

Guidance for teachers

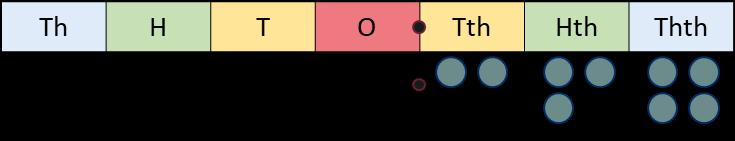
The calculation policy is divided into four sections: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. At the start of each section, you will find an overview of the progression of skills. Calculations involving decimal numbers and fractions are included. The calculation policy follows the same concrete, pictorial, abstract approach as our main schemes of learning. Where appropriate, sentence stems and key questions are included alongside the key representations. Where skills are divided into more than one section across the page, there is a progression in the level of difficulty from left to right. For example, when adding across a 10, children need to be able to add across 10 itself, before making links with related facts.

Progression of skills - Addition
Year group Skill
Nursery
Reception
Year 1
• Subitise to 3
• Count how many
• Make numbers to 5
• Add 1 more (through songs and rhymes)
• Conceptually subitise to 5
• 1 more
• Notice the composition of numbers within 10
• Combine 2 groups
• Add more
• Add together
• Add more
• Bonds within 10
• Related facts within 20
• Missing numbers

Progression of skills - Addition
Year group Skill
Year 2
Year 3
• Add 1s to any number (related facts)
• Add three 1-digit numbers
• Add across a 10
• Add multiples of 10
• Add 10s to any number
• Add two 2-digit numbers (not across a ten)
• Add two 2-digit numbers (across a ten)
• Missing numbers
• Add 1s, 10s and 100s to a 3-digit number
• Add two numbers (no exchange)
• Add two numbers across a 10 or 100
• Complements to 100
• Add fractions with the same denominator within 1 whole
• Calculate the duration of events

Progression of skills - Addition
Year group Skill
Year 4
Year 5

Year 6
• Add 1s, 10s and 100s to a 4-digit number
• Add up to two 4-digit numbers
• Add decimal numbers in the context of money
• Add fractions and mixed numbers with the same denominator beyond 1 whole
• Add using mental strategies
• Add whole numbers with more than 4 digits
• Add decimals with up to 2 decimal places
• Complements to 1
• Add fractions with denominators that are a multiple of one another
• Add integers up to 10 million
• Add decimals with up to 3 decimal places
• Order of operations
• Negative numbers
• Add fractions
Addition
Nursery

• Begin to have an understanding of numbers to 5
• We recommend focusing on noticing and representing small quantities, perceptual subitising and counting.
Progression of skills Key representations
Subitise to 3
Instantly see how many. How many do you see?



Count how many
Begin to count objects using 1-1 correspondence.
Make numbers to 5
Start by showing 1, 2 and 3 using fingers.



How many are there?




Show me…













Add 1 more
Through stories, songs and rhymes.


How many do I have now?







Count out … from a larger group.
E.g. Collect 3 beanbags for a game.


Begin to link numerals to quantities.

















Addition
Reception

• Have a deep understanding of numbers to 10, including the composition of each number.
• Subitise (recognise quantities without counting) up to 5
• Automatically recall (without reference to rhymes, counting or other aids) number bonds up to 5 and some number bonds to 10, including double facts.
Progression of skills Key representations
Conceptually subitise to 5
Notice the parts that make up the whole.
What do you see?
How do you see it?



1 more
Continue to link to stories, songs and rhymes.
1 more than … is …




Notice the composition of numbers within 10
Link to stories, songs and rhymes.
How many…?
How many…?
How many altogether?










How many ways can you make…?













Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
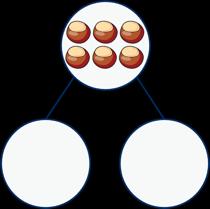
Combine 2 groups
2 groups are combined to find the total.
There are ….
There are ….
There are …. altogether. …. and …. make ….

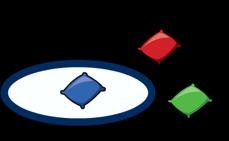

Add more A quantity is increased. First… Then…. Now…. I have …. I add …. more. Now I have….
















Addition
Year 1

• Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+) and equals (=) signs.
• Represent and use number bonds within 20
• Add 1-digit and 2-digit numbers to 20, including zero.
• Solve one-step problems that involve addition, using concrete objects and pictorial representations, and missing number problems such as 7 = + 2
Progression of skills Key representations
Add together (aggregation)
2 quantities are combined to find the total.
There are … There are …
There are … altogether. … is a part. … is a part. … is the whole.

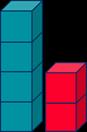
Add more (augmentation)
A quantity is increased.



First… Then… Now… I start at … I jump on … I land on …



Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
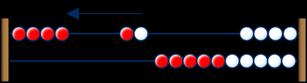
Bonds within 10
Include bonds for each number within 10


Encourage children to notice patterns. … is made of … and … … and … make … … can be partitioned into … and …
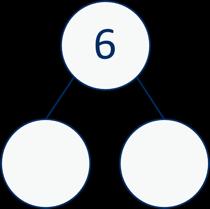
Related facts within 20
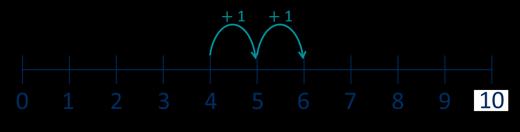
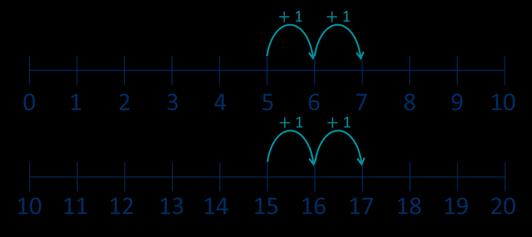
Make links to known facts. I know that … and ... = … so … and … = ... … more than … is … so … more than … is …

Missing numbers
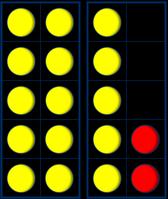
Make links to known facts. How many more do you need to make …? If … is the whole and … is a part, the other part must be… … plus … is equal to …






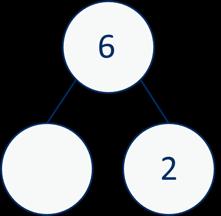

Addition
Year 2

• Recall and use addition facts to 20 fluently, and derive and use related facts up to 100
• Add numbers using concrete objects, pictorial representations, and mentally, including:
• a two-digit number and 1s
• a two-digit number and 10s
• 2 two-digit numbers
• adding 3 one-digit numbers
• Recognise and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and use this to check calculations and solve missing number problems.
Progression of skills Key representations
Add ones to any number (related facts)
Make links to known facts.
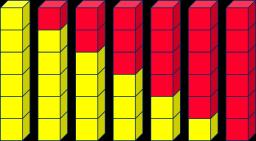
I know that … and ... = … so … and … = ... … more than … is … so … more than … is … What do you notice? Can you continue the pattern? 5 + 2 = 7
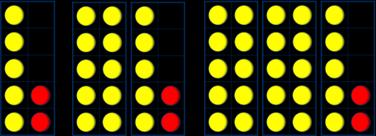
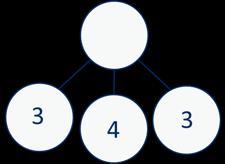
Add three 1-digit numbers
Prompt children to understand that addition can be done in any order and to make links to known facts. … and … are a bond to 10 10 +
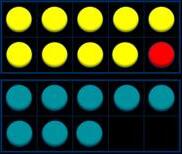
+ 2 = 17
+ 2 = 27…
What do you notice? Which addition is the easiest to calculate?
Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
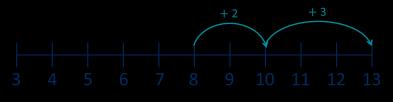
Add across a 10
Partition the number being added to make a full ten. … can be partitioned into … and … I add … to get to … then I add …

Add multiples of 10








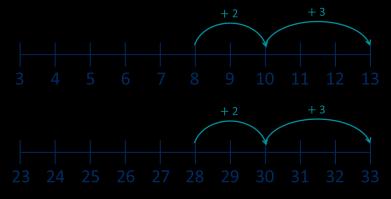
Make links to known facts within ten. … ones + … ones = … ones so … tens + … tens = … tens
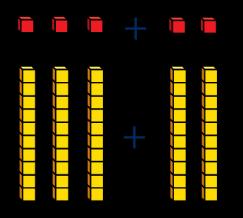
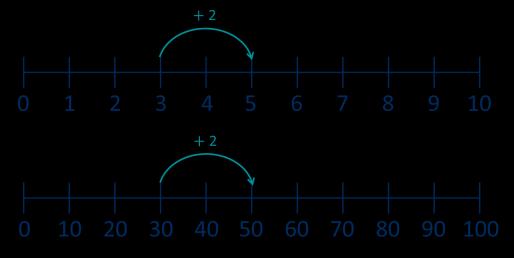
Add 10s to any number
3 + 2 = 5 30 + 20 = 50
Make links to known facts. … tens + … tens = … tens … tens and … ones = …
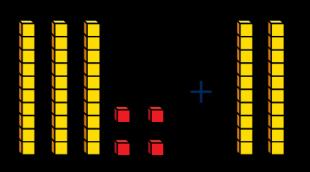
What is the same? What is different?
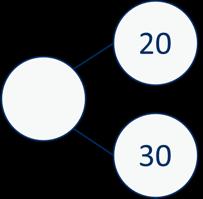
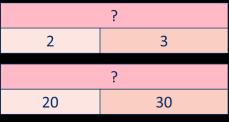
To add … I need to add 10 … times. I know that … and ... = … so … and … = ...
Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
Add 2-digit numbers (not across a ten)
Lining up ones and tens in columns will support with later written methods. … ones + … ones = … ones … tens + … tens = … tens

