
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
KSHITIJ K SAWANT 1
1 Undergraduate Student , Department of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science , Thakur College of Engineering and Technology , Kandivali (E), Mumbai - 400101 , Maharashtra , India
Abstract - Blockchain technology revolutionizes digital ecosystems with its transparency, security, and decentralization. Helixure : Spiral of Integrity exemplifies this potential as a blockchain-based web application, integrating core features like block creation, validation, mining, and immutable ledgers. Built with React and Firebase Firestore, Helixure simplifies blockchain interactions, enabling secure data managementandreal-timevalidation.Thispaperexplores blockchain fundamentals, applications like cryptocurrency, smart contracts, and tokenization, and addresses challenges such as scalability and regulation. Helixure bridges the gap between blockchain theory and practice,fosteringasecureandtransparentdigitalfuture whileempoweringuserswithanaccessibleandinnovative platform.
Keyword: Blockchain Technology, Helixure, Decentralized Ledger, Proof-of-Work, Cryptographic Security
1. Introduction
[1] Blockchain technology has become a cornerstone of digital innovation, redefining industries by offering secure, decentralized, and transparent solutions for managing and recording data. Its ability to create immutable ledgers and establish trust among participantswithoutcentralizedcontrolhasopenednew possibilities in fields such as finance, supply chain management,healthcare,andgovernance.Theevolution of blockchain has also introduced concepts like smart contracts, tokenization, and consensus mechanisms, further expanding its practical applications. This paper explores the multifaceted potential of blockchain technology, focusing on its core principles, working mechanisms, and wide-ranging applications. Additionally,itdelvesinto Helixure: Spiral of Integrity, ablockchain-basedwebapplicationdesignedtosimplify anddemonstratethepowerofdecentralizedsystems.By integrating essential blockchain functionalities, Helixure not only ensures secure and transparent data management but also serves as a practical tool for understanding the underlying mechanics of blockchain technology. The discussion extends to advancements in blockchain-enabled innovations like tokenization, which transforms how assets are represented and traded, and
the evolving landscape of consensus mechanisms that address challenges like energy consumption and scalability. Through a detailed examination of blockchain’s strengths, limitations, and future possibilities,thispaperhighlightsitstransformativerole in shaping the digital ecosystem and fostering a more decentralizedandequitabletechnologicalfuture.
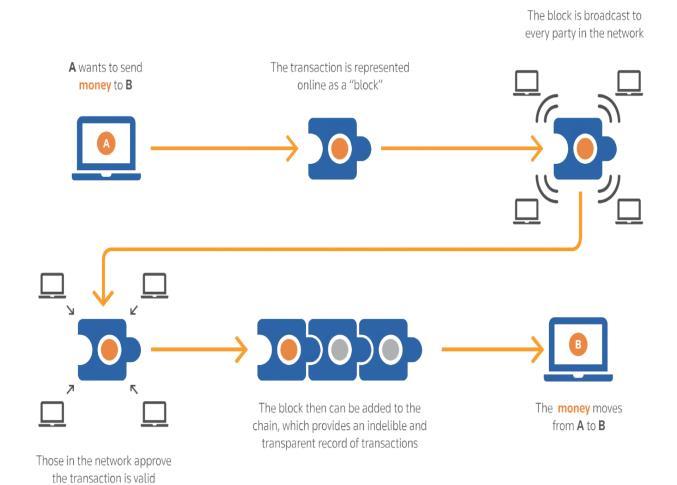
[1][2][8][9] Business runs on information. The faster it's received,themoreaccurateandbetteritis.Blockchainis ideal for delivering that information because it provides immediate, shared, and utterly transparent information storedonanimmutableledgerthatcanbeaccessedonly by permissioned network members. A blockchain network can track orders, payments, accounts, and production.Andbecausemembersshareasingleviewof the truth, You can see all the transaction details from beginning to end, which gives you greater confidence andopensupnewefficienciesandopportunities.
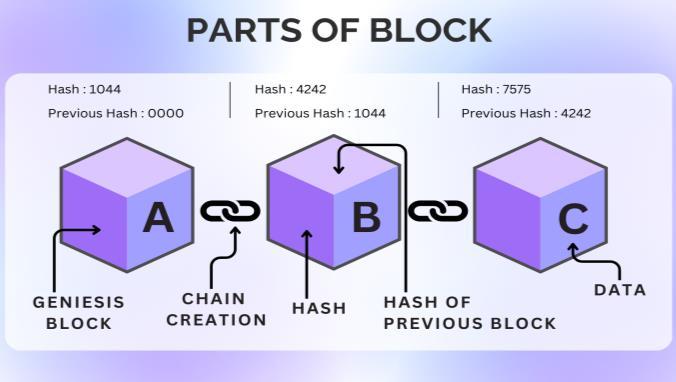
[3][7][14]Eachpiececontainssomedata,suchasthehashof theblocksandpreviousblocks.
