
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Mrs. J Preethi Lakshmi1 , Dr. T Aravind2 , Dr S. Praveenkumar3 , Mr. T.K Srinivasan4
1M.E Applied Electronics, Department of ECE, Saveetha Engineering College, Thandalam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
2 Professor, Department of ECE, Saveetha Engineering College, Thandalam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
3 Professor, Department of ECE, Saveetha Engineering College, Thandalam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
4Professor, Department of ECE, Saveetha Engineering College, Thandalam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. ***
Abstract Advanced techniques for detection and mitigation of cyber-attacks on IoT systems are in high demand due to their increasing prevalence. This work deals with the challenge by using machine learning algorithms, XGBoost and LightGBM, for classification of network traffic patterns based on the NSL-KDD dataset. The main problem here is the identification of different cyber-attacks, such as DoS, DDoS, and probing attacks, in real-time within IoT networks. The solution proposed incorporates XGBoost and LightGBM, which can be done to enhance classification accuracy to the maximum level and improve the scalability of the system while ensuring malware is effectively detected. The timeliness of response by the system is ensured by classifying network traffic as benign or malicious. The advantages of this approach include high detection accuracy, scalability, and enhanced security for the IoT infrastructures while ensuring robust protection against many cyber-attacks.
Keywords: IoT Security, Network Traffic Analysis, Cyber Threat Detection, Real-Time Monitoring, Malicious Activity, Scalable Protection, Attack Classification
TheInternetofThingshasrevolutionizedthewayweinteractwithtechnology,connectingawidevarietyofdevicesand enabling smarter environments. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT systems have become part of dailylife. However,thegrowthofIoT networkshasalsobroughtalongsignificantsecuritychallenges.Thenatureofthesesystems dependsoncontinuousconnectivity;thus,theyarepronetodifferentformsofcyber-attacks.Thesophisticationofcyber threatstargetingIoTdevicesandnetworks[1]hasemphasizedtherequirementforadvancedsecuritymechanismsthatcan detectandmitigatetherisksinreal-time.Asuccessfulcyber-attackonanIoTsystemmayhaveconsequencesrangingfroma meredatabreachtodisruptionofservicesorevenhijackingofconnecteddevices.Thus,ensuringthesecurityandintegrityof IoTsystemsisoneofthecriticalfactorsindeterminingtheircontinuedsuccessandadoption.Theformsinwhichcyber-attacks targetingIoTnetworkscomeincludeDenialofService(DoS),DistributedDenialofService(DDoS),andprobingattacks.DoS and DDoS attacks aim at overwhelming IoT devices or networks by flooding them with excessive traffic, rendering them unusable.
Probing attacks involve scanning and probing network devices for vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. Identifyingthesemalicious[2]activitiesinreal-timeisimportanttominimizetheirimpactandensurethesmoothoperationof IoTsystems.Traditionalsecuritymechanisms,suchasfirewallsandintrusiondetectionsystems(IDS),areusuallynotableto dealwiththedynamicnatureanddiversityofIoTtraffic.Duetothevarietyofdevices,networkprotocols,andcommunication patterns in IoT systems, developing a one-size-fits-all security solution is challenging. Hence, there is an urgent need for adaptiveandintelligentsecuritytechniquesthatcandetectemergingthreatsandrespondeffectivelytothem.Machinelearning hasbeenoneofthepromisingsolutionsfortheselimitationsoftraditionalsecuritysystems.Machinelearningalgorithmscan analyze large volumes of network traffic data, learning to distinguish between benign and malicious activity through the identificationofpatternsandanomalies.Amongthesemachinelearningtechniques,ensemblemethodssuchasXGBoostand LightGBMhavebeenwidelyusedforclassificationtasksbecausetheyareabletohandlecomplexandhigh-dimensionaldata.
Thesealgorithmscanbequiteappropriateforcybersecurityapplications,astheycanidentifysubtlepatternsinnetwork trafficthatmayindicatecyber-attacks.XGBoostishighlyperformantandscalable,whileLightGBMisefficientinhandling[3] largedatasets;thus,botharegoodchoicesfordealingwiththechallengeofIoTsecurity.Thisworkpresentsamethodfor improvingthedetectionandmitigationofcyber-attacksinIoTsystemsbycombiningXGBoostandLightGBMalgorithmsfor networktrafficclassification.Theproposedmethodologyistrainedandvalidatedonthewell-knownNSL-KDDdataset,widely usedtotrainandevaluatenetworkintrusiondetectionsystems.Thedatasetcontainslabelednetworktrafficdata,including normal andattack traffic,whichcanbeusedtoteachmodelstodifferentiatebetween benignandmalicious activities.By trainingthesealgorithmswiththisdataset,thesystemwilllearnhowtoclassifytrafficintodifferentcategories,suchasDoS,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
DDoS,probing,andbenign.Thisallowsthesystemtodetectcyber-attacksinrealtime.Thissystemthereforeaimstoprovidea robust,scalablesolutionforidentifyingandmitigatingcyber-attacksinIoTnetworks.