Add 2-digit numbers (across a ten)
Begin to exchange 10 ones for 1 ten.
There are …. ones, so I do/do not need to make an exchange. … ones = … ten and … ones
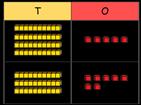
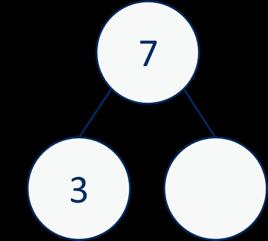
Missing numbers
Solve missing number problems and use the inverse to check.
How many more do you need to make …?
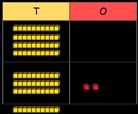


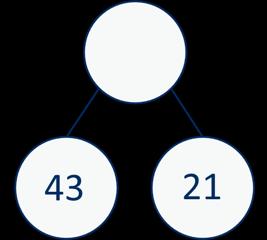
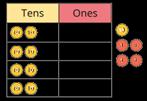
tens + 4 ones = 64
ones + 7 ones = 12 ones
ones = 1 ten and 2 ones
If … is a whole and … is a part, then … is the other part. … can be partitioned into … and …
Addition
Year 3

• Add numbers mentally, including: a three-digit number and ones, a three-digit number and tens, a three-digit number and hundreds.
• Add numbers with up to three digits, using formal written methods of columnar addition.
• Add fractions with the same denominator within 1 whole.
• Calculate the time taken by particular events or tasks.
Progression of skills Key representations
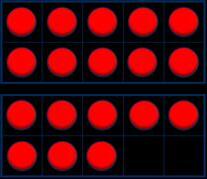
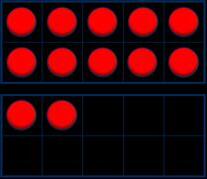
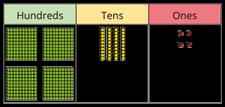
Add 1s, 10s or 100s to a 3-digit number
Emphasis on mental strategies including number bonds and related facts. Prompt children to notice which digit changes.
The ones/tens/hundreds column will increase by … What patterns do you notice?
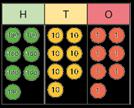
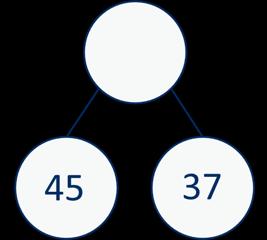
Add two numbers (no exchange)
Mental strategies and introduction of formal written method.
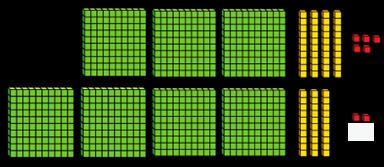
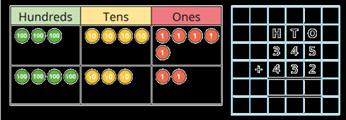
Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
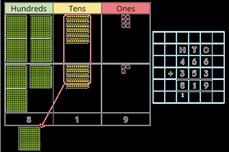
Add two numbers across a 10 or 100
Formal written method involving up to 2 exchanges including 3-digit plus 2-digit numbers.
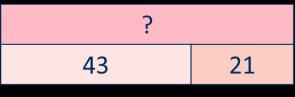
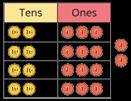
There are … ones, so I do/do not need to make an exchange. There are … tens, so I do/do not need to make an exchange. … ones = … ten and … ones.
… tens = … hundred and … tens.
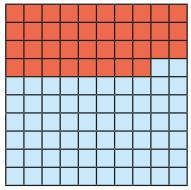
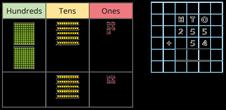
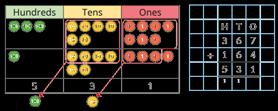
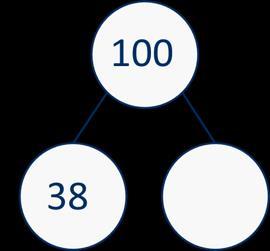
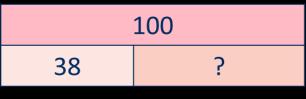
Complements to
Pairs


Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
Add fractions with the same denominator within 1 whole
Make links with known facts.
When adding fractions with the same denominator, I only add the numerator.
… fifths + … fifths = … fifths
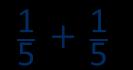
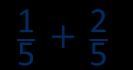
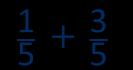
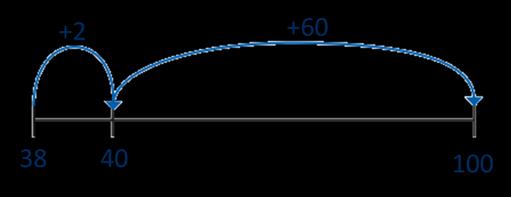
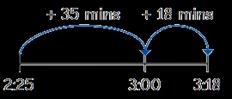
Calculate the duration of events
Find durations of time between a given start and end point. Children will need to calculate complements to 60


From … to … o’clock is … minutes.
From … o’clock to … is … minutes.
The total time taken is … minutes.


Addition
Year 4

• Add numbers with up to 4 digits using a formal written method.
• Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to 2 decimal places.
• Add fractions with the same denominator.
Progression of skills Key representations
Add 1s, 10s and 100s to a 4-digit number
Emphasis on mental strategies including number bonds and related facts. Prompt children to notice which digit changes.
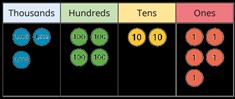
The ones/tens/hundreds/thousands column will increase by … What patterns do you notice? 2,350 + 3 = 2,350 + 30 = 2,350 + 300 = 2,350 + 3,000 = 6,040 + 200 = 6,040 + 500 = 6,040 + 900 =
Add up to two 4-digit numbers
Formal written method with up to 3 exchanges.
Encourage children to estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to calculations.
There are … ones/tens/hundreds so I do/do not need to make an exchange. I can exchange 10 … for 1 …
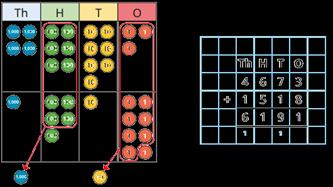
Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
Add decimal numbers in the context of money
Emphasis on partitioning and use of number lines rather than formal written calculations.
… pence + … pence = … pence
… pounds + … pounds = … pounds

45p + 25p = 70p
£2 + £3 = £5
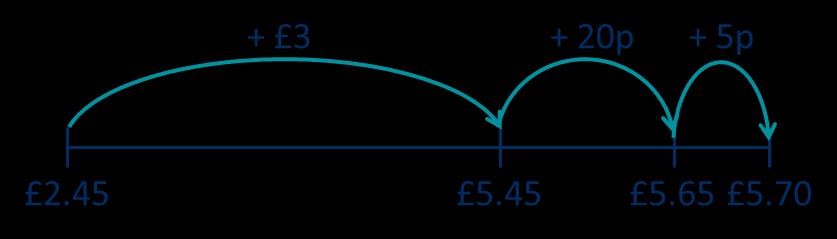
£5 + 70p = £5.70
Add fractions and mixed numbers with the same denominator beyond 1 whole

£3.25 can be partitioned into £3 + 20p + 5p
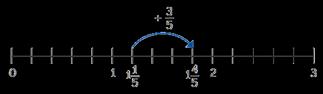
When adding fractions with the same denominator, I only add the numerator.
… fifths + … fifths = … fifths
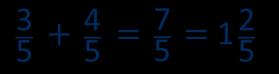


Addition
Year 5

• Add whole numbers with more than 4 digits, including using formal written methods.
• Add numbers mentally with increasingly large numbers.
• Add decimals, including a mix of whole numbers and decimals, decimals with different numbers of decimal places, and complements of 1
• Add fractions with the same denominator, and denominators that are multiples of the same number.
Progression of skills Key representations
Add using mental strategies
Add 1s, 10s, 100s, etc. to any number.
Use number bonds and related facts.
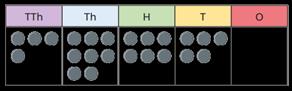
48,650 + 300 =
48,650 + 30,000 =
To add …, I can add … then subtract …
48,650 + 30 = , , 7 , ? ,
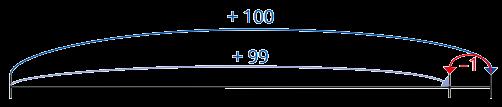
Add whole numbers with more than 4 digits
Encourage children to estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to calculations.
I can exchange 10 … for 1 …
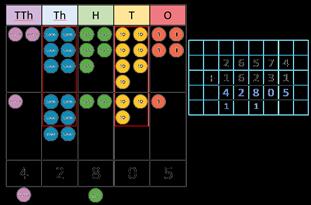

Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
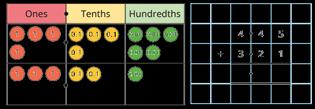
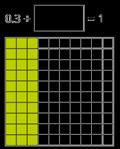
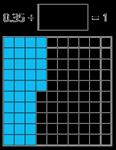
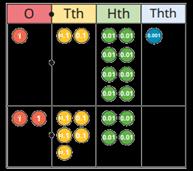
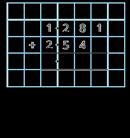
Add decimals with up to 2 decimal places
Progress from the same number of decimal places to a different number of decimal places, and from no exchange to exchange.
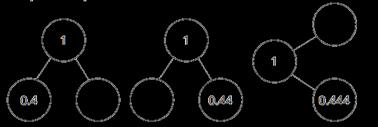
Complements to 1
Pairs of numbers with up to 3 decimal places which total 1
Encourage children to make links with bonds to 10 and complements to 100 and 1,000
I do/do not need to make an exchange because … I can exchange 10 … for 1 …


Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
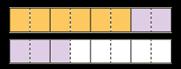
Add fractions with denominators that are a multiple of one another
Encourage children to convert fractions to the same denominator before adding.
Progress from adding fractions within 1 whole to adding fractions beyond 1 whole.

