
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Aariya Vora1 , Prajakta Jadhav2 , Ms.Suparna Naik3
1Student, Dept. of Computer Technology, Bharati Vidyapeeth’s Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Technology(poly.), Pune, India
2Student, Dept. of Computer Technology, Bharati Vidyapeeth’s Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Technology(poly.), Pune, India
3Lecturer, Dept. of Computer Technology, Bharati Vidyapeeth’s Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Technology(poly.), Pune, India
Abstract - Virtual Reality is changing the way people perceive reality, interact with people, and understand life. The paper aspires to explain virtual reality, its architecture, and lastly, the rapid growth of VR into most fields. Virtual reality is sprouting into all arenas: from games to health. With every passing day, Virtual Reality progresses toward a state in which there is no difference between what's real and what isn't. While this paper has also pointed out the challenges of VR, like realism and latency, with evolution in AI, displays, and haptics, it would be bona fide to state that a more accessible and realistic VR future is yet to come. As adoption continues to rise, virtual reality will change industries and redefine human- computer interactions.
Key Words: Immersive Experience, Impact, Realism, Human Computer Interactions
1.INTRODUCTION
Virtual Reality (VR) represents a transformative technology that immerses users into a computergenerated,interactive,three-dimensionalenvironment.Over the past few decades, VR has evolved from a concept primarilyassociatedwithsciencefictiontoacriticaltoolin fields such as not only gaming but also in education, healthcare,and industrial training. Theunderlying goal of VR is to simulate real or imagined environments which enables users to interact with them in ways that feel intuitiveandimmersive,oftenusingdevicessuchasheadmounted displays(HMDs), motion controllers, and haptic feedbacksystems.
As technological advancements have made VR more accessible, its potential applications have broadened significantly, expanding it into areas such as virtual trainingsimulations,therapeuticinterventions,andetc.With continued developments in hardware, software, and networkinfrastructureslike5G,VRispoisedtoplayakey role in the future of human-computer interaction, reshaping industries and redefining how we engage with digital content. This review paper explores the architectureofVRsystems,somerecent
applications, how VR impacts us, and future trends that promisetopushtheboundariesofvirtualexperienceseven further.
By examining these aspects, we aim to highlight the growing impact of VR in research and practical applications, as well as the key innovations that are drivingitsrapidadvancement.
One of the earliest and most notable milestones in VR history was the creation of the "Sensorama" by Morton Heilig in 1962. Heilig, often referred to as the "Father of Virtual Reality," developed this mechanical device to engage multiple senses and provided an immersive experiencethatpredictedwhatVRwouldlaterbecome.
In 1968, Ivan Sutherland, another VR pioneer, introduced the first head-mounted display (HMD), known as the "SwordofDamocles."

