Bio regulators and Peptides – The Science Behind the Biochemistry of Women’s Health

Holtorf, MD


Holtorf, MD


Youthful Hormone Restoration
Replacing hormones to more youthful levels



Augmentation, optimization, and replacement using peptides and bioregulators 1 2 3 4
While aging cannot be stopped, the “normal” aging process can be slowed with hormone optimization.
Hormone Optimization (Bioidentical vs. Synthetic)
Prevent age-related symptoms, conditions and illness, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, weight gain, mental decline, depression, osteoporosis, loss of libido and sexual function, frailty and cancer.
Significant improvement in quality of life.
Live longer but more importantly, live better longer.

Estrogen
30% drop by age 50, then a sharp drop with fluctuations in menopause.
Progesterone
75% loss from age 35 to 50, then continuing decline.
Human Growth
Hormone DHEA, Pregnenolone
Testosterone
50% loss from age 25 to 50 followed by an additional 50% loss by age 75
The term “bioidentical” refers to a hormone, though chemically synthesized, has the same molecular structure as the hormone produced in the human body, including progesterone, estriol, estradiol and testosterone (focus today on bioidentical estrogen and progesterone vs. synthetic HRT)
Nonbioidentical hormones are not structurally identical to human hormones and may either be chemically synthesized, such as MPA, or derived from a nonhuman source, such as CEE.
Bioidentical hormones often referred to as “natural hormones,” which can be confusing because bioidentical hormones are synthesized while some estrogens from a natural source, such as equine urine (Premarin), are not considered bioidentical because many of their components are foreign to the human body.

Endocrine Society
“There is little or no evidence to support the claim that bioidentical hormones are safer or more effective than the commonly used synthetic versions of hormone replacement therapy (HRT).”
Issucha stancesurprisingwhen consideringthatapproximately 70%ofthesesocieties’fundingis fromdrugcompanies?

North American Menopause Society (NAMS)
Mirrors the Endocrine Society
Ihireda privateinvestigatorto tracethesourceofNAMSfunding, whichwasimpossibleduetoa labyrinthofBigPharma funded nonprofits.
“The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a long-term study of a large number of women taking traditional hormone therapy or placebo, has raised concerns about hormone therapy. This has created an environment for the propagation in the lay media of the scientifically unproven idea that bioidentical hormones are safer and more effective than traditional hormone therapy.”
“No medical or scientific evidence exists to support the idea that the adverse and/or beneficial effects found in the WHI resulted from the molecular structure of the synthesized hormones.”
The proverb “There are none so blind as those who will not to see” fits well here.
Consensus statements and expert opinion by respected authorities/societies are the poorest level of evidence, below that of anecdotal cases
Only 11% of the recommendations, practice guidelines and consensus statements were based on quality evidence
Over half of the strongest recommendations were based on poor quality evidence, little more than the panel’s opinion.
Even the strongest (Class 1) recommendations, considered medical dogma and cited as a legal standard, were only supported by high-quality evidence 19% of the time and were not revised based on new evidence.
See, Why Doesn't My Doctor Know This; at the nonprofit, National Academy of Hypothyroidism and Integrative Science NAHIS.org link: https://nahypothyroidism.org/why-doesntmy-doctor-know-this/?
1. Amerling R, et al. “Guidelines have done more harm than good, ”Blood Purification2008;26;73-76.
2. Guirguis-Blake J, et al. “Current processes of the U.S.Preventive Services Task Force: refining evidence-based recommendation development”. Ann. Intern. Med2007; 147(2):117–22. 3. Barton MB, Miller T, Wolff T, et al. “How to read the new recommendation statement: methods updatefrom the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force,” Ann. Intern. Med 2007;147(2):123–7. 4. CEBM > EBM Tools > Finding the Evidence > Levels of Evidencehttp://www.cebm.net/levels_of_evidence.asp#levels.
5. Atkins D, et al. “Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations,”BMJ 2004;328 (7454):1490.
Sackett DL, et al. “Evidence based medicine:what it is and what it isn’t”. BMJ 312 (7023): 71–2. 8. Zoler ML. Half of cardiac guidelines are not evidence based: Expert opinion under scrutiny,” Internal Medicine News 2009;42(7):1,8. 1 2 3 4 5
Tricoci P, Allen JM, Kramer KM, et al. Scientific evidnce underlying the ACC/AHA clincal practice guidelines.JAMA 2009;301(8):831-841.