The denominator has been multiplied by … , so the numerator needs to be multiplied by… for the fractions to be equivalent.
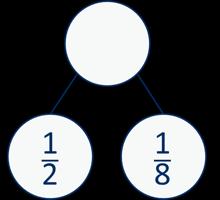

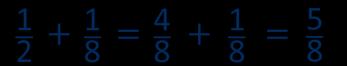

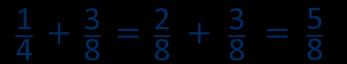
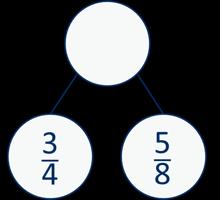
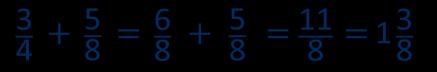
Addition
Year 6

• Add larger numbers, using the formal written method of columnar addition.
• Use their knowledge of the order of operations to carry out calculations involving the 4 operations.
• Calculate intervals across zero.
• Add fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions.
Progression of skills Key representations
Add integers up to 10 million
Encourage children to estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to calculations.
Add decimals with up to 3 decimal places
Progress to numbers with digits in different place value columns.
Encourage children to check that they have lined up the columns correctly.
I do/do not need to make an exchange because ...
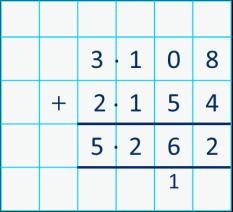
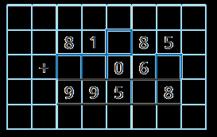
Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
Order of operations
Calculations in brackets should be done first. Multiplication and division should be performed before addition and subtraction.
*When no brackets are shown and the operations have the same priority, work left to right.
Negative numbers

… has greater priority than …, so the first part of the calculation I need to do is …
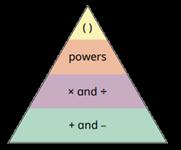
Children add to negative numbers and carry out calculations which cross 0 … plus … is equal to …


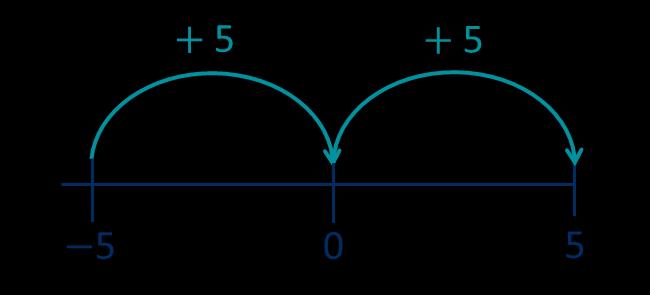
Addition
Progression of skills Key representations
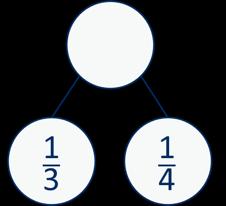
Add fractions
Convert fractions to the same denominator before adding. Progress from fractions where one denominator is a multiple of the other, to any fractions and then to mixed numbers.
The denominator has been multiplied by … , so the numerator needs to be multiplied by …
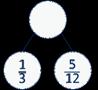

The lowest common multiple of … and … is … …is made up of … wholes and …

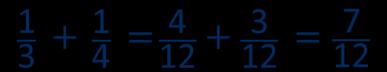
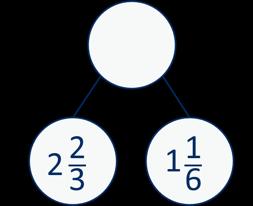
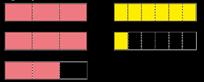
Progression of skills - Subtraction
Year group Skill
Nursery
Reception
Year 1
• Subitise to 3
• Count how many
• Make numbers to 5
• Take 1 away (through songs and rhymes)
• Conceptually subitise to 5
• 1 less
• Notice the composition of numbers within 10
• Partition
• Take away
• Find a part
• Take away
• Bonds within 10
• Related facts within 20
• Missing numbers

Progression of skills - Subtraction
Year group Skill
Year 2
• Subtract 1s from any number (related facts)
• Subtract across a 10
• Subtract multiples of 10
• Subtract 10s from any number
• Subtract two 2-digit numbers (not across a ten)
• Subtract two 2-digit numbers (across a ten)
• Missing numbers
Year 3
• Subtract 1s, 10s and 100s from a 3-digit number
• Subtract two numbers (no exchange)
• Subtract two numbers across a 10 or 100
• Complements to 100
• Subtract fractions with the same denominator within 1 whole

Progression of skills - Subtraction
Year group Skill
Year 4
• Subtract 1s, 10s, 100s and 1,000s from a 4-digit number
• Subtract up to two 4-digit numbers
• Subtract decimal numbers in the context of money
• Subtract fractions and mixed numbers with the same denominator

Year 5
Year 6
• Subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits
• Subtract using mental strategies
• Subtract decimals with up to 2 decimal places
• Complements to 1
• Subtract fractions with denominators that are a multiple of one another
• Subtract integers up to 10 million
• Subtract decimals with up to 3 decimal places
• Order of operations
• Negative numbers
• Subtract fractions
Subtraction
Nursery

• Begin to have an understanding of numbers to 5
• We recommend focusing on noticing and representing small quantities, perceptual subitising and counting.
Progression of skills Key representations
Subitise to 3
Instantly see how many. How many do you see?



Count how many
Begin to count objects using 1-1 correspondence.
Make numbers to 5
Start by showing 1, 2 and 3 using fingers.



How many are there?




Show me…













Take 1 away
Through stories, songs and rhymes.


How many do we have now?












Count out … from a larger group.


E.g. Collect a cup for everyone at the table.



Begin to link numerals to quantities.


















Subtraction
Reception

• Have a deep understanding of number to 10, including the composition of each number.
• Subitise (recognise quantities without counting) up to 5
• Automatically recall (without reference to rhymes, counting or other aids) number bonds up to 5 (and some subtraction facts) and some number bonds to 10, including double facts.
Progression of skills Key representations
Conceptually subitise to 5
Notice the parts that make up the whole.
What do you see?
How do you see it?



1 less
Continue to link to stories, songs and rhymes.


1 less than … is …



Notice the composition of numbers within 10
Link to stories, songs and rhymes.


How many…?
How many…?
How many altogether?







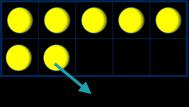



How many ways can you make…?












Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Partition
Using objects, explore different ways to partition a number into 2 or more parts.
There are … altogether. I can see … here and … there. … and … make …




Take away A quantity is reduced. First… Then… Now… I have … I take … away Now I have …

















Subtraction
Year 1

• Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving subtraction (–) and equals (=) signs.
• Represent and use number bonds and related subtraction facts within 20
• Subtract one-digit and two-digit numbers to 20, including zero.
• Solve one-step problems that involve subtraction, using concrete objects and pictorial representations, and missing number problems such as 7 = – 9
Progression of skills Key representations
Find a part
Link to number bonds and known facts. E.g. 2 + 4 = 6 so if 6 is the whole and 4 is a part, the other part must be 2
There are … in total.
are … How many are not …?







is the whole.
is a part.
is a part.



Take away A quantity is decreased. First… Then… Now… I start at … I jump back … I land on …






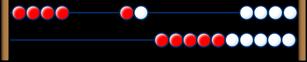


to …
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Bonds within 10
Focus on subtraction facts.
Encourage children to notice patterns. … is made of … and … … and … make … … can be partitioned into … and …





Related facts within 20
Make links to known facts. I know that … minus ... = … so … minus … = ... … less than … is … so … less than … is …



Missing numbers
Make links to known facts. How many do you need to subtract to make …? If … is the whole and … is a part, the other part must be…











Subtraction

• Recall and use subtraction facts to 20 fluently, and derive and use related facts up to 100
• Subtract numbers using concrete objects, pictorial representations, and mentally, including:
• a two-digit number and 1s
• a two-digit number and 10s
• 2 two-digit numbers
• Recognise and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and use this to check calculations and solve missing number problems.
Progression of skills Key representations
Subtract ones from any number (related facts)
Make links to known facts.
I know that … minus ... =
so … minus … = ... … less than … is … so … less than … is … What do you notice? Can you continue the pattern?



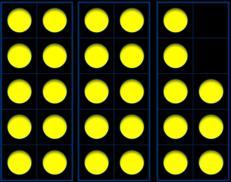
Subtract across a 10
Partition the number being subtracted to bridge through a ten. … can be partitioned into … and … Make links with related facts.


















Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Subtract multiples of 10
Make links to known facts within ten. … ones − … ones = … ones so … tens − … tens = … tens
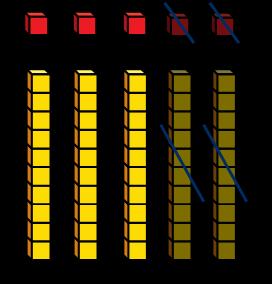
Subtract 10s from any number
Make links to known facts. … tens − … tens = … tens … tens and … ones = …
What is the same? What is different?

To subtract … I need to subtract 10 … times.

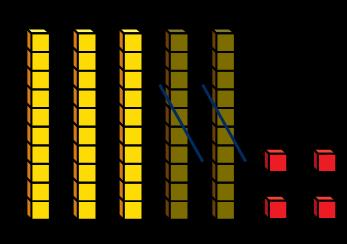
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Subtract two 2-digit numbers
(not across a ten)

Subtract two 2-digit numbers (across a ten)
Begin to exchange 1 ten for 10 ones.
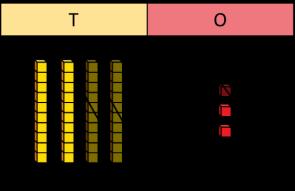

I need to make an exchange because I do not have enough ones to subtract … ones.








































Missing numbers
Solve missing number problems and use the inverse to check. How many do you need to subtract to make …?

If … is a whole and … is a part, then … is the other part.