3.1. Data: Thedatastoredinsideablockdependsonthe type of Blockchain used. For example, Bitcoin records transaction details, including the sender, receiver, and theamountofcoinsinvolved.
3.2. Hash: It is like a Fingerprint. It identifies a block and its contents, and it's always unique. Once created, the block calculatesitshash,andanychangesinsidethe block modify its hash code. Thus, the hash is handy for detectingchangestotheblock.Thehashoftheprevious
3.3. Block: This process effectively creates a chain of interconnectedblocks,atechniquethatensuresthehigh securityofBlockchainsystems.
3.4. Genesis Block: This is a special block as it cannot point to the previous block; hence, its previous hash codefieldis'0000'.
3.5. Chain Creation: In a chain, each block has a Hash code and a Previous block Hash code, which establishes thechainandconnectionsbetweentheblocks.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
4. Working
[1][4][9] Blockchain uses a peer-to-peer network rather than having a central entity to manage and monitor the chain.In thispeer-to-peer network, everyone isallowed to join. When a person joins this network, the person, also called a node, gets a full copy of Blockchain. When someonecreatesanewblock,thesystemsendsacopyto everyone on the network. Each node then verifies the block that it hasn't been tampered with. If everything checks out, each node adds this block to its Blockchain. Whensomeonetamperswithablock,thisactionchanges the hash code of the block and then the connection of that block with the blocks after it gets broken. So, the node needs to recalculate all other blocks to make the Blockchain valid again. To mitigate such problems, the Blockchain has something called proof-of-work. It's the mechanismthatslows.Downthecreationofnewblocks: All the nodes in this network create consensus. A consensusagreesaboutwhatblocksarevalidandwhich are invalid. Other nodes in the network reject the tampered blocks. So, to successfully tamper or change a blockwithintheBlockchain,thepersonmusttamperthe entire. Blocks in the chain redo the proof-of-work for each block and take control of More than 50% of the network.Onlythen will the tamperedblock be accepted byallthenodesinthenetwork.
5. Impacts
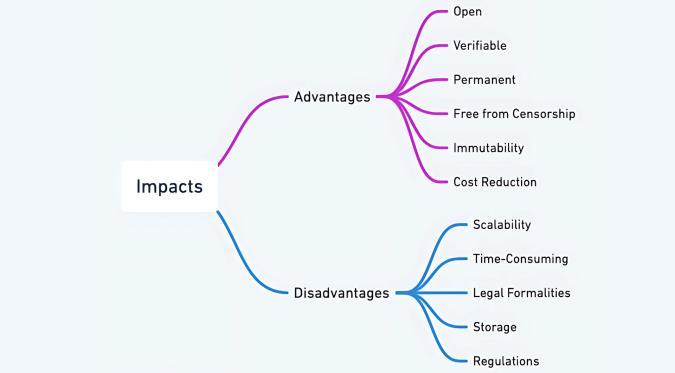
a. Open : One of the significant advantages of Blockchain technology is that it is accessible by all means; anyone can access it. One of the empoweringaspectsofBlockchaintechnologyis that it does not require permission from any central authority to join the distributed network.Thisaccessibilitygivesindividualsand businesses the freedom to contribute to the network and participate in the blockchain revolution.
b. Verifiable : Blockchain technology stores information in a decentralized manner so everyonecanverifyitscorrectness.Thisisdone usingzero-knowledgeproof,inwhichoneparty proves the correctness of the data to another partywithoutrevealinganythingaboutthedata.
c. Permanent : Records or information stored using Blockchain technology are permanent, which means one. You do not need to worry about data loss because the system stores duplicate copies at each local node within a decentralized network comprising multiple trustworthynodes.
d. Free from Censorship : Blockchain technology avoids censorship because no single party controls it. Trustworthy nodes validate transactions, and consensus protocols approve them using smart contracts. Blockchain technology employs advanced hashing techniques to store each transaction on a connected block, ensuring high security. Using the SHA 256 hashing technique further enhances the system's security, providing users with peace of mind and confidence in the integrityoftheirtransactions.
