
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Amina Meeran O.M1 , Erfana M.A2 , Milan Jaleel3, Parvathy Vijay4
1Bachelor of Technology in Civil Engineering, APJ Abdul Kalam Technological University, Kerala, India
2Bachelor of Technology in Civil Engineering, APJ Abdul Kalam Technological University, Kerala, India
3Bachelor of Technology in Civil Engineering, APJ Abdul Kalam Technological University, Kerala, India
4Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Ilahia College of Engineering and Technology, Kerala, India
Abstract - Black cotton soil is an expansive soil known for its significant swelling and shrinkage properties, posing challenges for lightly loaded structures due to its weak engineeringproperties.Thestudyexaminesthestabilizationof black cotton soil using eco-friendly additives Xanthan Gum (XG) and Coconut Fiber (CF) to enhance its geotechnical performance.TheexperimentalprogramincludedAtterberg's limits, Standard Proctor test, California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test, and Unconfined Compression Strength (UCS) test conducted on soil samples treated with varying percentages (0.25%, 0.5%, 0.75%, and 1%) of Xanthan Gum and Coconut Fiber. Results indicated that the liquid limit and plasticity index decreased whilethecompactionandstrengthproperties improvedsignificantly.Theoptimumcombinationof0.75%XG and 0.5% CF achieved the highest UCS of 79 kN/m² and improved cohesion to 39.5 kN/m². The CBR value at 5 mm penetration increased to 2.23%, demonstrating enhanced load-bearing capacity. Maximum dry density reduced with increasing XG and CF content due to lighter material incorporation,whiletheoptimummoisturecontentimproved, favouring better soil workability. The research validates the potentialof XGandCFassustainablesoilstabilizers,offeringa cost-effective solution for improving the engineering properties of expansive soils, ensuring stability in structural foundations.
Key Words: Black Cotton Soil, Soil Stabilization, Xanthan Gum (XG), Coconut Fiber (CF), Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS), California Bearing Ratio (CBR).
Soilisavitalsubstanceusedforconstructionpurposessoit is very important to acknowledge the properties and feasibilitiesofsoilbeforeusinginanykindofconstruction process.ManyareasinIndiaconsistofsoilswithhighclayor siltcontents,lowstrengthsandpoorbearingcapacities.The stabilizationofsoilisaneffectivemethodforimprovingsoil properties and pavement performance. There are many stabilizationmethodswhichincludesphysical,chemical,or polymer,amongthemusingdifferentstabilizingagents,may be effective to improve the soil properties rather than removing and replacing the materials. Availability or financial considerations may also taken as a determining factoronwhichastabilizingagentisselected.
Toaddresstheconcernsregardinghighcostsandsignificant environmental impactslike elevatedcarbon emissions, an eco-friendlycombinationofxanthangumwhichisanatural biopolymer derived from microbial fermentation and coconut fiber which is a renewable and biodegradable materialisused.
The main objective of soil stabilization is to improve the strength and stability of the soils and also to lower the constructioncost.Thestabilityandbearingcapacityofsoil dependsonshearstrength,whichisdirectlyproportionalto the soil type and conditions. In some situations, the soils whichdonothavethedesiredengineeringpropertieswill produce satisfactory strength when the additives on soil blendeachother.Thesematerialswillbemorestableand fulfilthedesiredconditions.
2.
Tostudythegeneralcharacteristicsofthesoil
To study the characteristics of soil with varying percentagesofXanthanGumandCoconutFiber.
Tocomparethetestresultsofblackcottonsoiland thesoilwithvaryingpercentagesofXanthanGum andCoconutFiber
3. METHODOLOGY
It involves the collection of materials and standard laboratorytestsintheblackcottonsoil.
3.1 Materials Used
3.1.1
Thissoilisalsoknownasregursoilwhichischaracterized by its dark color, high clay content and unique properties such as swelling when wet and shrinking when dry. The expansive and shrinkage behaviors can lead to significant challenges in construction, as they may cause foundation movement and cracking. To improve its performance of stabilization, sustainable materials like xanthan gum and coconutfiberareused.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The soil sample was collected from Perumatty, Palakkad, Kerala.

Fig -1: BC soil
3.1.2 Xanthan Gum
Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide commonly used as a thickening agent and a stabilizer in various industries produced by fermenting simple sugars with a bacterium calledXanthomonascampestris.

Fig -2: Xanthan Gum
Table -1: ChemicalcompositionofXanthanGum
3.1.3 Coconut Fiber

Fig -3: Coconut Fiber
Table -2: ChemicalcompositionofCoconut Fiber
Thesoilismixedatvarious combinations ofXG andCF to improve the strength and bearing capacity. The various combinations of samples which includes in this paper are follows:
Table -3: CompositionsofSample
Sample Name Particulars of the Sample
Sample1 Soil+XG-0%+CF-0%
Sample2 Soil+XG-0.25%+CF-0.25%
Sample3 Soil+XG-0.5%+CF-0.5%
Sample4 Soil+XG-0.75%+CF-0.75%
Sample5 Soil+XG-1%+CF-1%
Sample6 Soil+XG-0.25%+CF-0.5%
Sample7 Soil+XG-0.5%+CF-0.25%
Sample8 Soil+XG-0.5%+CF-0.75%
Sample9 Soil+XG-0.75%+CF-0.5%
Sample10 Soil+XG-0.75%+CF-1%
Sample11 Soil+XG-1%+CF-0.75%
Itisanaturalmaterialextractedfromtheouterhuskof coconuts. Itimprovesthemechanicalpropertiesofthesoil byaddingreinforcement,increasingitsshearstrength,and reducingerosion.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Thesoilsamplewithvaryingcompositionsof0,0.25%,0.5%, 0.75% and 1% of XG and CF are prepared and tests are performed.Theexperimentalstudiesaredoneasmentioned intable-3respectively.
It is to determine the liquid limit, plastic limit, shrinkage limit and plasticity index of BC soil. The liquid limit (LL) indicatesthemoisturecontentatwhichsoilchangesfrom plastictoliquidstatewhichismeasuredusingCasagrande apparatus,Theplasticlimit(PL)isthemoisturecontentat which the soil can be rolled into thin threads (3 mm diameter)withoutcrumblingandtheshrinkagelimit(SL)is themoisturecontentwherefurtherdryingdoesnotreduce soil volume. The difference between the liquid limit and plasticlimitiscalledplasticityindex(PI)whichmeasuresthe soil'splasticity.
Table -4: ValuesofAtterberg’sLimitTest