• Hear that because there is no study comparable to WHI cannot say bioidentical hormones are any safer
• Ridiculous, that is not evidence-based medicine
Physicians must translate both basic science results and clinical outcomes to decide on the safest, most efficacious treatment for patients.
Evidence-based medicine involves the synthesis of all available data when comparing therapeutic options for patients.

4
Rather, it demands an assessment of the current available data to decide which therapies are likely to carry the greatest benefits and the lowest risks for patients.
Evidence-based medicine does not mean that data should be ignored until a randomized control trial of a particular size and duration is completed.
• The WHI study demonstrated that when MPA was added to Premarin, there was a substantial increase in the risk of heart attack, stroke, blood clots and breast cancer.
• This was an expected outcome with MPA, as it has clearly been shown to not only negate any cardioprotective effects of estrogen, but also to actually promote cardiovascular disease and increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, blood clots and breast cancer.
• Studies show that bioidentical estrogen and progesterone, on the other hand, have an opposite effect. They maintain and augment the cardioprotective effects of estrogen and decrease the risk of heart attack, stroke and breast cancer

“A
different outcome would likely have occurred if transdermal estrogen and natural progesterone was used or if treatment had been started at an earlier point in menopause.”
Risks and Benefits of Estrogen Plus Progestin in Healthy Postmenopausal Women
Principal Results From the Women's Health Initiative Randomized Controlled Trial Writing Group for the Women’s Health Initiative Investigators. AMA. 2002;288:321333.
A follow-up analysis of the continued WHI data, estimates that 50,000 (potentially up to 91,000) women have died prematurely between 2002 and 2011 after they stopped taking hormone-replacement therapy (HRT) because of results of WHI
No women with hysterectomy who stopped taking estrogen in the WHI lived to age 70
Sarrel PM, Valentine YN, Vinante V, et al. The Mortality Toll of Estrogen Avoidance: An Analysis of Excess Deaths Among Hysterectomized Women Aged 50 to 59 Years American Journal of Public Health: September 2013, Vol. 103, No. 9, pp. 15831588.

20 years of studies have shown that bioidentical hormones are safer and not associated with risks of synthetic hormones
Why is there still a debate?
I reviewed all the data comparing bioidentical HRT to synthetic hormone replacement
Holtorf, K. The Bioidentical Hormone Debate: Are Bioidentical Hormones (Estradiol, Estriol, and Progesterone) Safer or More Efficacious than Commonly Used Synthetic Versions in Hormone Replacement Therapy? Postgraduate Medicine 2009 Jan;121(1):73-85. Can freely download at: https://integrativepeptides.com/published_studies


The N. A Menopause Society Actively tried to prevent the publication of this paper. Several journal editors let us know, with significant risk to their employment, that they were pressured to not publish the paper, intimately saying, "There was nothing we can do."
I had a PR company at the time who told me they could no longer work with me because they were working with Pfizer, the makers of Prempro, who felt it was a conflict of interest to work with both of us.


Surprising that bioidentical and synthetic hormones have different effects?

Premarin is composed of 200 molecules of estrogen. Most are foreign to human estrogen

Four studies of patients using HRT, including either progesterone or MPA, compared efficacy, patient satisfaction, and quality of life.
Women in all 4 studies reported greater satisfaction, fewer side effects, and improved quality of life when they were switched from synthetic progestins to progesterone replacement.
J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2000;9(4):381–387
Menopause. 2002;9:253–263
Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100(5 pt 1):853–863
Obstet Gynecol. 1998;92(6):982–988
Fitzpatrick et al. Study (Cross-Sectional Survey)
• Compared patient satisfaction and quality of life in 176 menopausal women on HRT with MPA vs. HRT with progesterone.
• Significant differences were seen for all somatic, vasomotor, and psychological symptoms, except for attraction, when bioidentical progesterone was used rather than MPA (P < 0.001).
Fitzpatrick et al. Study (Findings)
• 30% reduction in sleep problems
• 50% reduction in anxiety
• 60% reduction in depression
• 30% reduction in somatic symptoms
• 25% reduction in menstrual bleeding
• 40% reduction in cognitive difficulties
• 30% improvement in sexual function
• 65% of women felt that HRT combined with progesterone was better than the HRT combined with MPA