e. Immutability : Due to its decentralized structure, data cannot be tampered with in Blockchain technology. Any change will be reflectedinall thenodes,soonecannotcommit fraud here; hence, Somebody asserts that transactions are tamper-proof. Blockchain technology promotes transparency by making transaction histories visible to all network nodes. Each node has a copy of the transaction, and any changes are immediately visible to the other nodes, ensuring that all participants are well-informedaboutthesystem'soperations.
f. Cost Reduction : Blockchain does not need a thirdman,soitreducesbusinesscostsandgives theotherpartnertrust.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
[1][5][7]
a. Scalability : One of the most significant drawbacks of Blockchain technology is its inability to scale due to the fixed size of the blockforstoringinformation.Theblocksizeis1 MB, allowing it to hold only a few transactions on a single block. Verifying any transaction consumes a lot of energy, creating a problem; a survey found that by 2018, Blockchain transaction verification used 0.3 per cent of the world'selectricity.
b. Time-Consuming : Adding the following block inthechainisnotinstantaneous.Minersneedto compute nonce values many times, a timeconsuming process involving acceleration to meetthedemandsofindustrialapplications.
c. Legal Formalities : In some countries, Blockchain Technology applications, such as cryptocurrency, are banned due to environmental issues, and they are not promoting the use of Blockchain technology in thecommercialsector.
d. Storage : All network nodes store Blockchain databases, which leads to storage challenges as the growing number of transactions demands increasingstoragecapacity.
e. Regulations : Some financial institutions resist Blockchain, highlighting the need for additional technological advancements to enable broader adoption.
[8] People use Blockchain technology for various purposes,fromfinancialservicestoadministeringvoting systems.
6.1.
The most common use of Blockchain today is the backbone of cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin or Ethereum. When people buy, exchange, or spend cryptocurrency, transactions are recorded on a blockchain. The more people use cryptocurrency, the more widespread Blockchaincouldbecome.
Beyond cryptocurrency, individuals and organizations process transactions in fiat currencies like dollars and euros using Blockchain. This approach enables faster verificationandprocessing oftransactions, evenoutside regular banking hours, making it more efficient than traditionalmethods.
PeopleuseBlockchaintorecordandtransferownership ofvariousassets.Theymainlyrelyonitfordigitalassets likeNFTs,representingdigitalartandvideoownership.
However, people can also use Blockchain to process ownership of real-life assets, such as real estate deeds and vehicle titles. The parties involved first verify property ownership and the availability of funds on the Blockchain. They then complete and record the sale directly on the Blockchain. This process allows individuals to bypass manual paperwork submission to updatelocal government records,instantlyupdatingthe propertydeedontheBlockchain.
Another innovation in Blockchain is self-executing contracts, known as "smart contracts." Specified conditions trigger these digital agreements to activate automatically.Forexample,thesysteminstantlyreleases payment for goods when the buyer and seller fulfil all agreed-upon terms. Grey highlights the potential of smart contracts, stating, "Blockchain technology and coded instructions can automate legal agreements, significantly reducing or even eliminating the need for thirdpartiestoverifyperformance."
Supply chains involve massive amounts of information, especiallyasgoods gofrom one part of the worldto the other. With traditional data storage methods, it can be hard to trace the source of problems, like which vendor is poor- quality goods came from. Storing this information on Blockchain would make it easier to go back and monitor the supply chain, such as IBM's Food Trust, which uses blockchain technology to track food fromitsharvesttoitsconsumption.
Experts are investigating ways to use Blockchain to preventvotingfraud.Intheory,blockchainvotingwould allow people to submit votes that couldn't be tampered withandremovetheneedtomanuallycollectandverify paperballots.
7.1. Introduction
[14] Helixure is a blockchain-based web application designed to enhance secure and transparent data management. The platform integrates essential blockchain features, including the creation, validation, and mining of blocks, along with maintaining an

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
immutableandtamper-proofledger.BuiltwithReactfor thefrontendandNode.jswithFirebaseFirestoreforthe backend, Helixure demonstrates practical implementations of blockchain principles.The application allows users to create blocks containing transactions, dynamically compute hashes, and validate chains through proof-of-work. A key feature of Helixure is its intuitive interface, enabling users to view and edit transactions while maintaining the integrity of the Blockchain through real-time hash updates. The genesis block(startingblock)ensuresproperchaininitialization and robust error handling guarantees data consistency. Additionally, the system ensures cryptographic security byrecalculatingdependentblockhashesifmodifications are made, preserving the immutability of the ledger.Helixure's design emphasizes simplicity and security, making it an ideal educational and experimental platform to understand Blockchain technology's core mechanisms and real-world applications.
7.2.1.