International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
4.2 California Bearing Ratio Test (IS:2720-PART 16-1987)
This test is for assessing the strength and load-bearing capacityofsubgradesoils,whichformtheforstructuressuch asroads,pavements,andbuildings.BydeterminingtheCBR value, we can evaluate whether the soil is suitable for constructionorifitrequiresstabilizationorreplacement.The test results guide the design of proper foundation thicknesses,pavementlayers,andotherstructuralelements toensuredurabilityandstability.
Table -5: ValuesofCBRTest

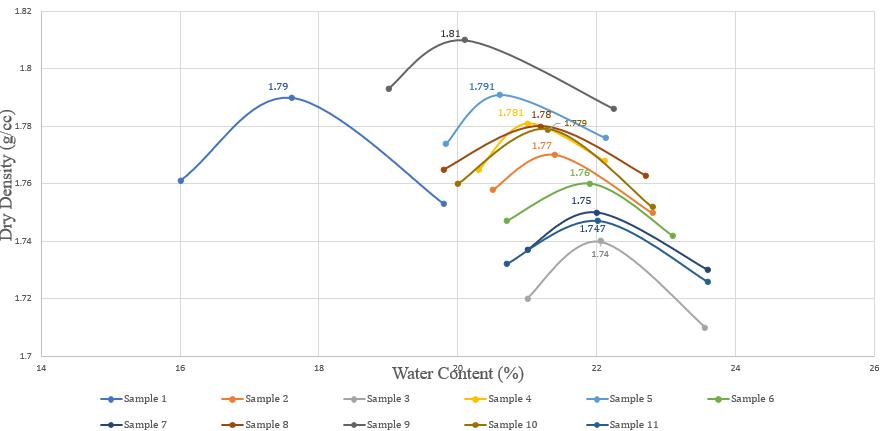
4.3 Standard
(IS: 2720-PART 7-1980)
Thistestisusedtodeterminetheoptimalmoisturecontent (OMC)andmaximumdrydensity(MDD)ofasoilsampleand also helps to establish the relationship between soil moisture and compaction, which is critical for ensuring stabilityandstrength.
Table -6: ValuesofCompactionTest
4.4 Unconfined Compression Test (IS: 2720- PART 10-1991)
Thistestisusedfordeterminingthecompressivestrengthof cohesive soils without lateral confinement. The test continues until the sample fails, and the corresponding stressatfailureisrecordedastheunconfinedcompressive strength(UCS).

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Table -7: ValuesofUCCTest



-9: UCC Graph 5.
The study concludes with several significant observations about the stabilization of black cotton soil using xanthan gum(XG)andcoconutfiber(CF):
The research confirms that the addition of 0.75% xanthangumand0.5%coconutfiberprovidesthe most effective stabilization. Thismix achievesthe highestcompressivestrengthandbearingcapacity,
marking it as the optimal percentage for soil enhancement.
The improvement in liquid limit and plastic limit reduces soil swelling, which is crucial for maintaining its structure under varying moisture conditions. And decrease in the shrinkage limit prevents soil shrinkage, ensuring dimensional stability.
The increase in UCC and CBR values highlights significantadvancementsinthesoil'sabilitytobear loads, resist settlement, and achieve greater stability.
TheuseofXGandCFasbiopolymersshowcasesthe potential of eco-friendly and sustainable soil stabilization methods. These additives not only enhance soil performance but also align with environmentalconservationgoals.
This paper emphasizes the importance of incorporating natural materials to promote sustainable construction practices as It paves the way for eco-conscious engineering solutions that balance strength, stability, and environmental responsibility.
[1] Arab, M.G., Mousa, R.A., Gabr, A.R., Azam, A.M., ElBadawy,S.M.,Hassan,A.F,“Resilientbehaviorofsodium alginate-treated cohesive soils for pavement applications”,JournalofMaterialsinCivilEngineering, vol.31,Nov2018,https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.19 43-5533.0002565.
[2] B. Irem, J. Akbar, & A. Selim, “Strength properties of xanthan gum and guar gum treated kaolin at differentwatercontents”,JournalofRockMechanicsand Geotechnical Engineering, vol 13,Ocb 2021,pp. 11601172,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.06.007.
[3] Jayaprakash Reddy, B.J.S. Vara,” Long-term and durabilitypropertiesofxanthangumtreateddispersive soils – An eco-friendly material, material today proceeding,vol44, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.472
[4] R. Joga, B.J. Varaprasad.” Effect of xanthan gum biopolymer on dispersive properties of soils”, World Journal of Engineering, vol 17Jul 2020, pp. 563-571, https://doi.org/10.1108/WJE-05-2020-0152