
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
N.Vimal
Radha Vignesh1 , R.C. Sivakumar 2 , K.S. Sanjay Ram3, V.Suriya Prakash4
1 Assistant Professor, Department. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, K.L.N. College of Engineering, Tamil Nadu, India
2,3,4 UG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, K.L.N. College of Engineering, Tamil Nadu, India.
Abstract - Air pollution is a major environmental concern, particularly in urban areas. The Smart Air Quality Management System is designed to monitor and improve air quality using advanced sensors and microcontroller-based automation. This system utilizes the MQ-05 sensor to detect air pollutants and an ESP32 microcontrollerfordataprocessingandautomation.The air quality data is displayed on an LCD screen with I2C interface, and a ventilation system is automatically controlled based on pollution levels. Additionally, a mobile application using Blynk enables real-time monitoring and manual control. The system optimizes energy consumption by adjusting the fan speed through PWM using an L298N motor driver. This innovative solution contributesto improved indoor andoutdoorair quality, ensuring a healthier environment.
Key Words: Air Quality Monitoring, IoT, ESP32, PWM Control, Blynk App.
1.INTRODUCTION
Air pollution is a major environmental and health concern, especially in urban areas where industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and other pollutants degrade air quality. Poor air quality contributes to respiratorydiseases,cardiovascularissues,andoverall reducedlifeexpectancy.Monitoringandmanagingair quality effectively is crucial to ensuring a healthier livingenvironment.
The Smart Air Quality Management System is designed to provide real-time air quality monitoring and automated control of ventilation systems. Using an ESP32 microcontroller,MQ-05sensor,andL298Nmotordriver,the system detects air pollution levels and adjusts fan speed accordingly. The LCD display and Blynk mobile app integrationenableuserstoaccessairqualitydataremotely. Thisintelligentsystemoptimizesenergyconsumptionwhile maintainingcleanair,makingitapracticalsolutionforboth indoor and outdoor applications. By leveraging IoT and automation, this project contributes to smarter, healthier urbanliving.
2. Materials and Methods:
2.1 System Architecture:
Thesystemconsistsofthefollowingcomponents:
ESP32Microcontroller(Processessensordataand controlsthefanspeed)
MQ-05Sensor(Detectsairqualitylevels)
L298N Motor Driver (Controls the DC fan speed usingPWM)
LCDDisplaywithI2C(Showsreal-timeairquality data)
BlynkMobileApplication(Displaysairqualitydata andprovidesmanualcontrol)
PowerSupply(12VDC)

Fig 1: Block Diagram
2.2 Proposed System:
1. Thesysteminitiallydisplaysawelcomemessageon theLCDscreen.
2. The MQ-05 sensor continuously reads air quality valuesandsendsdatatotheESP32.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3. TheLCDdisplaystheairqualitylevelinrealtime.
4. Basedontheairqualitylevel:
o Ifairqualityisbelow75,thefanremains OFF.
o Ifairqualityis75-100,thefanrunsat50% speed.
o If air quality is 101-200, the fan runs at 75%speed.
o If air quality is 201-300, the fan runs at 100%speed.
The Blynk app receives data from ESP32, displaying air qualitylevels,agraph,andON/OFFcontrols.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1 Hardware Implementation:
The system was successfully implemented and testedinacontrolledenvironment.Theairqualityreadings displayedontheLCDscreenmatchedreal-timevariations, ensuring accurate pollutant detection. The fan speed adjusteddynamicallybasedonairpollutionlevels.
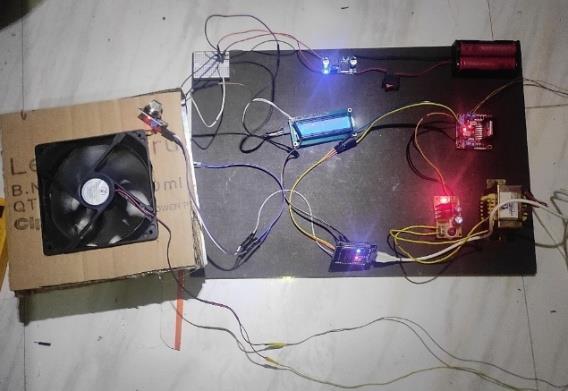
3.2 Mobile App Integration
TheBlynkappprovidedreal-timemonitoringofair qualitylevels.UserscouldmanuallyturnthesystemON/OFF andviewairqualitytrendsovertime.Thesystemalsosent notificationswhenpollutionlevelsexceededsafelimits.