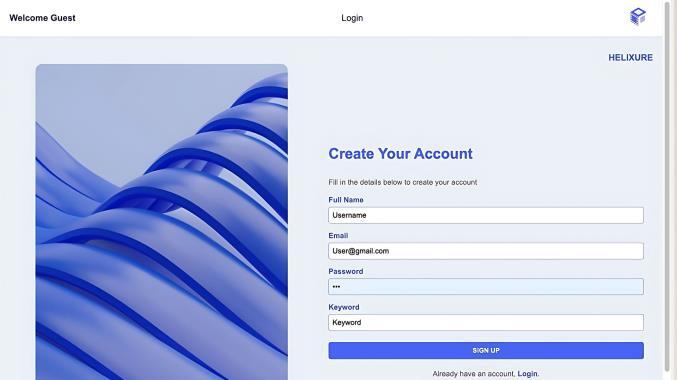
Fig-2 : [14]AccountCreationPage
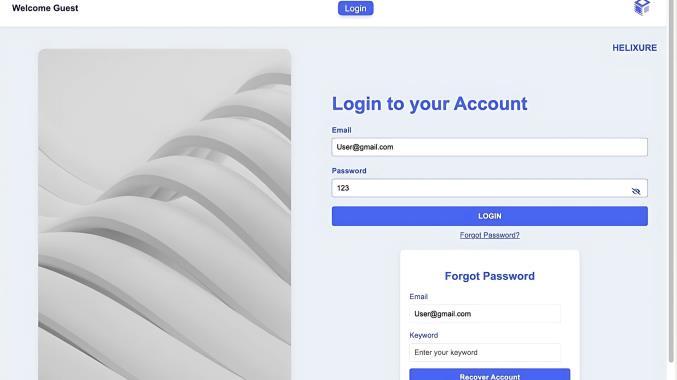
Fig-3 : [14]LoginPage
Usersbegintheirjourneyonthe Login Page,wherethey enter their email and password to access their account securely.
If the user is new, they can navigate to the Account Creation pagetosignup.Theyprovide:
● FullName
● EmailAddress
● Password
● Asecurekeyword(usedforaccountrecoveryin caseofpasswordloss).
The system validates the credentials or creates a new account and stores them securely in the Accounts Collection ofGoogleFirestore.
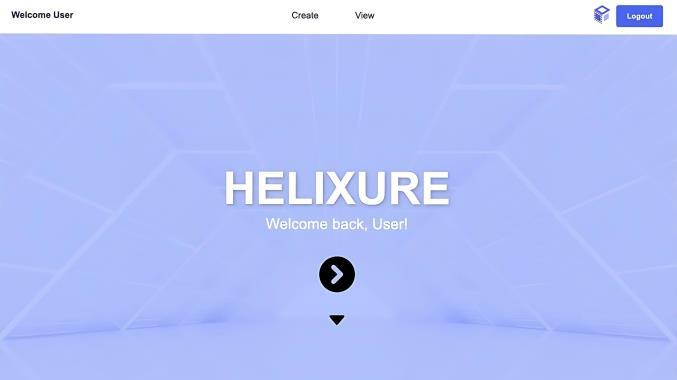
Fig-4 : [14]Hero/HomePage
Aftersuccessfullogin,usersaredirectedtothe Helixure Dashboard
Here, they are presented with two main navigation options:
● Create :Toinitiateblockcreationandmining.
● View :ToexploreexistingBlockchaindata.
The dashboard serves as the central hub for managing theBlockchainactivities.
7.2.3.
Users who select the Create option are taken to the Create Block page.
Thepagefeatures:
● Sender Field : Automatically filled with the logged-inuser'sname.
● Recipient Dropdown : A dropdown to select therecipientoftheblock.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
● Text Field : To input the content of the block (e.g.,transactiondetails).
● Add Block Button : Add block content to the miningsystem.
● Mine Blocks Button : To initiate the mining process, solving a computational Proof-of-Work (PoW).
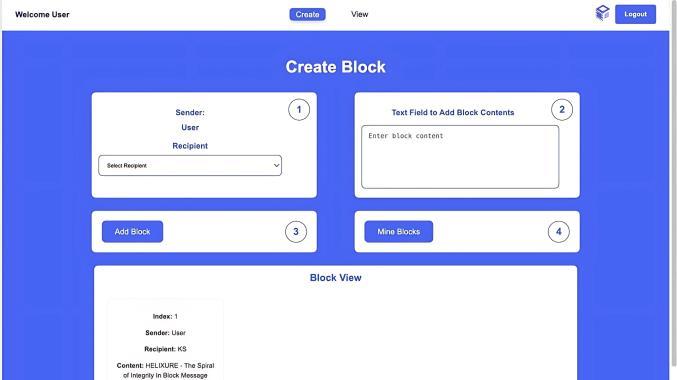
Fig-5 : [14]CreateaNewBlockchainBlock
7.2.4. Mining and Blockchain Storage
Once a block is created, it is mined to solve a Proof-ofWork (PoW) challenge:
● Thisensuresthevalidityoftheblock.
