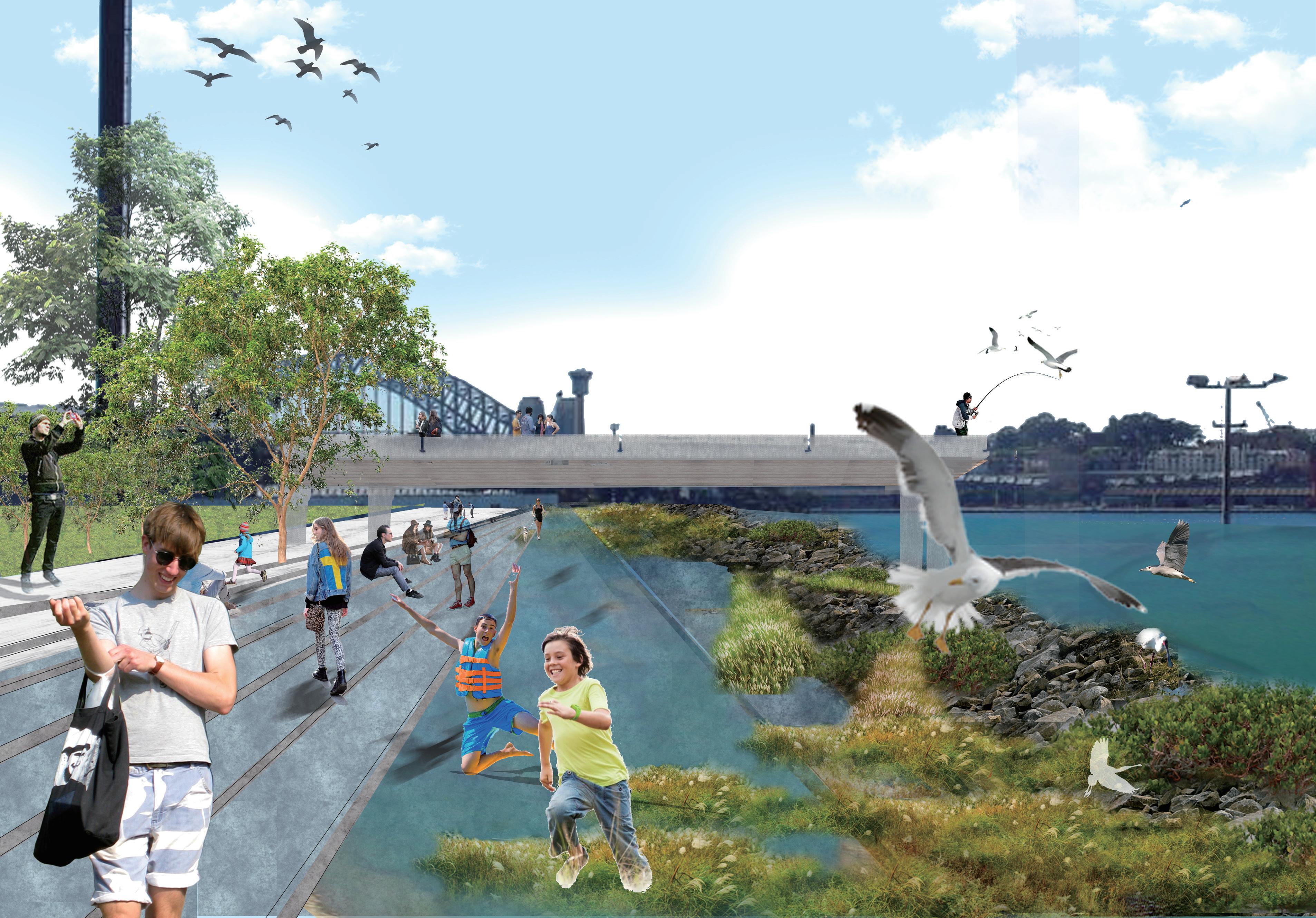
Between 2022-2025, we will use the cut and fill method to transform the original Hard-edge design of the Site into a Soft and adaptable edge design. The purpose is to extend the buffer zone between the waterfront and the tide, also increase the opportunities of restoring the intertidal zone habitat.
Restore the habitat of the intertidal zone and recall the original species (grey mangroves) on the site. Help the waterfront avoid flooding and tide erosion through mangrove forests. Meanwhile, the water quality of white bay will also be purified by intertidal species.
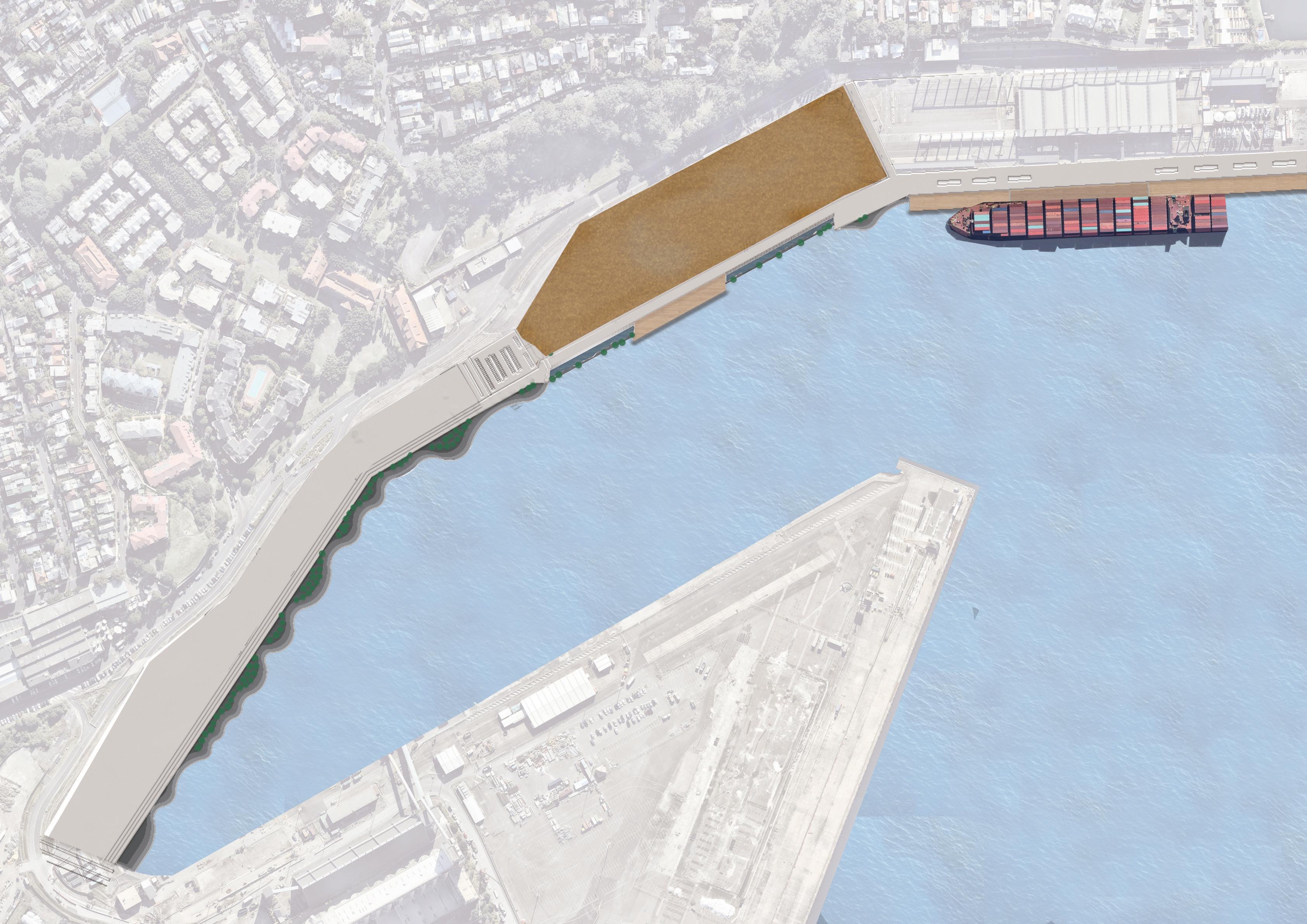