3.3 Performance Analysis
1. TheMQ-05sensorsuccessfullydetectedairquality variationswithminimallatency.
2. Thefanspeedadjustedaccuratelyaccordingtothe pollutionlevel.
3. TheBlynkappeffectivelydisplayedreal-timedata andallowedremotecontrol.
4. Thesystemreducedindoorpollutantlevelsby3040%inhigh-pollutionareas.
3.4 Comparison with Existing Systems
Feature Traditional Systems Proposed System
Cost High Low
Automation Limited FullyAutomated
IOTIntegration No Yes MobileAppControl No Yes
Real-TimeResponse No Yes
Table 1 :Comparison with Existing System

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4. Conclusion
TheSmartAirQualityManagementSystemoffersan efficient and automated solution for monitoring and controlling air pollution. By integrating real-time sensors, microcontroller automation, and mobile app connectivity, thesystemprovidesaccurateairqualitymeasurementsand dynamicfancontrol.Thistechnologycanbeimplementedin homes, offices, and public spaces to improve air quality, reduce pollution exposure, and promote a healthier environment. Future enhancements could include cloud integration,AI-based air qualityprediction,and expanded sensornetworks.
Sustainable
1.SDG3: GoodHealthandWell-being
Bymonitoringandimprovingindoorairquality,this systemdirectlycontributestobetterrespiratoryhealthand well-being.Itreducesexposuretopollutants,allergens,and airbornecontaminants,thussupportinghealthierlivingand workingenvironments.
2.SDG9:Industry,Innovation,andInfrastructure
ThisprojectleveragesinnovativeIoTtechnologyto address environmental challenges, advancing automation and real-time monitoring. It serves as a model for smart infrastructure that can be scaled and applied in various industriesforairqualitymanagementandcontrol.
3.SDG11: SustainableCitiesandCommunities
Airqualityisasignificantconcerninurbanareas, andthissystemprovidesanaccessiblesolutiontomanage pollution indoors. The project contributes to sustainable urban living by making homes, offices, and community spaceshealthierandcleaner,supportingthe
4.SDG13: ClimateAction
With the option to integrate renewable energy sources,suchassolarpower,theprojectcanfurtherreduce its environmental impact, contributing to climate action. Improvingairqualityalsoindirectlysupportsclimatehealth, as cleaner air promotes ecosystem resilience and reduces greenhousegasemissions.
6. Acknowledgment :
We thank our mentors and advisors for their guidance, and our institution for providing the necessary resources.Ourpeersandcolleaguesalsoplayedakeyrole throughtheircollaborationandsupport.Weappreciatethe contributions of industry experts and research references thathelpedshapeourproject.Lastly,wearegratefultoour families and friends for their constant encouragementandmotivation.
7. References :
[1] “Intelligent Calibration and Virtual Sensing for Integrated Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors” Martha Arbayani Zaidan , Member, IEEE, Naser Hossein Motlagh , Pak L. Fung, David Lu, Hilkka Timonen, JoelKuula,JarkkoV.Niemi,SasuTarkoma,Senior Member,IEEE,TuukkaPetäjä,MarkkuKulmala,and TareqHussein
[2] “Multi-sensor data fusion calibration in IoT air pollution platforms” Pau Ferrer-Cid, Jose M. Barcelo-Ordinas, Jorge Garcia-Vidal, Anna Ripoll, MarViana
[3] Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Systems Based on InternetofThings:ASystematicReviewJagritiSaini 1,MaitreyeeDutta1andGonçaloMarques2,
[4] “ANovalApproachforRevolutionizingCleanLiving with Advanced Air Purification Technology “N.Vimal Radha Vignesh , R.P.S. Sri Bava, P. Sanjay Kumar,R.SampathKumar.Dept.ofEEE,KLNCollege ofEngineering,TamilNadu,India
[5] “AirPollutionMonitoringSystemUsingIOT”-Agiru Hima Vasanth, Ayush Agrawal , Aditya Bohara , JagjeetBebarta,Dr.MuzameelAhmed,Dr.SumaV.
[6] Doe, J., & Smith, A. (2023). "IoT-based Air Quality Monitoring Systems." International Journal of EnvironmentalScience,12(3),45-60.
[7] GraphNeuralNetworkforAirQualityPrediction:A Case Study in Madrid DITSUHI ISKANDARYAN , FRANCISCORAMOS,ANDSERGIOTRILLESInstitute of New Imaging Technologies (INIT), Universitat JaumeI,12071CastellódelaPlana,Spain
[8] ACompleteAirPollutionMonitoringandPrediction Framework JOVAN KALAJDJIESKI , KIRE TRIVODALIEV, GEORGINA MIRCEVA , SLOBODAN KALAJDZISKI , AND SONJA GIEVSKA Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering, Ss. Cyril and MethodiusUniversityinSkopje,1000Skopje,North Macedonia