● Auniquehashisgeneratedfortheblock.
The mined block is then securely stored in the Blockchain Collection withinGoogleFirestore.
● Storedmetadataincludes:
● Hash :Uniqueidentifierfortheblock.
● Index :PositionintheBlockchain.
● Previous Hash : Hash of the preceding block.
● Proof :TheresultofthePoW.
● Timestamp :Dateandtimeofmining.
● Transactions : Details of the sender, recipient,andblockcontent.
7.2.5. Blockchain Viewing
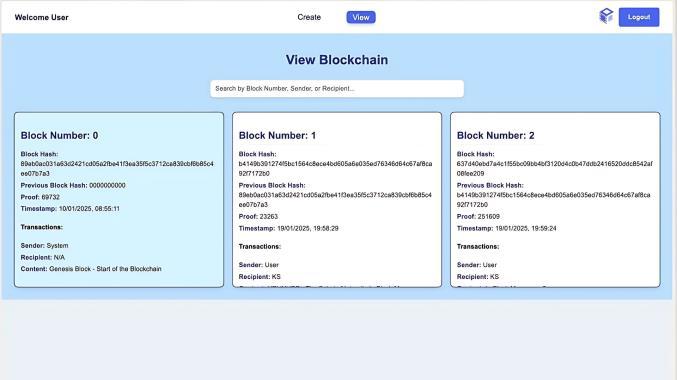
Fig-6 : [14]ViewandSearchBlockchain
Users can navigate to the View Blockchain page to exploretheblocks.
Eachblockdisplayskeymetadata:
● BlockHash
● PreviousBlockHash
● Proof
● Timestamp
● Transactions(Sender,Recipient,Content).
A Search Bar isavailable,allowinguserstofilterblocks basedon:
● BlockNumber
● SenderName
● RecipientName.
The interface provides a visually organized representationoftheBlockchain,ensuringtransparency.
7.2.6. Data Management in Firestore
Accounts Collection :
● Stores user account information, including email,fullname,password,andsecurekeyword.
● Ensuresrobustsecurityforusercredentials.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
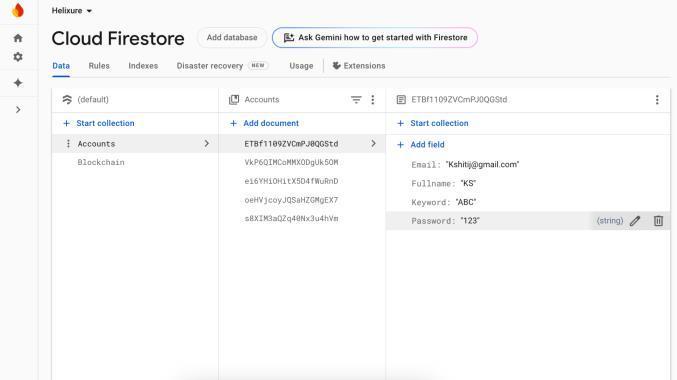
: [14]DataCollectionforAccountsinFirestore
Blockchain Collection :
● Maintains all mined blocks with complete metadata.
● Provides an immutable record of transactions forauditandverification.
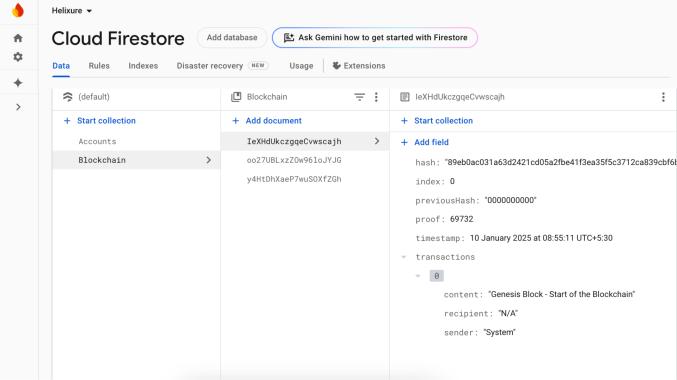
Fig-8 : [14]DataCollectionforBlockChaininFirestore
7.3. Benefits :
1. Immutability : Once a block is added to the Blockchain, its data cannot be altered without revalidatingthechain,ensuringdataintegrity.