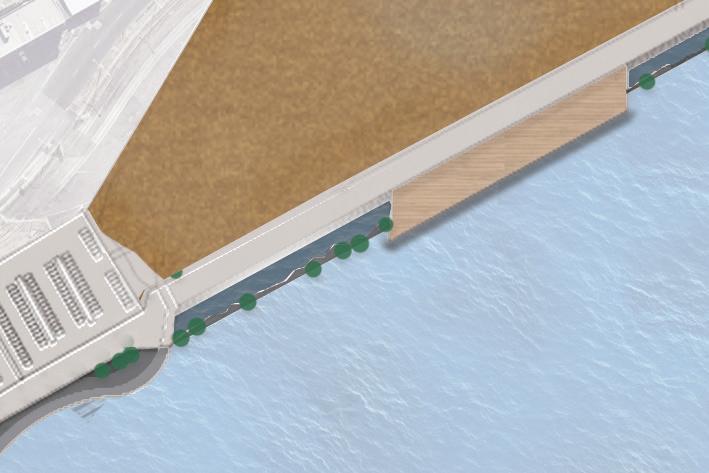
Phase 1 proposed works
Cutting the existing concrete water edge and creating the intertidal habitat area.
Using the cut and fill method to create the flood resilient promenade
Using the cut and fill method to create the water interaction zone fosters the interconnectivity between humans and water.
Constructed waterfronts above the intertidal habitat, to realize the coexistence of intertidal ecology and marine activities.
Cutting the existing concrete topping for preparing the parkland construction.
Set up the community car park nearby parkland