Cummings et al. Study (Randomized Trial)
• Compared HRT with MPA or progesterone in 23 postmenopausal women with no mood disorders.
• Found significantly more negative somatic effects but no differences in mood assessment with synthetic hormones.
• Negative effects included increased vaginal bleeding (P = 0.003) and increased breast tenderness (P = 0.02), with a trend for increased hot flashes with the use of MPA compared with progesterone.
Patients report greater satisfaction with HRTs that contain progesterone compared with those that contain a synthetic progestin.
Progesterone and synthetic progestins generally have indistinguishable effects on endometrial tissue, but they have significantly differing (opposite) physiological effects on breast tissue
• Progesterone consistently demonstrates antiestrogenic activity in breast tissue.7,16,22,24–29,31–34
• Progesterone also downregulates estrogen receptor-alpha (ER-α) in the breast, 27-29 induces breast cancer cell apoptosis,30,31 diminishes breast cell mitotic activity,7,16,22–24,26–28,31,32 and arrests human breast cancer cells in the G1 phase by upregulating cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and downregulates cyclin D1.23,32
• Increases the intracellular conversion of potent estrogens to their less potent counterparts.34,46,47
• Bind to estrogen receptors in breast tissue and display significant intrinsic estrogenic properties in breast tissue.
• Significantly increase estrogen-stimulated breast cell mitotic activity and proliferation with antiapoptotic effects 7–21 (but not in endometrial tissue).
• Increase the conversion of weaker endogenous estrogens into more potent estrogens,7,40–45 potentially contributing to their carcinogenic effects
• Promote the formation of the genotoxic estrogen metabolite 16hydroxyestrone.41
• Stimulate the conversion of inactive estrone sulfate into active estrone in breast tissue by stimulating sulfatase,43,44 as well as increasing 17-beta-hydroxysteroid reductase activity,7,40,42,43,45
Bioidentical progesterone and synthetic progestins have distinctly different effects due to their different chemical structures.
Progesterone
• Antiproliferative and antiestrogenic effects on both endometrial and breast tissue.
• Reduces risk of breast cancer by inhibiting proliferation.
• Antiestrogenic effects on endometrial tissue.
• Proliferative, estrogenic effects on breast tissue.
• Increase estrogen-induced breast tissue proliferation and breast cancer risk.

3
In contrast, both physiological and clinical data have indicated that progesterone is associated with a diminished risk for breast cancer.16,22,23,25,58,59,60,61,6670,99-101 1 2
Many studies have assessed the risk for breast cancer with the use of a synthetic progestin for HRT.
Despite significant variability in study design, synthetic progestins have been clearly and consistantly associated with an increased risk for breast cancer.7,8,58,71-98
The association of HRT and the incidence of breast cancer in more than 80,000 post-menopausal women was investigated who were followed for more than 8 postmenopausal years.
Compared with women who had never used any HRT, women who used estrogen only (various preparations) had no significant increase in breast CA

However, for women who used progesterone in combination with estrogen, there was a significant reduction in breast cancer risk (P = 0.001).
If a synthetic progestin was used in combination with estrogen, the risk for breast cancer increased significantly to 1.69 times that for control subjects (P = 0.01).
Fournier A, Berrino F, Clavel-Chapelon F. Unequal risks for breast cancer associated with different hormone replacement therapies: results from the E3N cohort study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;107(1):103–111.