Subtraction
Year 3

• Subtract numbers mentally, including: a three-digit number and ones, a three-digit number and tens, a three-digit number and hundreds.
• Subtract numbers with up to three digits, using formal written methods.
• Subtract fractions with the same denominator within 1 whole.
Progression of skills Key representations
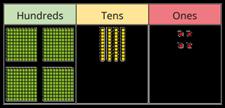
Subtract 1s, 10s and 100s from a 3-digit number
Emphasis on mental strategies including number bonds and related facts.
Prompt children to notice which digit changes.
The ones/tens/hundreds column will decrease by … What patterns do you notice?
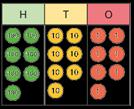
Subtract two numbers (no exchange)
Mental strategies and introduction of formal written method.
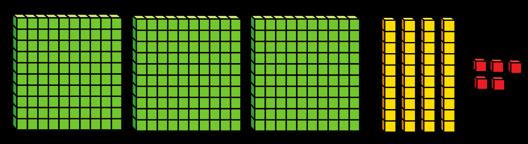

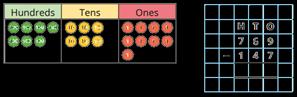
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
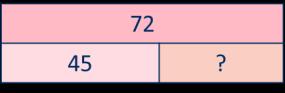
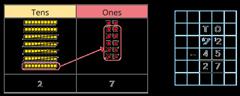
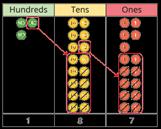
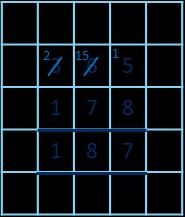
Subtract two numbers across a 10 or 100
Formal written method involving up to 2 exchanges including 3-digit subtract 2-digit numbers.
I need to subtract … ones. I do/do not need to make an exchange. I need to subtract ... tens. I do/do not need to make an exchange.
I can exchange 1 … for 10 …


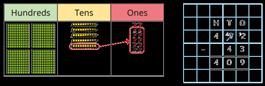
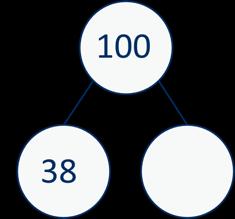
Complements to 100
Focus on subtraction facts.
Encourage children to notice patterns.


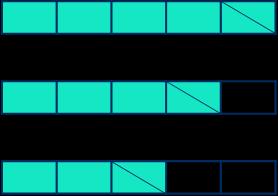
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Subtract fractions with the same denominator within 1 whole
Make links with known facts.

When subtracting fractions with the same denominator, I only subtract the numerator.
… fifths − … fifths = … fifths
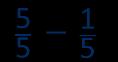
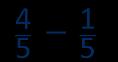
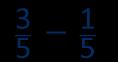

Subtraction
Year 4

• Subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using a formal written method.
• Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to 2 decimal places.
• Subtract fractions with the same denominator.
Progression
of skills Key representations
Subtract 1s, 10s, 100s and 1,000s from a 4-digit number
Emphasis on mental strategies including number bonds and related facts. Prompt children to notice which digit changes.
Subtract up to two 4-digit numbers
Formal written method with up to 3 exchanges. Encourage children to estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to calculations.
The ones/tens/hundreds/thousands column will decrease by … What patterns do you notice?

I need to subtract… ones/tens/hundreds. I do/do not need to make an exchange. I can exchange 1… for 10…
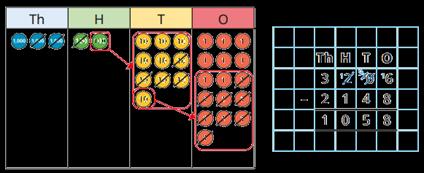
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Subtract decimal numbers in the context of money
Emphasis here is on partitioning and use of number lines rather than formal written calculations.
I can partition £… into £… and 100p
£… − £… = £…
100p − …p = …p

Subtract fractions and mixed numbers with the same denominator
Include subtracting fractions from wholes.
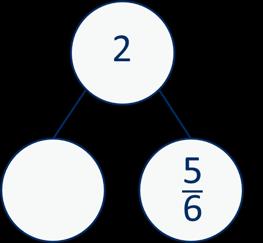
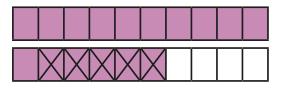
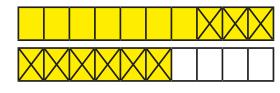
£5 − £3.26
£4 − £3 = £1
100p 26p = 74p
£5 - £3.26 = £1.74

100p
When subtracting fractions with the same denominator, I only subtract the numerator. … tenths … tenths = … tenths
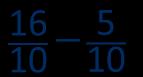
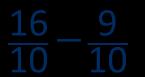
Subtraction
Year 5

• Subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits.
• Subtract numbers mentally with increasingly large numbers.
• Subtract decimals, including a mix of whole numbers and decimals, decimals with different numbers of decimal places, and complements of 1
• Subtract fractions with the same denominator, and denominators that are multiples of the same number.
Progression of skills Key representations
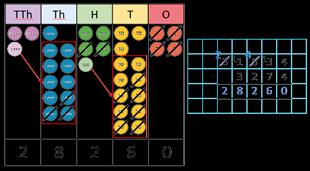
Subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits
Encourage children to estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to calculations.
I can exchange 1 … for 10 …

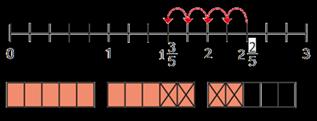
Subtract using mental strategies
Subtract 1s, 10s, 100s etc from any number.
Use number bonds and related facts.

To subtract …, I can subtract … then add …
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Subtract decimals with up to 2 decimal places
Progress from the same number of decimal places to a different number of decimal places and from no exchange to exchange.
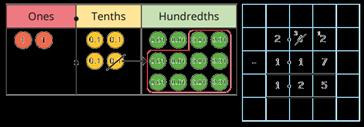



Complements to 1
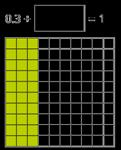
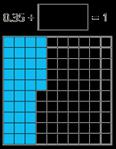
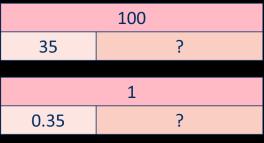
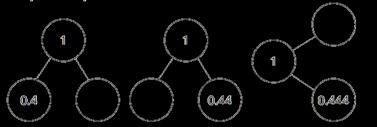
Encourage children to make links with bonds to 10 and complements to 100 and 1,000 when finding a missing part or subtracting from 1
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
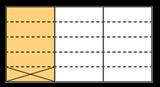
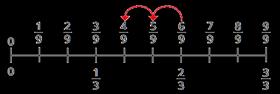
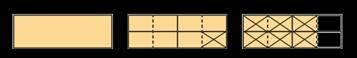
Subtract fractions with denominators that are a multiple of one another
Convert fractions to the same denominator before subtracting. Progress from subtracting fractions within 1 whole to subtracting from a mixed number.

The denominator has been multiplied by … , so the numerator needs to be multiplied by… for the fractions to be equivalent.
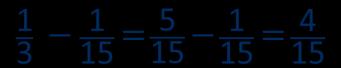
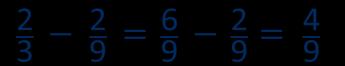

Subtraction
Year 6

• Subtract larger numbers, using the formal written methods of columnar subtraction.
• Use their knowledge of the order of operations to carry out calculations involving the 4 operations.
• Calculate intervals across zero.
• Subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions.
Progression of skills Key representations
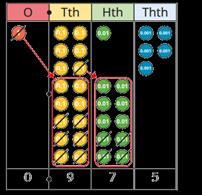
Subtract integers up to 10 million
Encourage children to estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to calculations.
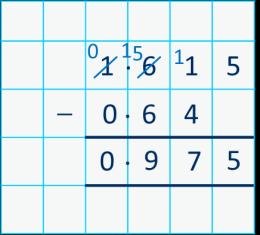
Subtract decimals with up to 3 decimal places
Progress from the same number of decimal and whole number places to a different number of decimal and whole number places.
I do/do not need to make an exchange because ...
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Order of operations
Children learn the order of priority for operations in a calculation. Calculations in brackets should be done first. Multiplication and division should be performed before addition and subtraction.

... has greater priority than … , so the first part of the calculation I need to do is …



Negative numbers
Children subtract from positive and negative numbers and calculate intervals across 0 … minus … is equal to …
Subtraction
Progression of skills Key representations
Subtract fractions
Convert fractions to the same denominator before subtracting. Progress from fractions where one denominator is a multiple of the other, to any fractions and then subtracting from a mixed number.
The denominator has been multiplied by … , so the numerator needs to be multiplied by…


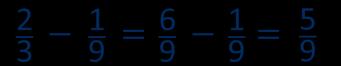

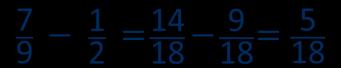


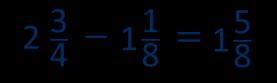
Progression of skills - Multiplication
Year group Skill
Nursery

• Continue with counting and subitising skills as a foundation for later work on equal groups. (see addition and subtraction sections)
Reception
• Double to 10
• Make equal groups
Year 1
• Count in 2s, 5s and 10s
• Add equal groups
• Make arrays
• Make doubles
Progression of skills - Multiplication
Year group Skill
Year 2
Year 3
• Link repeated addition and multiplication
• Use arrays
• Double
• The 2 times-table
• The 10 times-table
• The 5 times-table
• Missing numbers
• The 3 times-table
• The 4 times-table
• The 8 times-table
• Related facts
• Multiply a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - no exchange
• Multiply a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - with exchange
• Scaling
• Correspondence problems

Progression of skills - Multiplication
Year group Skill
Year 4
• Times-table facts to 12 × 12
• Multiply by 1 and 0
• Multiply 3 numbers
• Factor pairs
• Multiply by 10 and 100
• Related facts
• Mental strategies
• Multiply a 2 or 3-digit number by a 1-digit number
• Scaling
• Correspondence problems

Progression of skills - Multiplication
Year group Skill
Year 5
• Multiples and factors
• Square and cube numbers
• Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 1-digit number
• Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 2-digit number
• Multiply by 10, 100 and 1,000
• Mental strategies
• Multiply fractions by a whole number
• Multiply mixed numbers by a whole number
• Find the whole

Progression of skills - Multiplication
Year group Skill
Year 6
• Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 2-digit number
• Multiply by 10, 100 and 1,000
• Order of operations
• Multiply decimals by integers
• Multiply fractions by fractions
• Find the whole
• Calculations involving ratio

Multiplication
Reception

• Have a deep understanding of number to 10, including the composition of each number.
• Subitise (recognise quantities without counting) up to 5
• Automatically recall (without reference to rhymes, counting or other aids) number bonds up to 5 and some number bonds to 10, including double facts.
• Explore and represent patterns within numbers up to 10, including evens and odds, double facts and how quantities can be distributed equally.
Progression of skills Key representations
Double to 10
Prompt children to notice that double means twice as many and to notice that there are two equal groups.
Double … is … … is double …




Make equal groups
Provide opportunities to make equal groups when tidying up or during snack time. Encourage children to check that each group has the same amount.