Why is a healthy intertidal zone meaningful to the challenges of sea level rise on the site?
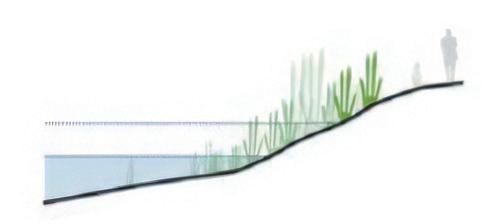

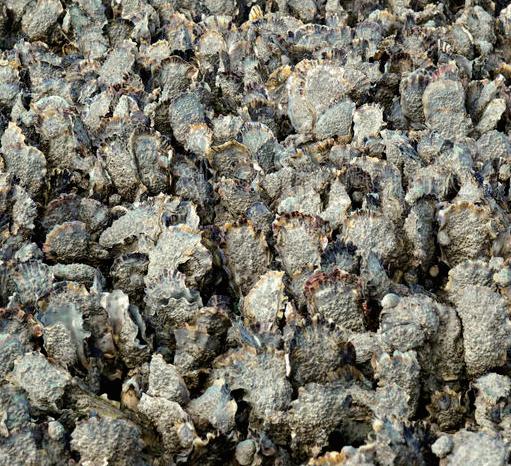
Some intertidal organisms (such as barnacles, oysters, etc.) can bioremediate contaminated seawater areas and ultimately improve the water quality of the site.
The intertidal zone is a buffer zone between the sea and the land during extreme weather. Indirectly protects the safety of the infrastructure and residents in the site.
The gravel and plants in the intertidal zone can disperse the wave energy of the tide. Reduce the erosion of tides by marine activities on the water edge.
Grey mangrove habitat
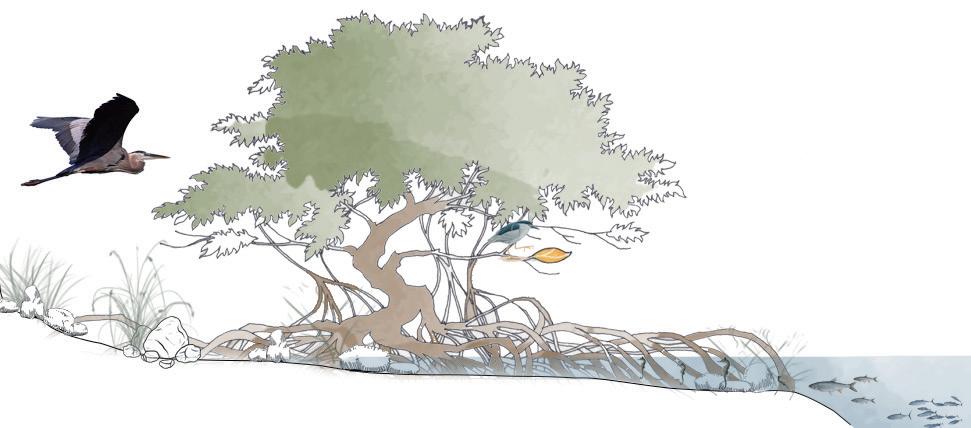
Client native specie Other native specie