ThecombinationofXGBoostandLightGBMcreatesasystemthatenjoyshighaccuracyinclassification,andsubsequently, minimizes false positives and false negatives. False positives occur when the system wrongly classifies benign traffic as malicious;thisleadstothegenerationofunnecessaryalertsandmaydisruptnormaloperations.Ontheotherhand,false negativesimplythatmalicioustrafficgoesundetected[4],andsuchcyber-attacksmaygounnoticed,therebyjeopardizingthe securityofthesystem.Thisworkensuresthattheproposedsolutionishighlyaccurate,andtherefore,IoTsystemsrespond quicklyandeffectivelyagainstcyberthreats.ThebenefitsofusingXGBoostandLightGBMinthistaskarenumerous.Both algorithmsarecapableofhandlinglarge-scaledatawithminimalcomputationalcost,makingthemwell-suitedforreal-time applications.Moreover,thesealgorithmscaneasilybetunedtooptimizetheirperformance,ensuringthattheycanadapttothe evolvingnatureofcyber-attacks.
ThisadaptabilityisparticularlyimportantinIoTenvironments,wherenewtypesofattacksareconstantlyemerging.Abig advantage of this proposed system is that it would offer scalability-the system can easily be deployed for different IoT applications,rangingfromsmallhomenetworkstolarge-scaleindustrialsettings.Byprovidingreliablewaystodetectand[5] mitigatecyberattacks,theoverallsecurityandresiliencyofIoTsystemsbenefit,thusfurtheringthegoalofprotectingsensitive dataandpreventinglossofservicesincriticalones.Inthefinalanalysis,withtheongoingexpansionofIoTsystems,thereisan emergingneedforprogressivelysophisticatedsecuritysolutions.Machinelearningprovidesastrongapproachtodealingwith newcybersecuritychallengesfacedbyIoTnetworks,especiallywithsuchalgorithmsasXGBoostandLightGBM.Thisworktries toprovetheefficiencyofthesemachinelearningmodelsinthedetectionandmitigationofcyber-attacksinrealtime,which wouldultimatelymakeIoTinfrastructuresmoresecureandreliable.
ThisworkisorganizedasSectionIIpresentingareviewoftheliteraturesurvey.SectionIIIdescribesthemethodology, highlightingitskeyfeaturesandfunctionality.SectionIVdiscussestheresults,analysingthesystem'seffectiveness.Lastly, SectionVconcludeswiththemainfindingsandexploresfutureimplications
With the increased use of cyber-physical systems (CPS) and the Industrial Internet of Things (I-IoT), security vulnerabilitieshavebecomemorepressingissuesinwirelesssensornetworks(WSNs),smartgrids,andwebapplications. Denial-of-service,advancedpersistentthreats,andransomwarearejustafewexamplesofthedifferenttypesofcyber-attacks thatthreatentheintegrityandfunctionalityofthesesystems.Recentresearchhasprimarilyfocusedondesigningadvanced detection techniques, including machine learning, deep learning, and graph-based models, for countering such threats. Lightweight algorithms, generative adversarial networks, and experimental evaluations have been used to develop more resilient CPSs. This work presents a review of recent works on security mechanisms that offer the challenges and their solutionsinprotectingcriticalinfrastructures.
Wirelesssensornetworksaresensitivetovarioussecuritythreats,ofwhichdenial-of-serviceisoneimportantthreat.The proposedworkintroducesa[6]light-weightdetectionmethodbasedonamachinelearningapproachthatusesadecisiontree algorithmwithGinifeatureselectiontorobustlydetectDoSattacksonwirelesssensornetworks.Itcomparestheperformance ofthisapproachwithothers,showingitseffectivenessatlowcomputationaloverhead,thusprovidingapotentialremedytothe limitationsofWSNs.Theresultssuggestthatthisapproachoutperformsexistingmodelsinaccuracyandprocessingtime.The proposedmethodisparticularlyadvantageousinmeetingWSNconstraintsforreal-timeapplications.
IndustrialInternetofThings(I-IoT)-enabledCyber-PhysicalSystems(CPS)areincreasinglyunderthreatfromAdvanced PersistentThreats(APTs),whichexploitvulnerabilitiesinthesystem.Anovelapproachhasbeenproposedintheformof GraphAttentionNetworks(GAN)todetectAPTs,capturingcomplex[7]behavioralpatternsthatothermethodsfailtocapture. Thisapproachusesmaskedself-attentionlayers,whichimprovestheaccuracyofdetectionandovercomesthelimitationsof traditionaldeeplearningmodels.Theapproachwasevaluatedontwodatasetsandshowedsuperiorperformanceinboth detectionaccuracyandpredictiontime.TheresultshighlightthecapabilityofGANforimprovedsecurityinI-IoTenvironments.
