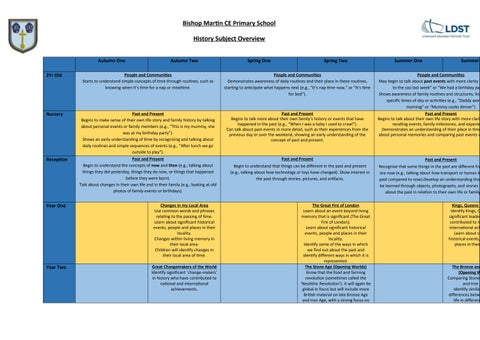
2Yr Old People and Communities
History Subject Overview
Starts to understand simple concepts of time through routines, such as knowing when it’s time for a nap or mealtime.
Nursery Past and Present
Begins to make sense of their own life story and family history by talking about personal events or family members (e.g., “This is my mummy, she was at my birthday party”).
Shows an early understanding of time by recognizing and talking about daily routines and simple sequences of events (e.g., "After lunch we go outside to play").
Reception Past and Present
Begin to understand the concepts of now and then (e.g., talking about things they did yesterday, things they do now, or things that happened before they were born).
Talk about changes in their own life and in their family (e.g., looking at old photos of family events or birthdays).
Year One
People and Communities
Demonstrates awareness of daily routines and their place in these routines, starting to anticipate what happens next (e.g., “It’s nap time now,” or “It’s time for bed”).
Past and Present
Begins to talk more about their own family’s history or events that have happened in the past (e.g., “When I was a baby I used to crawl”).
Can talk about past events in more detail, such as their experiences from the previous day or over the weekend, showing an early understanding of the concept of past and present.

People and Communities
May begin to talk about past events with more clarity to the zoo last week” or “We had a birthday party”).
Shows awareness of family routines and structures, linking specific times of day or activities (e.g., “Daddy works morning” or “Mummy cooks dinner”)
Past and Present
Begins to talk about their own life story with more clarity recalling events, family milestones, and experiences.
Demonstrates an understanding of their place in time about personal memories and comparing past events with
Year Two
Changes in my Local Area
Use common words and phrases relating to the passing of time. Learn about significant historical events, people and places in their locality.
Changes within living memory in their local area.
Children will identify changes in their local area of time.
Great Changemakers of the World
Identify significant ‘change-makers’ in history who have contributed to national and international achievements.
Past and Present
Begin to understand that things can be different in the past and present (e.g., talking about how technology or toys have changed). Show interest in the past through stories, pictures, and artifacts.
The Great Fire of London
Learn about an event beyond living memory that is significant (The Great Fire of London).
Learn about significant historical events, people and places in their locality.
Identify some of the ways in which we find out about the past and identify different ways in which it is represented.
The Stone Age (Opening Worlds)
Know that the food and farming revolution (sometimes called the ‘Neolithic Revolution’). It will again be global in focus but will include more British material on late Bronze Age and Iron Age, with a strong focus on
Past and Present
Recognise that some things in the past are different from are now (e.g., talking about how transport or homes looked past compared to now).Develop an understanding that be learned through objects, photographs, and stories about the past in relation to their own life or family
Kings, Queens
Identify Kings, Queens significant leaders contributed to national international achievements.
Learn about significant historical events, places in their
The Bronze and (Opening Worlds)
Comparing Stone and Iron
Identify similarities differences between life in different
environmental history exploring human relationships with and management of environment, and the impact of climate on human forms of life.
Year Three
Four Year Five
Year Six
Ancient Egypt
Location, origin in settlements around the Nile, living by the Nile and the role of the Nile in developing belief systems as well as agriculture.
How the power structures (pharaohs, the double crown) were linked to the geography of Egypt; how they were sustained through art, writing, belief systems.
Ancient Egyptian religion, government, art, great monuments, beliefs about death, farming.
How Egypt changed through timekingdoms, art, pyramids, beliefs and writing.
Year Three Ancient Egypt
Location, origin in settlements around the Nile, living by the Nile and the role of the Nile in developing belief systems as well as agriculture.
How the power structures (pharaohs, the double crown) were linked to the geography of Egypt; how they were sustained through art, writing, belief systems.
Ancient Egyptian religion, government, art, great monuments, beliefs about death, farming.
How Egypt changed through timekingdoms, art, pyramids, beliefs and writing.
