
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Mrs.Bharati Amit Patil,Mr.Ajit Swami,Mr.Atharva Babar,Mr.Prajyot Satpute
Assitant Professor,Department of computer Science,Dr.D.Y.Patil Arts,Commerce & Science College,Pimpri,Pune-18.
MSc(CS) Student, Dr.D.Y.Patil Arts,Commerce & Science College,Pimpri,Pune-18.
MSc(CS) Student, Dr.D.Y.Patil Arts,Commerce & Science College,Pimpri,Pune-18.
MSc(CS) Student, Dr.D.Y.Patil Arts,Commerce & Science College,Pimpri,Pune-18.
Abstract - Artificial Intelligence (AI) is redefining the healthcare landscape by enabling more precise, efficient, and personalized medical care. From predicting disease outbreaks to enhancing diagnostic accuracy, AI applications are transforming how healthcare is delivered. This paper explores the myriad applications of AI in healthcare, including predictive analytics, medical imaging, virtual health assistants, and patient monitoring. It also highlights challenges like ethical considerations, data privacy, and the need for transparent algorithms. Emerging AI technologies, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, are discussedinthecontextoftheirpotentialtoshapethe future of healthcare. By addressing these opportunities and challenges, this paper underscores the transformative power of AI in enhancing patient outcomes and optimizing healthcareworkflows.
Key Words: Artificial Intelligence, Healthcare, Predictive Analytics,MedicalImaging,PersonalizedMedicine,Ethical Considerations,andVirtualHealthAssistants.
Healthcare systems worldwide face increasing demands for efficiency, accuracy, and personalization. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool to address these challenges, leveraging vast amounts of data to generate actionable insights. With advancements in machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and robotics, AI is being integrated into various aspects of healthcare, from diagnostics to treatment and patientmanagement.
This paper investigates the transformative role of AI in healthcare, focusing on its applications in predictive analytics, medical imaging, and personalized medicine. It also highlights challenges such as ensuring data privacy, addressing algorithmic bias, and balancing human and AI decision-makinginclinicalsettings.
1. Predictive Analytics: AI can identify disease patterns, predict patient outcomes, and manage resourceallocationinhealthcarefacilities.
2. Medical Imaging: AI-driven image recognition algorithms improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosing conditions like cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
3. Personalized Medicine: AI enables tailored treatmentplansbyanalyzingpatient-specificgenetic, environmental,andlifestylefactors.
4. Virtual Health Assistants: AI systems enhance patient engagement by managing appointments, medication reminders, and providing health-related information.
1. Data Privacy:Handlingsensitivepatientinformation whileadheringtoregulationslikeHIPAAandGDPR.
2. Algorithmic Bias: Ensuring fairness and avoiding discriminatory outcomes in AI-driven healthcare systems.
3. Workflow Integration: Adapting traditional healthcare processes to incorporate AI solutions seamlessly.
4. Ethical Considerations:BalancingAIautonomywith humanoversightincriticalmedicaldecisions.
Predictive analytics, powered by AI, revolutionizes proactive healthcare management by analyzing vast amounts of structured and unstructured data. For instance:
● AIcanpredictthelikelihoodofhospitalreadmissions, enabling timely interventions to reduce costs and improvepatientoutcomes.
● Chronic disease management is enhanced through predictive models that monitor patient conditions, allowing for early detection of complications in diseasessuchasdiabetesandhypertension.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
● In public health, AI identifies patterns to predict and manage disease outbreaks like COVID-19, ensuring betterpreparedness.
AI's impact on medical imaging has been profound, with systems like IBM Watson and Google's DeepMind demonstrating exceptional diagnostic capabilities. Key examplesinclude:
● Cancer Detection: AI algorithms analyze mammograms and CT scans to detect early-stage tumors with higher accuracy than traditional methods.
● Radiology: AI automates image analysis, enabling radiologists to focus on complex cases, improving workflowefficiency.
● Pathology: AI-powered digital pathology tools identify microscopic abnormalities that might be overlookedbythehumaneye.
PersonalizedmedicineleveragesAItodevelopcustomized treatment plans by analyzing patient-specific data. For example:
● AI predicts individual responses to drugs, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing sideeffects.
● In drug discovery, AI reduces development timelines by identifying potential drug candidates faster than traditional methods. Companies like Atomwise and Insilico Medicine have already showcasedAI’scapabilitiesinthisdomain.
Monitoring
AIenhancespatientengagementthroughvirtualassistants andwearabletechnology:
● Virtual Assistants: NLP-powered assistants manage appointments, answer patient queries, and provide medical guidance. Examples include chatbotslikeBabylonHealthandAdaHealth.