It was found that the risk for breast cancer was significantly increased if synthetic progestins were used (RR = 1.69) (p > 0.01) but was reduced if progesterone was used (RR = 0.9) (p > 0.001)
Fournier A, et al. Breast cancer risk in relation to different types of hormone replacement therapy in the E3N-EPIC cohort. Int J Cancer. 2005;114:448–454.
• Examined the effects of estrogen and progesterone on women prior to breast surgery in a double-blind, placebocontrolled study.
• Patients were given placebo, estrogen, transdermal progesterone, or estrogen and transdermal progesterone for 10 to 13 days before breast surgery.
Estrogen increased cell proliferation rates by 230% (P < 0.05).
Progesterone decreased cell proliferation rates by 400% (P < 0.05).
Reference: Change, et al. Fertil Steril. 1995;63(4):785–791.
Progesterone, when given with estradiol, inhibited all estrogen-induced breast cell proliferation. Foidart et al.
conducted a randomized, double-blind study that also showed that progesterone eliminated estrogen-induced breast cell proliferation (P = 0.001).
Reference: Foidart, et al. Fertil Steril. 1998;69(5):963–969.
Chang et al examined the effects of estrogen and progesterone on women prior to breast surgery in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in which patients were given placebo, estrogen, transdermal progesterone, or estrogen and transdermal progesterone for 10 to 13 days before breast surgery.
Progesterone, when given with estradiol, inhibited all estrogeninduced breast cell proliferation.
Estrogen increased cell proliferation rates by 230% (P < 0.05), but progesterone decreased cell proliferation rates by 400% (P < 0.05).
Change, et al. Fertil Steril. 1995;63(4):785–791.
Foidart, et al. Fertil Steril. 1998;69(5):963–969.
Similarly, in a randomized, doubleblind study, Foidart et al also showed that progesterone eliminated estrogen-induced breast cell proliferation (P = 0.001).
A prospective epidemiological study demonstrated a protective role for progesterone against breast cancer.
In this study, 1083 women who had been treated for infertility were followed for 13 to 33 years. The premenopausal risk for breast cancer was 5.4 times higher in women who had low progesterone levels compared with those with normal levels (95% CI: 1.1–49). 3 4 Result
The result was significant, despite the fact that the high progesterone group had significantly more risk factors for breast cancer than the low progesterone group, highlighting the importance of this parameter.
Summary
Moreover, there were 10 times as many deaths from cancer in the low progesterone group compared with those with normal progesterone levels (95% CI: 1.3–422).
Cowan LD, Gordis L, Tonascia JA, Jones GS. Breast cancer incidence in women with a history of progesterone deficiency. Am J Epidemiol.1981;114(2):209–217.
Women with low progesterone have significantly worse breast cancer survival rates than those with more optimal progesterone levels.
Badwe RA, et al. Serum progesterone at the time of surgery and survival in women with premenopausal operable breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(4):445–448.
Mohr PE, et al. Serum progesterone and prognosis in operable breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1996;73(12):1552–1555.
Peck et al conducted a nested case-control study to examine third-trimester progesterone levels and maternal risk of breast cancer in women who were pregnant between 1959 and 1966.
Peck
Relative to those with progesterone levels in the lowest quartile (< 124.25 ng/mL), those in the highest quartile (> 269.97 ng/mL) had a 50% reduction in the incidence of breast cancer (RR = 0.49, CI 0.22–1.1, P for trend = 0.08).
The association was stronger for cancers diagnosed at or before age 50 years (RR = 0.3, CI: 0.1–0.9, P for trend = 0.04).
• Estrogen effects are mediated through 2 different estrogen receptors: estrogen receptor-alpha (ER-α) and estrogen receptor-beta (ER-β).106–111
• Estrogen receptor-α promotes breast cell proliferation, while ER-β inhibits proliferation and prevents breast cancer development106,112–117
• Estradiol equally activates ER-α and ER-β, while estrone selectively activates ER-α at a ratio of 5:1.118,119
• In contrast, estriol selectively binds ER-β at a ratio of 3:1.118,119
• Acting alone, estriol is a weak estrogen, but when given with estradiol, it functions as an antiestrogen.
• Significant number of studies showing that when given with estradiol there is a reduction in the risk of breast cancer.
• The 80/20 of estriol/estradiol is not physiologic, as the basis of this formulation was a study with flawed methodality

The WHI study demonstrated that the addition of MPA to Premarin® (CEE) resulted in a substantial increase in the risk of heart attack and stroke.71–73
This outcome with MPA is not surprising because synthetic progestins produce negative cardiovascular effects and negate the cardioprotective, including lipid effects of estrogen.71,73,148–172
Progesterone, in contrast, has the opposite effect because it maintains and augments the cardioprotective effects of estrogen, thus decreasing the risk for heart attack and stroke.
148–151,153,155,157,162,165,167,173–178

A number of studies have shown that coronary artery spasm, which increases the risk for heart attack and stroke, is reduced with the use of estrogen and/or progesterone.149–151-174,179,180
However, the addition of MPA to estrogen has the opposite effect, resulting in vasoconstriction,149–151,174 thus increasing the risk for ischemic heart disease.