ActiveDistributionNetworks(ADNs)arerevolutionizingtheenergysectorwiththeintegrationofadvancedtechnologies, includingrenewableenergysources,energystorage,andsmartgridcomponents.However,thistransformationmakesADNs vulnerabletocyber-attackstargetingtheir[8]communicationandcontrolsystems.Asurveyoncyber-physicalsecurityof ADNs identifies the challenging issues in ADN protection which are related to smart meters, protection relays, and communicationprotocols.TheworkaddressesexistingsolutionswithdirectionsforfurtherresearchtohardentheADNs.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Issuessuchassmartmeters,protectionrelays,andcommunicationprotocolsposechallengesthatneedtobeaddressedto assurethereliabilityofsmartgrids.
In cyber-physical systems, especially in IoT-driven infrastructures, intrusion detection is crucial for security. A deep learning-basedframeworkforreal-timemaliciousintrusionandattackdetectionusinggenerativeadversarialnetworksto improveaccuracyandreducefalsepositiveshasbeenproposed.Theproposed[9]approachdemonstratedhighperformancein detectingvariousattacks,includingDoSandbrute-forceattacks,onmultipledatasets.Resultsindicatedthatthisframework performs better compared to traditional intrusion detection methods based on the rate of detection and reliability. This methodensuresintegrityandconfidentialityforsensitiveinformationwithinIoTsystems.
Smart electric meters in smart grids can be heavily impacted by data integrity and system performance through cybersecurityattacks.Anexperimentwasdesignedforcheckingtheresilienceofcommercial-gradesmartmetersexposedto commonsecurity[10]attacks,fromwhichithasbeenlearntthatthesedevicesaresusceptibletodatatamperinganddataloss. Thisstudydepictsthefiascothroughwhichcyber-attackscouldfiddlethepowerusagedatasenttotheutilitycompanies,thus hamperingthegridoperations.Thisfiascowarnsandremindstoenhancethesecurityofsmartmetersforahighlyreliable smartgridinfrastructures.Thestudyenlightenstheneedforstrongdefensesandchallenges.
Ransomwareattacksareposingasignificantthreattocyber-physicalsystems,andunderstandingtheattackvectorsiskey todevelopingtherightdefensemechanisms.Thisworkintroducesanautomatedwebdefensemechanismagainstransomware attacksthatfocusesonthedetectionofmalware[11]spreadthroughwebapplications.Thisworkassessestheresilienceof variousbrowserstotheseattacksthroughtheuseofautomationtoolslikeSelenium,whichproposesa novel methodfor malwaredetection.Ithasbeenfoundthattheproposedapproachprovidesaveryhighsuccessrateinpreventingransomware attacks, particularly in headless environments. It emphasizes the significance of automated testing in the discovery and mitigationofnewmalwarethreats.
WithmanyIoTdevicesrapidlyincreasinginnumberandprevalence,concernsrelatedtotheirsecurityhavearisen.Agood researchstudyonintrusiondetectiontechniquestowardIoTnetworkshasbeenrecentlycarriedoutbasedondatasetsand [12]machinelearningclassifiersthatpointedouttrendsfrom2018to2024.Keyfindingsemergedintheformofhighsuccess toward identifying security breaches through supervised machine learning classifiers. Researchers have also highlighted availablepublicIoTdatasetsandfuturedirectionstowardIoTsecuritymeasures.Theseinsightsseektofacilitatetheeffortsof bothresearchcommunities,academicandindustrial,inthefaceofemergingthreatstoIoTecosystems.
Theproposedintrusiondetectionsystemforsmartconsumerelectronicsnetworksutilizedsoftware-definednetworking withdeeplearning.Here,thestudywasdevelopedontheaspectsofimplementingadeeplearning-basedIDSusingaCudaenabled[13]BidirectionalLongShort-TermMemorynetworkforattackdetectioninthegivennetworks.Experimentation provedthecorrectnessoftheproposedapproach,whichperformedwaybetterinidentifyingcyberthreatsthananyofthe recentsecuritysolutions.Themethodologyaddressesthechallengespresentedbythegrowingcomplexityanddecentralization ofsmartCEdevices.ThisemphasizesthemeritsofthepotentialofSDNanddeeplearninginsecuringIoT-drivenconsumer electronics.
ThemajorityofIoTusagenecessitatesadaptiveandsecureclassificationsystems.Thisworkintroducedtheuseofamultistage,multi-classclassifierforautomaticidentificationofIoTdevices[14]withminimallabeleddatausingsemi-supervised generativeadversarialnetworks.Itportrayedhighaccuracyandrobustfeatureslikenoiseresistanceanddetectingzero-day attacks.Theintegrationofthisclassifierwithasoftware-definednetworkoffersbetterIoTnetworkservicesattheedge.The workshowcaseshowgenerativeadversarialnetworkscantacklechallengesindeviceidentificationandprivacy.
TherapidriseofcyberthreatsinIoTnetworksnecessitatesadvanceddetectionsystems.Anewprivacy-preservingBERTbased [15] lightweight model, called Security BERT, was developed for IoT and IoT device cyber threat detection. This architectureoutperformedtraditionalmachinelearningmethodsinaccuracyandspeedwhilemaintainingacompactsize suitableforresource-constraineddevices.Incorporatingprivacy-preservingtechniquesmakestheoverallsystemevenmore suitableforreal-timetrafficanalysis.Thismodel,therefore,heraldsapromisingsolutiontoenhancethedetectionofcyber threatsinawiderangeofIoTnetworks.