Cradles
of Civilisations
The land between two rivers:
Ancient Mesopotamia – the unique ‘cradle’ (development of writing to record trade). Geographical overview of ancient civilisations of the world, inc. big map seeing where they all were & geographical similarities. Depth study of ancient Sumer in Mesopotamia via rivers & settlements and via art of ancient civilisations. Ziggurats.
Indus Valley Civilisations
Sites and artefacts in the Indus Valley (including the dancing girl, priest king, seals, threshing platforms, pots and potsherds, beads, weights, toys)
Bricks, buildings, baths, bathrooms, drainage Mohenjo Daro, Harappa, Lothal Similarities and differences between Indus Valley and Sumer and Egypt (e.g. writing, monuments)
Craftsmanship, trade, barter Puzzles for historians, including rulers and religion.
Persia & Greece
Start with ancient Persia and its empire to set geographical & political context. Ancient Greek city states, inc. Sparta and Athens. Why/how did they form? Homer’s Iliad GrecoPersian wars, inc. battle of Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis Ancient Greek language Peloponnese War Greek religion – gods and goddesses.
Ancient Greece
Athenian democracy and empire art, culture & learning in Ancient Greece.
Greek architecture, inc.
Parthenon Greek religion in Greek stories.
Greek literature, inc. epic poetry – inc Homer’s Odyssey.
Tragedy in Greek theatre
Philosophy and enquiry in
Ancient Greece, inc. Aristotle –depth on Aristotle.
Alexander the Great Where did Alexander come from?
Backstory of Philip of Macedon and the Macedonian empire. Alexander the Great: childhood, education, early battles, conquest of Persia, death. Know about the library of Alexander.
Cradles of Civilisations
The land between two rivers:
Ancient Mesopotamia – the unique ‘cradle’ (development of writing to record trade). Geographical overview of ancient civilisations of the world, inc. big map seeing where they all were & geographical similarities. Depth study of ancient Sumer in Mesopotamia via rivers & settlements and via art of ancient civilisations. Ziggurats.
Indus Valley Civilisations
Sites and artefacts in the Indus Valley (including the dancing girl, priest king, seals, threshing platforms, pots and potsherds, beads, weights, toys)
Bricks, buildings, baths, bathrooms, drainage Mohenjo Daro, Harappa, Lothal Similarities and differences between Indus Valley and Sumer and Egypt (e.g. writing, monuments)
Craftsmanship, trade, barter Puzzles for historians, including rulers and religion.
Persia & Greece
Start with ancient Persia and its empire to set geographical & political context. Ancient Greek city states, inc. Sparta and Athens. Why/how did they form? Homer’s Iliad GrecoPersian wars, inc. battle of Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis Ancient Greek language Peloponnese War Greek religion – gods and goddesses.
Ancient Greece
Athenian democracy and empire art, culture & learning in Ancient Greece.
Greek architecture, inc.
Parthenon Greek religion in Greek stories.
Greek literature, inc. epic poetry
– inc Homer’s Odyssey.
Tragedy in Greek theatre
Philosophy and enquiry in Ancient Greece, inc. Aristotle –depth on Aristotle.
Alexander the Great
Where did Alexander come from?
Backstory of Philip of Macedon and the Macedonian empire. Alexander the Great: childhood, education, early battles, conquest of Persia, death.
Know about the library of Alexander.
Year Four
Year Five
Year Six
The Roman Republic
Foundation myth of Romulus and Remus.
River Tiber civilisation. The early kings of Rome. Development of the Roman. Republic Punic wars, Hannibal, Roman army.
Roman religion, Roman myths & legends Roman roads.
Roman politics and government during the Republic.
The Roman Empire Roman army Julius Caesar, the early emperors (incl Augustus, Claudius, Nero), Jewish-Roman war. Persecutions of Christians in Rome. Amphitheatres and games.
Roman Britain
The ancient Britons – a land of diversity, a land of migrants (eg Celts).
Celtic language, Celtic culture. Rebellions: Caractacus, Boudicca. Roman town: Aquae Sulis Life on the frontier: Hadrian’s Wall Black Romans in Britain.
Christianity in Three Empires
Comparing Roman Republic vs Empire; Christianity across empires. Focus on three cities: Rome, Constantinople and Adulis representing three types of Christianity influenced by and influencing local culture. Examine the role of rulers in the spread of Christianity.
Islamic Civilisations – Arabia & Early Islam
Arabia before Muhammad Bedouin culture, trade and life in the desert; the place of the Makkah in the trade of the Middle East and the world. An oral culture and a land of poetry. Stories about the birth of Muhammad. Makkah, Medina and the birth of Islam.