Adams et al examined the cardioprotective effects of CEE and progesterone versus CEE and MPA in primates fed atherogenic diets for 30 months.



The CEE and progesterone combination resulted in a 50% reduction in atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries (P < 0.05). This result was independent of changes in lipid concentrations. 1 2 3 4
However, when MPA was combined with the CEE, almost all the cardioprotective effect (atherosclerotic plaque reduction) was reversed (P < 0.05).
Adams MR, et al.. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(1):217–221
Adams MR,et al.. Arteriosclerosis. 1990;10(6):1051–1057
Patients with CFS/FM, chronic illness, inflammation have pituitary dysfunction resulting in low FSH, LH and low Estrogen
Deficiency occurs many years before periods stop and labs are abnormal
High FSH an LH are late findings
Low estrogen levels are associated with accelerated aging, while optimal levels prevent aging
An estimate of the ages of 100 women age 35-55 was done on their first visit to an OB/Gyn’s office. This estimated age was then compared to their real age and the level of estrogen
Women with low estrogen looked significantly older than their age and those with more optimal levels looked much younger than their age
Those with the lowest level of estrogen looked 8 years older than their age and those with the most optimal levels looked 8 years younger than their age

A 16 year differential

Hot Flashes
Excessive Sweating Depression
Insomnia or unrestful sleep Irregular periods Fatigue
Decreased vaginal lubrication
Painful intercourse Muscle aches Dry eyes Pale skin
Increased wrinkles
Increased body hair Dropping breasts Recrrent UTI’s Incontinence
Partial hyst-lowers estrogen Migraines
PMS Anxiety Fibrocystic breasts
Swollen breasts
With PMS
Endometriosis Fibroids
Menstrual cramps Irritable Heavy periods
Migraines Insomnia
Try and check labs on 18-21st day of cycle
Suggestive of low estrogen and/or low tissue thyroid levels
Estradiol < 100
SHBG < 70 in luteal phase-consider treatment
FSH or LH > 8-10
LH > FSH think PCOS

Symptoms are a major key—different women need differing amounts
Increases binding proteins and inflammation and lowers thyroid, IGF-1, and cortisol
Increases clotting factors
Bioidentical Transdermal does not



Peptides are short chains of amino acid. They are similar to proteins, but are shorter in length, typically less than 50 amino acids long.
Bioregulators are two (2) to four (4) amino acids in length.

Peptides & bioregulators play vital roles, acting as the master regulators of most every known process in the body and serve to fine tune the body's processes. They can act as hormones, neurotransmitters, and metabolic and immune system regulators.

Due to their potent biological activities, peptides have significant therapeutic potential.
Increasing numbers of peptides and bioregulators are becoming clinically available that can safely improve, optimize or normalize specific functions of the body.
1. Khavinson V. Peptides and ageing. Neuroendocrinology Letters 2002;23(3):11-144
2. Anisimo VNN, et al. Effect of synthetic thymic and pineal peptide on biomarkers of ageing, survival and spontaneous tumor
3. incidence of female CBAmice Mech Ageing Dev 2001;122(1):41-68.


Peptides act as signaling molecules, binding to receptors on the cell surface and initiating a cascade of events that indirectly influence cellular activity, rapid onset and offset, but can lead to long-lasting epigenetic changes.
Bioregulator peptides bind to gene translation activators or inhibitors, influencing transcription patterns and affecting protein synthesis, altering transcription patterns toward a younger, healthier phenotype, with a slower onset and offset.


Unveiling the Secret Weapon of Soviet Super Soldiers and Olympic Athletes



Soviet Military Challenge
During the Cold War, Soviet submariners, supersonic jet fighters, and cosmonauts suffered from “premature aging effect” and physical decline.
This alarming problem prompted the formation of a top-secret project for the USSR Ministry of Defense to find a solution.
Their search led to a groundbreaking discovery with the potential to revolutionize our understanding of aging.