2. Transparency : All blocks, including transactions,hashes,andtimestamps,arevisible toauthorizedusers,promotingaccountability.
3. Security : The system uses cryptographic hashes and proof-of-work to secure data and preventunauthorizedtampering.
4. User-Friendly Interface : A clean and interactive interface built with React makes it easyforuserstointeractwiththeBlockchain.
5. Educational Value : Helixure is an excellent tool for students, developers, and Blockchain
enthusiaststounderstandBlockchainprinciples throughhands-oninteraction.
6. Customizability : The system can be extended or tailored for various use cases, such as document verification, supply chain tracking, or securemessaging.
a. Students : To learn about Blockchain fundamentalsandgainpracticalexperiencewith real-timeapplications.
b. Developers : To experiment with and expand Blockchain technology in a web-based environment.
c. Educators : To demonstrate Blockchain conceptsinteractivelyinclassroomorworkshop settings.
d. Small Businesses :ToexploreBlockchain'suse insecuringandmanagingtransactionrecords.
e. Blockchain Enthusiasts : To study and understand the inner workings of a decentralizedledger.
f. Researchers : To test Blockchain theories and develop enhanced use cases based on a flexible platform.
8.1.
[10] Consensus mechanisms are integral to Blockchain networks.Theyensurethat all participantsagreeonthe validity of transactions. They also determine how new blocks are added to the chain and maintain the network's integrity. Over time, consensus mechanisms haveevolvedtoaddressenergyconsumption,scalability, andsecuritychallenges.
Proof-of-Work is one of the earliest and most widely recognized consensus mechanisms used in Bitcoin and Ethereum (before the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade). Miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems, knownascryptographicpuzzles,tovalidatetransactions andaddnewblockstotheBlockchain.
Advantages :
● It provides a high level of security, making it robustagainstattacks.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
● Decentralized and trusted by the Blockchain community for its reliability.
Disadvantages :
● Extremely energy-intensive, as miners require significant computational power to solve puzzles.
● Limited scalability, as the process of mining is slowandresource-heavy.
Examples:Bitcoin,legacyEthereum.
8.3. Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Proof-of-Stake addresses PoW's energy inefficiencies by selectingvalidators based onthenumber of tokensthey hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral. The system incentivizes validators to act honestly by imposing the riskoflosingtheirstakedtokensiftheyactmaliciously.
Advantages :
● Significantly more energy-efficient compared to PoW.
● Faster transaction validation, allowing for greaterscalability.
Examples :Ethereum2.0,Cardano,Polkadot.
8.4. Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a variation of PoS in whichtokenholderselecta limitednumberofdelegates tovalidatetransactionsandmaintainthenetwork.These delegates are responsible for producing blocks and ensuringconsensus.
Advantages :
● High scalability, capable of handling a more significantnumberoftransactions.
● Faster consensus due to fewer participants (delegates)involvedinthevalidationprocess.
Examples :EOS,TRON,BitShares.
8.5. Proof-of-Authority (PoA)
Proof-of-Authority relies on a limited number of preapproved validators who are trusted entities. This mechanism is commonly used in private and permissionedblockchains,wheretransparencyandtrust aremorestraightforward.
Advantages :
● High-speed transaction processing, making it idealforenterpriseapplications.
● Efficient and straightforward for private blockchains.
Disadvantages :
● It is less decentralized, as it relies on fewer trustedentities.
● Itmaynotbesuitableforpublicblockchainsdue tothecentralizationoftrust.
Examples :VeChain,MicrosoftAzureBlockchain.
8.6. Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance ensures consensus evenwhensomenodesinthenetworkactmaliciouslyor fail. It is beneficial for enterprise blockchains and systemsrequiringhighthroughput.
How It Works :
● Nodes in the network communicate with one anothertoagreeonthevalidityoftransactions.
● The system tolerates failures or malicious behaviour from a certain percentage of nodes withoutcompromisingthenetwork'sintegrity.
Advantages :
● It is highly secure due to its ability to handle maliciousnodes.
● Lowlatency,allowingforfastconsensus.
Disadvantages :
● Scalability is limited in large networks due to thecommunicationoverheadbetweennodes.
Examples :HyperledgerFabric,Ripple.
Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Proof-of -Stake (PoS)
Delegated PoS (DPoS)

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Table 1 -TabularRepresentationofConsensus Mechanisms
9. Tokenization
9.1. Introduction
[11] Tokenization is a transformative process that converts real-world or virtual assets into digital tokens, enabling secure, transparent, and efficient transactions on a Blockchain. This guide explores the technology, applications,benefits,andchallengesoftokenization.