● Wearables: AI-integrated devices, such as Fitbit and Apple Watch, monitor real-time health metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, alerting users and healthcare providers to irregularities.
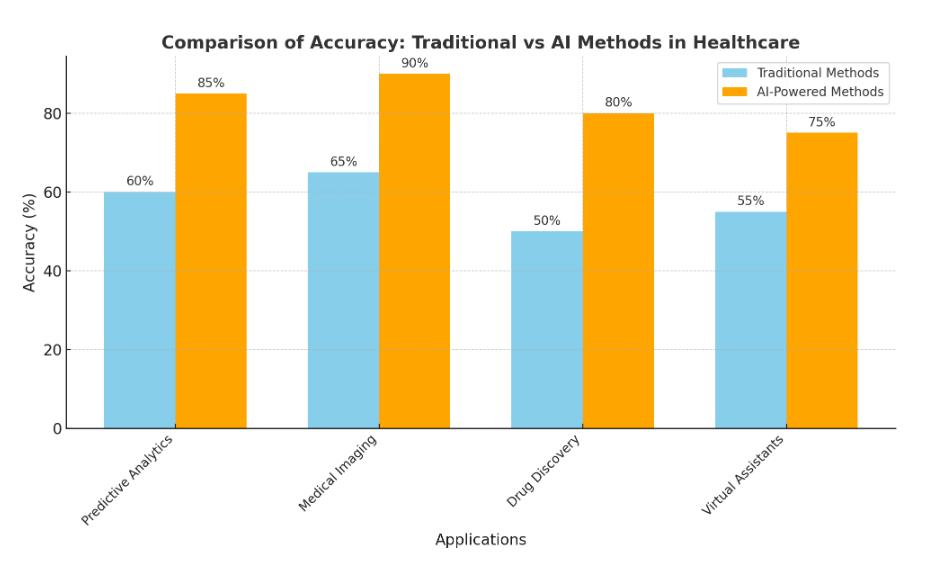
Figure 1: AccuracyImprovementacrossvariousAI applicationsinhealthcare
AIisincreasinglyappliedinmentalhealthcaretoimprove access to services and detect early signs of psychological distress.ChatbotsandNLPmodelsanalyzetextandspeech to identify signs of anxiety, depression, or PTSD. AIpowered platforms like Woebot and Wysa offer real-time counselingandemotionalsupport.
Robotic surgery systems like the da Vinci Surgical System assist surgeons in performing precise, minimally invasive procedures. These AI-powered tools reduce recovery times and improve outcomes by minimizing human error duringsurgery.
AI enables remote monitoring of patients with chronic conditions through wearable devices. These devices continuously collect data, which is analyzed to provide actionableinsightstohealthcareproviders.Thisapproach reduceshospitalvisitsandenhancespatientqualityoflife.
AI bridges gaps in healthcare access in rural areas by providing telemedicine services and diagnostic support through mobile applications. These tools connect patients with specialists, overcoming geographic and resource limitations.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
4.1 Data Privacy and Security
AI systems depend on extensive patient data to deliver accurate and reliable outcomes. Ensuring data confidentiality while complying with regulatory frameworkslikeHIPAAintheUSandGDPRinEuropeisa critical challenge. Mismanagement of sensitive data can leadtobreaches,underminingpatienttrust.
4.2 Algorithmic Bias and Transparency
The fairness of AI models is inherently tied to the quality and diversity of the data they are trained on. Biased datasets can result in discriminatory outcomes, particularly for underrepresented groups. Moreover, the "black box" nature of many AI systems creates challenges in understanding their decision-making processes, raising concernsaboutaccountabilityandreliability.
4.3 Ethical Concerns
As AI systems gain autonomy, ethical dilemmas arise in scenarios involving life-and-death decisions. Questions about the extent of human oversight and the potential misuseofAItechnologiesneedcarefulconsideration.
4.4 Integration into Existing Workflows
Integrating AI into traditional healthcare environments requires significant investments in infrastructure, staff training, and workflow redesign. Resistance from healthcare professionals, who may fear job displacement, isanotherbarriertowidespreadadoption.