Soviet scientists, led by Colonel Vladimir Khavinson, M.D., Ph.D., paired with Ivon Pavolv, made a groundbreaking discovery that specific organ extracts from fetal cows, including the pineal and thymus glands, could reverse premature aging effects in a tissue-specific manner.
This led to the isolation of ultra-short peptides, only 2-4camino acids in length, which were found to be orally bioavailable and able to enter cells and interact directly with DNA, modulating gene expression to promote youthful cellular function.
For decades, these peptide bioregulators were a closely guarded secret, used exclusively by the Soviet military and olympic athletes to maintain peak performance.

Western Discovery
It wasn't until after the fall of the Soviet Union that the West began to uncover the extensive research and incredible potential of these once-classified peptides.

High Bioavailability
Other uniquely beneficial properties of bioregulators are their resistance to enzymatic degradation in the GI tract and their ability to be transported through the intestinal and bloodbrain barriers, making them highly orally bioavailable.

Public Availability

Now, after years of research and development, these powerful peptide bioregulators are available to anyone looking to enhance their health, vitality, and longevity.

Cellular Bioavailability
They also readily pass across cell and nuclear membranes, allowing them to efficiently affect their target tissues.

With the ability to selectively activate youthful genes and suppress age-related genes, peptide bioregulators offer a way to not just slow aging but potentially reverse it, extending both lifespan and health span.

With over twenty natural bioregulator extracts and over thirty bioregulator peptide isolates available for commercial use, these peptides represent the cutting edge of health science, providing a practical solutions for those seeking to maintain youth and vitality.

1. Khavinson V. Peptides and ageing. Neuroendocrinology Letters 2002;23(3):11-144
2. Anisimo VNN, et al. Effect of synthetic thymic and pineal peptide on biomarkers of ageing, survival and spontaneous tumor incidence of female CBAmice. Mech Ageing Dev 2001;122(1):41-68.


2

Peptide bioregulators can potentially extend lifespan by regulating gene expression associated with aging processes, enhancing protein synthesis, and supporting healthy cellular function.
Peptide bioregulators promote the removal of senescent cells, reduce inflammaging, and suppress SASP secretion, targeting the root causes of aging and chronic illness.
1. Khavinson V. Peptides and ageing. Neuroendocrinology Letters 2002;23(3):11-144
2. Anisimo VNN, et al. Effect of synthetic thymic and pineal peptide on biomarkers of ageing, survival and spontaneous tumor incidence of female CBAmice. Mech Ageing Dev 2001;122(1):41-68.

Study the efficacy of ovary and pineal (epitalon) bioregulators in 214 women, aged 34 to 38 years old. Study Design


Therapeutics
The treatment group received ovarian bioregulator, two caps bid for four months and pineal bioregulator, one cap q 3 days for 4 months.
1. Gorgiladze, DE, et al. Assessing teh Effectiveness of Peptide Bioregulator Combinations for the treatment of Reduced Reproductive Function in Women. World Congress of the International Assoc. of Gerontology and Geriatrics. June 23, 2018:92-104. 1
2 3 4


All pts with reduced pineal-hypothalamicpituitary-estrogen/ progesterone axis dysfunction and associated age-related ovarian decline in women trying to unsuccessfully get pregnant.
Blood testing for FSH, LH, estradiol, and AMH will be determined along with antral follicle number vis U/S before treatment and after 2 and 4 months of treatment. Assessment
Parameter

p < 0.05 compared to pretreatment
Parameter
Increase in Number of Antral Follicles
Increase in Anti-Mullerian Hormone Levels
Two Months After Treatment Four Months After Treatment
(119 participants)
(209 participants)
(146 participants)
Parameter
Pregnancy Onset Without Hormonal Stimulation
p<0.05compared to pretreatment




Four days of treatment with epithalon induced telomerase activity from 11%cto 47%, increased the mean telomere length from 180 arb. units to 240 arb units (33%)(p<0.05), and increased maximum cell division (Hayflick Limit) from 26 to 67 divisions

• Elizabeth H. Blackburn, Carol W. Greider, Jack W. Szostak: The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2009". Nobel Foundation, 2009-10-05. Retrieved 2012-06-12.
• Breus, Michael 1. "How Sleep Affects Your Telomeres | Psychology Today" www.psychologytoday.com, Retrieved 14 August 2021.
• https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2015/01/telomere-extension-tums-back-agingclock-in-cultured cells html
• Khavinson Vikh, et al. Epithalon Peptide Induces Telomerase Activity and Telomere Elongation in Human Somatic Cells. Bull Exp Bio & Med2003,135(6):590-2
Oral Bioregulators Vilon and Epitalon's Effects on Gene Expression


In a study of the mitochondrial genome, vilon and epitalon changed the expression of 5 of 13 genes, increasing expression by 2-6-fold in 4 of the genes and reducing one by 55%.
Both substances inhibited pro-oncogenic genes and activated anticarcinogenic genes.