9.2. What is Tokenization?
Theprocesscreatesauniquedigitalrepresentationofan asset on a Blockchain through tokenization. These tokens represent ownership, rights, or other attributes oftheunderlyingasset.Tokenizedassetscaninclude:
1. Physical Assets : Real estate,art, gold, or other tangibleitems.
2. Financial Assets : Equities, bonds, money marketfunds.
3. Digital Assets : Intellectual property, nonfungibletokens(NFTs).
4. Data or Identity : Secure digital identities or anonymizedsensitivedata.
9.3. How Tokenization Works [12]
9.3.1. Asset Identification and Sourcing :
1. Identify the asset to tokenize and determine regulatory implications (e.g., is it a security or commodity?).
2. Real-world assets, if any, are secured or stored inneutralfacilities.
9.3.2. Creation of a Smart Contract :
1. A smart contract is programmed on a Blockchaintodefine:
a. Ownershipstructure.
b. Rightsandresponsibilitiesofinvestors.
c. Conditions for token issuance and distribution.
2. These contracts automate processes like dividendpayoutsandcompliancechecks.
9.3.3. Issuance of Digital Tokens :
1. Digitaltokensrepresentingfractionalownership oftheassetarecreated.
2. These tokens are tied to the underlying asset, ensuringitsvaluereflectsitsworth.
9.3.4. Distribution and Trading :
1. Blockchain-enabled platforms or digital wallets distributetokenstoinvestors.
2. Investors can trade tokens on exchanges or throughpeer-to-peernetworks.
9.2.5. Ongoing Maintenance : Regulatorycompliance,taxreporting,andassetservicing areautomatedandmanagedthroughBlockchain.
9.4. Types of Tokens [13]
1. Fungible Tokens : Interchangeable and identical tokens like stablecoins (e.g., USDT, USDC).
2. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) : Unique tokens represent ownership of a specific item, such as digitalartorcollectables.
3. Security Tokens : Represent shares, bonds, or otherregulatedsecurities.
4. Utility Tokens : Provide access to particular services or products within a Blockchain ecosystem.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
9.5. Applications of Tokenization [13]
a. Real Estate : A developer can tokenize a property into digital tokens representing fractional ownership. This process increases accessibility for smaller investors and enables faster transactions by eliminating intermediaries.
b. Fine Art : Tokenization allows investors to purchase fractional ownership of high-value artwork. It enhances liquidity in the art market and provides transparent ownership records to reducefraud.
c. Financial Services : Tokenization is used for equities and bonds to enable faster settlement times, while stablecoins facilitate efficient transactions. This approach lowers operational expenses and expands access to investment opportunities, making them more inclusive and accessibletoabroaderrangeofinvestors.
d. Commodities : The process tokenizes gold, oil, and other commodities, broadening access to high-valuemarketsandsimplifyingtrade.
e. Environmental Sustainability : The system tokenizescarboncreditstoensuretransparency in trading and tracking environmental goals, making sustainability efforts more effective and accountable.
f. Sports and Entertainment : The process tokenizes intellectual property, ticket revenues, and royalties to enable fractional ownership. This allows fans and investors to participate in revenue-sharingmodelsandsimplifiestrading.
g. Supply Chain Management : Tokenized goods improvevisibilityandtraceabilityacrosssupply chains, ensuring end-to-end transparency and reducingfraudwhileenhancingaccountability.
9.6. Benefits of Tokenization [13]
a. Accessibility : Fractional ownership lowers entrybarriersforinvestors.
b. Liquidity : Tokens make traditionally illiquid assets, like real estate or art, more straightforwardtotrade.
c. Transparency : Blockchain records ownership andtransactionsimmutably,reducingfraud.
d. Efficiency : Smart contracts automate compliance,payments,andservicing.
e. Programmability : Rules and conditions embeddedintokensallowautomationviasmart contracts.
f. Global Reach :Blockchainenablesparticipation from investors worldwide, transcending geographicbarriers.
9.7. Challenges in Tokenization [13]
a. Regulatory Uncertainty : Laws vary globally, creatingcompliancechallenges.
b. Scalability : Blockchain networks must handle large-scaletokenizationefforts.
c. Market Adoption : Investor education and awarenessarecriticalforwidespreadadoption.
d. Interoperability : Seamless trading across Blockchain networks requires cross-chain compatibility.