There are … groups of …
There are … altogether.
























Multiplication
Year 1

• Count in multiples of twos, fives and tens.
• Solve one-step problems involving multiplication, using concrete objects, pictorial representations and arrays with the support of the teacher.
Progression of skills Key representations
Count in 2s, 5s and 10s
Begin by counting objects that naturally come in 2s, 5s and 10s, for example pairs of socks or fingers.
There are … equal groups of …
There are … altogether.







Add equal groups (repeated addition)
Children should be able to write a repeated addition to represent equal groups and to draw pictures or use objects to represent a repeated addition.
There are … groups of …
There are … altogether.


Continue to colour in ...s
What do you notice?
Complete the number track/number line by counting in …s.


What is the same? What is different?
Use objects or a drawing to represent the equal groups and find how many in total.
Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
Make arrays
Children use their knowledge of adding equal groups to arrange objects in columns and rows.
There are … rows of … There are … altogether. There are … columns of … There are … altogether.
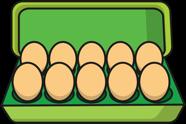

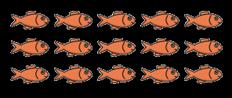


Make doubles
Children understand that doubles are two equal groups. Children may begin to explore doubles beyond 20 using base 10
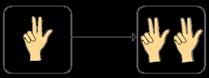








Double
Multiplication
Year 2

• Recall and use multiplication facts for the 2, 5 and 10 multiplication tables.
• Calculate mathematical statements for multiplication within the multiplication tables and write them using the multiplication (×) and equals (=) signs.
• Show that multiplication of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative).
Progression of skills Key representations
Link repeated addition and multiplication
Encourage children to make the link between repeated addition and multiplication.
There are … equal groups with … in each group.
There are … altogether.


Use arrays
Encourage children to see that multiplication is commutative.
There are … rows with … in each row.
There are … columns with … in each column.

Encourage children to make links with related facts.






Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
The 2 times-table
Encourage daily counting in multiples both forwards and back. Notice that all multiples of 2 are even numbers.
lots of 2 =
× 2 =




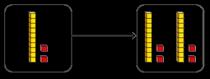
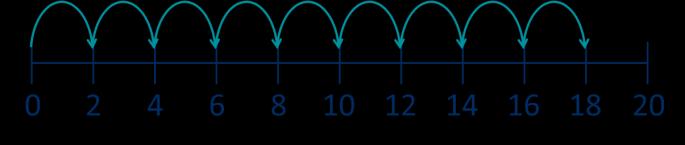
The 10 times-table
Encourage daily counting in multiples both forwards and back. Notice the pattern in the numbers.
















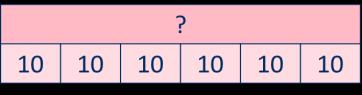






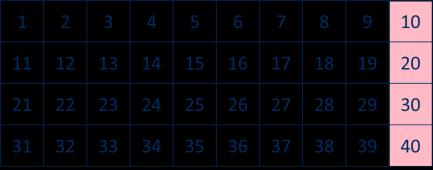
Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
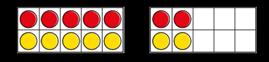
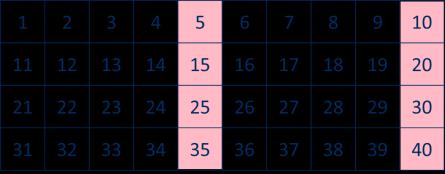
The 5 times-table
Encourage daily counting in multiples both forwards and back. Notice the pattern in the numbers.
lots of = … × 5 =







Missing numbers
Make links to known facts.


times is equal to …
Multiplication
Year 3

• Recall and use multiplication facts for the 3, 4 and 8 multiplication tables.
• Write and calculate mathematical statements for multiplication using the multiplication tables that they know, including for two-digit numbers times one-digit numbers, using mental and progressing to formal written methods.
• Solve problems, including missing number problems, involving multiplication, including positive integer scaling problems and correspondence problems in which n objects are connected to m objects.
Progression of skills Key representations
The 3 times-table
Encourage daily counting in multiples both forwards and back.

The 4 times-table
Encourage daily counting in multiples both forwards and back. Encourage children to notice links between the 2 and 4 times-tables.






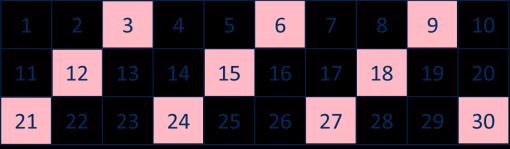









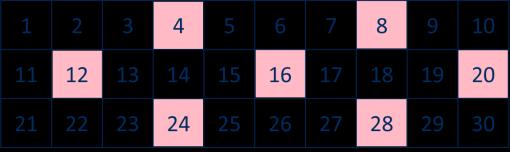
Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
The 8 times-table
Encourage daily counting in multiples both forwards and back. Encourage children to notice links between the 2, 4 and 8 times-tables.




… lots of 8 = × 8 = , … times = 8 × … = … times is equal to … 3 × 8 = 24 24 = 3 × 8

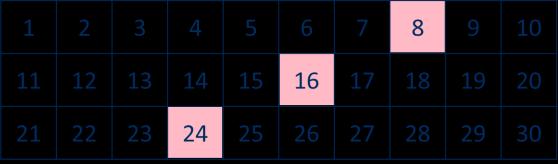
Related facts
Use knowledge of multiplying by 10 to scale times-table facts.

… × … ones is equal to … ones so … × … tens is equal to … tens.






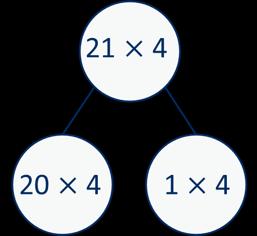
Multiply a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - no exchange
Children apply their understanding of partitioning to represent and solve calculations using the expanded method. … tens multiplied by … is equal to … tens. …ones multiplied by … is equal to … ones.
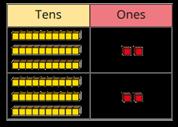
30 × 2 = 60
× 2 = 4
× 2 = 64 3 × 4 = 12 3 × 40 = 120
Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
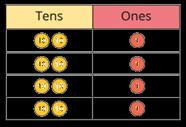
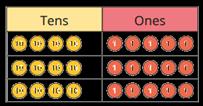
Multiply a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - with exchange
Children apply their understanding of partitioning to represent and solve calculations using the expanded method.
Scaling
Children focus on multiplication as scaling ( …. times the size) as opposed to repeated addition.

… tens multiplied by … is equal to … tens.
… ones multiplied by … is equal to … ones.

There are …. times as many … as …

… is … times the size of …
… is … times the length/height of …
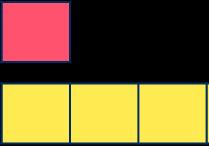
There are 3 times as many triangles as circles.
Miss Smith is twice the height of Jo.


Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
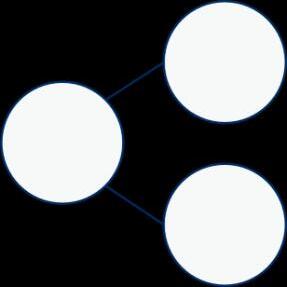
Correspondence problems
(How many ways?)
Encourage children to work systematically to find all the different possible combinations.
For every … , there are … possible ... There are … × … possibilities altogether.

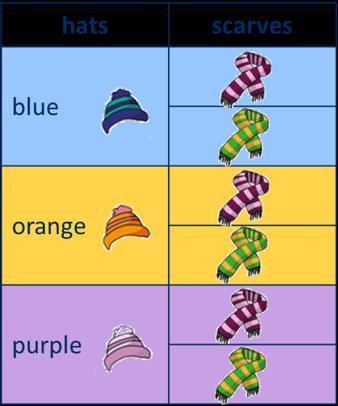

For every hat, there are two possible scarves.
3 × 2 = 6 There are 6 possibilities altogether.
Multiplication
Year 4

• Recall multiplication facts for multiplication tables up to 12 × 12
• Use place value, known and derived facts to multiply mentally, including: multiplying by 0 and 1; multiplying together three numbers.
• Recognise and use factor pairs and commutativity in mental calculations.
• Multiply two-digit and three-digit numbers by a one-digit number using formal written layout.
• Solve problems involving multiplying and adding, including using the distributive law to multiply two-digit numbers by one digit, integer scaling problems and harder correspondence problems such as n objects are connected to m objects.
Progression of skills Key representations
Times-table facts to 12 × 12
Encourage daily counting in multiples both forwards and back. Encourage children to notice links between related times-tables.
… groups of … = … times … is equal to …



Multiply by 1 and 0 Any number multiplied by 1 is equal to …
Any number multiplied by 0 is equal to …



Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
Multiply 3 numbers
Children use their understanding of commutativity to multiply more efficiently.

To work out … × … × …, I can first calculate … × … and then multiply the answer by …

Factor pairs
Children explore equivalent calculations using different factors pairs.

Multiply by 10 and 100
Some children may overgeneralise that multiplying by 10 or 100 always results in adding zeros. This will cause issues later when multiplying decimals.
When I multiply by 10, the digits move … place value column to the left.
… is 10 times the size of …

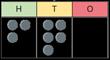
When I multiply by 100, the digits move … place value columns to the left. … is 100 times the size of …


Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
Related facts
Use knowledge of multiplying by 10 and 100 to scale times-table facts.
… × … ones is equal to … ones so … × … tens is equal to … tens and … × … hundreds is equal to … hundreds.