The glories of Islamic achievement in art, architecture, learning and science in Cordoba. How Muslims, Christians and Jews lived and worked together, collaborated on great architectural projects together and built a culture of learning together. The great library of Cordoba –how knowledge of medicine, technology, art, theology and geography was built through the work of peoples from all three religions.
2027 – 2028
Year Three Ancient Egypt
Location, origin in settlements around the Nile, living by the Nile and the role of the Nile in developing belief systems as well as agriculture.
How the power structures (pharaohs, the double crown) were linked to the geography of Egypt; how they were sustained through art, writing, belief systems.
Ancient Egyptian religion, government, art, great monuments, beliefs about death, farming.
How Egypt changed through timekingdoms, art, pyramids, beliefs and writing.
Year Four
The Roman Republic Foundation myth of Romulus and Remus.
River Tiber civilisation. The early kings of Rome.
Development of the Roman. Republic Punic wars, Hannibal, Roman army.
Roman religion, Roman myths & legends Roman roads.
Cradles of
Civilisations
The land between two rivers: Ancient Mesopotamia – the unique ‘cradle’ (development of writing to record trade). Geographical overview of ancient civilisations of the world, inc. big map seeing where they all were & geographical similarities. Depth study of ancient Sumer in Mesopotamia via rivers & settlements and via art of ancient civilisations. Ziggurats.
Indus Valley Civilisations
Sites and artefacts in the Indus Valley (including the dancing girl, priest king, seals, threshing platforms, pots and potsherds, beads, weights, toys) Bricks, buildings, baths, bathrooms, drainage Mohenjo Daro, Harappa, Lothal Similarities and differences between Indus Valley and Sumer and Egypt (e.g. writing, monuments)
Craftsmanship, trade, barter Puzzles for historians, including rulers and religion.
Persia & Greece
Start with ancient Persia and its empire to set geographical & political context. Ancient Greek city states, inc. Sparta and Athens. Why/how did they form? Homer’s Iliad GrecoPersian wars, inc. battle of Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis Ancient Greek language Peloponnese War Greek religion – gods and goddesses.
Ancient Greece
Athenian democracy and empire art, culture & learning in Ancient Greece.
Greek architecture, inc.
Parthenon Greek religion in Greek stories.
Greek literature, inc. epic poetry – inc Homer’s Odyssey.
Tragedy in Greek theatre Philosophy and enquiry in Ancient Greece, inc. Aristotle –depth on Aristotle.
Alexander the Great Where did Alexander come from?
Backstory of Philip of Macedon and the Macedonian empire. Alexander the Great: childhood, education, early battles, conquest of Persia, death. Know about the library of Alexander.
The Roman Empire Roman army Julius Caesar, the early emperors (incl Augustus, Claudius, Nero), Jewish-Roman war. Persecutions of Christians in Rome. Amphitheatres and games.
Roman Britain
The ancient Britons – a land of diversity, a land of migrants (eg Celts).
Celtic language, Celtic culture. Rebellions: Caractacus, Boudicca. Roman town: Aquae Sulis Life on the frontier: Hadrian’s Wall Black Romans in Britain.
Christianity in Three Empires
Comparing Roman Republic vs Empire; Christianity across empires.
Focus on three cities: Rome, Constantinople and Adulis representing three types of Christianity influenced by and influencing local culture. Examine the role of rulers in the spread of Christianity.
Islamic Civilisations – Arabia & Early Islam
Arabia before Muhammad
Bedouin culture, trade and life in the desert; the place of the Makkah in the trade of the Middle East and the world. An oral culture and a land of poetry.
Stories about the birth of Muhammad. Makkah, Medina
Islamic Civilisation – Muslim Cordoba
The glories of Islamic achievement in art, architecture, learning and science in Cordoba. How Muslims, Christians and Jews lived and worked together, collaborated on great architectural projects together
Year Five
Year Six
Roman politics and government during the Republic.
Islamic Civilisations – Baghdad
Where, why and how it was built. What it looked like.
How we know about it through archaeology, artefacts and written sources.
Why it is so important in understand medieval Islam. The House of Wisdom, books and paper, translation of the ancient texts from Greek.
The contribution of Baghdad and Islamic scholars to learning astronomy, mathematics and mapping the world; science, technology and medicine.
How Islamic scholars preserved the learning of the ancient world and moved it forwards, feeding into all the advances in European knowledge that came in the Renaissance.