Increasingattentionhasbeenonnetworkintrusiondetectionsystemswithvulnerabilitiesduetoadversarialattacks, especiallypoisoningattacks.TheauthorsproposedanAIGANframework[16]basedongenerativeadversarialnetworksthat producesadversarialdatatomeasuretherobustnessofmachinelearningmodels.Thisworkanalyzedhowadversarialsamples affecteddifferentclassifiersformachinelearning.TheauthorshaveshownsomemajorvulnerabilitiesofIoT-basedNIDS.It

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
bringsoutthefactthatitisessentialtounderstandandcounteradversarialimpactonsecuritysystems.Thisworkbringsout thechallengesthatIoTnetworksfaceinresistingadversarialthreats.
Withthegrowingpresenceofcyber-physicalsystems(CPS)incriticalinfrastructures,thedetectionofcyberattackson thesesystemshasbecomeamatterofutmostimportance.AstudyhasbeenconductedtoinvestigateAI-basedmodels[17]such asXGBoostandLSTMforcyberattackdetectioninCPS.Thesemodelsweretestedonseveralbenchmarkdatasetsandwere foundtohavesuperiorperformanceovertraditionalmethods,thushavingpotentialinimprovingCPSsecurity.Byfocusingon metrics, the study presents a promising direction for futurecyberattack detection models. Recommendations for further researchareprovidedtoaddresstheevolvingsecuritychallengesinCPS.
Theuseofattackgraphs forvulnerabilityassessmentinindustrialIoTnetworkshasgarneredincreasingattention.A comprehensive review on attack graph methods is conducted within the period 2016 to 2021. The different modeling techniques that [18] were identified, along with an evaluation of the effectiveness of those techniques in identifying vulnerabilitiesacrossIoTnetworks,hasbeendiscussedinthisstudy.Thisworkdrawsattentiontoattackgraphsasimportant toolsfordeterminingpotentialsecuritygapsandguidingfurtherresearchinthisarea.Insightsderivedfromthisworkprovide valuableguidanceforresearchersandpractitionersfocusedonIoTsecurity.
Withthedevelopmentofmachinelearningandcloudcomputingservices,modelextractionattacksareoneofthemajor threats.AnewframeworkcalledSwiftTheftwasproposedtoefficientlyextractmodelsfromcloud-baseddeepneuralnetworks. Thedistinguishingfeatureofthismethodistheselectionof[19]themostinformativequerysamplesthatreducesthetime takenformodelextraction.Intheexperiments,itwasobservedthatSwiftTheftincreasesthesimilarityofthemodelwhile drastically reducing the attack time. This study points out the challenges that still exist in the defense of AI-based model extractionattacksincloudenvironments.
LogpoisoningattacksarecriticalthreatstotheintegrityofIoTsystems.Researchershavestudiedseverallogpoisoning techniquesthattargetLinux-basedIoTplatformsandproposed[20]anewmethodforevadingprotectivemechanisms.The studyalsointroducedapersistencetechniquethatensuresattackersmaintaincontrolovertargeteddevices.Theproposed solutionalsoreducesthevulnerabilityoflogpoisoning.ItemployedaPythonimplementationfordetectingloginjectionsand itsneutralization;theemphasiswillbeonpreventativemeasuresagainstanIoTecosystembecomingavictimtosuchattacks.
Themethodologyforthisworkisonthedetectionandmitigationofadvancedcyber-attacksinIoTusingadvancedmachine learningtechniques.Datapreprocessingincludesmakingsurethatnovalueshavebeenmissedinthedataset;otherwise,the replacementwouldbedoneaccordingly,andnormalizingoffeatureswasdonesothatalldatapointsareonthesamescaleand fallwithinasimilarrangeforeffectiveanalysis.Thetrainedmodelwillbeevaluatedwithrespecttoitsclassificationcapability innetworktrafficasbeingeitherbenignormalicious.Thefinalintegrationisperformedintoareal-timeIoTenvironmentfor timelydetectionandresponseofcyberthreats.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
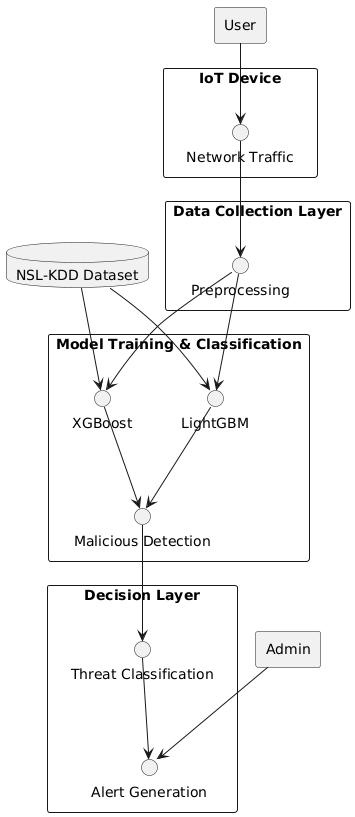
A. Data Preprocessing
Preprocessingisnecessaryafteracquiringthedatasettomakesureitisappropriateformachinelearninganalysis. These coversencodingcategoricalvariables,addressingmissingvalues,andnormalizingnumericalcharacteristics.Preprocessing guaranteesthatthedataisformattedcorrectlyforthemodelstocomprehend.Furthermore,featureselectionapproachesare usedtoeliminateredundantorunnecessarycharacteristics,enhancingthemodels'effectivenessandperformance.Byproperly cleaningandorganizingthedataforanalysis,thisstagepreparesthedatasetfortrainingthemachinelearningalgorithms
B. Model Development
Inthisstep,twointensemachinelearningalgorithmscalledXGBoostandLightGBMaredevelopedfortheclassificationof networktraffic.XGBoostisselectedbasedonitsboostingmethodbecauseitrefinesthemodelbyfocusingontheerrorsof prioriterations,thusmakingitmoreaccurateovertime.LightGBMchoosesitsgradientboostingmethod,optimizedforspeed and memory, which makes it efficient in large-scale datasets. Both models are set to solve the classification problem of identifyingmaliciousactivityinIoTnetworktraffic.