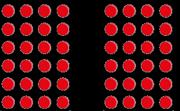
Mental strategies
Partition 2 or 3-digit numbers to multiply using informal methods.
… tens multiplied by … is equal to … tens. …ones multiplied by … is equal to … ones.


Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
Multiply a 2 or 3-digit number by a 1-digit number
The short multiplication method is introduced for the first time, initially in an expanded form.
To multiply a 2-digit number by … , I multiply the ones by … and the tens by …

To multiply a 3-digit number by … , I multiply the ones by … , the tens by … and the hundreds by …
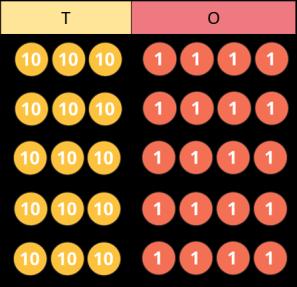
Scaling
Children focus on multiplication as scaling ( … times the size).
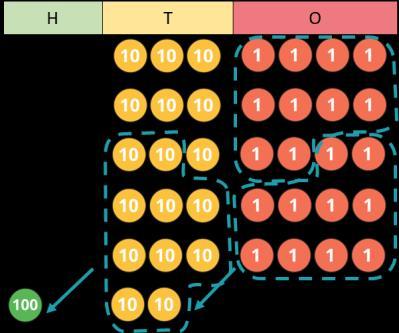
… is … times the size of …
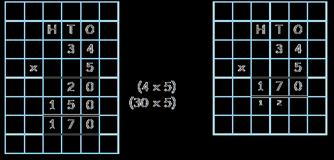
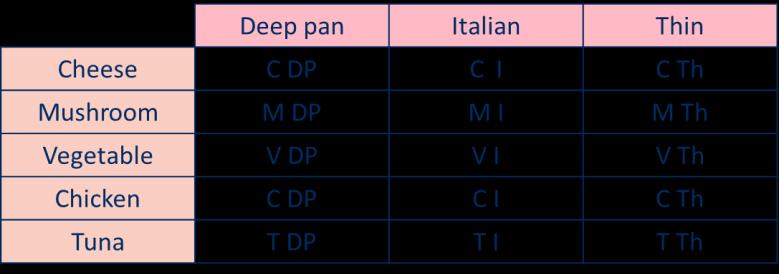
Correspondence problems
Encourage children to use tables to show all the different possible combinations.
A computer mouse costs £7 A red ribbon is 6 cm. A keyboard costs 6 times as much. A yellow ribbon is 7 times as long.
For every … , there are … possibilities. There are … × … possibilities altogether.
A pizza company offers a choice of 5 toppings and 3 bases.
5 × 3 = 15
Multiplication
Year 5

• Identify multiples and factors, including finding all factor pairs of a number, and common factors of two numbers
• Recognise and use square numbers and cube numbers, and the notation for squared (²) and cubed (³)
• Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a one- or two-digit number using a formal written method, including long multiplication for two-digit numbers.
• Multiply numbers mentally drawing upon known facts.
• Multiply whole numbers and those involving decimals by 10, 100 and 1000
• Multiply proper fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers, supported by materials and diagrams.
Progression of skills Key representations
Multiples and factors




Encourage children to notice patterns and make links with known facts. … is a multiple of … because

… is a factor of … because
The common factors of … and … are … Square and cube numbers
Factors of 20 Factors of 12

1, 2, 4 and 8 are factors of 8


Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
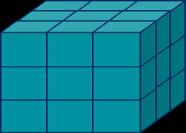
Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 1-digit number
This builds on the short multiplication method introduced in Y4

To multiply a 4-digit number by … , I multiply the ones by … , the tens by … , the hundreds by … and the thousands by …
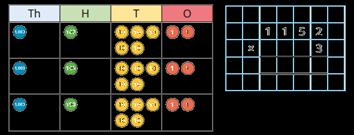
Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 2-digit number
Numbers are first partitioned using an area model then long multiplication is introduced for the first time.
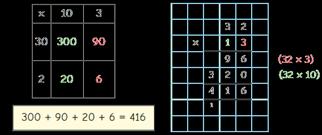
I can partition … into … and …
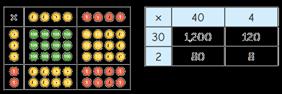
32 × 44 = 1,200 + 80 + 120 + 8
32 × 44 = 1,408
First, I multiply by the … Then I multiply by the ...
Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
Multiply by 10, 100 and 1,000
Some children may overgeneralise that multiplying by a power of 10 always results in adding zeros. This will cause issues later when multiplying decimals.
Mental strategies
Children continue to use efficient mental strategies such as partitioning and knowledge of factor pairs and related facts to multiply.
To multiply by 10/100/1,000, I move all the digits … places to the left.
… is 10/100/1,000 times the size of …
234 × 10 = 2,340
234 × 100 = 23,400
234 × 1,000 = 234,000
2.34 × 10 = 23.4
2.34 × 100 = 234
2.34 × 1,000 = 2,340
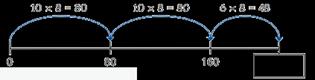
The most efficient strategy to calculate … × … is …
To calculate … × 12, I can do … × … × …
For example: 121 × 12
I could calculate 100 × 12 plus 20 × 12 plus 1 × 12
I could calculate 121 × 10 plus 121 × 2
I could calculate 121 × 6 × 2
I could calculate 121 × 4 × 3

Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
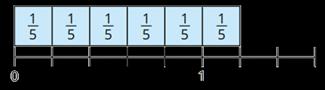
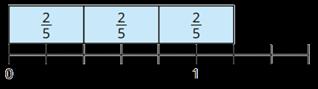
Multiply fractions by a whole number
Make links with repeated addition.
E.g. 1 × 4 = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1

To multiply a fraction by an integer, I multiply the numerator by the integer and the denominator remains the same.

Multiply mixed numbers by a whole number I can partition into and

Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations

Find the whole Children multiply to find the whole from a given part. If 1 is … , then the whole is … × … If is … , then 1 is … and the whole is … × …
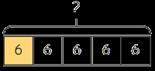
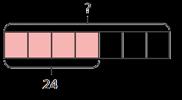
Multiplication
Year 6

• Identify common factors and common multiples.
• Multiply multi-digit numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit whole number using the formal written method of long multiplication.
• Multiply numbers by 10, 100 and 1,000
• Multiply one-digit numbers with up to two decimal places by whole numbers.
• Use their knowledge of the order of operations to carry out calculations involving the 4 operations.
• Multiply simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in its simplest form.
• Solve problems involving the relative sizes of two quantities where missing values can be found by using integer multiplication and division facts.
• Solve problems involving the calculation of percentages.
Progression of skills Key representations
Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 2-digit number
To multiply by a 2-digit number, first multiply by the ones, then multiply by the tens and then find the total.
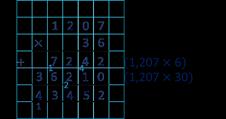
Multiply by 10, 100 and 1,000
Some children may overgeneralise that multiplying by a power of 10 always results in adding zeros.
To multiply by 10/100/1,000, I move all the digits … places to the left.
… is 10/100/1,000 times the size of …
234 × 10 = 2,340
234 × 100 = 23,400
234 × 1,000 = 234,000
0.234 × 10 = 2.34
0.234 × 100 = 23.4
0.234 × 1,000 = 234
Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
Order of operations
Calculations in brackets should be done first. Multiplication and division should be performed before addition and subtraction.

… has greater priority than …, so the first part of the calculation I need to do is …



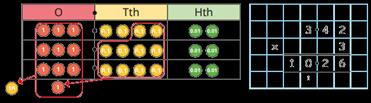
Multiply decimals by integers
This is the first time children multiply decimals by numbers other than 10, 100 or 1,000 Encourage them to make links with known facts and whole number multiplication.

Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
Multiply fractions by fractions
Encourage children to give answers in their simplest form.

When multiplying a pair of fractions, I need to multiply the numerator and multiply the denominator.
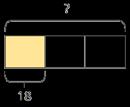
Find the whole
Children multiply to find the whole from a given part.
Multiplication
Progression of skills Key representations
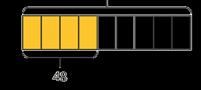
Calculate percentages
Children first learn how to find 1%, 10%, 20%, 25% and 50% before using multiples of these amounts to find any percentage.
There are … lots of … % in 100%
To find … %, I need to divide by …
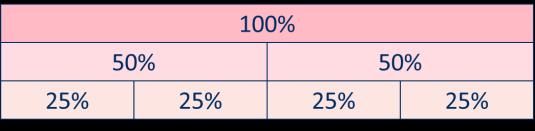
2 % of … = …÷ 4 … % is made up of … %, and … %
0% of … = …÷ 2
Calculations involving ratio
Encourage children to see the multiplicative relationship between ratios. They will need to multiply or divide each value by the same number to keep the ratio equivalent. Double number lines and ratio tables help children to see both horizontal and vertical multiplicative relationships.