• Khavinson V. Peptides and ageing. Neuroendocrinology Letters 2002.23(3)11-144
• Anisimo VNN, et al. Effect of synthetic thymic and pineal peptide on biomarkers of ageing, survival and spontaneoüs tumor Incidence of feriale CBAmice. Mech Ageing Dev 2001;122(1):41-68
• Khavinson Vich, et al. Experimental studies of the pineal gland preparation Epithalamin. The Pineal Gland and Cancer: Neuroimmurioendocrine Mechanisms in Malignaricy 2001-294-306
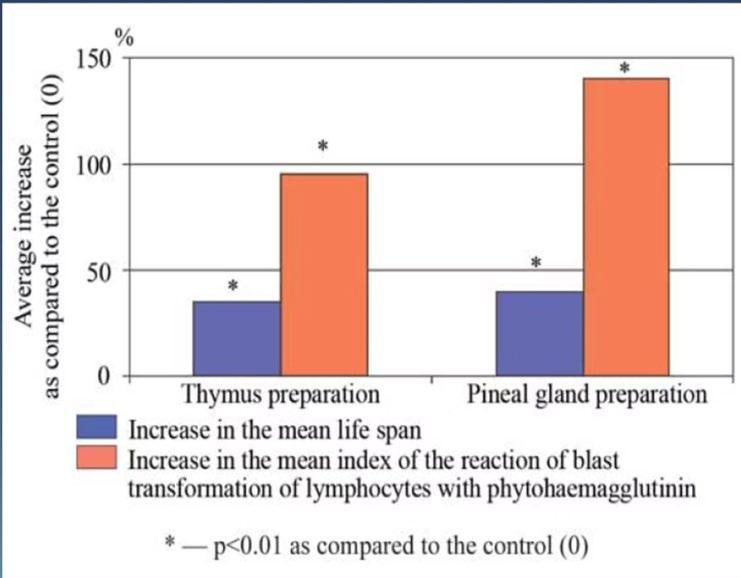
Increase in mean and maximum lifespan in animals consistently seen with both thymic and pineal gland peptides with direct correlation to increased cellular immunity with the subsequent reliable reduction in cancer in both animals and humans.
“The obtained results demonstrate a high efficiency of epitalon therapy for prophylaxis of age-related pathology, including cancer, showing a new physiological way to slow down pathological processes and to extend human life spans"58
66. Khavinson V. Peptides and ageing. Neuroendocrinology Letters 2002;23(3):11-144
71. Anisimo VNN, et al. Effect of synthetic thymic and pineal peptide on biomarkers of ageing, survival and spontaneous tumor incidence of female CBAmice. Mech Ageing Dev 2001;122(1):41-68

• Female mice carrying the breast cancer gene HER-2/neu (genetically prone) received epitalon five times per week from the 2nd month of life until death.
• The percent of mice that developed breast cancer was 3.7-fold higher in the control group (73% reduction in the treatment group).
• Epitalon also decelerated the rate of reproductive system aging, with only 8% of aged mice having irregular menstrual cycles vs. 52% of aged control mice.

VNN, et al. Effect of synthetic thymic and pineal peptide on biomarkers of ageing, survival and spontaneous tumor incidence of female CBA mice. Mech Ageing Dev 2001;122(1):41-68.

• Extracted from the thyroid glands of young animals
• Stabilizes thyroid function and thyroid hormone levels.
• Can normalize thyroid function and reverse hypo and hyperthyroidism and autoimmune thyroiditis, including Hashimoto’s and Grave’s disease.
• Reduces the size of thyroid nodules.
• Improves pineal-hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis and mitochondrial function.
• Prevents stem cell aging.
• Activates telomerase and stem cell function.
• Supports the healthy functioning of the neurologic, immune, and cardiovascular systems.
• Improves hypercholesterolemia, insulin resistance, and metabolic function.
• Rejuvenates hair, nails and skin.
• Shown to improve physical performance, endurance, cognitive function, mood disorders, bone density, antioxidant activity, quality of life, and survival rate.
• Improved longevity in old and elderly patients.
• Reduced cancer rates and the incidence of chronic infections.