C. Training of the Models
Both XGBoost and LightGBM models are then trained after the data has been pre-processed and the models have been developed.Aftersplittingthedatasetintosubsetsfortestingandtraining,usethetrainingsubsettoteachthemodelshowto correctlyidentifynetworktraffic.Hyperparametersareadjustedtooptimizemodelperformance,allowingthemodelstobe able to handle the network data complexity. Cross-validation techniques are used to evaluate the models' performance,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
guaranteeing that the models perform adequately on unseen data and generalize appropriately across different network conditions.
Thisisthefinalstepinthetrainingprocess,whichdetermineswhetherthemodelcanidentifymaliciousorbenignnetwork data.Thisstagedoesnotbaseitsevaluationonsuchmetricsasaccuracyorprecisionexplicitlybutratherontheperformance ofthemodelsinpracticalconditions.Testingiscarriedoutwiththetestingdatasettosimulaterealtrafficandmakesurethat the models can perform satisfactorily in dynamic environments. To make sure that the system can detect cyber-attacks efficientlywithoutbeingover-sensitiveorproducingfalsealarms,itisveryimportanttotestthemodelforvarioustraffic patternsandattackscenarios.
Oncethemodelshavebeentested,theyarethenincorporatedintoanIoTsystemtodetectreal-timeattacks.Here,modelskeep onanalyzingtheincomingnetworktrafficandcategorizeitasbenignormalicious.Realtimeexecutionwouldimmediately informtheappropriateactionsregardingmitigationsonmalicioustrafficandensuringharmprotection.Therefore,timely reactionstowardsrespondingcyberthreatsguaranteepossibledamagesofbeinglimitedfromwhereriskswillhavereached themwhenacting.
Basedonoptimizingtechniques,systemscanalsoperformwithoptimizedoperationstowardsworkingwithitsowninvaried dynamicenvironmentscreatedthroughIoTendequipment.Furthersimplicityofthemodelscanbegainedthroughmodel pruning without affecting their performance. Lastly, assembling techniques may also be added wherein multiple models combinetoprovideformorerobustdecisions.Optimizationconcentrateseffortsontheincreaseofthenetwork system's toleranceforhighflowratesofdatainrealtime,therebyeasilyscalingup.Theseenhancementsensuretheattackdetection systemstaysbothcorrectandefficientevenasnetworktrafficpatternschange,andIoTenvironmentsexpand.
Theoutcomesofthedeployedsystemshowhowmachinelearninghasagreatdealofpromisefordetectingcyberattacksin InternetofThingsnetworks.Themodeldemonstratedasignificantcapacitytocategorizenetworktrafficaseitherbenignor maliciouswhentrainedandevaluatedusingtheNSL-KDDdataset.Thesystemreliablyidentifiedcyberthreatsbysuccessfully differentiatingbetweenseveralattacktypes,includingDoS,DDoS,andprobing.BecauseIoTsystemsarebecomingmoreand moresusceptibletocriminalactivity,thisfeatureiscrucialformaintainingtheirintegrityandsecurity
Intermsofperformance,thesystemshowedsomekeystrengthsthatcontributedtoitssuccess.Onemodelexcelledat identifyingcomplexrelationshipsbetweenfeatures,whichhelpedindetectingsubtlepatternsinnetworktraffic.Thisimproved the model's capacity to identify attack behaviours that had not been identified before. The other model demonstrated exceptionalspeedandmemoryefficiency,whichmadeitappropriateforreal-timeanalysis,particularlyinsettingswithhigh trafficvolumes.Thebalancebetweendetectionaccuracyandcomputationalefficiencyisvitalformaintainingtheperformance ofIoTsystemsundervaryingconditions.