To find 30%, I can find 10% and then multiply it by 3
To find 23%, I can use 10% × 2 and 1% × 3
To find 99%, I can find 1%, then subtract from 100%
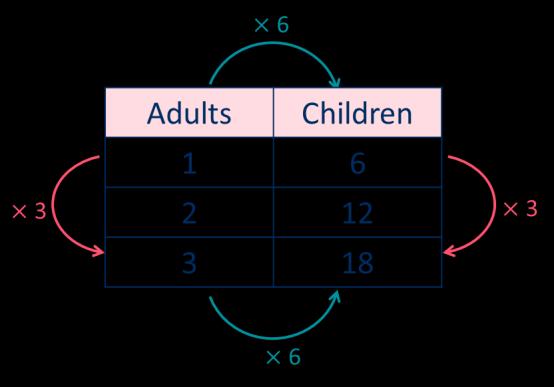
For every … , there are … The ratio of adults to children is 1 : 6

Progression of skills - Division
Year group Skill
Nursery

• Continue with counting and subitising skills as a foundation for later work on equal groups. (see addition and subtraction sections)
Reception
• Sharing
• Grouping
Year 1
• Make equal groups – grouping
• Make equal groups – sharing
• Find a half
• Find a quarter
Progression of skills - Division
Year group Skill
Year 2
Year 3
• Divide by 2
• Divide by 10
• Divide by 5
• Missing numbers
• Unit fractions
• Non-unit fractions
• Divide by 3
• Divide by 4
• Divide by 8
• Related facts
• Divide a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - no exchange
• Divide a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - with remainders
• Unit fractions of a set of objects
• Non-unit fractions of a set of objects

Progression of skills - Division
Year group Skill
Year 4
• Division facts to 12 × 12
• Divide a number by 1 and itself
• Related facts
• Divide a 2 or 3-digit number by a 1-digit number
• Divide by 10 and 100
Year 5
• Mental strategies
• Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a 1-digit number
• Divide by 10, 100 and 1,000
• Fraction of an amount

Progression of skills - Division
Year group Skill
Year 6
• Short division
• Mental strategies
• Long division
• Order of operations
• Divide by 10, 100 and 1,000
• Divide decimals by integers
• Decimal and fraction equivalents
• Divide a fraction by an integer
• Fraction of an amount
• Calculate percentages
• Calculations involving ratio

Division
Reception

• Have a deep understanding of number to 10, including the composition of each number.
• Subitise (recognise quantities without counting) up to 5
• Automatically recall (without reference to rhymes, counting or other aids) number bonds up to 5 and some number bonds to 10, including double facts.
• Explore and represent patterns within numbers up to 10, including evens and odds, double facts and how quantities can be distributed equally.
Progression of skills Key representations
Sharing
Provide practical activities such as sharing items during snack time. Encourage children to check whether items have been shared fairly (equally).
Grouping
Provide opportunities to make equal groups when tidying up or during snack time. Encourage children to check that each group has the same amount.
There are … altogether. They are shared equally between … groups.


There are … groups of …
There are … altogether.






Division
Year 1

• Solve simple one-step problems involving division, using concrete objects, pictorial representations and arrays with the support of the teacher.
• Recognise, find and name a half as one of two equal parts of a quantity.
• Recognise, find and name a quarter as one of four equal parts of an object, shape or quantity.
Progression of skills Key representations
Make equal groupsgrouping
Encourage children to physically move objects into equal groups. They can also circle equal groups when using pictures.
There are … altogether.
How many groups of … can you make?


Make equal groups –sharing
Encourage children to check that the objects have been shared fairly and each group is the same.
Circle groups of 2
There are … groups of 2

… have been shared equally between…
There are … on/in each …


Take … cubes.
Take … cubes. Make equal groups.
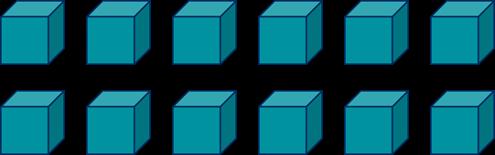
There are … groups of …
Share them between …

12 shared between … is …
Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Find a half
Start with practical opportunities to share a quantity into 2 groups.
Progress to circling half of the objects in a picture and then to finding the whole from a given half.
To find half, I need to share into 2 equal groups.




Half of … is … If … is half, what is the whole? is half of …
Find a quarter
Start with practical opportunities to share a quantity into 4 groups.
Progress to using pictures or bar models to find a quarter and then to finding the whole from a given quarter.
There are … in each group.
To find a quarter, I need to share into 4 equal groups.

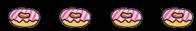
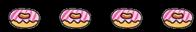
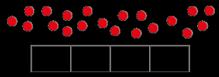
There are … in each group.
A quarter of … is … If … is one quarter, what is the whole? is one quarter of …
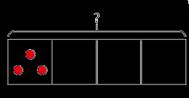
Division
Year 2

• Recall and use division facts for the 2, 5 and 10 multiplication tables.
• Calculate mathematical statements for division within the multiplication tables and write them using the division (÷) and equals (=) signs.
• Recognise, find, name and write fractions 1 , 1 , 2 and of a quantity.
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide by 2
Encourage children to compare the grouping and sharing structures of division and to make links with times-table facts and halving.





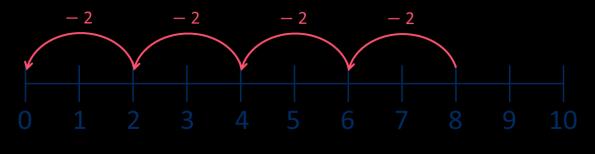
Divide by 10
Encourage children to compare the grouping and sharing structures of division and to make links with times-table facts.
There are … equal groups of 10













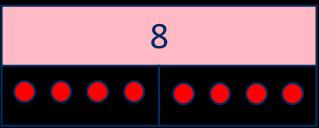




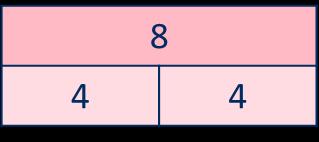










Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide by 5
Encourage children to compare the grouping and sharing structures of division and to make links with times-table facts.
There are … equal groups of
=










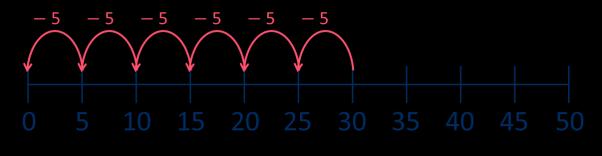


shared equally between is …
















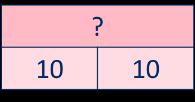
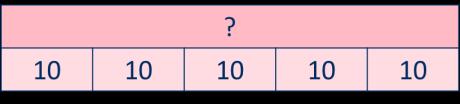
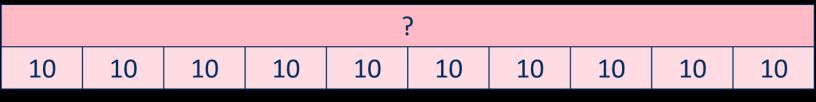
Missing numbers
Bar models are useful to show the link between multiplication and division. … divided by 2/ /10 is equal to …
Division
Progression of skills Key representations
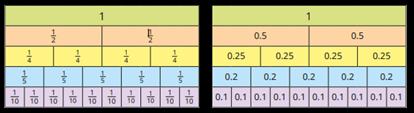
Unit fractions
In Y2 the focus is on finding 1 2 , 1 and 1 Bar models are useful to show the link between division and finding a fraction.
Non-unit fractions
In Y2 the focus is on finding 2 and Prompt children to notice that 2 is equivalent to 1 2
The objects have been shared fairly into … groups. 1 of … is ...











The objects have been shared fairly into … groups. of … is ...













There are … equal parts. There is … part circled. 1 is circled.

There are … equal parts. There are … parts circled. is circled.
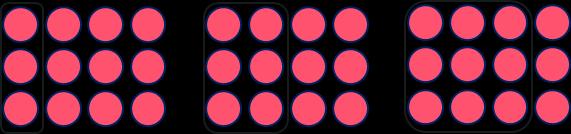
Division
Year 3

• Recall and use division facts for the 3, 4 and 8 multiplication tables.
• Write and calculate mathematical statements for division using the multiplication tables that they know, including for two-digit numbers times one-digit numbers, using mental and progressing to formal written methods.
• Recognise, find and write fractions of a discrete set of objects: unit fractions and nonunit fractions with small denominators.
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide by 3
Encourage children to compare the grouping and sharing structures of division and to make links with times-table facts.
There are … groups of in …


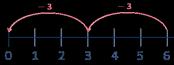
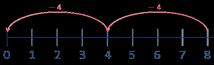
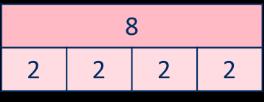
Divide by 4
Encourage children to compare the grouping and sharing structures of division and to make links with times-table facts.
There are … groups of in …



been shared equally into equal groups.



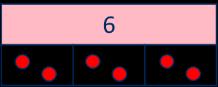
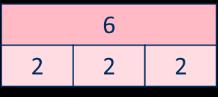
… has been shared equally into equal groups.












Division
Progression of skills Key representations
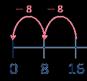
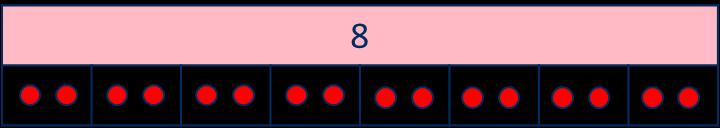
Divide by 8
Encourage children to compare the grouping and sharing structures of division and to make links with times-table facts.
There are … groups of in …


Related facts
Link to known times-table facts.

= … has been shared equally into equal groups.






Divide a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - no exchange
Partition into tens and ones to divide and then recombine. … tens divided by … is equal to … tens. … ones divided by … is equal to … ones.



Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number - with remainders
Encourage children to partition numbers flexibly to help them to divide more efficiently.
… tens divided by … is equal to … tens. … ones divided by … is equal to … ones.
There are … groups of … There are … remaining.

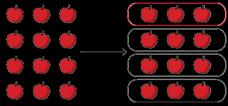
Unit fractions of a set of objects
Bar models are useful to show the link between division and fractions, for example, dividing by 3 and finding a third.


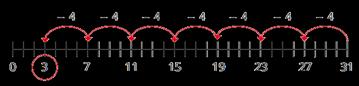
The whole is divided into … equal parts.
Each part is 1 of the whole. 1





Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Non-unit fractions of a set of objects
Bar models are a useful representation and show the links with division and multiplication.
The whole is divided into … equal parts.

Each part is 1 of the whole. of 12 apples is 9 apples.
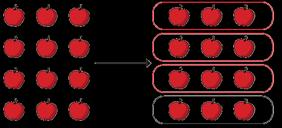
1 of … is …, so of … is … of 12 is 9




2 of 36 is 24

Division
Year 4

• Recall division facts for multiplication tables up to 12 × 12
• Use place value, known and derived facts to divide mentally, including: dividing by 1
• Find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as ones, tenths and hundredths.
Progression of skills Key representations
Division facts to 12 × 12
Encourage children to compare the grouping and sharing structures of division and to make links with times-table facts.
There are … groups of … in …
… has been shared equally into … equal groups.