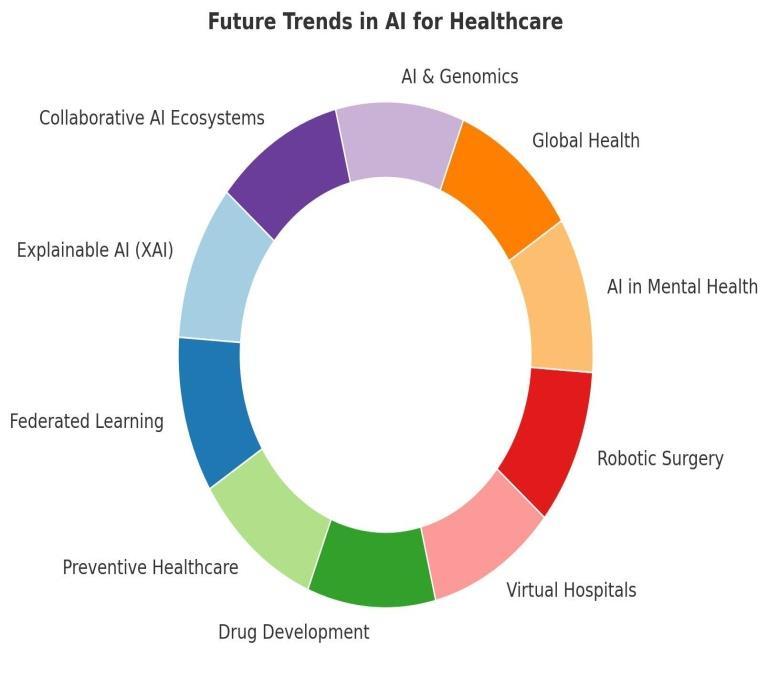
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare is expected to grow exponentially, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for efficient, personalized medical care. Below are some key future trends that are likely to shape the future of healthcare:
1. Explainable AI (XAI)
●AIsystemswillevolvetobecomemoretransparent, enabling healthcare providers to understand and trustAI-drivendecisions.
●Example: AI models in radiology explaining how theyidentifyabnormalitiesinimagingscans.
2. Federated Learning for Data Privacy
●Federated learning will allow AI systems to learn from decentralized patient data without compromisingprivacy.
●This approach will enable collaboration among hospitals and research institutions globally while adhering to privacy regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
3. AI-Powered Preventive Healthcare
●AI will focus on predicting and preventing diseases beforesymptomsappear.
●Example: Wearable devices providing early alerts forconditionslikeheartattacksorstrokesbasedon real-timedata.
4. AI-Driven Drug Development
●AI will streamline drug discovery processes by identifying new drug candidates faster and more cost-effectively.
●Example: AI models predicting molecular interactionstofindtreatmentsforrarediseases.
5. Virtual Hospitals and Remote Care
●AI-powered virtual hospitals will allow patients to receive consultations, monitoring, and treatment fromtheirhomes.
●Example: AI chatbots and telemedicine platforms handling initial consultations before involving specialists.
6. Advanced Robotics in Surgery
●Autonomous roboticsystemsequipped withAI will enhance surgical precision and reduce recovery times.
●Example: AI-assisted robotic surgeries for minimallyinvasiveprocedures.
7. AI in Mental Health and Wellness
●AI will play a significant role in detecting mental healthissueslikedepressionoranxietyearly.
●Example: Sentiment analysis through AI-powered appslikeWysaorWoebot.
8. AI for Global Health
●AI will help address healthcare disparities in underservedregionsthroughtelemedicineandlowcostdiagnostictools.
●Example: AI-powered mobile apps offering basic diagnosticsinruralareas.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
9. Integration of AI with Genomics
●AI will advance precision medicine by analyzing genomic data to provide personalized treatment plans.
●Example: Identifying genetic markers for cancer andtailoringtherapiesaccordingly.
10. Collaborative AI Ecosystems
●Hospitals, research labs, and AI companies will collaboratetocreateecosystemswhereAItoolsare seamlesslyintegratedintohealthcareworkflows.
●Example:AIplatformsinteroperableacrossvarious healthcaresystemsforbettercoordination.
6. Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence has brought about transformative changes in healthcare, from improving diagnostic precision to enabling predictive and preventive care. Despite challenges like ensuring data security and mitigating algorithmic bias, AI continues to open new frontiers in personalized medicine, drug discovery, and patientengagement.
The future of AI in healthcare lies in addressing these challenges while exploring emerging technologies like explainableAIandfederatedlearning.Bydoingso,AIwill not only enhance healthcare delivery but also empower clinicians and patients, ultimately leading to a more efficient,equitable,andeffectivehealthcareecosystem.
References
1. Higdon, R., Stewart, E., Roach, J. C., Dombrowski, C., et al.(2019).PredictiveAnalyticsinHealthcare.MaryAnn LiebertInc.
2. Nnamdi, M. (2020). Predictive Analytics in Healthcare. ResearchGate.
3. Badawy, M., Ramadan, N., & Hefny, H. A. (2020). Healthcare Predictive Analytics Using Machine LearningandDeepLearningTechniques.
4. Van Calster, B., Wynants, L., Timmerman, D., et al. (2019). Predictive Analytics in Health Care: How Can WeKnowItWorks?