Thesystempassedreal-timeclassificationtesting.Itclassifiedandsortedincomingnetworktrafficontimeandwithahigh degreeofaccuracyasbenignormalicious.Theclassificationwasdoneefficiently,andallmalicioustrafficdetectedwasmet withpromptmitigationactivitiesthatprotectedtheIoTinfrastructure.Thisprovidesprotectionagainstdamagebeforean attackcancausesignificantdisruptionordataloss.Thesystem'sreal-timedetectionandresponsecapabilitiestothreatsare amongthemostcriticalfeatures,especiallyinthefast-pacedanddynamicenvironmentofIoTnetworks.
ThetechnologyimprovedthesecuritycapabilitiesofIoTsystemsbyofferingstrongdefenseagainstvariouscyberattacks.It performedwellineliminatingfalsepositivesandfalsenegatives,sotherewasnocasewherelegitimatetrafficwasflaggedas malicious. True threats, on the other hand, are identified and blocked; this is because false alarms have the tendency to introduceunnecessaryinterference,whileundetectedattackscanhaveasubstantialeffectontheintegrityofthesystem.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
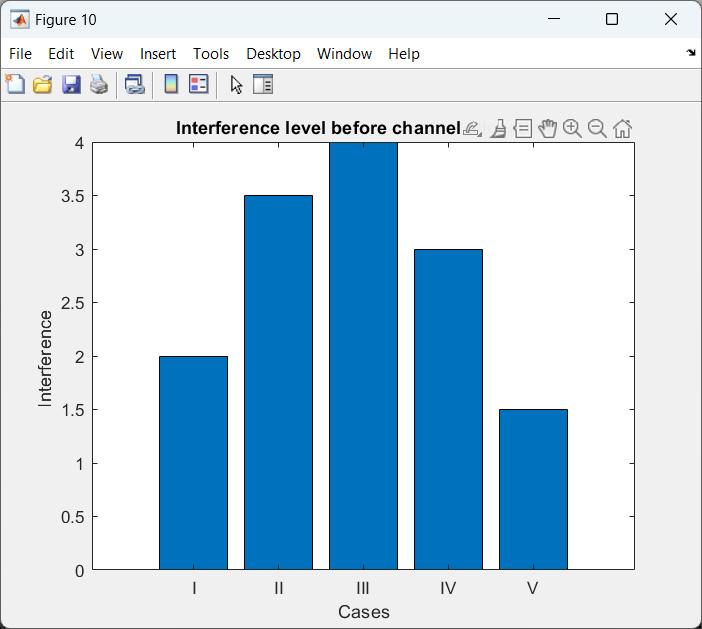
Althoughtheoutcomewaspositive,thereisstillmuchtobedoneintermsofoptimizingtheperformanceofthesystem. Whilethesystemperformedwellinidentifyingmosttypesofattacks,somecomplexornewattackvectorswerenotidentified insomeinstances.Furtheroptimizationisrequired,suchashyperparametertuning,modelensembling,ortheadditionofmore securityfeatures,toimprovedetectionratesforthesemorecomplexorpreviouslyunknownthreats.Suchmeasureswould allowthesystemtokeeppacewiththeevolvingnatureofcyber-attacksintheIoTenvironmentasshowninfigure2.
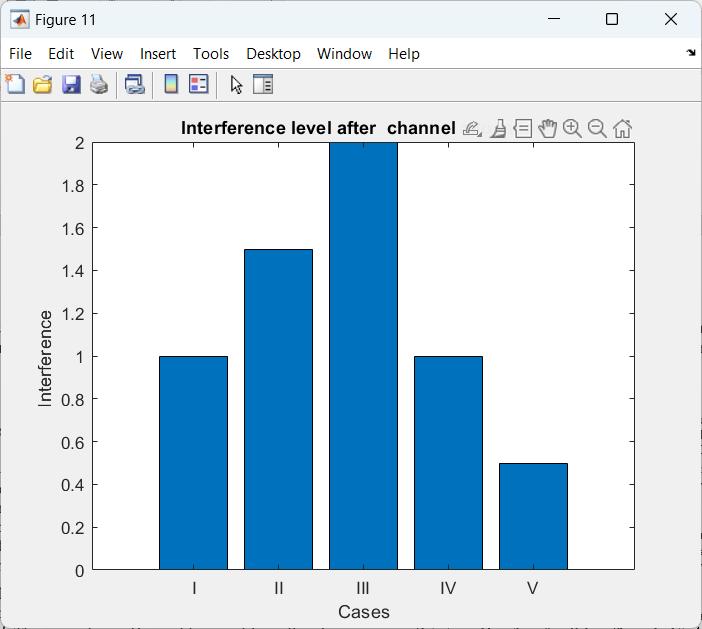
Fromfigure3,thefactthatthesystemneedstoconstantlyadapttotheemergingthreats.Ascyber-attacksevolveandnew tactics are discovered, the system needs to be updated with new data to maintain the high accuracy. If the system is not continuallyretrained,itsabilitytodetectnewattacktypesmaydegradewithtime.Thisunderlinestheneedforanadaptive, responsiveapproachtocybersecurity,wherethesystemlearnsfromthenewattackpatternsandintegratesthemintoits detectionframework.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Buttofurtherexploreitsscalability,currentsystemprovidesanalysisanddetectionatreal-timewhilethesolutiondoesnot compromisewhenitcomestoefficiencyandspeedinlargeIoTenvironmentswithimmensenetworktrafficintermsofbig data.Pruningofmodelandparallelprocessingcanbemadetoensureproperhandlingofvastdataevenatthetimewhenthe networkcontinuestogrowovertimeasshowninfigure4.