Year Three Ancient Egypt
Location, origin in settlements around the Nile, living by the Nile and the role of the Nile in developing belief systems as well as agriculture.
How the power structures (pharaohs, the double crown) were linked to the geography of Egypt; how they were sustained through art, writing, belief systems.
Ancient Egyptian religion,
Anglo – Saxon Britain
Christianity arrives in the British Isles.
Early monasteries in British Isles; Bede.
Offa and Cynethryth of Mercia. How archaeologists learn about Anglo-Saxons – art, everyday life, villages, Sutton Hoo.
Vikings in Britain
Changing Rulers, Changing Worlds
Case study of Jorvik in 910, told through fictional story of two Viking children. Consolidates stories from Norse culture and views expansion of Wessex/Mercia from perspective of Vikings.
Why we must tell differing stories and reasons why some stories go missing (changing interpretations of the period).
Aethelflaed presses north into Tamworth, Derby and Leicester, her closeness to attacking York and uniting the country before her death in 918. Athelstan coronation and creation of England.
Vikings shaping Britain: i) government (focus on Canute); ii) Viking-British cultural fusions.
Norse Culture
Comparing Norse epics with other ancient stories.
Know about sagas, art, poetry, folklore. Norse gods, goddesses, stories and customs. What does Beowulf have in common with stories from contrasting world civilisations?
and the birth of Islam. and built a culture of learning together.
The great library of Cordoba –how knowledge of medicine, technology, art, theology and geography was built through the work of peoples from all three religions.
Vikings in Britain – Rulers, Changing Worlds
The first Viking raids and invasions King Alfred of the Kingdom of Wessex.
The ‘Great Heathen Army’ Alfred in Athelney, his victory over Guthrun, Guthrun’s baptism and the Danelaw Scandinavian settlements in Britain.
Local History, Post 1066 –Transatlantic Slave
Define what an enslaved person is.
Describe the triangular Atlantic slave trade.
Understand the abolition of the slave trade and slavery in Britain.
Know who Harriet Tubman was.
Know about the Underground Railroad.
Understand what modern slavery is.
Cradles of Civilisations
The land between two rivers:
Ancient Mesopotamia – the unique ‘cradle’ (development of writing to record trade). Geographical overview of ancient civilisations of the world, inc. big map seeing where they all were & geographical similarities. Depth study of ancient Sumer in Mesopotamia via rivers & settlements and via art of ancient
Indus Valley Civilisations
Sites and artefacts in the Indus Valley (including the dancing girl, priest king, seals, threshing platforms, pots and potsherds, beads, weights, toys)
Bricks, buildings, baths, bathrooms, drainage Mohenjo Daro, Harappa, Lothal Similarities and differences between Indus Valley and Sumer and Egypt (e.g. writing, monuments) Craftsmanship, trade, barter Puzzles
Persia & Greece
Start with ancient Persia and its empire to set geographical & political context. Ancient Greek city states, inc. Sparta and Athens. Why/how did they form? Homer’s Iliad GrecoPersian wars, inc. battle of Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis Ancient Greek language Peloponnese War Greek
Ancient Greece
Athenian democracy and empire art, culture & learning in Ancient Greece.
Greek architecture, inc. Parthenon Greek religion in Greek stories.
Greek literature, inc. epic poetry – inc Homer’s Odyssey.
Tragedy in Greek theatre Philosophy and enquiry in
Ancient Greece, inc. Aristotle –
Alexander the Great Where did Alexander come from?
Backstory of Philip of Macedon and the Macedonian empire. Alexander the Great: childhood, education, early battles, conquest of Persia, death.
Know about the library of Alexander.
government, art, great monuments, beliefs about death, farming.
How Egypt changed through timekingdoms, art, pyramids, beliefs and writing. civilisations. Ziggurats. for historians, including rulers and religion.
Year Four The Roman Republic
Foundation myth of Romulus and Remus.
River Tiber civilisation. The early kings of Rome. Development of the Roman. Republic Punic wars, Hannibal, Roman army.
Roman religion, Roman myths & legends Roman roads.
Roman politics and government during the Republic.
The Roman Empire Roman army Julius Caesar, the early emperors (incl Augustus, Claudius, Nero), Jewish-Roman war. Persecutions of Christians in Rome. Amphitheatres and games.
Roman Britain
The ancient Britons – a land of diversity, a land of migrants (eg Celts).
Celtic language, Celtic culture.