Benifits native species



Scale: 1:10@A3




































Goal:
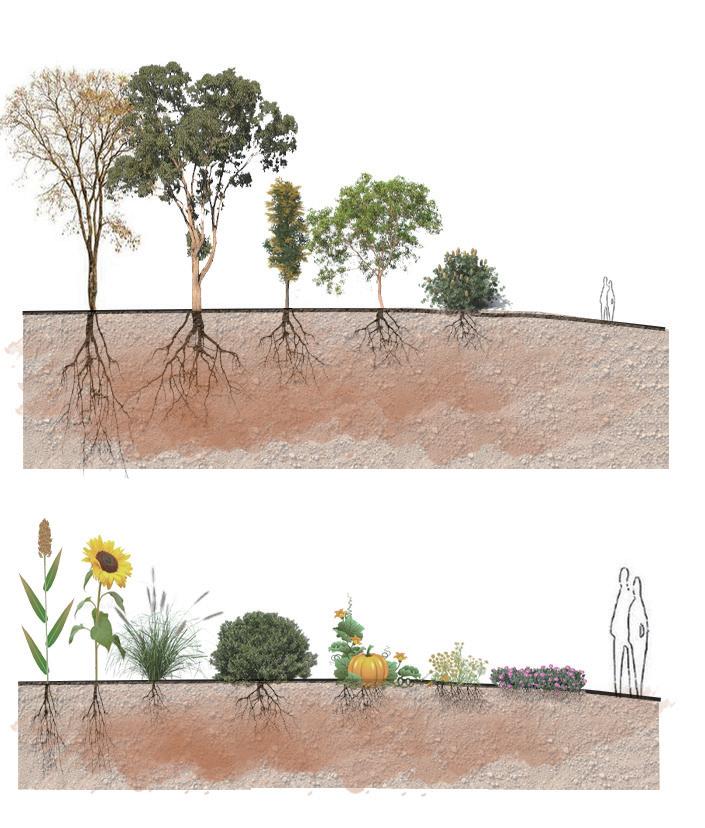
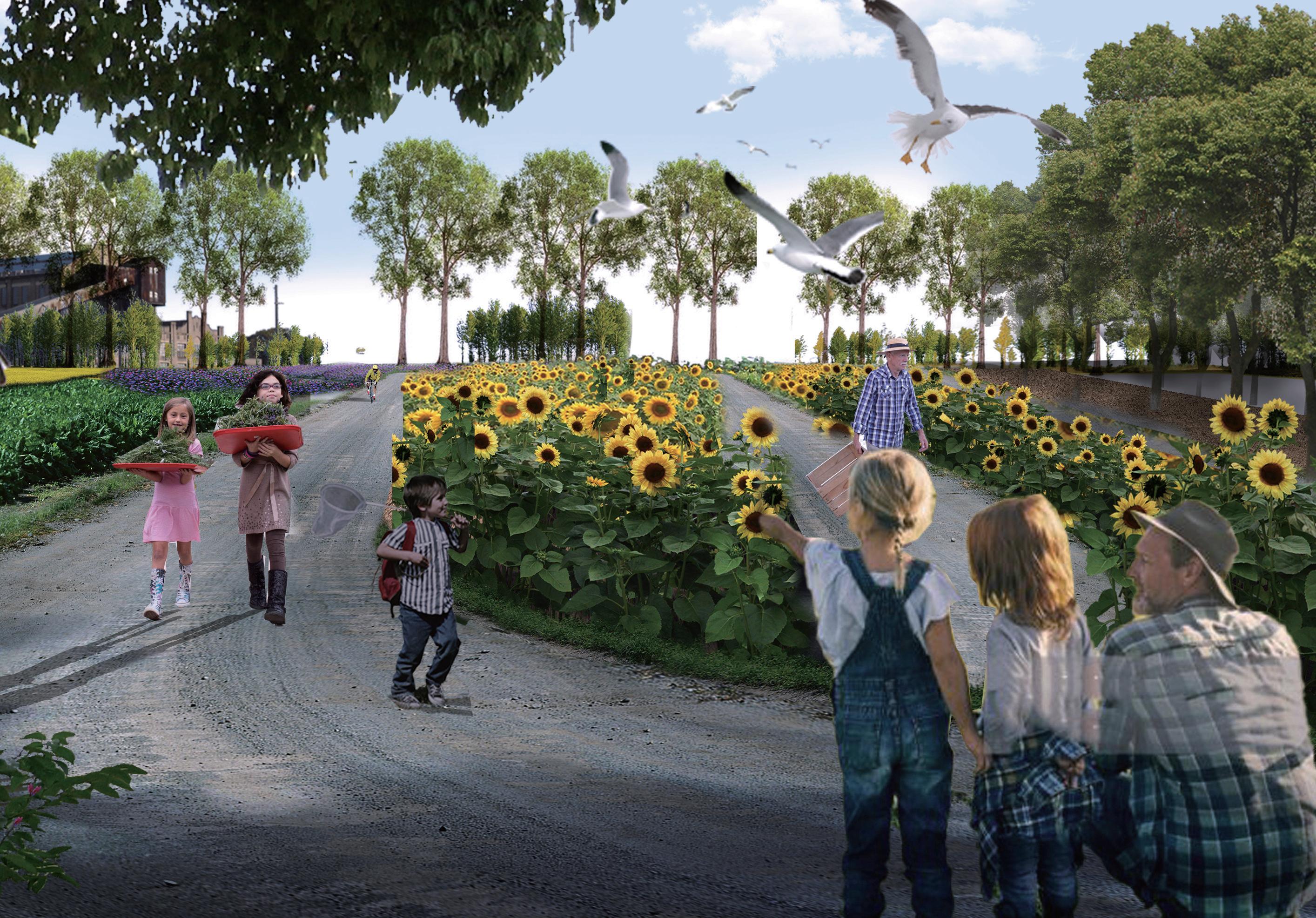
Increase the green space and shadow on the site by using the phytoremediation and vermiremediation method to reduce the toxic level of waterfront soil and indirectly reduce the marine pollution and toxic tide of the white bay.