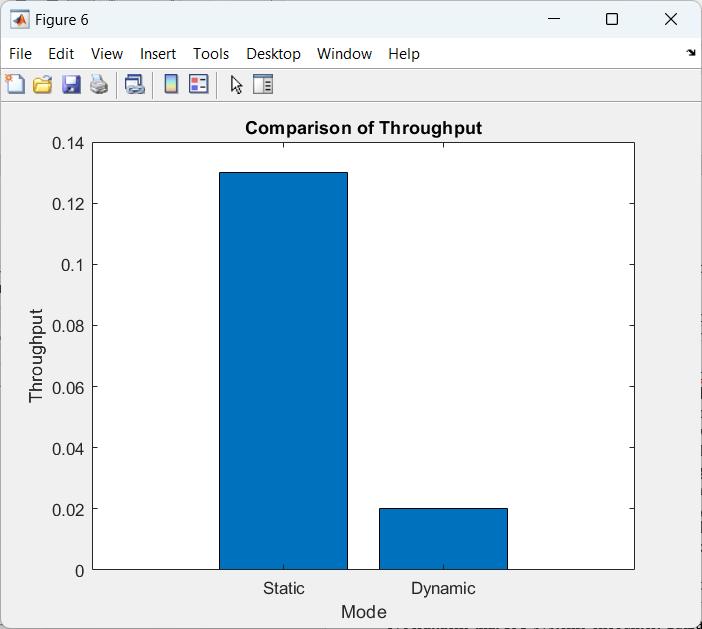
Fromfigure5,thefindingsdemonstratehowmachinelearningmethodsmaysignificantlyimprovethesecurityofInternet ofThingssystems.Byenablingreal-timethreatidentificationandmitigation,machinelearningforcyberattackdetectionlowers therisksassociatedwithillicitactivity.Bycontinuouslyimprovingthesystem'sperformanceandadaptingtonewthreats,IoT networkscanbebetterprotectedagainsttheincreasingsophisticationofcyber-attacks.Thisapproachnotonlyimproves detectionratesbutalsostrengthenstheoverallresilienceofIoTinfrastructures,ensuringthattheyremainsecureinaneverevolvingdigitallandscape.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The work reveals the possibility of applying machine learning in improving the cyber security of IoT systems by the effectivedetectionandmitigationofcyber-attacksinrealtime.Thenetworktrafficclassificationalgorithm,advancedthrough theuseoftheNSL-KDDdataset,identifiednumerousattacks,includingDoS,DDoS,andprobingattacks.Thesystemcould classifythenetworktrafficintobenignormaliciouswithhighaccuracy,providingrobustprotectionagainstevolvingcyber threats.Thisproposedsolutionfindsa balancebetween detectionaccuracyandcomputational efficiency,whichmakesit scalableforenvironmentswithhighvolumesoftraffic.Bothmodelsshowedmuchpromise,withonefocusingonhandling complexrelationshipsbetweenfeaturesandtheotheroptimizedforspeedandmemoryusage,especiallyinlargedatasets.This approachensuresthatthesystemcanprocessnetworktrafficinrealtimewhilemaintaininghighlevelsofsecurity.
However, the analysis points out some suboptimal areas despite the system's overall performance. The system's performance might be enhanced by adding additional security measures like model assembling and hyperparameter adjustment,asitseemsthatcertainintricateattackpathswereoverlooked.Furthermore,astimegoeson,evenmorenovel attackpatternswillemerge,necessitatingongoingmodelretraining.Thisstudyemphasizeshowmachinelearningisbecoming moreandmoresignificantincybersecurity,especiallywhenitcomestoIoTdevices,whereconventionalsecuritymeasures mightnotbeenough.Machinelearningmodelscanofferdynamic,real-timeprotectionmechanismsbycontinuouslylearning fromfreshdata andadjustingtonewthreats.All thingsconsidered,thisresearchhelpscreatescalable,efficient defences againstthegrowingvarietyofcyberattacksthatIoTsystemsencounter,guaranteeingthesecurityanddependabilityofthese vitalinfrastructures.
[1] B.I.Hairab,M.SaidElsayed,A.D.JurcutandM.A.Azer,"AnomalyDetectionBasedonCNNandRegularizationTechniques Against Zero-Day Attacks in IoT Networks," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 98427-98440, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3206367.
[2] U.B.ClintonandN.Hoque,"MU-IoT:ANewIoTIntrusionDatasetforNetworkandApplicationLayerAttacksAnalysis,"in IEEEAccess,vol.12,pp.166068-166092,2024,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3494052.