Rebellions: Caractacus, Boudicca.
Roman town: Aquae Sulis Life on the frontier: Hadrian’s Wall Black Romans in Britain.
religion – gods and goddesses. depth on Aristotle.
Year Five Islamic Civilisations – Baghdad
Where, why and how it was built. What it looked like.
How we know about it through archaeology, artefacts and written sources.
Why it is so important in understand medieval Islam. The House of Wisdom, books and paper, translation of the ancient texts from Greek.
The contribution of Baghdad and Islamic scholars to learning astronomy, mathematics and mapping the world; science, technology and medicine.
How Islamic scholars preserved the learning of the ancient world and moved it forwards, feeding into all the advances in European knowledge that came in the Renaissance.
Anglo – Saxon Britain
Christianity arrives in the British Isles.
Early monasteries in British Isles; Bede.
Offa and Cynethryth of Mercia.
How archaeologists learn about Anglo-Saxons – art, everyday life, villages, Sutton Hoo.
Vikings in Britain
Changing Rulers, Changing Worlds Case study of Jorvik in 910, told through fictional story of two Viking children. Consolidates stories from Norse culture and views expansion of Wessex/Mercia from perspective of Vikings.
Why we must tell differing stories and reasons why some stories go missing (changing interpretations of the period).
Aethelflaed presses north into Tamworth, Derby and Leicester, her closeness to attacking York and uniting the country before her death in 918. Athelstan coronation and creation of England.
Vikings shaping Britain: i) government (focus on Canute); ii) Viking-British cultural fusions.
Christianity in Three Empires
Comparing Roman Republic vs Empire; Christianity across empires. Focus on three cities: Rome, Constantinople and Adulis representing three types of Christianity influenced by and influencing local culture.
Examine the role of rulers in the spread of Christianity.
Islamic Civilisations – Arabia & Early Islam
Arabia before Muhammad Bedouin culture, trade and life in the desert; the place of the Makkah in the trade of the Middle East and the world. An oral culture and a land of poetry.
Stories about the birth of Muhammad. Makkah, Medina and the birth of Islam.
The glories of Islamic achievement in art, architecture, learning and science in Cordoba. How Muslims, Christians and Jews lived and worked together, collaborated on great architectural projects together and built a culture of learning together.
The great library of Cordoba –how knowledge of medicine, technology, art, theology and geography was built through the work of peoples from all three religions.
Norse Culture
Comparing Norse epics with other ancient stories.
Know about sagas, art, poetry, folklore. Norse gods, goddesses, stories and customs. What does Beowulf have in common with stories from contrasting world civilisations?
Vikings in Britain – Rulers, Changing Worlds
The first Viking raids and invasions King Alfred of the Kingdom of Wessex.
The ‘Great Heathen Army’ Alfred in Athelney, his victory over Guthrun, Guthrun’s baptism and the Danelaw Scandinavian settlements in Britain.
Local History, Post 1066 –Transatlantic Slave
Define what an enslaved person is.
Describe the triangular Atlantic slave trade.
Understand the abolition of the slave trade and slavery in Britain. Know who Harriet Tubman was.
Know about the Underground Railroad. Understand what modern slavery is.
Maya rulers, customs and structure
Medieval African Kingdoms
Material culture, society, government and technology in the medieval kingdom of Benin and material culture, society, government and technology in
Cities in Time – Shock Cities
The story of 19th century industrial Manchester told through the life of Abel Heywood, who first arrived in the slums of Manchester in 1819 and rose to oversee numerous city
Cities in Time – Greek & Roman Pompeii
Greek and Roman Pompeii Viking and medieval London 10th to 16th century Samarqand.
Britain in the Era of WW2
The impact of war and post-war developments.
It will include evacuation, the impact of WW2 on cities, towns and rural areas, and on diverse
Local History - Skelmersdale
Understand why Skelmersdale was known as a mining town.
Know about the Tawd Vale disaster.
Locate mines on a map.
Maya language, art, cities and architecture.
Maya calendar and mathematics. Maya religious belief and practice including creation myth and ritual bloodletting. Historians’ explanations for what happened to the Maya civilisation.
Ethiopia. improvements become mayor and build the new town hall. Recurring characteristics of cities beginning. Compare to Liverpool.
people. Impact on small towns; the involvement of diverse peoples in a global war; the causes and effect of post-war migration to Britain, including Windrush; the causes and effects of the establishment of the NHS and mass secondary schooling. Know how