Phytoremediation begins
Phytoremediation finished
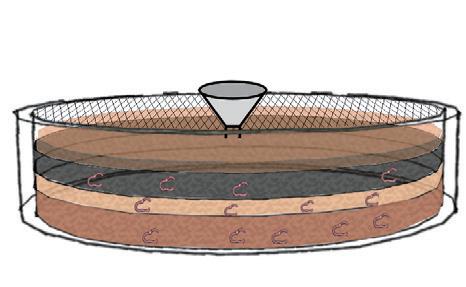
Phytoremediation technology can be characterised as environmentally friendly, effective, sustainable.From 2025, the site will set up a phytoremediation nursery to provide the plants needed in the future. The roots of plants filter and absorb heavy metal pollutants in the soil. This method indirectly improves the water quality of White bay.
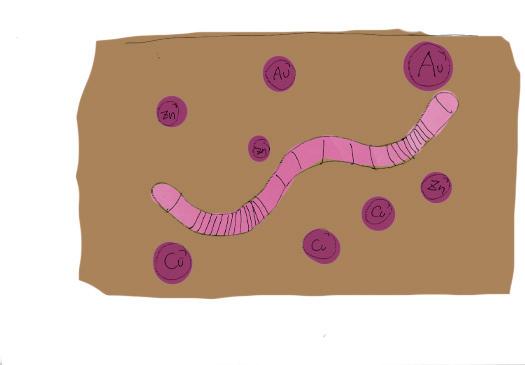

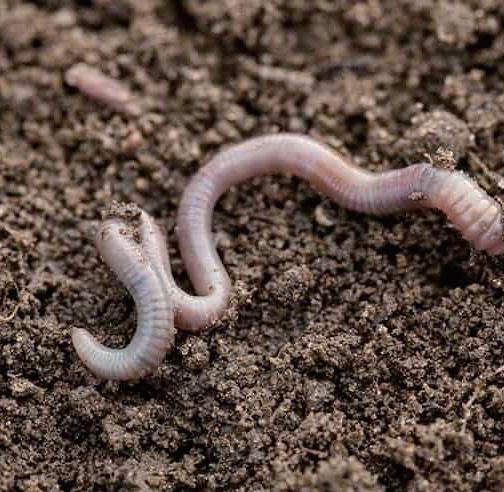
Vermiremediation process
Vermiremediation technology can be characterised as environmentally friendly, effective, sustainable.The site will use vermiremidiation method to purify contaminations in the soil. From 2025 onwards, the site will recycle part of the organic waste from the surrounding communities to cultivate vermiremidiation of earthworm species. The mature earthworms will cooperate with phytoremediation plants to purify the pollutants in the soil of the site.