10. Conclusion

Fig-9 : [14]Helixure-TheSpiralofIntegrity
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing industries with its ability to provide transparency, security, and decentralization. Fromfinancialservicesandsupplychainmanagementto environmental sustainability and entertainment, blockchainapplicationscontinuetogrow,solvingcritical challengesandunlockingnewopportunities.
Inthiscontext, Helixure: Spiral of Integrity exemplifies blockchain's potential to bridge the gap between theory and real-world application. By integrating robust

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
features like proof-of-work, cryptographic hashing, and immutable ledgers into an intuitive web platform, Helixure simplifies blockchain interactions and is a powerful educational tool. Its design emphasizes accessibility, enabling users to understand and leverage theprinciplesofblockchaintechnologyeffectively.
As blockchain evolves, it holds immense promise to foster innovation, democratise access to resources, and ensure greater accountability in digital ecosystems. Helixure’s success underscores the importance of such platforms in driving awareness and adoption of blockchain technology, paving the way for a more transparent,secure,anddecentralizedfuture.
[1] H. A. K. (n.d.). WhatIsBlockchainTechnology&How Does It Work. Simplilearn. Retrieved January 25, 2025, fromhttps://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/blockchaintutorial/blockchain-technology
[2] Golosova, Julija, .Romanovs, & Andrejs (2018). The Advantages and Disadvantages of the Blockchain Technology (6th ed., pp. 1-6). IEEE Explore. https://doi.org/10.1109/AIEEE.2018.8592253
[3] Choudhry, M., Singh, M., Vaibhav, Mathur, Siddhant, Saini, & Yash (2022). AReviewonBehaviouralBiometric Authentication (pp. 1-6). 2022 International Conference on Computing, Communication, Security and Intelligent Systems (IC3SIS). https://doi.org/10.1109/IC3SIS54991.2022.9885576
[4] Energy, E. C. (2023, December 1). Exploring the convergence of biometrics geolocation and blockchain. Utilities One. https://utilitiesone.com/exploring-theconvergence-of-biometrics-geolocation-and-blockchain
[5] Sampath, P. and Shukla, Vijay and Kumar, Santosh and Gehlot, Anita and Samatha, V. and Kumar, T. Sampath (2023). An Analysis of Cyber security Risks and Authentication Systems (pp. 1330-1335). 2023 10th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10112477
[6] Okano, Takaaki and Izumi, Shintaro and Kawaguchi, Hiroshi and Yoshimoto, Masahiko} (2017). Non-contact biometric identification and authentication using microwave Doppler sensor (pp. 1-4). 2017 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS). https://doi.org/10.1109/BIOCAS.2017.8325160
[7] Zheng, Zibin and Xie, Shaoan and Dai, Hongning and Chen, Xiangping and Wang, Huaimin (2017). Architecture, Consensus, and Future Trends (pp. 557-
564). 2017 IEEE International Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress). https://doi.org/10.1109/BigDataCongress.2017.85
[8] Bansal, Pranshu and Panchal, Rohit and Bassi, Sarthak and Kumar, Amit (2020). Blockchain for Cybersecurity: A Comprehensive Survey (pp. 260-265). 2020 IEEE 9th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT). https://doi.org/10.1109/CSNT48778.2020.9115738
[9] Brooke Becher (n.d.). Blockchain: What It Is, How It Works,WhyItMatters.RetrievedJanuary25,2025,from https://builtin.com blockchain
[10] Parma Bains (2022, January 26). Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms: A Primer for Supervisors. FinTech Notes, FinTech Notes No 2022/003(2664-5912), 26. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/fintechnotes/Issues/2022/01/25/Blockchain-ConsensusMechanisms-511769
[11] (2024, June 25). What is tokenization? McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/featuredinsights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-tokenization
[12] Deltec Bank. “Asset Tokenization Technology.” Googleusercontent.com, lh6.googleusercontent.com/i1clvSxU8NxHb8LpeC9EWMiDfwAT9qQ6vL45pEPCrrQ mmqeVG3i8XupyFIAQ4yRCjx9Dav1chWJSzsUo8wfvP3Hsy3kfil-4i_ClJ8P2-R_TH7Ob1VLGq5_OI-8urpcZUwNwrBaole0WLBfp8ke4. Accessed 19 Jan. 2025.
[13] DBT DBT. “What Is Asset Tokenization?” Deltec Bank and Trust, 28 June 2023, www.deltecbank.com/news-and-insights/what-is-assettokenization/. Accessed 19 Jan. 2025.
[14] Kshitij K Sawant (2025, January 7). HelixureBlockchain Management System. Github. Retrieved January 25, 2025, from https://github.com/KshitijSawant1/Helixure Spiral-ofIntegrity-