• The study involved 25 patients with primary hypothyroidism, including 11 men and 14 women aged 56 to 67 years. The control group consisted of 19 patients, including 7 men and 12 women.
• Patients in both groups complained of significant fatigue, poor endurance, drowsiness, memory impairment, frequent headaches, dizziness, and an increased incidence of angina. In most cases, signs of thyroid atrophy were detected by palpation.

• The control group was prescribed conventional therapy of T4 for three months.
• Patients of the primary group received thyroid bioregulator 1-2 capsules 2 times a day before meals for three months. Testing
• The patients’ biochemical analysis of blood (serum T3 and T4) was performed along with a thyroid ultrasound and EKG examination before and after the trial.

Compared to the control group receiving T4 therapy, those receiving the Thyroid Bioregulator noted improvement in the clinical manifestations of the disease in 78% of cases, and the most significant effect was observed in persons of the older age group with pronounced signs of thyroid atrophy.
After 20 days of treatment, the Thyroid Bioregulator group noted increased working capacity and endurance, decreased frequency and intensity of headaches, and decreased angina compared to the control group on T4 therapy.

1
After treatment with T4, the total T3 reached the low normal range, but T4 levels did not change from a pretreatment T3 level that averaged 60% below the lowest level of normal and a T4 level that was 35% below the lowest level of normal.

2
On the other hand, the addition of the thyroid bioregulator resulted in a 300% increase in the T3 level from baseline and a 40% increase over T4 replacement alone, with T4 levels doubling and 60% higher than T4 alone.

3
After stopping the therapy, the T4 and T3 levels in the Thyroid Bioregulator group remained in the normal range for 3-4 months.

A 4-month study on the efficacy of thyroid vs. thyroid axis bioregulator therapy for autoimmune Thyroiditis with hypothyroidism compared to standard therapy of L-thyroxine 50 mcg/day for four months.
Two hundred eighteen patients (218) with autoimmune thyroiditis aged between 39 and 51-years old were randomized
Eighty-nine (89) people received standard treatment of Lthyroxine 50 mg daily for 4 months
Forty-two (42) people received peptide thyroid bioregulator therapy in addition to the standard treatment scheme
Eighty-seven (87) people received peptide thyroid-axis bioregulator therapy in addition to the standard treatment.
BEFORE TREATMENT
GROUP 1STANDARD TREATMENT (ST)
GROUP 2ST+THYROID BIOREGULATOR
GROUP 3ST+THYROID AXIS BIOREGULATOR



Group II: Fifteen (15) young and fifteen (15) old rats in group II received physiologic saline for 40 days after having pituitary removed. 1 2 3

Experiment on the effects of Thyroid Axis Bioregulators on sixty (60) young rats (4 days old) and forty-five (45) old rats (24 months old) after undergoing hypophysectomy (pituitary removed).
Group I: Fifteen (15) young and ten (10) old rats were sham-operated with all others undergoing Hypophysectomy
Group III: Fifteen (15) young rats and ten (10) old rats received THYROID AXIS BIOREGULATOR C44 (TABaC44), 4
5

Group IV: Fifteen (15) young rats and ten (10) old hypophysectomized (pituitary removed) rats received THYROID AXIS BIOREGULATOR Alpha-24C (TAB-A24C) in group IV.

• The young and old rats treated with saline quickly experienced a 43% and 30% weight loss and growth retardation with sluggishness, suppressed excitement and anorexia.
• While those given TAB-C44 had a 19% and 21% weight loss, and the TABA24C group only had a 7% and 6% weight loss, respectively.
• Normal thyroid architecture was much more consistently maintained in the TAB-C44 and ATB-A groups compared to the saline group.
• TAB-C44 and TAB-A24C prevented the signs of hypothyroidism and normalized the structure and function of the thyroid gland.
• TSH, T3 and T4 levels plummeted 8090% after hypophysectomy, but the decline was significantly blunted by TAB-C44 and TAB-A24C.