Set up an amphitheater in open space parkland nearby the community car park
Set up a phytoremediation nursery in the parkland, all phytoremediation plantings on the Site will be provided by the phytoremediation nursery.
Set up a Vermiculture Garden in the parkland, cooperated with phytoremediation method to reduce the toxic level of the Site.
Constructed stormwater ponds for site runoff management
Street trees and other plantings on the site are provided by phytoremediation nursery
educational center in parkland











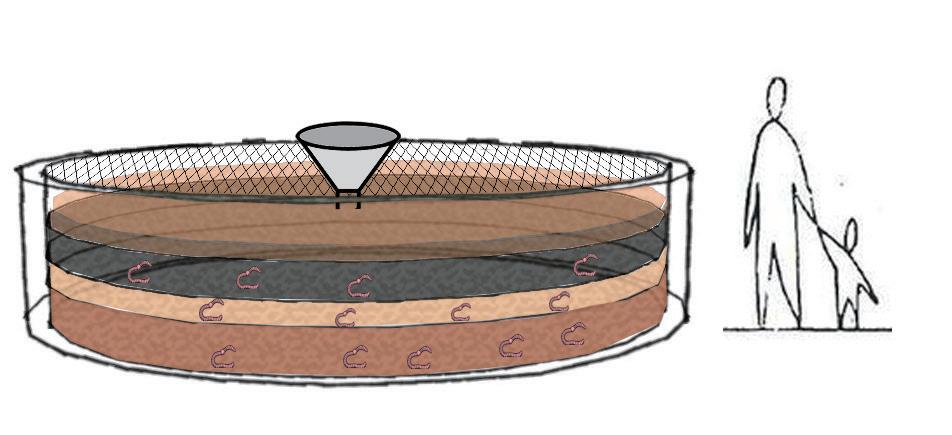



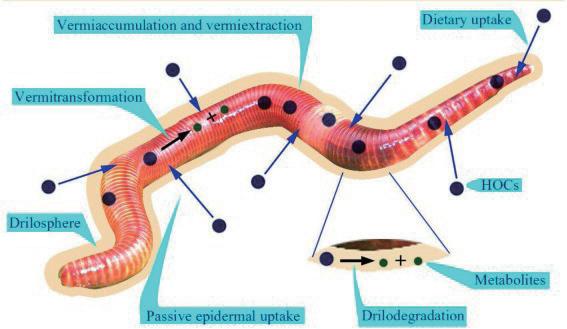
Vermiremediation technology can be characterised as environmentally friendly, effective, sustainable
Theory background Community engagement


The site will recycle part of the organic waste from the surrounding communities to cultivate vermiremidiation of earthworm species.

The mature earthworms will cooperate with phytoremediation plants to purify the pollutants in the soil of the site
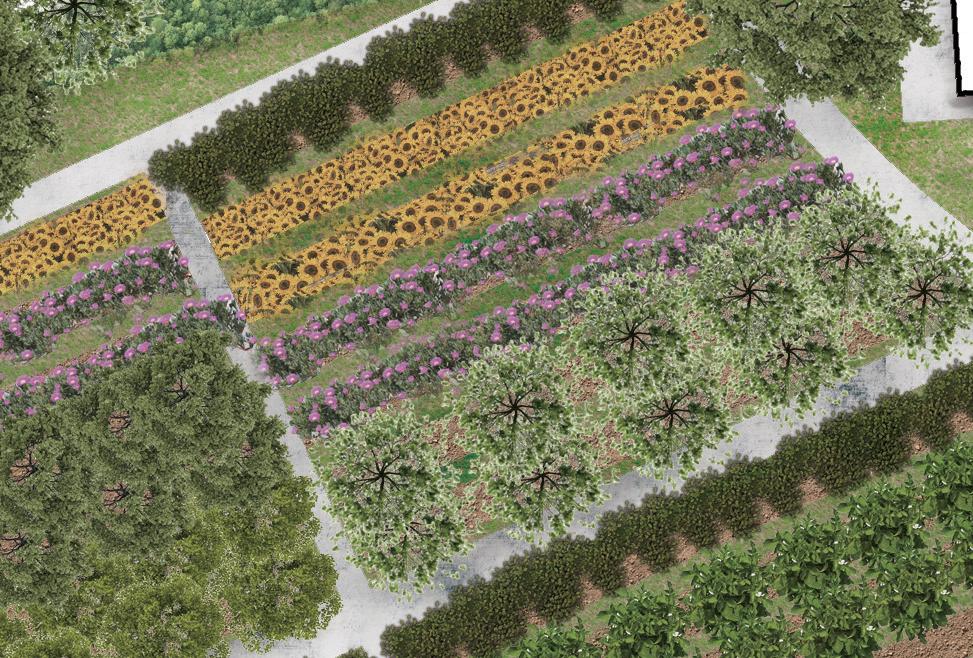