Divide a number by 1 and itself
Children may try to divide a number by zero and it should be highlighted that this is not possible.






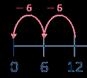
When I divide a number by 1, the number remains the same.
5 shared between 1 is 5

There are 5 groups of 1 in 5

When I divide a number by itself, the answer is 1
5 shared between 5 is 1

There is 1 group of 5 in 5

Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Related facts
Link to known times-table facts. … ÷ … is equal to … so … tens ÷ … is equal to … tens and … hundreds ÷ … is equal to … hundreds.

Divide a 2 or 3-digit number by a 1-digit number
Progress from divisions with no exchange, to divisions with exchange and then divisions with remainders.
I can partition … into … tens and … ones.

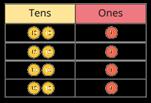

I cannot share the hundreds/tens equally, so I need to exchange 1 … for 10 …
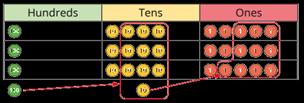
Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide by 10 and 100
Encourage children to notice that dividing by 100 is the same as dividing by 10 twice.
When I divide by 10, the digits move 1 place value column to the right. … is one-tenth the size of …
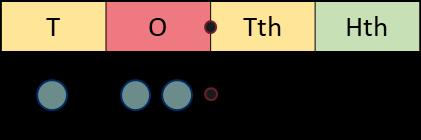
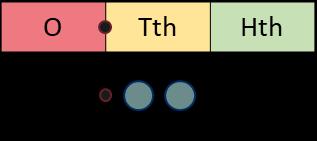
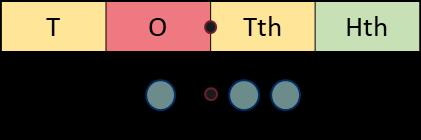

When I divide by 100, the digits move 2 place value columns to the right. … is one-hundredth the size of …

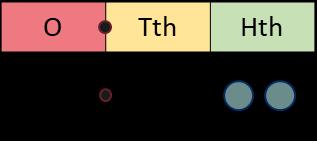
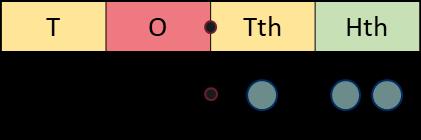
Division
Year 5

• Divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts.
• Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit number using the formal written method of short division and interpret remainders appropriately for the context.
• Divide whole numbers and those involving decimals by 10, 100 and 1,000
Progression of skills Key representations
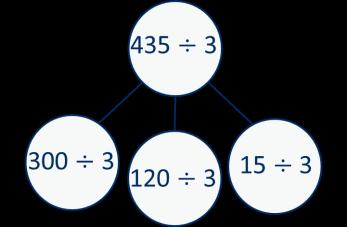
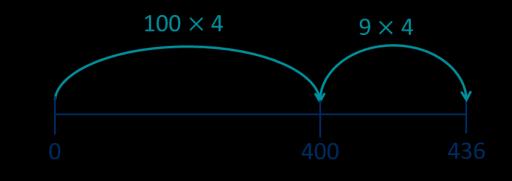
Mental strategies I can partition … into … and … to help me to divide more easily.

Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a 1-digit number
The short division method is introduced for the first time.
I can show groups of … on a number line.
There are … groups of … hundreds/tens/ones/ in … I can exchange 1 … for 10 …

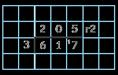
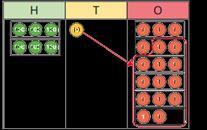
To divide by …, I can divide by … and then divide the result by …

Division
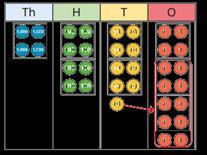
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide by 10, 100 and 1,000
Encourage children to notice that dividing by 100 is the same as dividing by 10 twice, and that dividing by 1,000 is the same as dividing by 10 three times.
To divide by 10/100/1,000, I move all the digits … places to the right. … is one-tenth/one-hundredth/one-thousandth the size of …
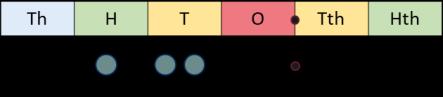
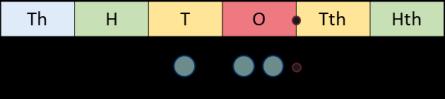
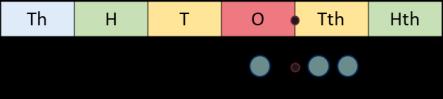

Fraction of an amount
Bar models support children to understand that to find a fraction of an amount, we divide by the denominator and multiply by the numerator.

÷ 10 = 12
÷ 100 = 1.2
To find of … , I need to divide by … and multiply by … If 1 is … , then the whole is … × …



Division
Year 6

• Perform mental calculations, including with mixed operations and large numbers.
• Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit whole number using the formal written method of long division, and interpret remainders as whole number remainders, fractions, or by rounding, as appropriate for the context.
• Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit number using the formal written method of short division where appropriate, interpreting remainders according to the context.
• Divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1,000 giving answers up to three decimal places.
• Use written division methods in cases where the answer has up to two decimal places.
• Associate a fraction with division and calculate decimal fraction equivalents.
• Divide proper fractions by whole numbers [for example, 1 ÷ 2 = 1 ]
• Solve problems involving the calculation of percentages.
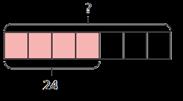
Progression of skills Key representations
Short division
Encourage children to interpret remainders in context, for example knowing that “ remainder 1” could mean complete boxes with 1 left over so 5 boxes will be needed.
There are … groups of … hundreds/tens/ones/ in … I can exchange 1 … for 10 …
Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Mental strategies
Include partitioning and number line strategies outlined in Y5 as well as division using factors.
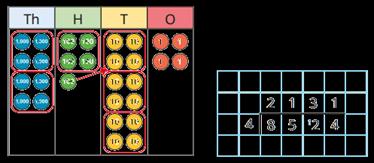
Long division
The long division method is introduced for the first time. Two alternative methods are shown.
Order of operations
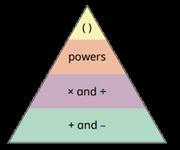
Calculations in brackets should be done first, then powers. Multiplication and division should be performed before addition and subtraction.
To divide by … , I can first divide by … and then divide the answer by …
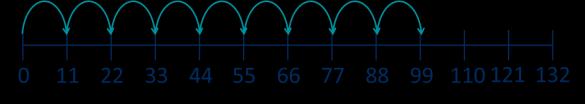
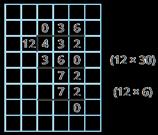
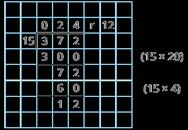
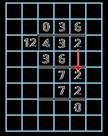
240 ÷ 60 = 240 ÷ 10 ÷ 6


480 ÷ 24 = 480 ÷ 4 ÷ 6 9,120 ÷ 15 = 9,120 ÷ 5 ÷ 3

Method 1
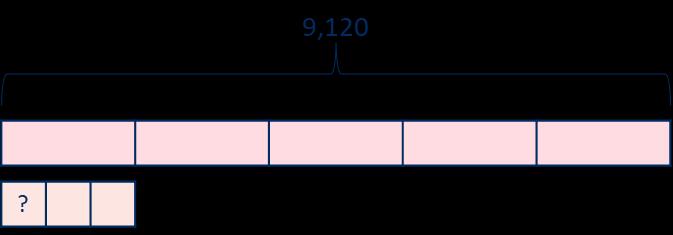
Method 2
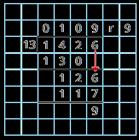
… has greater priority than …, so the first part of the calculation I need to do is …





















(6 + 4) ÷ 2 = 5 6 + 4 ÷ 2 = 8
Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide by 10, 100 and 1,000
Encourage children to notice that dividing by 100 is the same as dividing by 10 twice, and that dividing by 1,000 is the same as dividing by 10 three times.
Divide decimals by integers
To divide by … , I move the digits … places to the right.
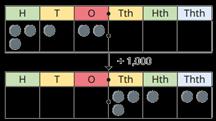
This is the first time children divide decimals by numbers other than 10, 100 or 1,000



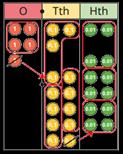
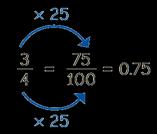
Decimal and fraction equivalents The fraction … is equivalent to the decimal … is equal to


Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Divide a fraction by an integer
This is the first time children divide fractions by an integer.

… ones divided by 2 is … ones so … sevenths divided by 2 is … sevenths. I am dividing by … , so I can split each part into … equal parts. … is equivalent to … so …÷ … = …÷ …


Fraction of an amount
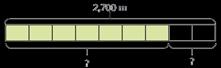
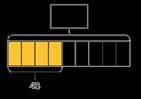
Children divide and multiply to find fractions of an amount. Bar models can still be used to support understanding where needed.


To find 1 I divide by … If 1 is equal to …, then are equal to … If is equal to …, then the whole is equal to …
Division
Progression of skills Key representations
Calculate percentages
Children first learn how to find 1%, 10%, 20%, 25% and 50% before using multiples of these amounts to find any percentage.
There are … lots of … % in 100%
To find … %, I need to divide by …

0% of … = …÷ 2
2 % of … = …÷ 4 … % is made up of … %, and … %

Calculations involving ratio
Encourage children to see the multiplicative relationship between ratios. They will need to multiply or divide each value by the same number to keep the ratio equivalent. Double number lines and ratio tables help children to see both horizontal and vertical multiplicative relationships.
For every … , there are …

To find 30%, I can find 10% and then multiply it by 3
To find 23%, I can use 10% × 2 and 1% × 3
To find 99%, I can find 1%, then subtract from 100%
For every 6 children on a school trip, there is 1 adult.