[3] M.Bouzidi,N.Gupta,F.A.Cheikh,A.ShalaginovandM. Derawi,"ANovelArchitecturalFrameworkonIoTEcosystem, SecurityAspectsand Mechanisms:AComprehensive Survey," inIEEEAccess,vol.10,pp. 101362-101384, 2022,doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3207472.
[4] H. H. Addeen, Y. Xiao and T. Li, "A CVAE-Based Anomaly Detection Algorithm for Cyber Physical Attacks for Water DistributionSystems,"inIEEEAccess,vol.12,pp.48321-48334,2024,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3384295.
[5] M.Ali,M.Shahroz,M.F.Mushtaq,S.Alfarhood,M.SafranandI.Ashraf,"HybridMachineLearningModelforEfficientBotnet Attack Detection in IoT Environment," in IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 40682-40699, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3376400.
[6] M. A. Elsadig, "Detection of Denial-of-Service Attack in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Lightweight Machine Learning Approach,"inIEEEAccess,vol.11,pp.83537-83552,2023,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3303113.
[7] S.H.Javedetal.,"APTAdversarialDefenceMechanismforIndustrialIoTEnabledCyber-PhysicalSystem,"inIEEEAccess, vol.11,pp.74000-74020,2023,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3291599.
[8] M.Khalaf,A.Ayad,M.H.K.Tushar,M.KassoufandD.Kundur,"ASurveyonCyber-PhysicalSecurityofActiveDistribution NetworksinSmartGrids,"inIEEEAccess,vol.12,pp.29414-29444,2024,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3364362.
[9] I. A. Kandhro et al., "Detection of Real-Time Malicious Intrusions and Attacks in IoT Empowered Cybersecurity Infrastructures,"inIEEEAccess,vol.11,pp.9136-9148,2023,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3238664.
[10] H.Kumar,O.A.AlvarezandS.Kumar,"ExperimentalEvaluationofSmartElectricMeters’ResilienceUnderCyber SecurityAttacks,"inIEEEAccess,vol.11,pp.55349-55360,2023,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3278738.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[11] M.U.Rana,M.A.Shah,M.A.Al-NaeemandC.Maple,"RansomwareAttacksinCyber-PhysicalSystems:Countermeasure of Attack Vectors Through Automated Web Defenses," in IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 149722-149739, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3477631.
[12] S.A.Abdulkareem,C.HengFoh,M.Shojafar,F.CarrezandK.Moessner,"NetworkIntrusionDetection:AnIoTandNon IoT-RelatedSurvey,"inIEEEAccess,vol.12,pp.147167-147191,2024,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3473289.
[13] D.Javeed,M.S.Saeed,I.Ahmad,P.Kumar,A.JolfaeiandM.Tahir,"AnIntelligentIntrusionDetectionSystemforSmart ConsumerElectronicsNetwork,"inIEEETransactionsonConsumerElectronics,vol.69,no.4,pp.906-913,Nov.2023,doi: 10.1109/TCE.2023.3277856.
[14] S.NukavarapuandT.Nadeem,"iKnight–GuardingIoTInfrastructureUsingGenerativeAdversarialNetworks,"inIEEE Access,vol.10,pp.132656-132674,2022,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3224583.
[15] M.A.Ferragetal.,"RevolutionizingCyberThreatDetectionWithLargeLanguageModels:APrivacy-PreservingBERTBased Lightweight Model for IoT/IIoT Devices," in IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 23733-23750, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3363469.
[16] Z.Liu,J.Hu,Y.Liu,K.Roy,X.YuanandJ.Xu,"Anomaly-BasedIntrusiononIoTNetworksUsingAIGAN-aGenerative AdversarialNetwork,"inIEEEAccess,vol.11,pp.91116-91132,2023,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3307463.
[17] M.Abdullahietal.,"ComparisonandInvestigationofAI-BasedApproachesforCyberattackDetectioninCyber-Physical Systems,"inIEEEAccess,vol.12,pp.31988-32004,2024,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3370436.
[18] O.S.M.B.H.Almazrouei,P.Magalingam,M.K.HasanandM.Shanmugam,"AReviewonAttackGraphAnalysisforIoT VulnerabilityAssessment:Challenges,OpenIssues,andFutureDirections,"inIEEEAccess,vol.11,pp.44350-44376,2023, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3272053.
[19] W.Yang,X.Gong,Y.Chen,Q.WangandJ.Dong,"SwiftTheft:ATime-EfficientModelExtractionAttackFramework AgainstCloud-BasedDeepNeuralNetworks,"inChineseJournalofElectronics,vol.33,no.1,pp.90-100,January2024,doi: 10.23919/cje.2022.00.377.
[20] H.A.Noman,O.M.F.Abu-SharkhandS.A.Noman,"LogPoisoningAttacksinIoT:Methodologies,Evasion,Detection, Mitigation, and Criticality Analysis," in IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 118295-118314, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3438383.