Fig.1Firsthead-mounteddisplayincomparisonwith currentVR
NowcomesthehighlightofwhatVRprovidesisthefactor of “presence”. Presence in Virtual Reality on almost all articles describes the sensation of truly "being there" in a virtual environment, despite knowing it is computergenerated.Itactsonapsychologicalstatewhereusersfeel fullyimmersedandinteractnaturally,asifthevirtualworld werereal.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
PresenceisafundamentalgoalofVR,asitdirectlyimpacts theuser’semotion.beused. Otherfonttypesmaybeused ifneededforspecialpurposes.
Stimulating the user’s presence, the VR technology can be generalizedintomajorthreetypes:
FullyimmersiveVR
SemiimmersiveVR
MobileVR
These types reflect the varying levels of immersion and interaction,cateringtodifferentneedsandindustries.
2. VR Architecture
The architecture consists of several interconnected components that work together to create immersive and interactivevirtualenvironments.Here’sabreakdownhow thesegmentationoccursinfollowingway:
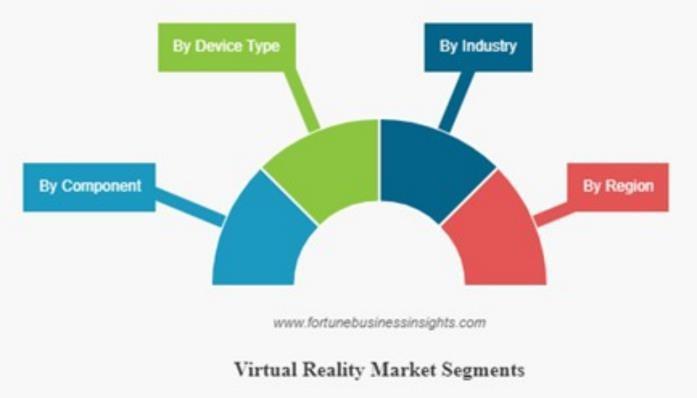
Fig.2elaboratesthesegmentationinVRSegment categorizations:
ByComponent
1. Hardware: Includes head-mounted displays (HMDs),motioncontrollers,trackingsystems,and hapticdevicesthatcreateimmersiveexperiences.
2. Software: VR engines (e.g., Unity, Unreal Engine), graphics rendering, physics simulations, and AI forcreatingdynamicvirtualenvironments.
3. Input Devices: Motion controllers, gloves, and sensors for user interaction, along with spatial audioandhapticfeedback.
ByDevice
1. PC-Based VR: High-end systems like Oculus Rift, idealforgamingandsimulations.
2. Console-Based VR: PlayStation VR, optimized for entertainment.
3. Standalone VR: Self-contained devices like Oculus Questforportabilityandconvenience.
ByIndustry
ByRegion
3. How VR Impacts us
3.1 Brain Simulation
Virtual Reality acts as a brain simulator, immersing users in environments that trick the senses into perceiving the virtual as real. By providing carefully crafted sensory inputs visual, auditory, and tactile VR engages the brain's natural processes for interpreting reality, triggering emotional and physical reactions similar to thoseinreallife.
VR effectively blurs the line between the virtual and real, demonstrating how easily the brain can be influenced to experiencethingsthatdon’tphysicallyexist.
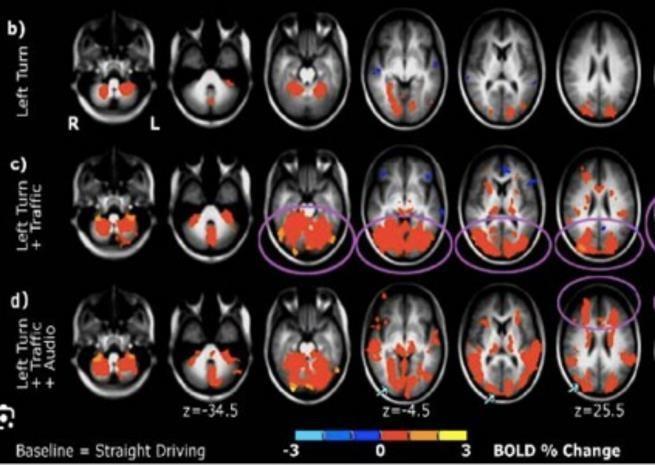
Fig.3illustratestheinfluenceonVRonahumanbrainafter experiencinga,3Denvironment.
3.2
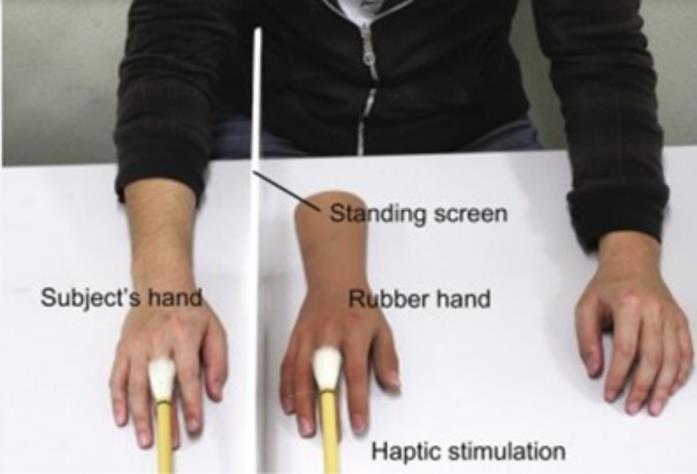
Virtual Reality (VR) can be beneficial for amputees by leveraging principles from the ‘Rubber Hand Illusion’ to enhance body ownership and sensory integration. The "rubber hand illusion," whereby a virtual hand replaces the real hand of the user and stroking of the virtualhand thusinducesanillusoryfeeloftouchupontherealhand.
By using VR to simulate the presence and movement of a virtual limb, amputees can receive visual feedback that alignswiththeirremainingsensations.VRtherapycan also aid in rehabilitation by allowing amputees fostering both physicalandpsychologicalrecovery.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3.3 Cognitive Thinking
It boosts spatial awareness and navigation skills by allowing users to explore and interact with complex virtualenvironments.Additionally,itfostersempathy and perspective-taking bysimulatingdifferentviewpointsand situations. Overall, VR's immersive nature supports cognitive development and therapeutic interventions by activelyengagingthemind.
3.4 Embodiment, Perspective and Perception VR'simpactextendsbeyondmerevisuals.
It fosters a sense of embodiment, where users feel physically present within the virtual environment. This is achievedbytrackinghead movements,creatingaparallax effect that mimics natural head movement. This embodimentleadstoashiftinperspectiveandperception.

Fig.5Thisexplainstheembodimentandbodyperceptionin virtualreality.
Although most people endup relating VR togaming,there arenumerousotherfieldswhereitfindsapplication:
Professional Sports Training: VR is being used by professionalsportsteamsliketheNFL,NBA,andUS Olympic Ski Team for training. It allows athletes to practice plays and strategies in a safe, controlledenvironment.
Health: Virtual reality enhances healthcare by providing immersive therapy for pain management, mental health treatment, rehabilitation exercises, and surgical training, offeringrealisticsimulationsthatimprovepatient outcomesandtrainingefficiency.
Automotive Design and Prototyping: Ford, BMW, and Volkswagen are already using VR to redesign the experience of car buying and their vehicles themselves. Virtual reality lets customers virtually see and explore car features and interiors, while engineerscanviewandtestprototypesincontext.
Therapy: VR has therapeutic uses, such as reducing anxiety in patients with dementia or Alzheimer's. It can transport them to calming virtual environments, providing a sense of comfort and reducing stress. Additionally, VR is being explored as an alternative to morphine for painmanagement.