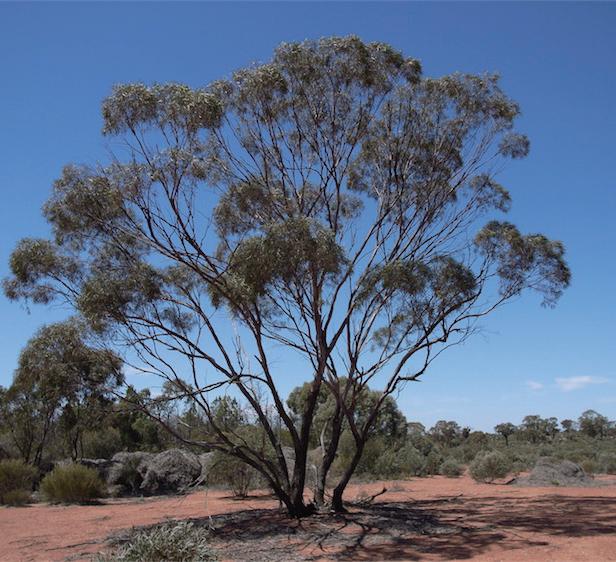
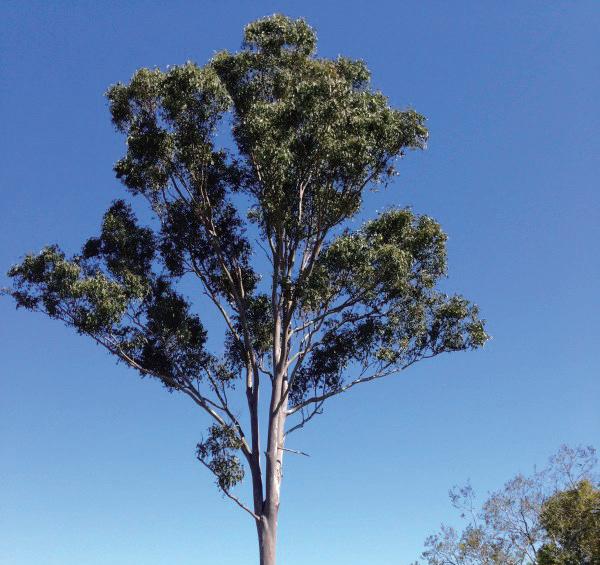
Native trees species for phytoremediation





Intertidal area native species for phytoremediation




Phytoremediation meadow
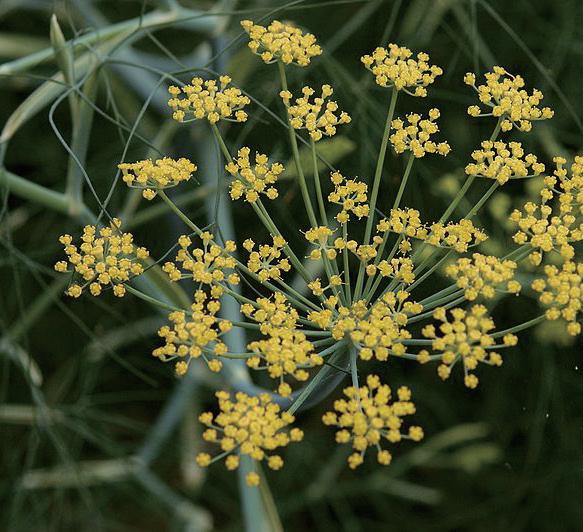
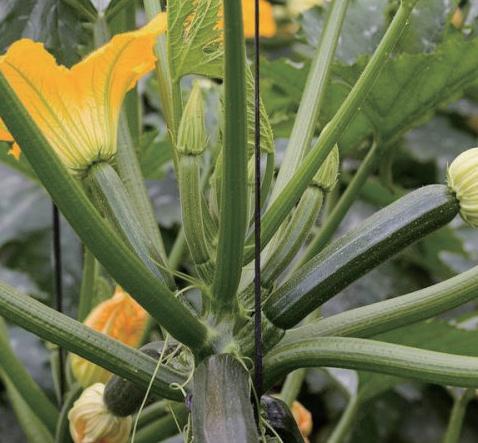