Fig.6ThisdisplaysthelistofindustrieswheretheVR exists.
Despite its potential, VR faces challenges that hinder its widespreadadoption:
Realism:CurrentVRexperienceslackthevisualand haptic fidelity to fully represent the real world. Limited resolution, field of view, and lack of

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
advanced haptic feedback create a sense of disconnectionfortheusers.
Latency Issues: Delays between user actions and their virtual representation create nausea and dizziness-a significant barrier for user comfort andlong-termengagement.
Hardware Limitations: Current VR headsets can be bulky, uncomfortable, and expensive, limiting their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, the processing power required for high-fidelity VR experiences necessitates powerful computers, further increasing the cost barrier.
Researchers are actively tackling VR's challenges, paving thewayforamoreimmersiveandaccessiblefuture:
AI and 5G: VR, powered by AI and 5G, will create immersive, real-time experiences. AI will analyze user behavior to tailor content, while 5G will enable low-latency, high-bandwidth interactions, revolutionizing fields like education, healthcare, andgaming.
High-Resolution Displays: Advancements in display technology are leading to higher resolution screens, offering sharper visuals and a morerealisticexperience.
ReducedLatency:Improvedprocessingpowerand communication protocols areminimizing latency, creating smoother and more responsive VR experiences.
Haptic Feedback Suits: With the advancement in haptic technology, suits are being designed that will cause greater immersion by offering a wider rangeofhapticfeedbackortactilesensations.
Asthesechallengesareovercome,theVRmarketispoised forsignificantgrowth.
Asthetechnologybecomesmoreaccessibleand affordable, we can expect a broader range of industries to adopt VR solutions.
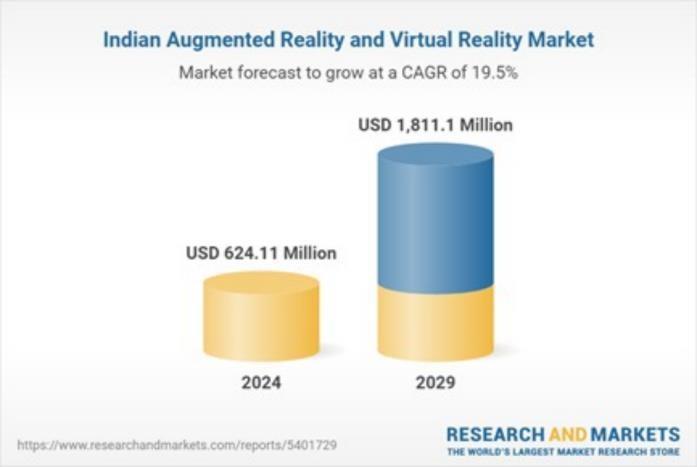
Fig.3theabovestatisticsshowtheadoptionofVRby 19.5%inIndiafromtheyears2024to2029.
Virtual reality is changing the way humans connect with digital worlds, bringing together imagination and reality. From games and healthcare to education and industrial applications, virtual reality is rewriting the book on human-computerinteractionbydeliveringimmersiveand intuitiveexperiences.Withrealism,latency,andhardware limitations still lingering as current challenges, rapid development in AI, 5G, and haptic technology will propel the industry toward a future that is much more seamless andaccessible.
The future of VR is going to expand its transformative potential across various sectors, making it a cornerstone of the next generation of technological innovation. With research and investment still ongoing, the future of VR promisesaworldwerevirtualandphysicalrealitiesblend seamlessly,unlockingunprecedentedpossibilities.
We wouldlike to extendoursinceregratitudetoall those who contributed to the completion of this paper presentation on virtual reality. Special thanks to our mentors and advisors for their guidance and support throughout the research process. Additionally, we appreciatetheassistanceofourcolleaguesandpeerswho offeredtheirfeedbackandsuggestions.
[1]International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research,Volume 4, Issue 4, April-2013 308 ISSN 2229-5518
[2]Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep; 19(18): 11278.Published online 2022 Sep 8. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811278

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
[3]2017 International Conference on Information Communication and Embedded Systems (ICICES)IEEE;DOI:10.1109/ICICES.2017.8070720
[4]Richard Lamb, in International Encyclopedia of Education(FourthEdition),2023
[5]Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and their effect on learning style in the creative design process Tilanka Chandrasekera, Oklahoma State University, USA [6]https://ww.researchgate.net/publication/ 2617390_Virtual_Reality - History, Applications, TechnologyandFuture.
[6]https://www.researchgate.net /publication/ 354065442VR -Researchpaper