Earthworm species for vermiremidiation



species for intertidal bioremidiation





Eucalyptus polybractea


Eucalyptus tereticornis












Give an educational function to the process of intervention of the site’s sea level rise. Educational programs effectively foster the interconnectivity of the entire area and pass the knowledge of interventions and the site’s memories to the next generation.
Phytoremidiation&vermiremidiation study area
Intertidal & flood resilience study area
The intertidal study boardwalk is a part of the educational programs on the Site. It directly connects to the main street of the parkland. Aim to foster the interconnectivity between the phytoremidiation&vermiremidiation study area and intertidal & flood resilience study area to form a complete educational journey

According to the The Bays precinct transformation plan, Affordable housing and modern communities are the trend of White bay in the future. The new community will begin construction simultaneously as the opening of The bays precinct metro station in 2030.

Future community at The Bays precinct will be settled behind the flood resilient promenade
Set up an intertidal study boardwalk to foster the interconnectivity between the phytoremidiation&vermiremidiation study area and intertidal & flood resilience study area to form a complete educational journey
Set up green open space around the residentials
Set up the community car park nearby residentials





























Do




"We
hope to live in a high quality, healthy and safe environment, at the same time as it ensures that our future generations share a sense of the area’s history and memories. "
Marceau, Bays Precinct Taskforce Community Representative
Page 1:
1-Leitch, A. M., and Inman, M. (2012) Supporting Local Government to communicate coastal inundation. Resource kit prepared for the Sydney Coastal Councils Group Inc. CSIRO Climate Adaptation Flagship, Brisbane, Australia. 2-Phillips, N., 2015. Aboriginal stories of sea level rise preserved for thousands of years. [online] Smh.com.au. Available at: <https://www.smh.com.au/technology/aboriginal-stories-of-sea-level-rise-preserved-for-thousands-of-years-20150212-13d3rz.html>.
3-Church, JA, Hunter, JR, McInnes, KL and White, N. (2006) Sea level rise around the Australian coastline and the changing frequency of extreme events. Australian Meteorological Magazine 55: 253-260. Page 2:
1-Leitch, A. M., and Inman, M. (2012) Supporting Local Government to communicate coastal inundation. Resource kit prepared for the Sydney Coastal Councils Group Inc. CSIRO Climate Adaptation Flagship, Brisbane, Australia. Page 9;
Data Procured from- UrbanGrowth NSW Site Wide Remedial Concept Plan The Bays Precinct Urban Transformation Area© UrbanGrowth NSW, p112 Page 10:
Data produred from· https ://www. worldweatheronl ine. com/bal main-weather-averages/new-south-wales/au .aspx
Analysis produced from: Wei seng Wong Page 11:
1-Urban Growth NSW, Water Quality Strategy The Bays, October 2016 2-City of Sydney Floodplain Management Plan, no date
3-Parramatta River Catchment Group, no date North Sydney Water Management Plan, 2010-20151435–1450 City of Sydney Council, Inner West Council, 4-Leichhardt Council, Leichhardt Floodplain Risk Management Study and Plan, 2017. 5-TERRIOR. 2021. BAYS WEST STRATEGIC PLACE FRAMEWORK. 1st ed. SYDNEY: NSW Government, pp.132- 133 Page 12:
*sourced from <https://coastalrisk.com.au/viewer>
Page 13:
*Note. Information on this map is sourced from <https://www.ses.nsw.gov.au/resources-folder/tsunami-evacuation-map/>. Page31:
Powerplants is a design-led, multi-disciplinary phytoremediation research project at Sydney's White Bay Power Station. Photo: Jedidiah-Cranfield